目录
【1】引入POSIX信号量
【1.1】初始化信号量
【1.2】销毁信号量
【1.3】等待信号量
【1.4】发布信号量
【2】基于环形队列的生产消费模型
【2.1】生产消费模型打印数字模型
【2.2】生产消费模型计算公式模型
【2.3】生产消费模型计算公式加保存任务模型
【1】引入POSIX信号量
POSIX信号量和SystemV信号量作用相同,都是用于同步操作,达到无冲突的访问共享资源目的。 但POSIX可以用于线程间同步。
什么是信号量:信号量本身是一把计数器,只要拥有信号量,就在未来一定能够拥有临界资源的一部分,申请信号量的本质就是对临界资源种特定小块资源的预定机制,线程要访问临界资源种的某一区域,需要先申请信号量,所有人必须要先看到信号量,信号量本身必须是公共资源。
【计数器】
-
递减or递增 sem_t sem = 10;
-
sem-- : 申请资源 - 必须保证操作的原子性 - P
-
sem++: 归还资源 - 必须保证操作的原子性 - V
【信号量核心操作】PV原语。
【1.1】初始化信号量
#include <semaphore.h>
int sem_init(sem_t *sem, int pshared, unsigned int value);
// 参数:
// pshared:0表示线程间共享,非零表示进程间共享
// value:信号量初始值【1.2】销毁信号量
int sem_destroy(sem_t *sem);【1.3】等待信号量
// 功能:等待信号量,会将信号量的值减1
int sem_wait(sem_t *sem); //P()【1.4】发布信号量
// 功能:发布信号量,表示资源使用完毕,可以归还资源了。将信号量值加1。
int sem_post(sem_t *sem);//V()【2】基于环形队列的生产消费模型
环形队列采用数组模拟,用模运算来模拟环状特性。
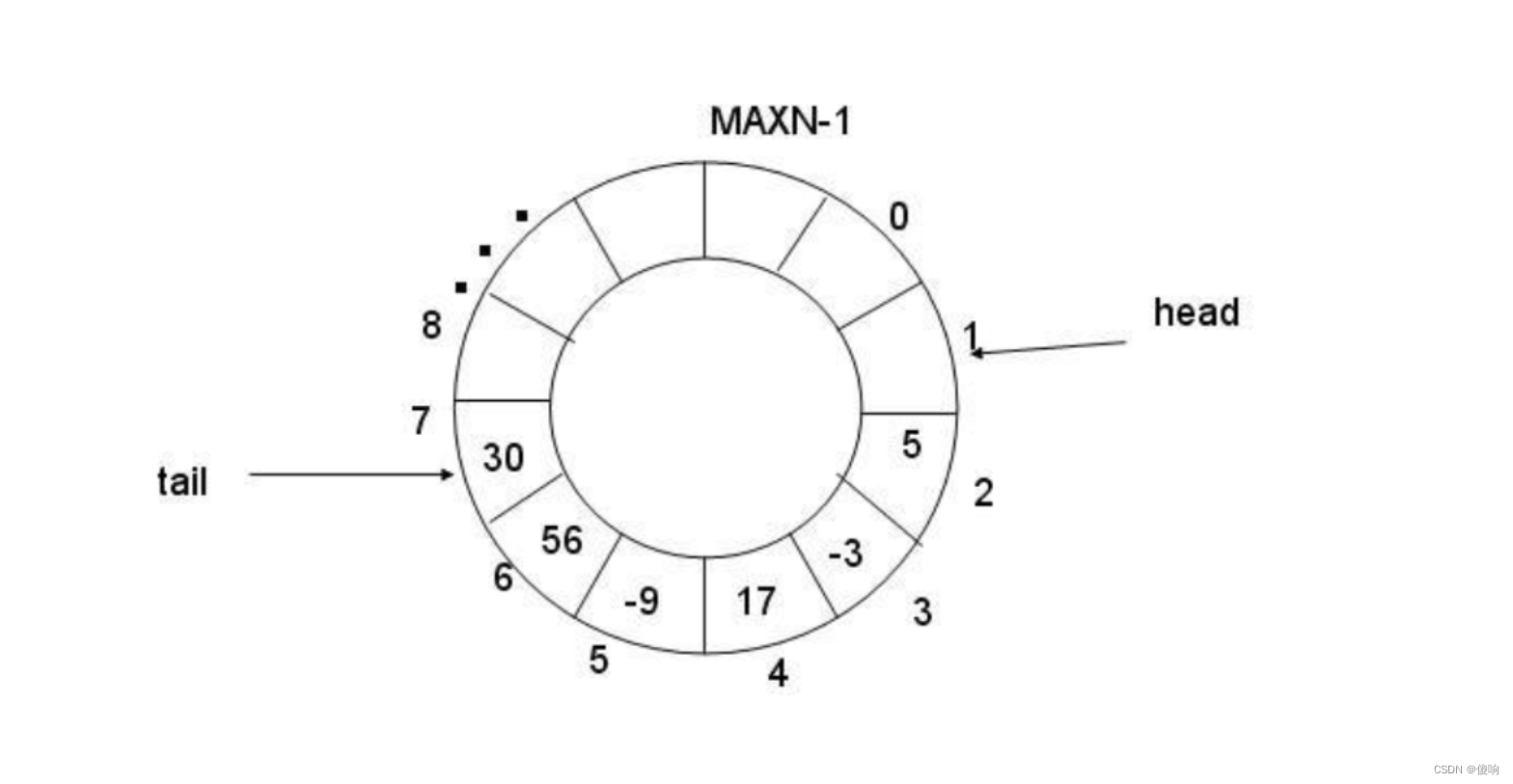
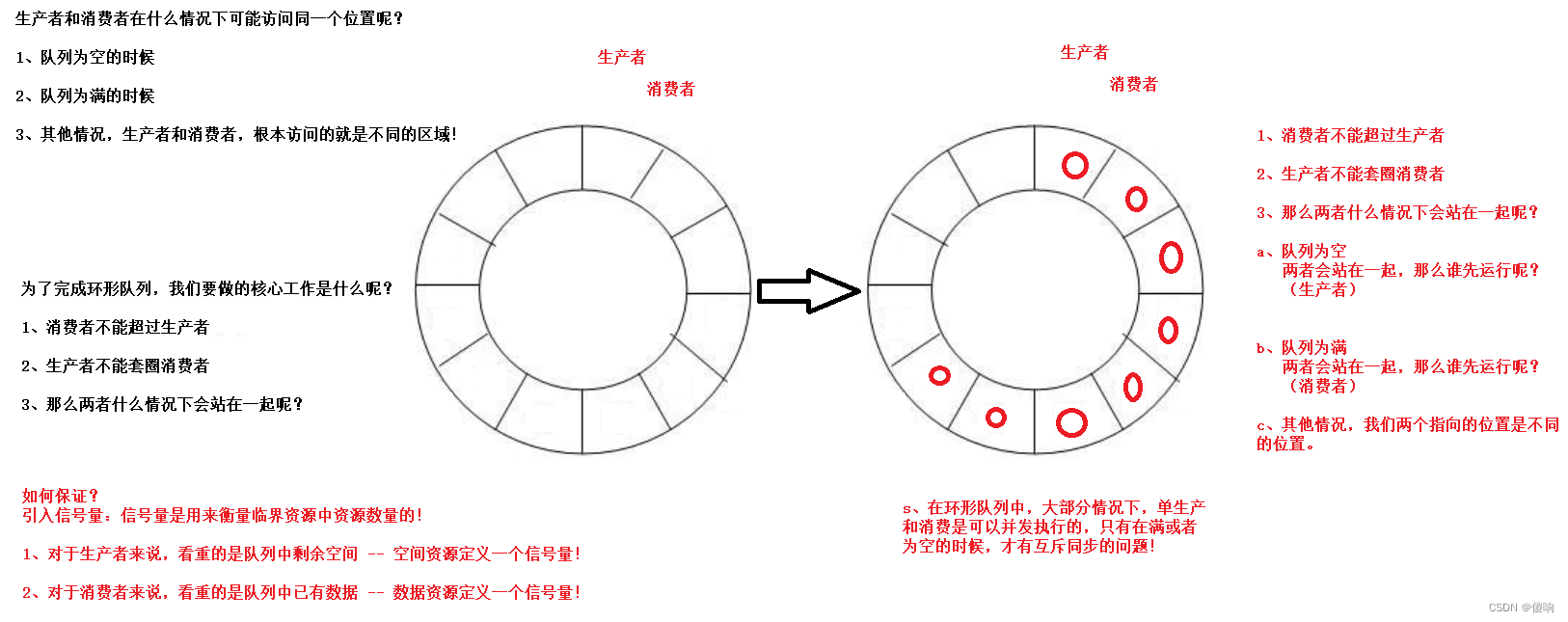
环形结构起始状态和结束状态都是一样的,不好判断为空或者为满,所以可以通过加计数器或者标记位来判断满或者空。另外也可以预留一个空的位置,作为满的状态。
【2.1】生产消费模型打印数字模型
【makefile文件】
cc=g++
standard=-std=c++11
ringQueue:RingQueue.cc
$(cc) -o $@ $^ $(standard) -l pthread
.PHONY:clean
clean:
rm -rf ringQueue【RingQueue.hpp文件】
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <cassert>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
static const int g_maxCapacity = 5;
/* 环形队列类 */
template <class T>
class RingQueue
{
public:
/* 构造函数 */
RingQueue(const int& capacity = g_maxCapacity)
: _cyclicQueue(capacity)
, _capacity(capacity)
{
// 对于生产者来说的初始化:关注空间资源,初始化也是空间的大小
int pN = sem_init(&_pSpaceSem, 0, capacity);
assert(pN == 0); (void)pN;
// 对于消费者来说的初始化:关注数据资源,初始化肯定是0,因为没有数据
int cN = sem_init(&_cDataSem, 0, 0);
assert(cN == 0); (void)cN;
// 位置清零
_pSubcript = _cSubcript = 0;
// 生产者锁初始化
pthread_mutex_init(&_pMutex, nullptr);
// 消费者锁初始化
pthread_mutex_init(&_cMutex, nullptr);
}
/* 析构函数 */
~RingQueue()
{
// 生产者信号量销毁
sem_destroy(&_pSpaceSem);
// 消费者信号量销毁
sem_destroy(&_cDataSem);
// 生产者锁销毁
pthread_mutex_destroy(&_pMutex);
// 消费者锁销毁
pthread_mutex_destroy(&_cMutex);
}
public:
/* 生产任务 */
void Push(const T& in)
{
// 生产前:申请空间信号量,保证一定可以进行生产,空间信号量-1
P(_pSpaceSem);
// 加锁
pthread_mutex_lock(&_pMutex);
_cyclicQueue[_pSubcript++] = in;
_pSubcript %= _capacity;
// 解锁
pthread_mutex_unlock(&_pMutex);
// 生产完:占用一个空间,数据信号量+1
V(_cDataSem);
}
/* 消费任务 */
void Pop(T* out)
{
// 消费前:申请数据信号量,保证一定可以进行消费,数据信号量-1
P(_cDataSem);
// 加锁
pthread_mutex_lock(&_pMutex);
*out = _cyclicQueue[_cSubcript++];
_cSubcript %= _capacity;
// 解锁
pthread_mutex_unlock(&_pMutex);
// 消费完:少了一个空间,空间信号量+1
V(_pSpaceSem);
}
private:
/* 等待信号量,会将信号量的值减1 */
void P(sem_t& sem)
{
int n = sem_wait(&sem);
assert(n == 0); (void)n;
}
/* 发布信号量,表示资源使用完毕,可以归还资源了。将信号量值加1 */
void V(sem_t& sem)
{
int n = sem_post(&sem);
assert(n == 0); (void)n;
}
private:
std::vector<T> _cyclicQueue; // 环形队列容器
int _capacity; // 环形队列容量
int _pSubcript; // 生产者脚步(下标)
int _cSubcript; // 消费者脚步(下标)
sem_t _pSpaceSem; // 生产者信号量(生产者看重的是空间资源)
sem_t _cDataSem; // 消费者信号量(消费者看重的是数据资源)
pthread_mutex_t _pMutex; // 生产者锁
pthread_mutex_t _cMutex; // 消费者锁
};【RingQueue.cc文件】
#include "RingQueue.hpp"
#include <cstdlib>
#include <ctime>
/* 生产者线程 */
void* ProducerRoutine(void* args)
{
// 获取传递的线程数据
RingQueue<int>* rq = static_cast<RingQueue<int>*>(args);
while(true)
{
sleep(1);
// 生产者生产中.....
int data = rand() % 100 + 1;
rq->Push(data);
std::cout << "生产完成,生产的数据是:" << data << std::endl;
}
}
/* 消费者线程 */
void* ConsumerRoutine(void* args)
{
// 获取传递的线程数据
RingQueue<int>* rq = static_cast<RingQueue<int>*>(args);
while(true)
{
sleep(2);
// 消费者消费中.....
int data = 0;
rq->Pop(&data);
std::cout << "消费完成,消费的数据是:" << data << std::endl;
}
}
/* 程序入口函数 */
int main()
{
// 定义随机数种子
srand((unsigned int)time(nullptr) ^ getpid());
// 线程数据
RingQueue<int>* rq = new RingQueue<int>();
// 定义生产者线程和消费者线程
// 生产者:Producer 消费者:Consumer
pthread_t tP, tC;
pthread_create(&tP, nullptr, ProducerRoutine, (void*)rq);
pthread_create(&tC, nullptr, ConsumerRoutine, (void*)rq);
pthread_join(tP, nullptr);
pthread_join(tC, nullptr);
delete rq;
return 0;
}【2.2】生产消费模型计算公式模型
【makefile文件】
cc=g++
standard=-std=c++11
ringQueue:RingQueue.cc
$(cc) -o $@ $^ $(standard) -l pthread
.PHONY:clean
clean:
rm -rf ringQueue【RingQueue.hpp文件】
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <cassert>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
static const int g_maxCapacity = 5;
/* 环形队列类 */
template <class T>
class RingQueue
{
public:
/* 构造函数 */
RingQueue(const int& capacity = g_maxCapacity)
: _cyclicQueue(capacity)
, _capacity(capacity)
{
// 对于生产者来说的初始化:关注空间资源,初始化也是空间的大小
int pN = sem_init(&_pSpaceSem, 0, capacity);
assert(pN == 0); (void)pN;
// 对于消费者来说的初始化:关注数据资源,初始化肯定是0,因为没有数据
int cN = sem_init(&_cDataSem, 0, 0);
assert(cN == 0); (void)cN;
// 位置清零
_pSubcript = _cSubcript = 0;
// 生产者锁初始化
pthread_mutex_init(&_pMutex, nullptr);
// 消费者锁初始化
pthread_mutex_init(&_cMutex, nullptr);
}
/* 析构函数 */
~RingQueue()
{
// 生产者信号量销毁
sem_destroy(&_pSpaceSem);
// 消费者信号量销毁
sem_destroy(&_cDataSem);
// 生产者锁销毁
pthread_mutex_destroy(&_pMutex);
// 消费者锁销毁
pthread_mutex_destroy(&_cMutex);
}
public:
/* 生产任务 */
void Push(const T& in)
{
// 生产前:申请空间信号量,保证一定可以进行生产,空间信号量-1
P(_pSpaceSem);
// 加锁
pthread_mutex_lock(&_pMutex);
_cyclicQueue[_pSubcript++] = in;
_pSubcript %= _capacity;
// 解锁
pthread_mutex_unlock(&_pMutex);
// 生产完:占用一个空间,数据信号量+1
V(_cDataSem);
}
/* 消费任务 */
void Pop(T* out)
{
// 消费前:申请数据信号量,保证一定可以进行消费,数据信号量-1
P(_cDataSem);
// 加锁
pthread_mutex_lock(&_pMutex);
*out = _cyclicQueue[_cSubcript++];
_cSubcript %= _capacity;
// 解锁
pthread_mutex_unlock(&_pMutex);
// 消费完:少了一个空间,空间信号量+1
V(_pSpaceSem);
}
private:
/* 等待信号量,会将信号量的值减1 */
void P(sem_t& sem)
{
int n = sem_wait(&sem);
assert(n == 0); (void)n;
}
/* 发布信号量,表示资源使用完毕,可以归还资源了。将信号量值加1 */
void V(sem_t& sem)
{
int n = sem_post(&sem);
assert(n == 0); (void)n;
}
private:
std::vector<T> _cyclicQueue; // 环形队列容器
int _capacity; // 环形队列容量
int _pSubcript; // 生产者脚步(下标)
int _cSubcript; // 消费者脚步(下标)
sem_t _pSpaceSem; // 生产者信号量(生产者看重的是空间资源)
sem_t _cDataSem; // 消费者信号量(消费者看重的是数据资源)
pthread_mutex_t _pMutex; // 生产者锁
pthread_mutex_t _cMutex; // 消费者锁
};【Task.hpp文件】
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <functional>
/* 计算任务 */
class CalTask
{
public:
using func_t = std::function<int(int, int, char)>;
public:
/* 构造函数 */
CalTask() {}
/* 构造函数 */
CalTask(int x, int y, char op, func_t func)
: _x(x), _y(y), _op(op), _callBalk(func)
{
}
public:
/* 仿函数 */
std::string operator()()
{
int result = _callBalk(_x, _y, _op);
char buffer[64];
snprintf(buffer, sizeof(buffer), "%d %c %d = %d\n", _x, _op, _y, result);
return buffer;
}
public:
/* 返回打印公式 */
std::string ToTaskString()
{
char buffer[64];
snprintf(buffer, sizeof(buffer), "%d %c %d = ?\n", _x, _op, _y);
return buffer;
}
private:
int _x;
int _y;
char _op;
func_t _callBalk;
};
/* 执行计算的方法 */
int MyCalculate(int x, int y, char op)
{
int result = 0;
switch (op)
{
case '+':
result = x + y;
break;
case '-':
result = x - y;
break;
case '*':
result = x * y;
break;
case '/':
{
if (y == 0)
{
std::cerr << "div zero error!" << std::endl;
result = -1;
}
else
{
result = x / y;
}
break;
}
case '%':
{
if (y == 0)
{
std::cerr << "mod zero error!" << std::endl;
result = -1;
}
else
{
result = x % y;
}
break;
}
default:
break;
}
return result;
}【RingQueue.cc文件】
#include <cstdlib>
#include <ctime>
#include "RingQueue.hpp"
#include "Task.hpp"
static std::string oper = "+-*/%";
const std::string ThreadName()
{
char buffer[64];
snprintf(buffer, sizeof(buffer), "Thread[0x%x]", pthread_self());
return buffer;
}
/* 生产者线程 */
void* ProducerRoutine(void* args)
{
// 获取传递的线程数据
RingQueue<CalTask>* rq = static_cast<RingQueue<CalTask>*>(args);
while(true)
{
sleep(1);
// 生产者生产中.....
int x = rand() % 100 + 1;
int y = rand() % 100 + 1;
char op = oper[rand() % oper.size()];
CalTask t(x, y, op, MyCalculate);
rq->Push(t);
std::cout << ThreadName() << "生产者生产任务:" << t.ToTaskString() << std::endl;
}
}
/* 消费者线程 */
void* ConsumerRoutine(void* args)
{
// 获取传递的线程数据
RingQueue<CalTask>* rq = static_cast<RingQueue<CalTask>*>(args);
while(true)
{
sleep(2);
// 消费者消费中.....
CalTask t;
rq->Pop(&t);
std::cout << ThreadName() << "消费者消费任务:" << t() << std::endl;
}
}
/* 程序入口函数 */
int main()
{
// 定义随机数种子
srand((unsigned int)time(nullptr) ^ getpid());
// 线程数据
RingQueue<CalTask>* rq = new RingQueue<CalTask>();
// 定义生产者线程和消费者线程
// 生产者:Producer 消费者:Consumer
pthread_t tP, tC;
pthread_create(&tP, nullptr, ProducerRoutine, (void*)rq);
pthread_create(&tC, nullptr, ConsumerRoutine, (void*)rq);
pthread_join(tP, nullptr);
pthread_join(tC, nullptr);
创建生产消费线程
//pthread_t t_p[4]; // Producer(生产者)
//pthread_t t_c[8]; // Consumer(消费者)
pthread_create(&t_p, nullptr, ProducerRoutine, rq);
//for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
//{
// pthread_create(t_p + i, nullptr, ProducerRoutine, rq);
//}
//
pthread_create(&t_c, nullptr, ConsumerRoutine, rq);
//for(int i = 0; i < 8; i++)
//{
// pthread_create(t_c + i, nullptr, ConsumerRoutine, rq);
//}
//
//
//
线程等待
pthread_join(t_p, nullptr);
//for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
//{
// pthread_join(t_p[i], nullptr);
//}
pthread_join(t_c, nullptr);
//for(int i = 0; i < 8; i++)
//{
// pthread_join(t_c[i], nullptr);
//}
delete rq;
return 0;
}【2.3】生产消费模型计算公式加保存任务模型
【Makefile文件】
# 创建替换变量并且复制对应的含义
cc := g++
standard := -std=c++11
# 创建依赖关系
myThreadRingQueue: ThreadRingQueue.cc
$(cc) -o $@ $^ $(standard) -l pthread
# 创建辅助命令
clean:
rm -rf myThreadRingQueue
.PHONY: clean【ThreadBase.hpp】
#pragma once
#include <cstdio>
#include <cassert>
#include <iostream>
#include <functional>
#include <string>
#include <pthread.h>
class ThreadBase;
/* 线程上下文数据封装类 */
class ThreadBaseConnectText
{
public:
ThreadBaseConnectText()
: _textThis(nullptr)
, _textArgs(nullptr)
{}
public:
ThreadBase* _textThis;
void* _textArgs;
};
/* 基于原生线程库的线程封装类 */
class ThreadBase
{
private:
const int ctNum = 64;
public:
// 定义仿函数
using func_t = std::function<void*(void*)>;
public:
public:
/* - 构造函数
* - func: 线程回调函数
* - args:线程回调函数参数
* - num : 编写线程名称设定的编号
*/
ThreadBase(func_t func, void* args = nullptr, const int& num = 1)
: _threadCallBack(func)
, _threadArgs(args)
{
// 自定义线程名称
char nameBuffer[ctNum];
snprintf(nameBuffer, sizeof(nameBuffer), "thread-%d", num);
_threadName = nameBuffer;
// 创建线程连接上下文 - 手动释放内存 - 【01】
ThreadBaseConnectText* connectText = new ThreadBaseConnectText();
connectText->_textThis = this;
connectText->_textArgs = _threadArgs;
int state = pthread_create(&_threadId, nullptr, StartRoutine, (void*)connectText);
assert(state == 0); (void)state;
}
/* - 析构函数
*/
~ThreadBase()
{}
public:
/* - 线程等待
*/
void Join()
{
int state = pthread_join(_threadId, nullptr);
assert(state == 0); (void)state;
}
public:
/* - 获取线程名称
*/
std::string GetThreadName()
{
return _threadName;
}
/* - 获取线程Id
*/
std::string GetThreadId()
{
char buffer[ctNum];
snprintf(buffer, sizeof(buffer), "0x%x", _threadId);
return buffer;
}
public:
/* - 线程函数
*/
static void* StartRoutine(void* args)
{
ThreadBaseConnectText* connectText = static_cast<ThreadBaseConnectText*>(args);
void* retVal = connectText->_textThis->Run(connectText->_textArgs);
// 释放内存 - 【01】
delete connectText;
// 返回
return retVal;
}
private:
/* - StartRoutine专用函数(因为C/C++混编的原因)
*/
void* Run(void* args)
{
// 调用回调线程
return _threadCallBack(args);
}
private:
std::string _threadName; // 线程名称
pthread_t _threadId; // 线程Id
func_t _threadCallBack; // 线程回调函数
void* _threadArgs; // 线程回调函数参数
};【ThreadMutex.hpp】
#pragma once
#include <pthread.h>
/* 原生线程锁类封装 */
class Mutex
{
public:
/* - 构造函数
*/
Mutex(pthread_mutex_t* mutex)
: _pMutex(mutex)
{}
/* - 析构函数
*/
~Mutex()
{}
public:
/* - 加锁函数
*/
void Lock() { pthread_mutex_lock(_pMutex); }
/* - 解锁函数
*/
void UnLock() { pthread_mutex_unlock(_pMutex); }
private:
pthread_mutex_t* _pMutex; // 内部的线程锁
};
class LockGuardMutex
{
public:
/* - 构造函数
*/
LockGuardMutex(pthread_mutex_t* mutex)
: _mutex(mutex)
{
_mutex.Lock();
}
/* - 析构函数
*/
~LockGuardMutex()
{
_mutex.UnLock();
}
private:
Mutex _mutex;
};【ThreadRingQueue.cc】
#include <ctime>
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include <unistd.h>
#include "ThreadRingQueue.hpp"
#include "ThreadBase.hpp"
#include "ThreadMutex.hpp"
#include "ThreadTask.hpp"
static std::string oper = "+-*/%";
/* - 生产者线程函数
*/
void* ProducerThread(void* args)
{
sleep(1);
ThreadRingQueue<TaskCalculate>* pRQ = (static_cast<ThreadRingQueues<TaskCalculate, TaskSave>*>(args))->_cTask;
while(true)
{
int x = rand() % 100 + 1;
int y = rand() % 100 + 1;
char op = oper[rand() % oper.size()];
TaskCalculate cTask(Calculate, x, y, op);
pRQ->Push(cTask);
std::cout << "生产者在生产任务-> " << "[" << cTask.TaskString() << "] - - 生产者当前位置:" << pRQ->GetPosP() << std::endl;
sleep(1);
}
return nullptr;
}
/* - 消费者线程函数
*/
void* ConsumerThread(void* args)
{
sleep(1);
ThreadRingQueue<TaskCalculate>* cRQ = (static_cast<ThreadRingQueues<TaskCalculate, TaskSave>*>(args))->_cTask;
ThreadRingQueue<TaskSave>* sRQ = (static_cast<ThreadRingQueues<TaskCalculate, TaskSave>*>(args))->_sTask;
while(true)
{
TaskCalculate cTask;
cRQ->Pop(&cTask);
std::string message = cTask();
std::cout << "消费者在消费任务-> " << "[" << cTask() << "] - - 消费者当前位置:" << cRQ->GetPosC() << std::endl;
TaskSave sTask(FileSave, message);
sRQ->Push(sTask);
std::cout << "ConsumerThread-推送保存完成..." << std::endl;
sleep(3);
}
return nullptr;
}
/* - 保存者线程函数
*/
void* SaveThread(void* args)
{
sleep(1);
ThreadRingQueue<TaskSave>* sRQ = (static_cast<ThreadRingQueues<TaskCalculate, TaskSave>*>(args))->_sTask;
while(true)
{
TaskSave sTask;
sRQ->Pop(&sTask);
sTask();
std::cout << "SaveThread-保存任务完成..." << std::endl;
sleep(3);
}
return nullptr;
}
/* = 程序入口函数
*/
int main()
{
// 定义随机数种子
srand((unsigned int)time(nullptr));
// 定义共享资源
ThreadRingQueues<TaskCalculate, TaskSave>* RQ = new ThreadRingQueues<TaskCalculate, TaskSave>();
RQ->_cTask = new ThreadRingQueue<TaskCalculate>;
RQ->_sTask = new ThreadRingQueue<TaskSave>;
std::unique_ptr<ThreadBase> ptr_pTd(new ThreadBase(ProducerThread, (void*)RQ, 1));
std::cout << "创建生产者线程完成-> 线程名:" << ptr_pTd->GetThreadName() << " 线程Id:" << ptr_pTd->GetThreadId() << std::endl;
sleep(10);
std::unique_ptr<ThreadBase> ptr_cTd(new ThreadBase(ConsumerThread, (void*)RQ, 2));
std::cout << "创建生产者线程完成-> 线程名:" << ptr_cTd->GetThreadName() << " 线程Id:" << ptr_cTd->GetThreadId() << std::endl;
sleep(5);
std::unique_ptr<ThreadBase> ptr_sTd(new ThreadBase(SaveThread, (void*)RQ, 3));
std::cout << "创建生产者线程完成-> 线程名:" << ptr_sTd->GetThreadName() << " 线程Id:" << ptr_sTd->GetThreadId() << std::endl;
ptr_pTd->Join();
ptr_cTd->Join();
// ptr_sTd->Join();
delete RQ->_cTask;
delete RQ->_sTask;
delete RQ;
return 0;
}【ThreadRingQueue.hpp】
#pragma once
#include <cstdio>
#include <cassert>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
static const size_t gCapacity = 10;
template <class T>
class ThreadRingQueue
{
public:
/* - 构造函数
*/
ThreadRingQueue(const size_t& capacity = gCapacity)
: _capacity(capacity)
, _v(capacity)
{
// 初始化信号量
int n = 0;
n = sem_init(&_pSem, 0, _capacity); assert(n == 0);
n = sem_init(&_cSem, 0, _capacity); assert(n == 0);
(void)n;
// 生产者和消费者的位置初始化
_pSubscript = _cSubscript = 0;
// 初始化互斥锁
pthread_mutex_init(&_pMutex, nullptr);
pthread_mutex_init(&_cMutex, nullptr);
}
/* - 析构函数
*/
~ThreadRingQueue()
{
// 释放信号量
sem_destroy(&_pSem);
sem_destroy(&_cSem);
// 释放互斥锁
pthread_mutex_destroy(&_pMutex);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&_cMutex);
}
public:
/* - 生产任务
*/
void Push(const T& in)
{
// 生产前:保证可以生产->空间信号量-1
P(_pSem);
// 加锁
pthread_mutex_lock(&_pMutex);
_v[_pSubscript++] = in;
_pSubscript %= _capacity;
// 解锁
pthread_mutex_unlock(&_pMutex);
// 生产完:占用一个空间->数据信号量+1
V(_cSem);
}
/* - 消费任务
*/
void Pop(T* out)
{
// 消费前:保证可以消费->数据信号量-1
P(_cSem);
// 加锁
pthread_mutex_lock(&_pMutex);
*out = _v[_cSubscript++];
_cSubscript %= _capacity;
// 解锁
pthread_mutex_unlock(&_pMutex);
// 消费完:减少一个空间->空间信号量+1
V(_pSem);
}
public:
/* - 获取生产者当前位置
*/
size_t GetPosP()
{
return _pSubscript;
}
/* - 获取消费者当前位置
*/
size_t GetPosC()
{
return _cSubscript;
}
private:
/* - 等待信号量:会将信号量的值减1。
*/
void P(sem_t& sem)
{
int n = sem_wait(&sem); assert(n == 0);
(void)n;
}
/* - 发布信号量:表示资源使用完毕,可以归还资源了。将信号量值加1
*/
void V(sem_t& sem)
{
int n = sem_post(&sem); assert(n == 0);
(void)n;
}
private:
std::vector<T> _v; // 环形队列容器
size_t _capacity; // 环形队列容量
int _pSubscript; // 生产力位置下标
int _cSubscript; // 消费者位置下标
sem_t _pSem; // 生产者资源
sem_t _cSem; // 消费者资源
pthread_mutex_t _pMutex; // 生产者互斥锁
pthread_mutex_t _cMutex; // 消费者互斥锁
};【ThreadTask.hpp】
#pragma once
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <functional>
#include "ThreadRingQueue.hpp"
class TaskCalculate;
class TaskSave;
template<class C, class S>
class ThreadRingQueues
{
public:
ThreadRingQueue<C>* _cTask;
ThreadRingQueue<S>* _sTask;
};
class TaskCalculate
{
private:
// 定义仿函数
using func_t = std::function<int(const int, const int, const char)>;
public:
/* - 无参构造函数
*/
TaskCalculate()
{}
/* - 带参数的构造函数
*/
TaskCalculate(func_t func, const int x, const int y, const char op)
: _func(func)
, _x(x)
, _y(y)
, _op(op)
{}
public:
/* - ()运算符重载
*/
std::string operator()()
{
int result = _func(_x, _y, _op);
char buffer[64];
snprintf(buffer, sizeof(buffer), "%d %c %d = %d", _x, _op, _y, result);
return buffer;
}
public:
std::string TaskString()
{
char buffer[64];
snprintf(buffer, sizeof(buffer), "%d %c %d = ?", _x, _op, _y);
return buffer;
}
private:
int _x; // 第一个计算值
int _y; // 第二个计算值
char _op; // 第三个计算值
func_t _func; // 仿函数类型
};
int Calculate(const int x, const int y, const char op)
{
int calRet = 0;
switch(op)
{
case '+':
{
calRet = x + y;
break;
}
case '-':
{
calRet = x - y;
break;
}
case '*':
{
calRet = x * y;
break;
}
case '/':
{
if (y == 0)
{
std::cerr << "div zero error!" << std::endl;
calRet = -1;
}
else
{
calRet = x / y;
}
break;
}
case '%':
{
if (y == 0)
{
std::cerr << "mod zero error!" << std::endl;
calRet = -1;
}
else
{
calRet = x % y;
}
break;
}
default:
{
break;
}
}
return calRet;
};
class TaskSave
{
private:
using func_t = std::function<void(const std::string&)>;
public:
/* - 无参构造函数
*/
TaskSave()
{}
/* - 带参构造函数
*/
TaskSave(func_t func, const std::string& msg)
: _func(func)
, _msg(msg)
{}
public:
/* - ()运算符重载
*/
void operator()()
{
_func(_msg);
}
private:
std::string _msg;
func_t _func;
};
void FileSave(const std::string& msg)
{
// 创建打开文件目录
std::string target = "./Log.txt";
// 打开文件
FILE* fpath = fopen(target.c_str(), "a+");
if(fpath == nullptr)
{
std::cerr << "fopen fail!" << std::endl;
return;
}
// 写入文件
fputs(msg.c_str(), fpath);
fputs("\n", fpath);
// 关闭文件
fclose(fpath);
}




![[C++ 网络协议] 多线程服务器端](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/44204df4ae1e418a80cee48eeaf2137e.png)