SQL 接收
首先看定义在fe/fe-core/src/main/java/org/apache/doris/qe/QeService.java文件中的public class QeService类,该类is the encapsulation of the entire front-end service, including the creation of services that support the MySQL protocol是整个前端服务的封装。其中包含两个最重要的类MysqlServer和ConnectScheduler,构造MysqlServer实例需要port端口和ConnectScheduler连接调度器。然后提供start成员函数,其主要是调用mysqlServer.start()函数。
public class QeService {
private static final Logger LOG = LogManager.getLogger(QeService.class);
private int port; private MysqlServer mysqlServer; // MySQL protocol service
public QeService(int port, ConnectScheduler scheduler) {
this.port = port; this.mysqlServer = new MysqlServer(port, scheduler);
}
public void start() throws Exception { // Set up help module
try { HelpModule.getInstance().setUpModule(HelpModule.HELP_ZIP_FILE_NAME);
} catch (Exception e) { LOG.warn("Help module failed, because:", e); throw e; }
if (!mysqlServer.start()) { LOG.error("mysql server start failed"); System.exit(-1); }
LOG.info("QE service start.");
}
}
Apache Doris 兼容 Mysql 协议,用户可以通过 Mysql 客户端和其他支持 Mysql 协议的工具向 Doris 发送查询请求。其中最核心的类就是定义在fe/fe-core/src/main/java/org/apache/doris/mysql/MysqlServer.java文件中的public class MysqlServer(mysql protocol implementation based on nio)。由于其是基于nio的,所以可以有private XnioWorker xnioWorker和private ExecutorService taskService = ThreadPoolManager.newDaemonCacheThreadPool( Config.max_mysql_service_task_threads_num, "mysql-nio-pool", true)线程池成员。而acceptListener即是当新连接来时提供调用的handler回调函数。AcceptListener类(public class AcceptListener implements ChannelListener<AcceptingChannel<StreamConnection>>)为listener for accept mysql connections,其最重要的成员函数就是public void handleEvent(AcceptingChannel<StreamConnection> channel)。
public MysqlServer(int port, ConnectScheduler connectScheduler) {
this.port = port;
this.xnioWorker = Xnio.getInstance().createWorkerBuilder().setWorkerName("doris-mysql-nio").setWorkerIoThreads(Config.mysql_service_io_threads_num).setExternalExecutorService(taskService).build();
this.acceptListener = new AcceptListener(connectScheduler); // connectScheduler only used for idle check.
}
handleEvent函数首先accept流连接,然后创建ConnectContext对象,通过调用connectScheduler.submit(context)提交到连接调度器中,启动worker执行connectScheduler.registerConnection(context)注册ConnectContext对象,然后创建ConnectProcessor类ConnectProcessor processor = new ConnectProcessor(context),最后执行context.startAcceptQuery(processor),流程交到ConnectProcessor线程中。
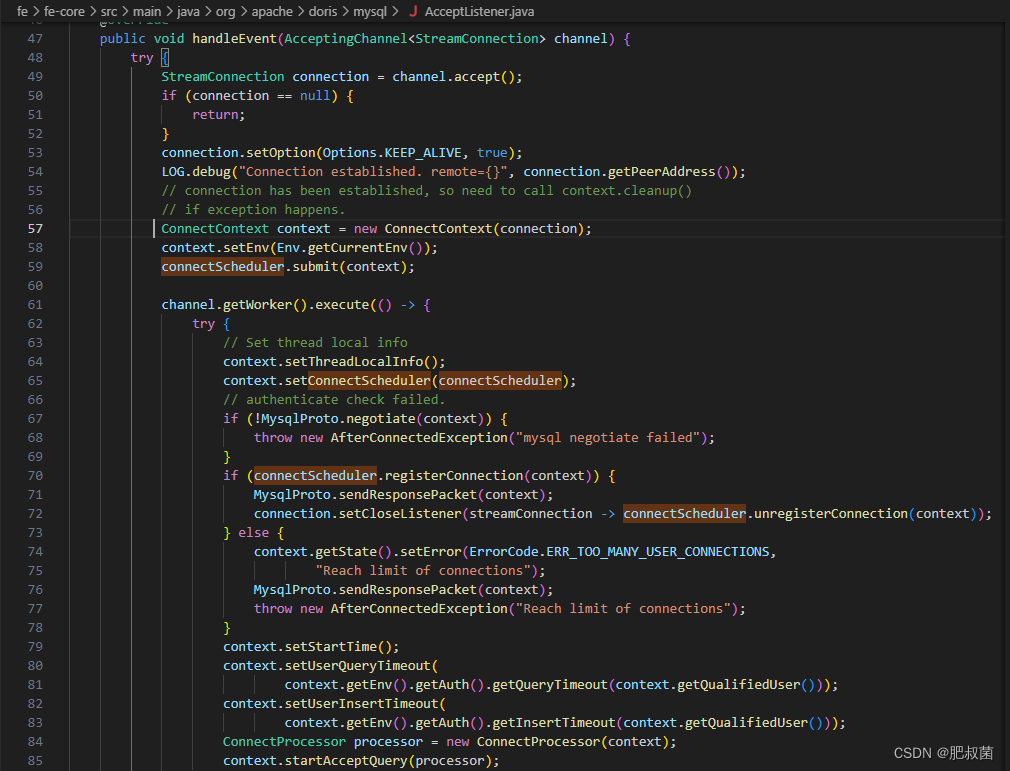
MysqlServer Listener() 负责监听客户端发送来的 Mysql 连接请求,每个连接请求都被封装成一个 ConnectContext 对象,并被提交给 ConnectScheduler。ConnectScheduler 会维护一个线程池,每个 ConnectContext 会在线程池中由一个 ConnectProcessor 线程处理。
MysqlServer start函数,调用createStreamConnectionServer创建服务端,调用server.resumeAccepts进入服务状态。
// start MySQL protocol service. return true if success, otherwise false
public boolean start() {
try {
if (FrontendOptions.isBindIPV6()) {
server = xnioWorker.createStreamConnectionServer(new InetSocketAddress("::0", port), acceptListener, OptionMap.create(Options.TCP_NODELAY, true, Options.BACKLOG, Config.mysql_nio_backlog_num));
} else {
server = xnioWorker.createStreamConnectionServer(new InetSocketAddress(port), acceptListener, OptionMap.create(Options.TCP_NODELAY, true, Options.BACKLOG, Config.mysql_nio_backlog_num));
}
server.resumeAccepts();
running = true;
LOG.info("Open mysql server success on {}", port);
return true;
} catch (IOException e) {
LOG.warn("Open MySQL network service failed.", e);
return false;
}
}
ConnectScheduler为The scheduler of query requests(Now the strategy is simple, we allocate a thread for it when a request comes)。作为连接调度器,必然会维护连接数,这里的private final int maxConnections; private final AtomicInteger numberConnection; private final AtomicInteger nextConnectionId;就是该用途。由于每个连接请求都被封装成一个 ConnectContext 对象,因此在连接调度器维护了map private final Map<Integer, ConnectContext> connectionMap = Maps.newConcurrentMap()用于保存ConnectionId和ConnectContext 对象的映射关系,private final Map<String, AtomicInteger> connByUser = Maps.newConcurrentMap()则是用于维护用户与连接数量的映射关系。
// submit one MysqlContext to this scheduler. return true, if this connection has been successfully submitted, otherwise return false. Caller should close ConnectContext if return false.
public boolean submit(ConnectContext context) {
if (context == null) { return false; }
context.setConnectionId(nextConnectionId.getAndAdd(1));
return true;
}
// Register one connection with its connection id.
public boolean registerConnection(ConnectContext ctx) {
if (numberConnection.incrementAndGet() > maxConnections) { numberConnection.decrementAndGet(); return false; }
// Check user
connByUser.putIfAbsent(ctx.getQualifiedUser(), new AtomicInteger(0));
AtomicInteger conns = connByUser.get(ctx.getQualifiedUser());
if (conns.incrementAndGet() > ctx.getEnv().getAuth().getMaxConn(ctx.getQualifiedUser())) {
conns.decrementAndGet(); numberConnection.decrementAndGet(); return false;
}
connectionMap.put(ctx.getConnectionId(), ctx);
return true;
}
ConnectContext When one client connect in, we create a connect context for it. We store session information here. Meanwhile ConnectScheduler all connect with its connection id. 上述流程中调用了startAcceptQuery函数,该函数只有一行代码,即执行mysqlChannel.startAcceptQuery(this, connectProcessor)。如下所示,即注册ReadListener。而ReadListener类最重要的函数就是handleEvent,其中最重要的就是获取worker执行函数体 connectProcessor.processOnce()。
public void startAcceptQuery(ConnectContext connectContext, ConnectProcessor connectProcessor) {
conn.getSourceChannel().setReadListener(new ReadListener(connectContext, connectProcessor));
conn.getSourceChannel().resumeReads();
}
public class ReadListener implements ChannelListener<ConduitStreamSourceChannel> {
@Override
public void handleEvent(ConduitStreamSourceChannel channel) {
// suspend must be call sync in current thread (the IO-Thread notify the read event), otherwise multi handler(task thread) would be waked up by once query.
XnioIoThread.requireCurrentThread(); ctx.suspendAcceptQuery();
// start async query handle in task thread.
channel.getWorker().execute(() -> {
ctx.setThreadLocalInfo();
try {
connectProcessor.processOnce();
if (!ctx.isKilled()) { ctx.resumeAcceptQuery();
} else { ctx.stopAcceptQuery(); ctx.cleanup();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
LOG.warn("Exception happened in one session(" + ctx + ").", e); ctx.setKilled(); ctx.cleanup();
} finally {
ConnectContext.remove();
}
});
}
ConnectProcessor类用于Process one mysql connection, receive one packet, process, send one packet。其最重要的人口函数即是processOnce()。从channel中读取数据包,调用dispatch命令分发该数据包到不同的命令执行函数。
// Process a MySQL request
public void processOnce() throws IOException {
ctx.getState().reset(); executor = null; // set status of query to OK.
// reset sequence id of MySQL protocol
final MysqlChannel channel = ctx.getMysqlChannel(); channel.setSequenceId(0);
try {
packetBuf = channel.fetchOnePacket(); // read packet from channel
if (packetBuf == null) {
LOG.warn("Null packet received from network. remote: {}", channel.getRemoteHostPortString());
throw new IOException("Error happened when receiving packet.");
}
} catch (AsynchronousCloseException e) {
// when this happened, timeout checker close this channel killed flag in ctx has been already set, just return
return;
}
dispatch(); // dispatch
finalizeCommand(); // finalize
ctx.setCommand(MysqlCommand.COM_SLEEP);
}
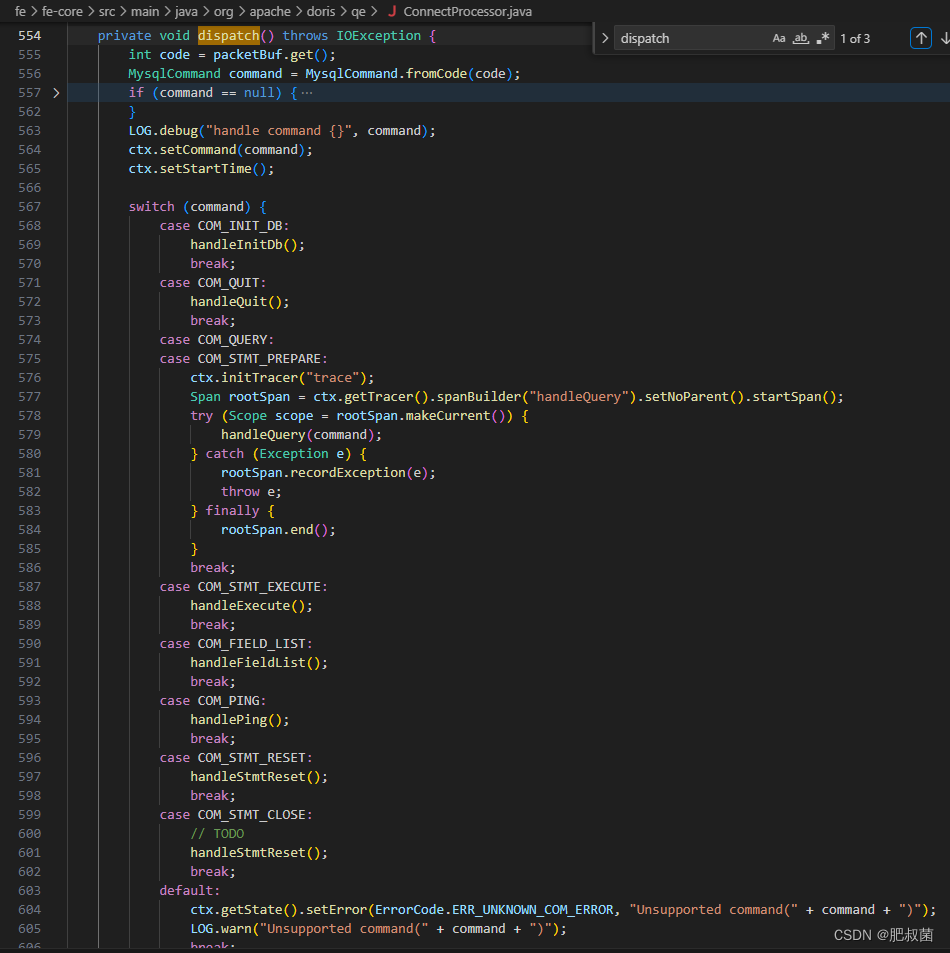
finalizeCommand函数在请求执行结束后,用于向客户端反馈应答数据包。
// When any request is completed, it will generally need to send a response packet to the client
// This method is used to send a response packet to the client
private void finalizeCommand() throws IOException {
ByteBuffer packet;
if (executor != null && executor.isForwardToMaster() && ctx.getState().getStateType() != QueryState.MysqlStateType.ERR) {
ShowResultSet resultSet = executor.getShowResultSet();
if (resultSet == null) { packet = executor.getOutputPacket();
} else {
executor.sendResultSet(resultSet); packet = getResultPacket();
if (packet == null) { LOG.debug("packet == null"); return; }
}
} else {
packet = getResultPacket();
if (packet == null) { LOG.debug("packet == null"); return;
}
}
MysqlChannel channel = ctx.getMysqlChannel();
channel.sendAndFlush(packet);
// note(wb) we should write profile after return result to mysql client
// because write profile maybe take too much time
// explain query stmt do not have profile
if (executor != null && executor.getParsedStmt() != null && !executor.getParsedStmt().isExplain()
&& (executor.getParsedStmt() instanceof QueryStmt // currently only QueryStmt and insert need profile
|| executor.getParsedStmt() instanceof LogicalPlanAdapter
|| executor.getParsedStmt() instanceof InsertStmt)) {
executor.updateProfile(true);
StatsErrorEstimator statsErrorEstimator = ConnectContext.get().getStatsErrorEstimator();
if (statsErrorEstimator != null) {
statsErrorEstimator.updateProfile(ConnectContext.get().queryId());
}
}
}
本文只说 mysql 协议如何接收 SQL 语句, 如果感兴趣的同学可以看看 Apache Doris FE Web 的 Rest Api。
https://www.modb.pro/db/415009
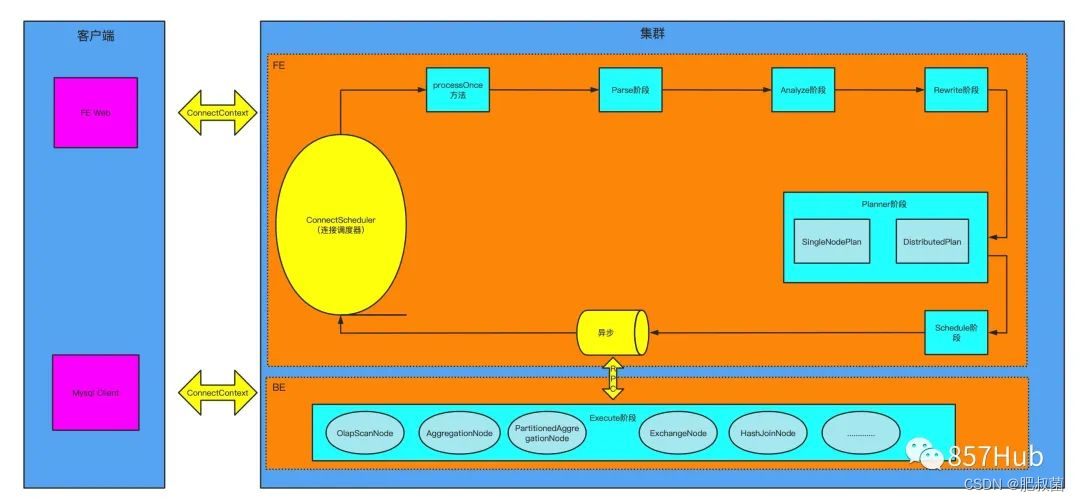
Doris SQL解析具体包括了五个步骤:词法分析、语法分析、生成单机逻辑计划,生成分布式逻辑计划、生成物理计划。具体代码实现上包含以下五个步骤:Parse、Analyze、SinglePlan、DistributedPlan、Schedule。
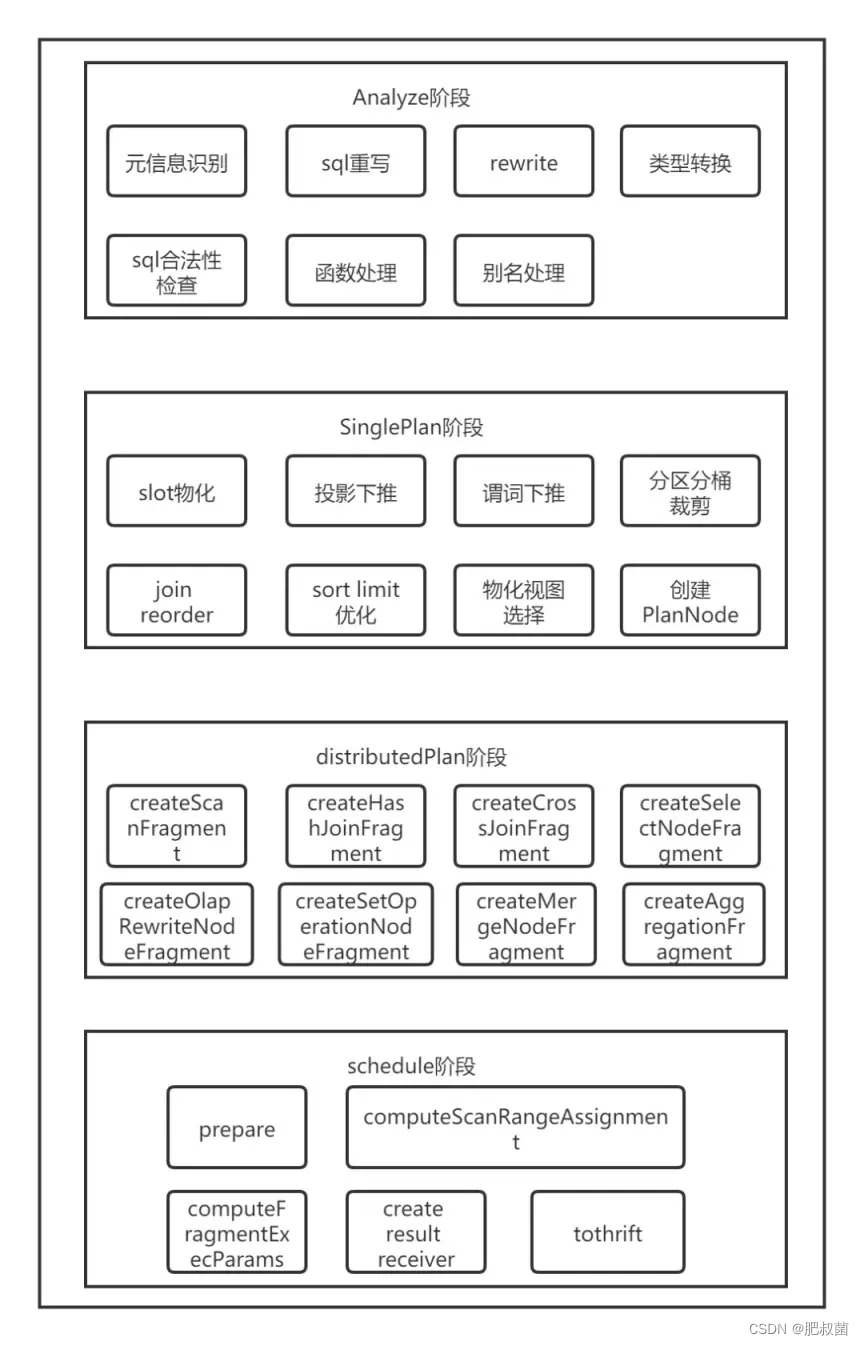
Parse阶段
词法分析采用jflex技术,语法分析采用java cup parser技术,最后生成抽象语法树(Abstract Syntax Tree)AST,这些都是现有的、成熟的技术,在这里不进行详细介绍。
AST是一种树状结构,代表着一条SQL。不同类型的查询select, insert, show, set, alter table, create table等经过Parse阶段后生成不同的数据结构(SelectStmt, InsertStmt, ShowStmt, SetStmt, AlterStmt, AlterTableStmt, CreateTableStmt等),但他们都继承自Statement,并根据自己的语法规则进行一些特定的处理。例如:对于select类型的sql, Parse之后生成了SelectStmt结构。
SelectStmt结构包含了SelectList,FromClause,WhereClause,GroupByClause,SortInfo等结构。这些结构又包含了更基础的一些数据结构,如WhereClause包含了BetweenPredicate(between表达式), BinaryPredicate(二元表达式), CompoundPredicate(and or组合表达式), InPredicate(in表达式)等。