上一节实现了错误处理中间件,这一节来实现兼容老的路由写法
看个 express 的二级路由的例子
const express = require("express");
const userRouter = require("./routes/userRouter");
const articleRouter = require("./routes/articleRouter");
const app = express();
// 对用户进行操作,对文章进行操作
app.use("/user", userRouter);
app.use("/article", articleRouter);
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log(`server start 3000`);
console.log(`在线访问地址:http://localhost:3000/`);
});
/routes/userRouter.js
const express = require("express");
let router = express.Router(); // 是个构造函数
router.get("/add", function (req, res) {
res.end("/user-add");
});
router.get("/remove", function (req, res) {
res.end("/user-remove");
});
module.exports = router;
/routes/articleRouter.js
const express = require("express");
let router = express.Router(); // 是个构造函数
router.get("/add", function (req, res) {
res.end("/article-add");
});
router.get("/remove", function (req, res) {
res.end("/article-remove");
});
module.exports = router;
上面的核心方法就是 express.Router(),下面来实现该方法
new 特点:当 new 一个函数时,这个函数返回一个引用类型,那么这个引用类型会作为 this
在 express.js 里添加 Router
const Application = require("./application");
function createApplication() {
// 通过类来实现分离操作
return new Application();
}
// 提供一个 Router 类,这个类可以 new 也可以当做函数来执行
createApplication.Router = require("./router");
module.exports = createApplication;
然后声明一个 proto 对象,通过让路由的实例可以通过链找到原来的方法就能兼容老的路由写法
const url = require("url");
const Route = require("./route");
const Layer = require("./layer");
const methods = require("methods");
function Router() {
// 创建路由系统
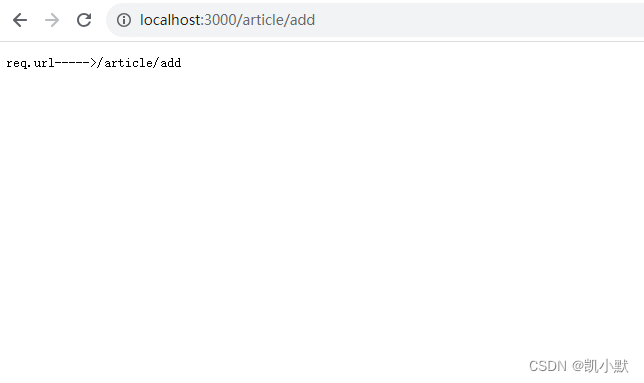
let router = (req, res, next) => {
// 二级路由
res.end("req.url----->" + req.url);
};
// 兼容老的路由写法
// 维护所有的路由
router.stack = [];
// router 链上得有 get 等方法
// 让路由的实例可以通过链找到原来的方法
router.__proto__ = proto;
return router;
}
let proto = {};
proto.route = function (path) {
// 产生 route
let route = new Route();
// 产生 layer 让 layer 跟 route 进行关联
let layer = new Layer(path, route.dispatch.bind(route));
// 每个路由都具备一个 route 属性,稍后路径匹配到后会调用 route 中的每一层
layer.route = route;
// 把 layer 放到路由的栈中
this.stack.push(layer);
return route;
};
methods.forEach((method) => {
proto[method] = function (path, ...handlers) {
// 1.用户调用 method 时,需要保存成一个 layer 当道栈中
// 2.产生一个 Route 实例和当前的 layer 创造关系
// 3.要将 route 的 dispatch 方法存到 layer 上
let route = this.route(path);
// 让 route 记录用户传入的 handler 并且标记这个 handler 是什么方法
route[method](handlers);
};
});
proto.use = function (path, ...handlers) {
// 默认第一个是路径,后面是一个个的方法,路径可以不传
if (typeof path === "function") {
handlers.unshift(path);
path = "/";
}
// 如果是多个函数需要循环添加层
for (let i = 0; i < handlers.length; i++) {
let layer = new Layer(path, handlers[i]);
// 中间件不需要 route 属性
layer.route = undefined;
this.stack.push(layer);
}
};
proto.handle = function (req, res, out) {
console.log("请求到了");
// 需要取出路由系统中 Router 存放的 layer 依次执行
const { pathname } = url.parse(req.url);
let idx = 0;
let next = (err) => {
// 遍历完后没有找到就直接走出路由系统
if (idx >= this.stack.length) return out();
let layer = this.stack[idx++];
if (err) {
console.log("统一对中间件跟路由错误处理");
// 找错误处理中间件
if (!layer.route) {
// 如果是中间件自己处理
layer.handle_error(err, req, res, next);
} else {
// 路由则跳过,继续携带错误向下执行
next(err);
}
} else {
// 需要判断 layer 上的 path 和当前请求路由是否一致,一致就执行 dispatch 方法
if (layer.match(pathname)) {
// 中间件没有方法可以匹配,不能是错误处理中间件
if (!layer.route) {
if (layer.handler.length !== 4) {
layer.handle_request(req, res, next);
} else {
next();
}
} else {
// 将遍历路由系统中下一层的方法传入
// 加速匹配,如果用户注册过这个类型的方法在去执行
if (layer.route.methods[req.method.toLowerCase()]) {
layer.handle_request(req, res, next);
} else {
next();
}
}
} else {
next();
}
}
};
next();
};
module.exports = Router;
测试demo如下
const express = require("./kaimo-express");
const userRouter = require("./routes2/userRouter");
const articleRouter = require("./routes2/articleRouter");
const app = express();
// 对用户进行操作,对文章进行操作
app.use("/user", userRouter);
app.use("/article", articleRouter);
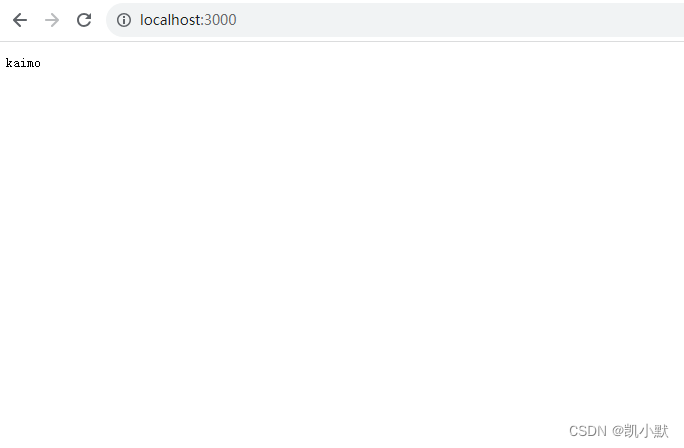
app.use("/", (req, res, next) => {
res.end("kaimo");
});
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log(`server start 3000`);
console.log(`在线访问地址:http://localhost:3000/`);
});
另外两个文件改成 引用自己实现的 express 即可
const express = require("../kaimo-express");