最近在面试过程中遇到了手写nms的问题,结束后重新实现并调通了nms和softmax的代码。
1、NMS
原理(通俗易懂):
先假设有6个候选框,根据分类器类别分类概率做排序,从小到大分别属于车辆的概率分别为A、B、C、D、E、F。
从最大概率矩形框F开始,分别判断A~E与F的重叠度IOU是否大于某个设定的阈值;
假设B、D与F的重叠度超过阈值,那么就扔掉B、D(因为超过阈值,说明D与F或者B与F,有很大部分是重叠的,保留概率最大的F即可);并标记第一个矩形框F,是我们保留下来的。
从剩下的矩形框A、C、E中,选择概率最大的E,然后判断E与A、C的重叠度,删除重叠度大于一定阈值的框;并标记E是我们保留下来的第二个矩形框。
一直重复这个过程,找到所有曾经被保留下来的矩形框。
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
// // 左上坐标和框的宽高(x,y,w,h)
struct Box
{
int x;
int y;
int w;
int h;
float score;
};
bool sort_score(Box box1, Box box2)
{
return box1.score > box2.score ? true : false;
}
float iou(Box box1, Box box2)
{
int x1 = max(box1.x, box2.x);
int y1 = max(box1.y, box2.y);
int x2 = min(box1.x + box1.w, box2.x + box2.w);
int y2 = min(box1.y + box1.h, box2.y + box2.h);
// 判断两框是否相交,若不相交,返回0
if (x1 >= x2 || y1 >= y2)
{
return 0;
}
float over_area = (x2 - x1)*(y2 - y1);
float both_area = box1.w*box1.h + box2.w*box2.h - over_area;
float iou = over_area / both_area;
int x3 = min(box1.x, box2.x);
int y3 = min(box1.y, box2.y);
int x4 = max(box1.x + box1.w, box2.x + box2.w);
int y4 = max(box1.y + box1.h, box2.y + box2.h);
float all_area = (x4 - x3)*(y4 - y3);
float area1 = (all_area - both_area) / all_area;
float giou = iou - area1;
// 正常nms返回的是iou的值,此处实现giou,也可添加diou\ciou
return giou;
}
vector<Box>nms(vector<Box>&vec_boxs, float threshold)
{
vector<Box>results;
//按分值从大到小排序
std::sort(vec_boxs.begin(), vec_boxs.end(), sort_score);
while (vec_boxs.size() > 0)
{
results.push_back(vec_boxs[0]);
int index = 1;
while (index < vec_boxs.size())
{
float iou_value = iou(vec_boxs[0], vec_boxs[index]);
cout << "iou:" << iou_value << endl;
// iou大于阈值,使用erase剔除
if (iou_value > threshold)
{
vec_boxs.erase(vec_boxs.begin() + index);
}
else
index++;
}
vec_boxs.erase(vec_boxs.begin());
}
return results;
}
int main()
{
vector<Box>input;
Box box1 = { 0, 0, 100, 101, 0.9 };
Box box2 = { 5, 6, 90, 110, 0.7 };
input.push_back(box1);
input.push_back(box2);
vector<Box>res;
res = nms(input, 0.65);
for (int i = 0; i < res.size(); i++)
{
printf("%d %d %d %d %f", res[i].x,res[i].y, res[i].w, res[i].h, res[i].score);
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
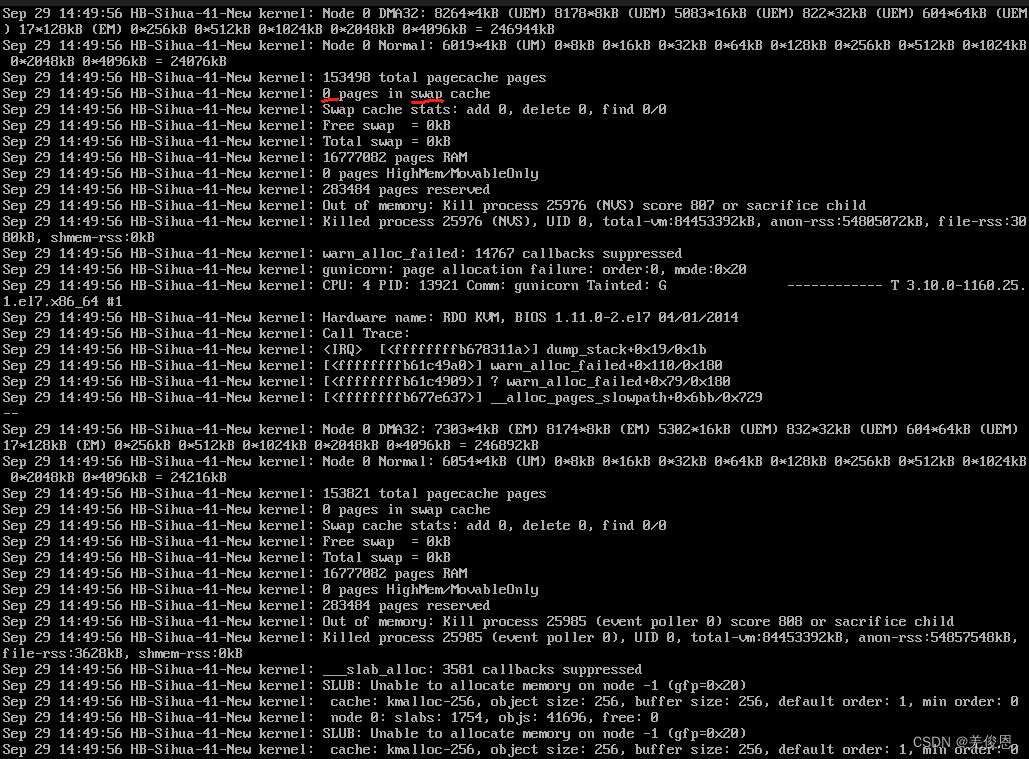
结果为:
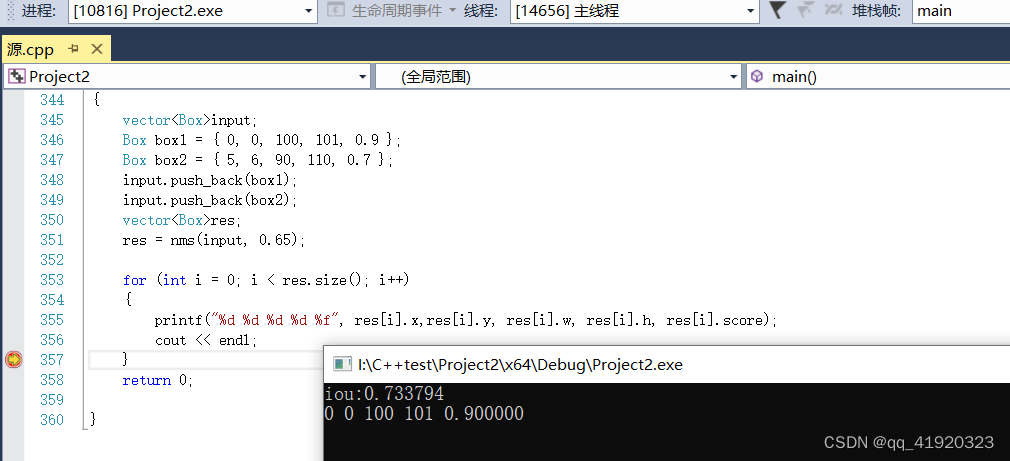
2、softmax
softmax是逻辑回归在多分类问题上的推广,大概的公式如下:
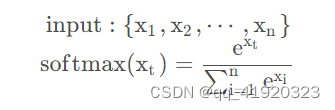
即判断该变量在总体变量中的占比。
2.1 简单实现
用vector来封装输入和输出,简单的按公式复现。
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<math.h>
using namespace std;
vector<double>softmax(vector<double>input)
{
double total = 0;
for (auto x : input)
{
total += exp(x);
}
vector<double>result;
for (auto x : input)
{
result.push_back(exp(x) / total);
}
return result;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<double>input;
while (n--)
{
double x;
cin >> x;
input.push_back(x);
}
for (auto y : softmax(input))
{
cout << y << ' ';
}
}
输入n:数字个数
回车键后依次输入四个数值。
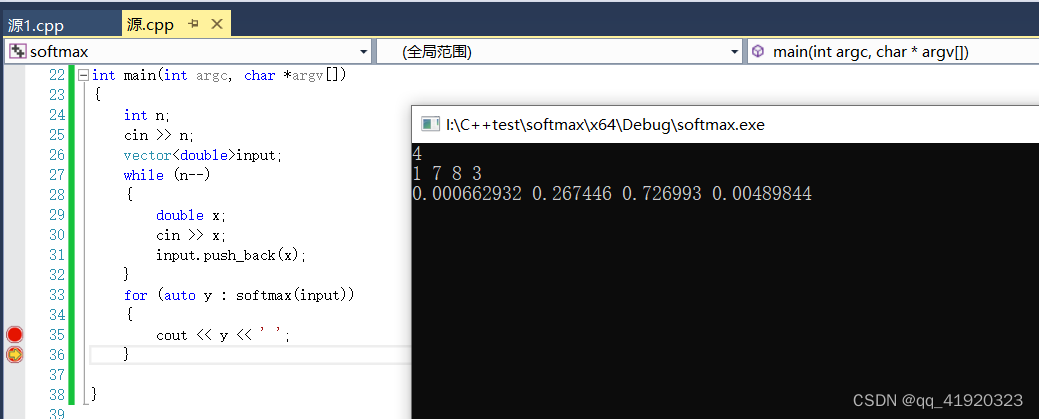
经过测试正常。
2.2 改进
若输入数值中有一个数值特别大,如(1 3 4 1000),此时由于e^{1000}已经溢出了双精度浮点(double)所能表示的范围,所以变成了NaN。
改进原理:
注意观察softmax的公式:
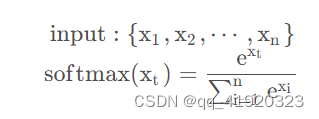
如果我们给上下同时乘以一个很小的数,最后答案的值是不变的。
那我们可以给每一个输入都减去一个值a,防止数值超出精度范围。
大致表示如下:

a值得取值也比较简单,取输入数值中的最大值即可。
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<math.h>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
vector<double>softmax(vector<double>input)
{
double total = 0;
double MAX = input[0];
for (auto x : input)
{
MAX = max(x, MAX);
}
for (auto x : input)
{
total += exp(x - MAX);
}
vector<double>result;
for (auto x : input)
{
result.push_back(exp(x - MAX) / total);
}
return result;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<double> input;
while (n--)
{
double x;
cin >> x;
input.push_back(x);
}
for (auto y : softmax(input))
{
cout << y << ' ';
}
}
输出为:

第三行为输出结果,数值正常。