大家好,我是微学AI,今天给大家介绍一下计算机视觉的应用15-图片旋转验证码的角度计算模型的应用,解决旋转图片矫正问题,在CV领域,图片旋转验证码的角度计算模型被广泛应用于解决旋转图片矫正问题,有效解决机器识别图片验证码的问题。旋转图片验证码常用于验证用户身份,但由于图片可能被以不同角度旋转,识别难度比较大。本文提出了一种基于深度学习的角度计算模型,能够准确估计旋转图片的角度,通过旋转角度进行自动矫正。
本文已经通过使用深度卷积神经网络对旋转图片进行特征提取和表示学习,从而获得高层抽象表示。通过添加回归头,利用旋转角度标签数据进行训练,使模型能够预测旋转图片的角度。实验结果表明,我们提出的模型在多个数据集上取得了优秀的性能,能够有效解决旋转图片矫正问题。该模型具有良好的鲁棒性和广泛的适应性,可在实际应用中提高验证码的识别准确率和用户体验。

一、数据集怎么生成的
我将采用以下的步骤进行:
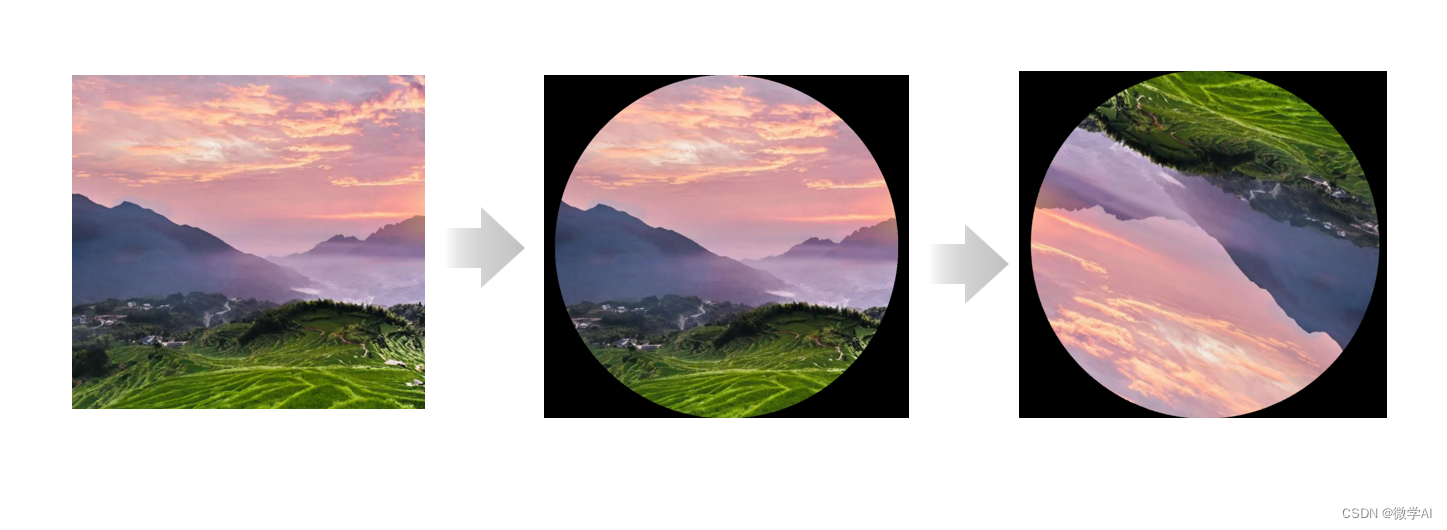
1.首先我们可以选择下载大批量的风景图片,然后进行图片处理。
2.利用opencv将图片用圆形进行截取,生成圆形图片.
3.对圆形图片进行随机从60度-180度之间进行旋转,并保存为字典数据:包含裁剪后的图片地址和旋转角度标签的值,代码如下:
import cv2
import numpy as np
def crop_to_circle(image_path):
# 加载图像
image = cv2.imread(image_path)
# 创建一个与图像大小相同的黑色背景
mask = np.zeros_like(image)
# 获取图像的中心点坐标
height, width, _ = image.shape
center = (width // 2, height // 2)
# 定义半径为图像宽高中的较小值
radius = min(center[0], center[1])
# 在mask上绘制一个白色圆形区域
cv2.circle(mask, center, radius, (255, 255, 255), -1)
# 将mask作为掩模,将图像与掩模进行按位与操作
masked_image = cv2.bitwise_and(image, mask)
cropped_image = "circular_cropped_image.jpg"
# 保存裁剪后的图像
cv2.imwrite(cropped_image, masked_image)
# 随机生成旋转角度
random_angle = np.random.randint(60, 181)
# 对图像进行旋转
M = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D(center, random_angle, 1.0)
rotated_image = cv2.warpAffine(masked_image, M, (width, height))
# 显示结果
cv2.imshow("Original Image", image)
cv2.imshow("Circular Cropped + Rotated Image", rotated_image)
# 保存裁剪加旋转后的图像
rotated_image_path = "rotated_image.jpg"
cv2.imwrite(rotated_image_path, rotated_image)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
return cropped_image, rotated_image_path,random_angle
# 使用示例
image_path = "111.png"
cropped_image,rotated_image_path,random_angle = crop_to_circle(image_path)
# 保存图片地址和旋转角度标签的字典数据
data = {
"image_path":"111.png",
'cropped_image':cropped_image,
"rotated_path": rotated_image_path,
"rotation_angle": random_angle
}
print(data)

二、旋转图片识别原理
假设我们有一张图片,我们想要将其逆时针旋转一个角度为 θ θ θ。我们可以将旋转过程分解为以下几个步骤:
1.坐标平移:将图片的中心点移到原点 ( 0 , 0 ) (0, 0) (0,0)处。我们可以将每个像素点的坐标减去图片中心的坐标,使得图片的中心对齐原点。
2.旋转变换:对于每个像素点 P ( x , y ) P(x, y) P(x,y),应用旋转矩阵变换来计算新的坐标 P ′ ( x ′ , y ′ ) P'(x', y') P′(x′,y′)。旋转矩阵表示为:
R ( θ ) = [ cos ( θ ) − sin ( θ ) sin ( θ ) cos ( θ ) ] R(\theta) = \begin{bmatrix} \cos(\theta) & -\sin(\theta) \\ \sin(\theta) & \cos(\theta) \end{bmatrix} R(θ)=[cos(θ)sin(θ)−sin(θ)cos(θ)]
其中, θ θ θ是旋转角度, cos \cos cos和 sin \sin sin是余弦和正弦函数。
3.坐标平移:将图片的中心点移到原来的位置。我们可以将每个像素点的坐标加上图片中心的坐标,使得图片回到原来的位置。
4.插值处理:在旋转后的坐标上可能会出现小数点的坐标值,而像素点的坐标是整数。因此,我们需要使用插值方法来确定旋转后坐标上的像素值。常用的插值方法有最近邻插值、双线性插值等。
三、选用模型
本文主要采用resnet50的改造模型,模型的具体结构这边省略了,为了方便大家快速使用,这里提高训练好的模型下载:
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1aJQ4OD6LwQlLlVwJsMj6aA?pwd=rypw
提取码:rypw
我们可以构建models文件夹,将resnet50_keras2.hdf5文件放入文件夹中。
代码实现:
from keras.applications.imagenet_utils import preprocess_input
from keras.models import load_model
from keras.optimizers import SGD
import keras.backend as K
import os
import math
import cv2
import numpy as np
import requests
class RotateCaptcha():
def __init__(self):
# 加载模型
model_location = os.path.join('.', 'models', 'resnet50_keras2.hdf5')
self.model = load_model(model_location, custom_objects={'angle_error': self.angle_error})
self.model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy',
optimizer=SGD(lr=0.01, momentum=0.9),
metrics=[self.angle_error])
# 图像长宽尺寸
self.size = (224, 224)
def showImg(self, image):
'''
展示图片
'''
cv2.imshow('image', image)
cv2.waitKey(0)
def getImgFromDisk(self, imgPath):
image = cv2.imread(imgPath)
image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
return image
def predictAngle(self, image):
diameter = image.shape[0] # 直径
side_length = math.floor((diameter / 2) * 1.414) # 圆内正方形最大边长
cropped = math.floor((diameter - side_length) / 2)
image = image[cropped:cropped + side_length, cropped:cropped + side_length]
image = cv2.resize(image, self.size)
image = np.expand_dims(image, axis=0)
x = preprocess_input(image)
y_pred = np.argmax(self.model.predict(x), axis=1)
return y_pred[0]
def rotate(self, image, angle):
image_size = (image.shape[1], image.shape[0])
image_center = tuple(np.array(image_size) / 2)
# 将 OpenCV 3x2旋转矩阵转换为3x3
rot_mat = np.vstack(
[cv2.getRotationMatrix2D(image_center, angle, 1.0), [0, 0, 1]]
)
rot_mat_notranslate = np.matrix(rot_mat[0:2, 0:2])
image_w2 = image_size[0] * 0.5
image_h2 = image_size[1] * 0.5
# 获取图像角点的旋转坐标
rotated_coords = [
(np.array([-image_w2, image_h2]) * rot_mat_notranslate).A[0],
(np.array([image_w2, image_h2]) * rot_mat_notranslate).A[0],
(np.array([-image_w2, -image_h2]) * rot_mat_notranslate).A[0],
(np.array([image_w2, -image_h2]) * rot_mat_notranslate).A[0]
]
# 查找新图像的大小
x_coords = [pt[0] for pt in rotated_coords]
x_pos = [x for x in x_coords if x > 0]
x_neg = [x for x in x_coords if x < 0]
y_coords = [pt[1] for pt in rotated_coords]
y_pos = [y for y in y_coords if y > 0]
y_neg = [y for y in y_coords if y < 0]
right_bound = max(x_pos)
left_bound = min(x_neg)
top_bound = max(y_pos)
bot_bound = min(y_neg)
new_w = int(abs(right_bound - left_bound))
new_h = int(abs(top_bound - bot_bound))
trans_mat = np.matrix([
[1, 0, int(new_w * 0.5 - image_w2)],
[0, 1, int(new_h * 0.5 - image_h2)],
[0, 0, 1]
])
affine_mat = (np.matrix(trans_mat) * np.matrix(rot_mat))[0:2, :]
result = cv2.warpAffine(
image,
affine_mat,
(new_w, new_h),
flags=cv2.INTER_LINEAR
)
return result
def angle_difference(self, x, y):
return 180 - abs(abs(x - y) - 180)
def angle_error(self, y_true, y_pred):
diff = self.angle_difference(K.argmax(y_true), K.argmax(y_pred))
return K.mean(K.cast(K.abs(diff), K.floatx()))
if __name__ == '__main__':
rotateCaptcha = RotateCaptcha()
rotated_image = rotateCaptcha.getImgFromDisk('222.jpg')
predicted_angle = rotateCaptcha.predictAngle(rotated_image) # 预测还原角度
print("需旋转角度:{}".format(predicted_angle))
corrected_image = rotateCaptcha.rotate(rotated_image, -predicted_angle)
rotateCaptcha.showImg(corrected_image)
运行结果:
1/1 [==============================] - 1s 668ms/step
需旋转角度:51
生成结果会返回需要选择的角度,我们根据角度进行下一步的验证码旋转,进行验证。