多维时序 | MATLAB实现PSO-BP多变量时间序列预测(粒子群优化BP神经网络)
目录
- 多维时序 | MATLAB实现PSO-BP多变量时间序列预测(粒子群优化BP神经网络)
- 效果一览
- 基本介绍
- 程序设计
- 参考资料
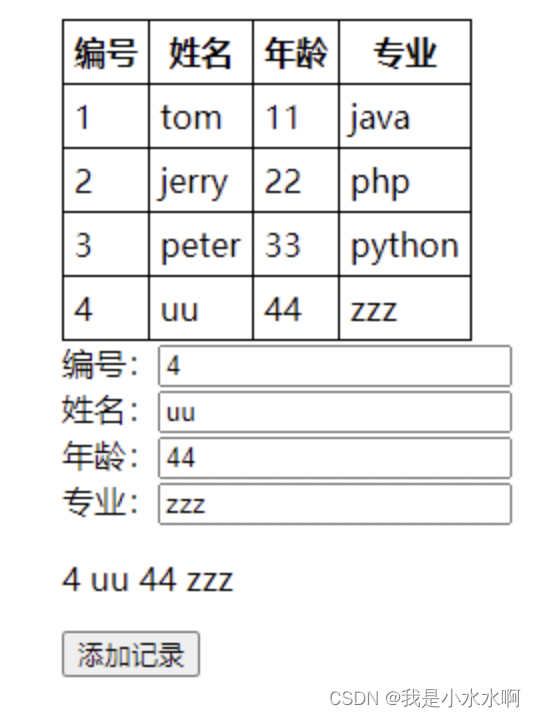
效果一览







基本介绍
1.Matlab实现PSO-BP粒子群优化BP神经网络多变量时间序列预测;
2.运行环境为Matlab2018b;
3.输入多个特征,输出单个变量,考虑历史特征的影响,多变量时间序列预测;
4.data为数据集,PSO_BPNTS.m为主程序,运行即可,所有文件放在一个文件夹;
5.命令窗口输出R2、MSE、MAE、MAPE和MBE多指标评价;
程序设计
- 完整程序和数据下载:私信博主回复MATLAB实现PSO-BP多变量时间序列预测(粒子群优化BP神经网络)。
%------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
%% 清空环境变量
warning off % 关闭报警信息
close all % 关闭开启的图窗
clear % 清空变量
clc % 清空命令行
%------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
P_train = res(temp(1: 700), 1: 7)';
T_train = res(temp(1: 700), 8)';
M = size(P_train, 2);
P_test = res(temp(701: end), 1: 7)';
T_test = res(temp(701: end), 8)';
N = size(P_test, 2);
%% 数据归一化
[p_train, ps_input] = mapminmax(P_train, 0, 1);
p_test = mapminmax('apply', P_test, ps_input);
[t_train, ps_output] = mapminmax(T_train, 0, 1);
t_test = mapminmax('apply', T_test, ps_output);
%% 节点个数
inputnum = size(p_train, 1); % 输入层节点数
hiddennum = 5; % 隐藏层节点数
outputnum = size(t_train, 1); % 输出层节点数
%% 建立网络
net = newff(p_train, t_train, hiddennum);
%% 设置训练参数
net.trainParam.epochs = 1000; % 训练次数
net.trainParam.goal = 1e-6; % 目标误差
net.trainParam.lr = 0.01; % 学习率
net.trainParam.showWindow = 0; % 关闭窗口
%% 参数初始化
c1 = 4.494; % 学习因子
c2 = 4.494; % 学习因子
maxgen = 30; % 种群更新次数
sizepop = 5; % 种群规模
Vmax = 1.0; % 最大速度
Vmin = -1.0; % 最小速度
popmax = 1.0; % 最大边界
popmin = -1.0; % 最小边界
%% 节点总数
numsum = inputnum * hiddennum + hiddennum + hiddennum * outputnum + outputnum;
for i = 1 : sizepop
pop(i, :) = rands(1, numsum); % 初始化种群
V(i, :) = rands(1, numsum); % 初始化速度
fitness(i) = fun(pop(i, :), hiddennum, net, p_train, t_train);
end
%% 个体极值和群体极值
[fitnesszbest, bestindex] = min(fitness);
zbest = pop(bestindex, :); % 全局最佳
gbest = pop; % 个体最佳
fitnessgbest = fitness; % 个体最佳适应度值
BestFit = fitnesszbest; % 全局最佳适应度值
%% 迭代寻优
for i = 1: maxgen
for j = 1: sizepop
% 速度更新
V(j, :) = V(j, :) + c1 * rand * (gbest(j, :) - pop(j, :)) + c2 * rand * (zbest - pop(j, :));
V(j, (V(j, :) > Vmax)) = Vmax;
V(j, (V(j, :) < Vmin)) = Vmin;
% 种群更新
pop(j, :) = pop(j, :) + 0.2 * V(j, :);
pop(j, (pop(j, :) > popmax)) = popmax;
pop(j, (pop(j, :) < popmin)) = popmin;
% 自适应变异
pos = unidrnd(numsum);
if rand > 0.85
pop(j, pos) = rands(1, 1);
end
% 适应度值
fitness(j) = fun(pop(j, :), hiddennum, net, p_train, t_train);
end
for j = 1 : sizepop
% 个体最优更新
if fitness(j) < fitnessgbest(j)
gbest(j, :) = pop(j, :);
fitnessgbest(j) = fitness(j);
end
% 群体最优更新
if fitness(j) < fitnesszbest
zbest = pop(j, :);
fitnesszbest = fitness(j);
end
end
BestFit = [BestFit, fitnesszbest];
end
参考资料
[1] https://blog.csdn.net/kjm13182345320/article/details/128163536?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502
[2] https://blog.csdn.net/kjm13182345320/article/details/128151206?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502