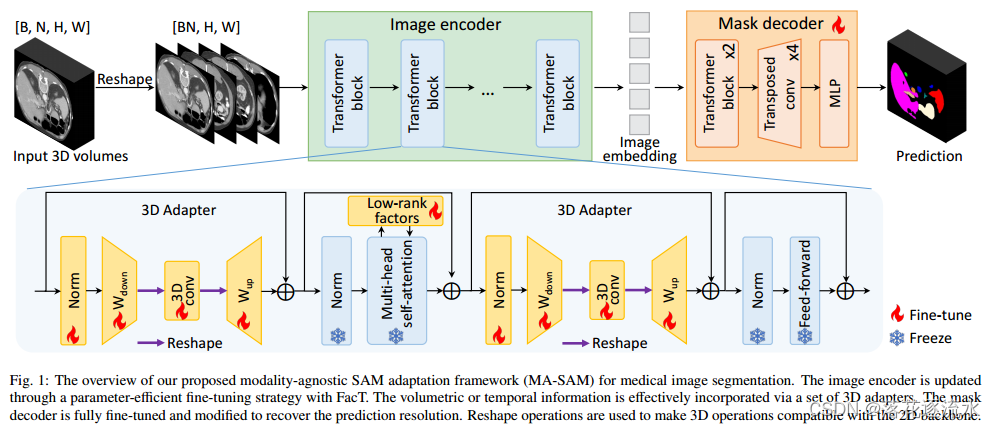
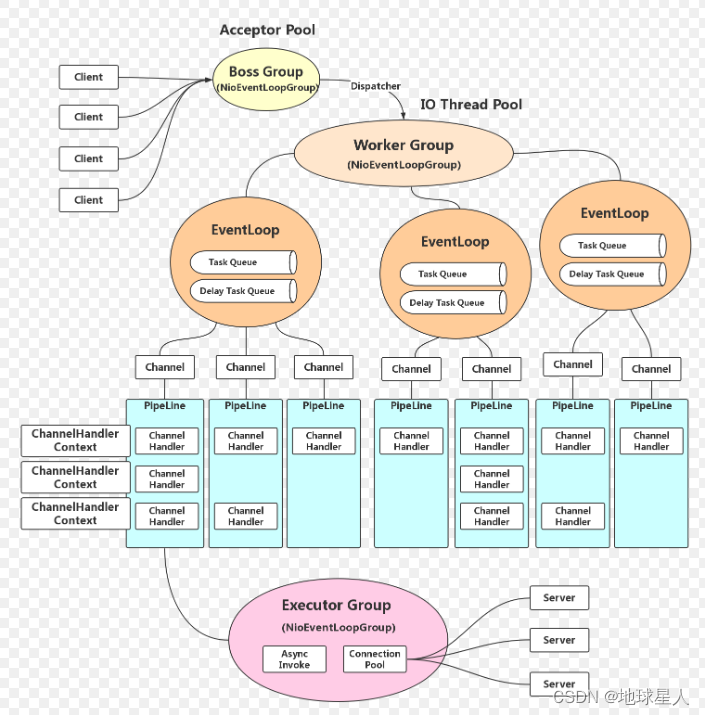
1、netty的基本工作流程
在netty中存在以下的核心组件:
- ServerBootstrap:服务器端启动辅助对象;
- Bootstrap:客户端启动辅助对象;
- Channel:通道,代表一个连接,每个Client请对会对应到具体的一个–Channel;
- ChannelPipeline:责任链,每个Channel都有且仅有一个ChannelPipeline与之对应,里面是各种各样的Handler;
- handler:用于处理出入站消息及相应的事件,实现我们自己要的业务逻辑;
- EventLoopGroup:I/O线程池,负责处理Channel对应的I/O事件;
- ChannelInitializer:Channel初始化器;
- ChannelFuture:代表I/O操作的执行结果,通过事件机制,获取执行结果,通过添加监听器,执行我们想要的操作;
- ByteBuf:字节序列,通过ByteBuf操作基础的字节数组和缓冲区。
我们结合其核心组件通过下图,可以清晰的看明白netty的基本工作原理:
2、代码示例
客户端配置:
package com.xsd.netty;
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.net.SocketAddress;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
public class AppClient implements Serializable {
public void run() {
//定义线程池 EventLoopGroup
NioEventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
//启动一个客户端需要辅助类bootstrap
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
try {
bootstrap = bootstrap.group(group)
.remoteAddress(new InetSocketAddress(8080))
//初始化一个channel
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
//为这个Channel通道添加一个Handler处理器
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new MyChannelHandler2());
}
});
//尝试连接服务器
ChannelFuture channelFuture = null;
channelFuture = bootstrap.connect().sync();
//获取channel,并写出数据
channelFuture.channel().writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("hello netty".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)));
//阻塞程序,等待接收消息
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
group.shutdownGracefully().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new AppClient().run();
}
}
服务端配置:
package com.xsd.netty;
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
public class AppServer {
private int port;
public AppServer(int port) {
this.port = port;
}
public void start() {
// 1.创建eventloop,老板只负责处理请求,之后会将请求分发至worker
NioEventLoopGroup boss = new NioEventLoopGroup(2);
NioEventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup(10);
try {
//2.需要一个服务器引导程序
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
//3.配置服务器
serverBootstrap = serverBootstrap.group(boss, worker)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
//为这个Channel通道添加一个Handler处理器
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new MyChannelHandler());
}
});
//4.绑定端口
ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(port).sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
boss.shutdownGracefully().sync();
worker.shutdownGracefully().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new AppServer(8080).start();
}
}
服务端的处理器:
package com.xsd.netty;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandler;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
public class MyChannelHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
ByteBuf byteBuf = (ByteBuf)msg;
System.out.println("服务端已经接收到了消息,-->" + byteBuf.toString(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
//可以通过ctx获取channel
ctx.channel().writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("hello client".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)));
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
//出现异常的时候执行的动作(打印并关闭通道)
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
}
客户端的处理器:
package com.xsd.netty;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandler;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
@ChannelHandler.Sharable
public class MyChannelHandler2 extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
ByteBuf byteBuf = (ByteBuf)msg;
System.out.println("客户端已经接收到了消息,-->" + byteBuf.toString(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
//可以通过ctx获取channel
//ctx.channel().writeAndFlush("hello client");
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
//出现异常的时候执行的动作(打印并关闭通道)
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
}