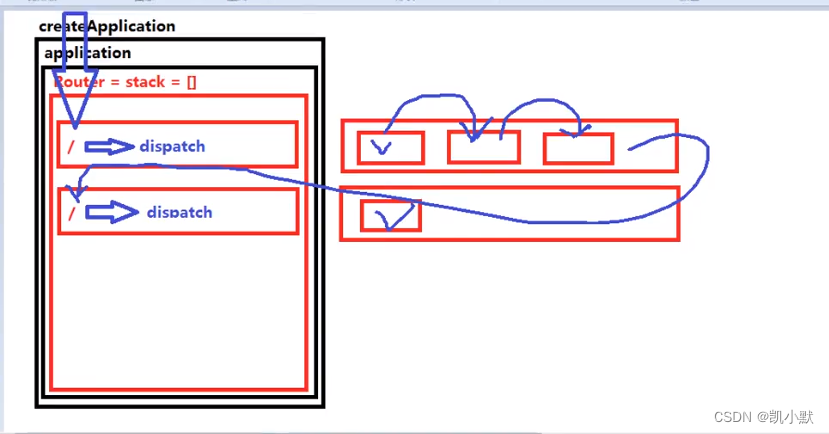
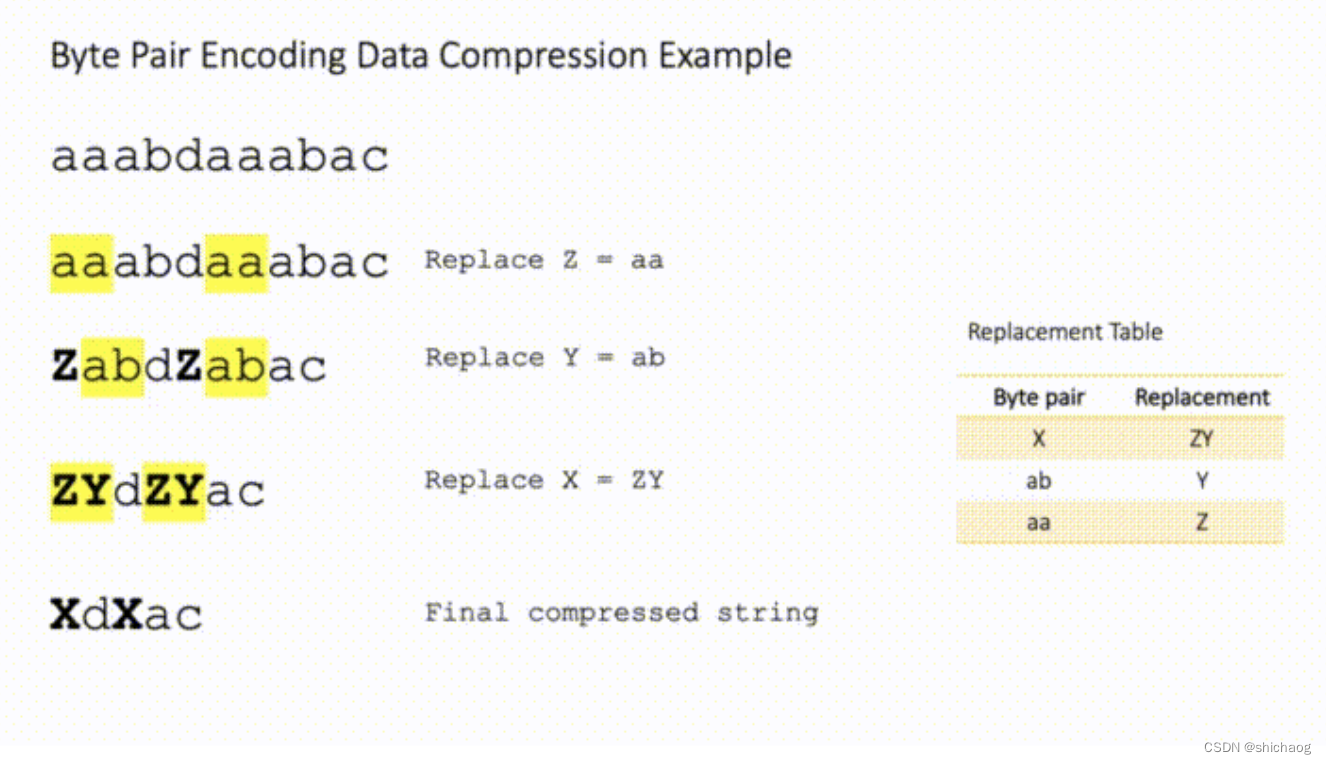
上一节实现了实现应用和路由的分离,这一节来构建 layer 和 route 的关系
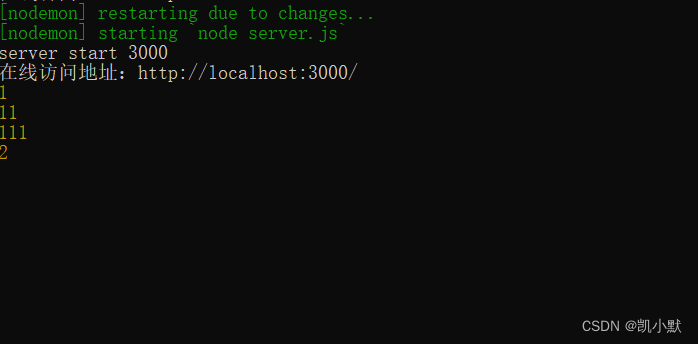
先看个例子如下:路由中间件,将处理的逻辑拆分成一个个的模块
const express = require("express");
const app = express();
app.get(
"/",
(req, res, next) => {
console.log(1);
next();
},
(req, res, next) => {
console.log(11);
next();
},
(req, res, next) => {
console.log(111);
next();
}
);
app.get("/", (req, res, next) => {
console.log(2);
res.end("end");
});
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log(`server start 3000`);
console.log(`在线访问地址:http://localhost:3000/`);
});
执行过程示意图:
实现示意图:
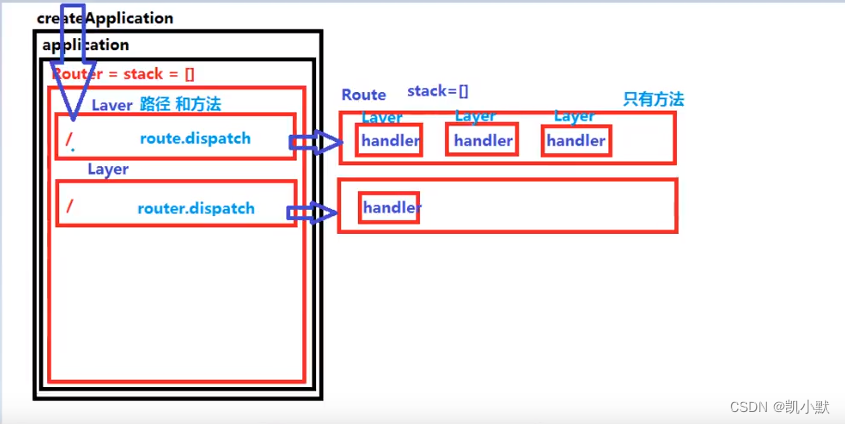
下面新建 layer.js 和 route.js 的文件
layer.js
function Layer(path, handler) {
this.path = path;
this.handler = handler;
}
module.exports = Layer;
route.js
const Layer = require("./layer");
function Route() {
this.stack = [];
}
Route.prototype.dispatch = function () {
// 稍后调用此方法时,回去栈中拿出对应的 handler 依次执行
};
Route.prototype.get = function (handlers) {
handlers.forEach((handler) => {
// 这里的路径没有意义
let layer = new Layer("/", handler);
layer.method = "get";
this.stack.push(layer);
});
};
module.exports = Route;
router/index.js
const Route = require("./route");
const Layer = require("./layer");
function Router() {
// 维护所有的路由
this.stack = [];
}
Router.prototype.route = function (path) {
// 产生 route
let route = new Route();
// 产生 layer 让 layer 跟 route 进行关联
let layer = new Layer(path, route.dispatch.bind(route));
// 每个路由都具备一个 route 属性,稍后路径匹配到后会调用 route 中的每一层
layer.route = route;
// 把 layer 放到路由的栈中
this.stack.push(layer);
return route;
};
// 用户调用 get 时,传入的 handler 不一定是一个
Router.prototype.get = function (path, ...handlers) {
// 1.用户调用 get 时,需要保存成一个 layer 当道栈中
// 2.产生一个 Route 实例和当前的 layer 创造关系
// 3.要将 route 的 dispatch 方法存到 layer 上
let route = this.route(path);
// 让 route 记录用户传入的 handler 并且标记这个 handler 是什么方法
route.get(handlers);
};
Router.prototype.handle = function (req, res, next) {};
module.exports = Router;









![如何使用Java语言判断出geek是字符串参数类型,888是整数参数类型,[hello,world]是数组参数类型,2.5是双精度浮点数类型?](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/47c055fe13074ad1b1d269563eb90ac1.png#pic_center)