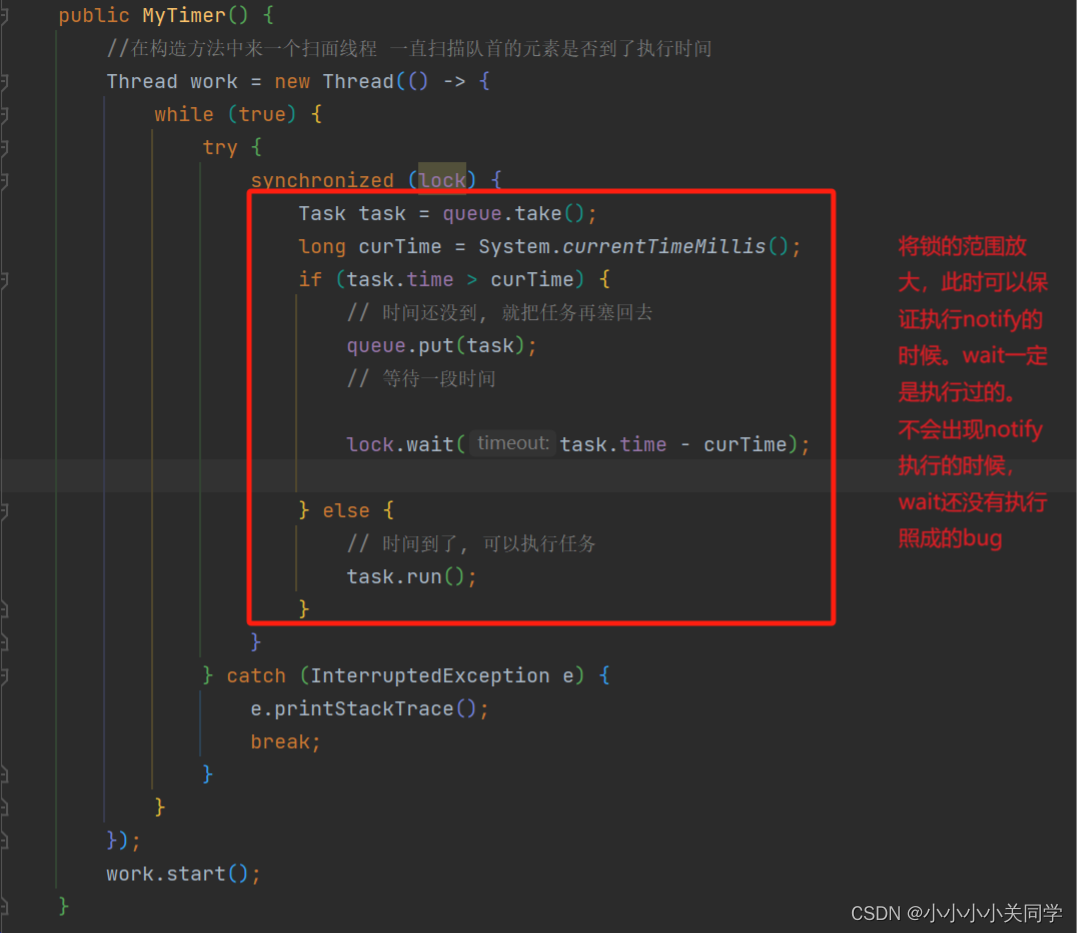
共享内存(shared memory)是可用IPC技术中最快的一种。一旦内存被映射到共享内存区域的进程的地址空间中,在进程之间传递数据时就不会发生内核(kernel)参与。然而,在共享内存区域存储和提取数据时,进程之间需要某些形式的同步(例如互斥锁、条件变量、读写锁、记录锁、信号量)。
注:不允许共享对象文件名中任何位置出现"/"(不包括前导"/")
关键步骤:
(1).使用shm_open函数创建共享内存对象;
(2).使用mmap函数将共享内存区域映射到RAM,使其在内存中拥有可读写的地址.
共享内存总结:
(1).异步;
(2).物理内存数据大小限制;
(3).多个进程可以同时访问但需要同步管理;
(4).随机访问。
注:以上内容主要来自网络整理。
测试代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
const char* SHARED_OBJ_NAME = "shm_test"; // disallows '/' from anywhere in the filename(not counting leading '/'): shm_test will be generated in /dev/shm/ directory
// shared data struct
typedef struct message {
int pid;
int counter;
} message;
bool write_message(int pid, int value)
{
auto fd = shm_open(SHARED_OBJ_NAME, O_CREAT | O_RDWR, S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR); // create and open a new shared memory object, return a file descriptor
if (fd == -1) {
fprintf(stderr, "fail to shm_open: %s\n", strerror(errno));
exit(1);
}
auto ret = ftruncate(fd, sizeof(message)); // truncate a file to a specified length
if (ret == -1) {
fprintf(stderr, "fail to ftruncate: %s\n", strerror(errno));
exit(1);
}
message* msg_ptr = (message*)mmap(nullptr, sizeof(message), PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, fd, 0); // create a new mapping in the virtual address space of the calling process
if (msg_ptr == MAP_FAILED) {
fprintf(stderr, "fail to mmap: %s\n", strerror(errno));
exit(1);
}
fprintf(stdout, "Process %d: Increase the counter\n", pid);
msg_ptr->pid = pid;
msg_ptr->counter = value;
ret = munmap(msg_ptr, sizeof(message)); // delete the mappings for the specified address range
if (ret == -1) {
fprintf(stderr, "fail to munmap: %s\n", strerror(errno));
exit(1);
}
// remember to close to not hit an error of opening too many files
close(fd);
return true;
}
bool read_message(int curr_pid, int& curr_value)
{
int fd = shm_open(SHARED_OBJ_NAME, O_RDWR, S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR);
if (fd == -1) {
fprintf(stderr, "fail to shm_open: %s\n", strerror(errno));
exit(1);
}
auto ret = ftruncate(fd, sizeof(message));
if (ret == -1) {
fprintf(stderr, "fail to ftruncate: %s\n", strerror(errno));
exit(1);
}
message* msg_ptr = (message*)mmap(nullptr, sizeof(message), PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, fd, 0);
if (msg_ptr == MAP_FAILED) {
fprintf(stderr, "fail to mmap: %s\n", strerror(errno));
exit(1);
}
if (msg_ptr->pid == curr_pid) {
fprintf(stderr, "Process %d: No new msg available\n", curr_pid);
munmap(msg_ptr, sizeof(message));
close(fd);
shm_unlink(SHARED_OBJ_NAME);
return false;
} else {
fprintf(stdout, "Process %d: Receive %d from PID %d\n", curr_pid, msg_ptr->counter, msg_ptr->pid);
curr_value = msg_ptr->counter;
munmap(msg_ptr, sizeof(message));
}
close(fd);
shm_unlink(SHARED_OBJ_NAME); // remove an object previously created by shm_open
return true;
}
int main()
{
// reference: https://biendltb.github.io/tech/inter-process-communication-ipc-in-cpp/
write_message(-1, 0); // Init the initial value
// create a child process by calling folk,
pid_t pid = fork();
if (pid < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "fail to fork\n");
return -1;
}
if (pid != 0) { // parent process
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
int value;
// only write message if reading sucessfully
if (read_message(pid, value))
write_message(pid, ++value);
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(100));
}
int status;
auto pid2 = wait(&status); // system call suspends execution of the calling thread until one of its children terminates
fprintf(stdout, "process ID of the terminated child: %d\n", pid2);
if (WIFEXITED(status)) { // returns true if the child terminated normally
fprintf(stdout, "child process ended with: exit(%d)\n", WEXITSTATUS(status));
}
if (WIFSIGNALED(status)) { // returns true if the child process was terminated by a signal
fprintf(stderr, "child process ended with: kill -%d\n", WTERMSIG(status));
}
}
if (pid == 0) { // child process
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
int value;
if (read_message(pid, value))
write_message(pid, ++value);
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(100));
}
exit(0);
}
fprintf(stdout, "====== test finish ======\n");
return 0;
}编译脚本build.sh内容如下:
#! /bin/bash
if [ -d build ]; then
echo "build directory already exists, it does not need to be created again"
else
mkdir -p build
fi
cd build
cmake ..
make
rc=$?
if [[ ${rc} != 0 ]];then
echo "#### ERROR: please check ####"
exit ${rc}
fi
echo "==== build finish ===="CMakeLists.txt内容如下:
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.22)
project(samples_multi_process)
set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE Release) # only works under linux
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "${CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS} -Wall -O2 -std=c++17")
file(GLOB samples ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/test_*.cpp)
#message(STATUS "samples: ${samples}")
foreach(sample ${samples})
string(REGEX MATCH "[^/]+$" name ${sample})
string(REPLACE ".cpp" "" exec_name ${name})
#message(STATUS "exec name: ${exec_name}")
add_executable(${exec_name} ${sample})
target_link_libraries(${exec_name} rt)
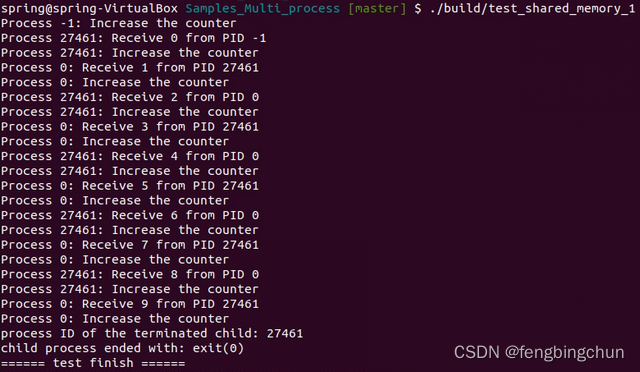
endforeach()执行结果如下所示:
GitHub:https://github.com/fengbingchun/Linux_Code_Test