目录
一、Thymeleaf介绍
(1)依赖
(2)视图
(3)控制层
二、变量输出
三、操作字符串
四、操作时间
五、条件判断
六、遍历集合
(1)迭代遍历
(2)将遍历的状态变量封装到一个对象中
七、遍历Map
八、获取域中的数据
(1)控制层
(2)视图
九、Thymeleaf中的URL写法
一、Thymeleaf介绍
Thymeleaf是一款用于渲染XML/HTML5内容的模板引擎,类似JSP。它可以轻易的与SpringMVC等Web框架进行集成作为Web应用的模板引擎。在SpringBoot中推荐使用Thymeleaf编写动态页面。
Thymeleaf最大的特点是能够直接在浏览器中打开并正确显示模板页面,而不需要启动整个Web应用。
Thymeleaf在有网络和无网络的环境下皆可运行,它即可以让美工在浏览器查看页面的静态效果,也可以让程序员在服务器查看带数据的动态页面效果。没有数据时,Thymeleaf的模板可以静态地运行;当有数据返回到页面时,Thymeleaf标签会动态地替换掉静态内容,使页面动态显示。
(1)依赖
<!--添加Thymeleaf起步依赖--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency>
(2)视图
一定要注意templates的html文件不能直接访问,需要编写controller跳转到页面中
<!DOCTYPE html> <!-- 引入thymeleaf命名空间,方便使用thymeleaf属性 --> <html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>thymeleaf入门</title> </head> <body> <!-- thymeleaf支持el表达式 --> <h2 th:text="${name}"></h2> </body> </html>
(3)控制层
@Controller public class PageController { // 页面跳转 @GetMapping("/show") public String showPage(Model model){ model.addAttribute("name","Hello Thymeleaf"); return "index"; } }
二、变量输出
th:text
作用:将model的值作为内容放入标签中。
th:value
作用:将model的值放入input标签的value属性中
<!DOCTYPE html> <!-- 引入thymeleaf命名空间,方便使用thymeleaf属性 --> <html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>thymeleaf入门</title> </head> <body> <!-- thymeleaf支持el表达式 --> <h1>name=<span th:text="${name}"></span></h1> <input th:value="${name}"> </body> </html>
三、操作字符串
Thymeleaf提供了一些内置对象可以操作数据,内置对象可直接在模板中使用,这些对象是以#引用的,操作字符串的内置对象为strings。
方法 说明 ${#strings.isEmpty(key)} 判断字符串是否为空,如果为空返回true,否则返回false ${#strings.contains(msg,'T')} 判断字符串是否包含指定的子串,如果包含返回true,否则返回false ${#strings.startsWith(msg,'a')} 判断当前字符串是否以子串开头,如果是返回true,否则返回false ${#strings.endsWith(msg,'a')} 判断当前字符串是否以子串结尾,如果是返回true,否则返回false ${#strings.length(msg)} 返回字符串的长度 ${#strings.indexOf(msg,'h')} 查找子串的位置,并返回该子串的下标,如果没找到则返回-1 ${#strings.substring(msg,2,5)} 截取子串,用法与JDK的subString方法相同 ${#strings.toUpperCase(msg)} 字符串转大写 ${#strings.toLowerCase(msg)} 字符串转小写
<!DOCTYPE html> <!-- 引入thymeleaf命名空间,方便使用thymeleaf属性 --> <html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>thymeleaf入门</title> </head> <body> <!-- thymeleaf支持el表达式 --> <span th:text="${#strings.length(name)}"></span> <span th:text="${#strings.startsWith(name,'n')}"></span> </body> </html>
四、操作时间
操作时间的内置对象为dates
方法 说明 ${#dates.format(key)} 格式化日期,默认的以浏览器默认语言为格式化标准 ${#dates.format(key,'yyyy/MM/dd')} 按照自定义的格式做日期转换 ${#dates.year(key)} 取年 ${#dates.month(key)} 取月 ${#dates.day(key)} 取日
添加数据 model.addAttribute("date",new Date(130,01,01));<!DOCTYPE html> <!-- 引入thymeleaf命名空间,方便使用thymeleaf属性 --> <html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>thymeleaf入门</title> </head> <body> <!-- thymeleaf支持el表达式 --> <span th:text="${#dates.format(date)}"></span> <span th:text="${#dates.format(date,'yyyy/MM/dd')}"></span> <span th:text="${#dates.year(date)}"></span> <span th:text="${#dates.month(date)}"></span> </body> </html>
五、条件判断
th:if 用于条件判断
th:switch/th:case th:switch/th:case与Java中的switch语句等效。
th:case="*"表示Java中switch的default,即没有case的值为true时显示th:case="*"的内容。
添加数据 model.addAttribute("age",3);<!DOCTYPE html> <!-- 引入thymeleaf命名空间,方便使用thymeleaf属性 --> <html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>thymeleaf入门</title> </head> <body> <!-- thymeleaf支持el表达式 --> <span th:if="${age}==1">我是1</span> <span th:if="${age}==2">我是2</span> <span th:if="${age}==3">我是3</span> </body> </html>
<!DOCTYPE html> <!-- 引入thymeleaf命名空间,方便使用thymeleaf属性 --> <html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>thymeleaf入门</title> </head> <body> <!-- thymeleaf支持el表达式 --> <div th:switch="${age}"> <span th:case="1">我是1</span> <span th:case="2">我是2</span> <span th:case="3">我是3</span> <span th:case="4">我是4</span> <span th:case="*">我是不知道</span> </div> </body> </html>
六、遍历集合
(1)迭代遍历
th:each 迭代器,用于循环迭代集合
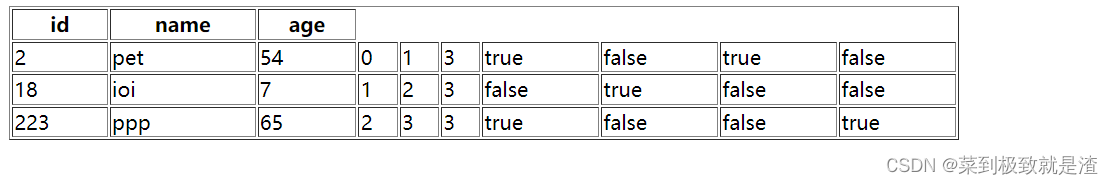
@GetMapping("/c1") public String t1(Model model){ List<Users> users=new ArrayList<>(); Users users1=new Users("2","pet",54); Users users2=new Users("18","ioi",7); Users users3=new Users("223","ppp",65); users.add(users1); users.add(users2); users.add(users3); model.addAttribute("li",users); return "index"; }<body> <!-- thymeleaf支持el表达式 --> <table border="1" width="50%"> <tr> <th>id</th> <th>name</th> <th>age</th> </tr> <tr th:each="u:${li}"> <td th:text="${u.id}"></td> <td th:text="${u.name}"></td> <td th:text="${u.age}"></td> </tr> </table> </body>
(2)将遍历的状态变量封装到一个对象中
thymeleaf将遍历的状态变量封装到一个对象中,通过该对象的属性可以获取状态变量:
状态变量 含义 index 当前迭代器的索引,从0开始 count 当前迭代对象的计数,从1开始 size 被迭代对象的长度 odd/even 布尔值,当前循环是否是偶数/奇数,从0开始 first 布尔值,当前循环的是否是第一条,如果是返回true,否则返回false last 布尔值,当前循环的是否是最后一条,如果是则返回true,否则返回false
<tr th:each="user,status : ${li}"> <td th:text="${user.id}"></td> <td th:text="${user.name}"></td> <td th:text="${user.age}"></td> <td th:text="${status.index}"></td> <td th:text="${status.count}"></td> <td th:text="${status.size}"></td> <td th:text="${status.odd}"></td> <td th:text="${status.even}"></td> <td th:text="${status.first}"></td> <td th:text="${status.last}"></td> </tr>
七、遍历Map
遍历Map出来的每一项是键值对,key获取键,value获取值
@GetMapping("/c1") public String t1(Model model){ Map<String,Users> map=new HashMap<>(); map.put("u1",new Users("16","张三",90)); map.put("u2",new Users("90","李四",12)); map.put("u4",new Users("1","王一",16)); model.addAttribute("us",map); return "index"; }<body> <!-- thymeleaf支持el表达式 --> <table border="1" width="50%"> <tr> <th>键</th> <th>id</th> <th>name</th> <th>age</th> </tr> <tr th:each="u:${us}"> <th th:text="${u.key}"></th> <th th:text="${u.value.id}"></th> <th th:text="${u.value.name}"></th> <th th:text="${u.value.age}"></th> </tr> </table> </body>
八、获取域中的数据
(1)控制层
@GetMapping("/c1") public String t1(HttpServletRequest request, HttpSession session){ request.setAttribute("q1","我是request数据"); session.setAttribute("s1","我绝对是session"); ServletContext servletContext=session.getServletContext(); servletContext.setAttribute("c1","我真的是context'数据"); return "index"; }
(2)视图
<body> <!-- thymeleaf支持el表达式 --> request1=<span th:text="${#request.getAttribute('q1')}"></span> request2=<span th:text="${#httpServletRequest.getAttribute('q1')}"></span> session=<span th:text="${session.s1}"></span> session1=<span th:text="${#httpSession.getAttribute('s1')}"></span> context1=<span th:text="${application.c1}"></span> context2=<span th:text="${#servletContext.getAttribute('c1')}"></span> </body>
九、Thymeleaf中的URL写法
在Thymeleaf中路径的写法为@{路径}
<a th:href="@{show2?id=1&name=gq}">静态参数一</a> <a th:href="@{show2(id=2,name=gq)}">静态参数二</a> <a th:href="@{'show2?id='+${id}+'&name='+${name}}">动态参数一</a> <a th:href="@{show2(id=${id},name=${name})}">动态参数二</a>

![[Linux打怪升级之路]-缓冲区](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/297efc010473415ea72a4abd03e9ea42.png)




![[Linux入门]---Linux指令②](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/fe205d16f28744aab8b2f70e994e7ba2.png)