1.贪心算法
1.1贪心算法与背包问题的区别
贪心算法能够通过局部最优去推出全局最优,而背包问题不行,需要用动态规划的方法来解决。
1.2套路
贪心算法没有套路!!
主要想清楚怎么得到该阶段的局部最优解,如何通过局部最优解得到全局最优解,如果举不出反例就可以了。
2.leetcode刷题
2.1第121题-买卖股票的最佳时机
给定一个数组 prices ,它的第 i 个元素 prices[i] 表示一支给定股票第 i 天的价格。
你只能选择 某一天 买入这只股票,并选择在 未来的某一个不同的日子 卖出该股票。设计一个算法来计算你所能获取的最大利润。
返回你可以从这笔交易中获取的最大利润。如果你不能获取任何利润,返回 0 。
示例 1:
输入:[7,1,5,3,6,4]
输出:5
解释:在第 2 天(股票价格 = 1)的时候买入,在第 5 天(股票价格 = 6)的时候卖出,最大利润 = 6-1 = 5 。
注意利润不能是 7-1 = 6, 因为卖出价格需要大于买入价格;同时,你不能在买入前卖出股票。
class Solution(object):
def maxProfit(self, prices):
"""
:type prices: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
# 贪心算法
# 局部最优解推出全局最优解
# 记录最大价格和最小价格的索引,记录局部最大利润
# 如果局部最大价格索引大于局部最小索引,更新索引,局部最大利润也更新
max_profit = 0
min_ind = -1
max_ind = -1
for i in range(1,len(prices)):
if prices[i] > prices[i-1]:
temp = prices[i]-prices[i-1]
if min_ind == -1:
min_ind = i-1
else:
if prices[i-1] < prices[min_ind]:
min_ind = i-1
if max_ind == -1:
max_ind = i
else:
if prices[i] >= prices[max_ind]:
max_ind = i
if max_profit < temp:
max_profit = temp
if max_profit < prices[i]-prices[min_ind]:
max_profit = prices[i]-prices[min_ind]
return max_profit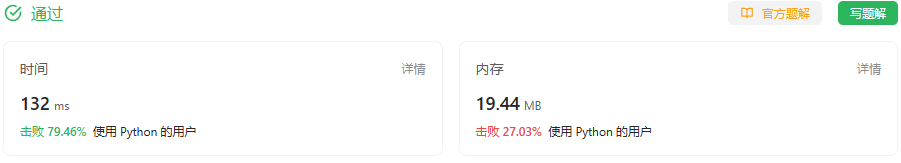





![[Unity开发小技巧]快速切换打包平台](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/0cf71241185946a997546f57c2467b82.png)