✅作者简介:人工智能专业本科在读,喜欢计算机与编程,写博客记录自己的学习历程。
🍎个人主页:小嗷犬的个人主页
🍊个人网站:小嗷犬的技术小站
🥭个人信条:为天地立心,为生民立命,为往圣继绝学,为万世开太平。
本文目录
- Seaborn 简介
- Seaborn 安装
- Seaborn 使用
- Seaborn 样例数据集
- Seaborn 样式设置
- Seaborn 颜色设置
- Seaborn 绘图函数
- 绘图示例
- 示例 1
- 示例 2
- 示例 3
- 示例 4
- 示例 5
- 示例 6
- 示例 7
- 示例 8
- 示例 9
- 示例 10
- 示例 11
- 示例 12
- 示例 13
- 示例 14
- 示例 15
- 示例 16
- 示例 17
- 示例 18
- 示例 19
- 示例 20
- 示例 21
- 示例 22
- 示例 23
- 示例 24
- 示例 25
- 示例 26
- 示例 27
- 示例 28
- 示例 29
- 示例 30
- 示例 31
- 示例 32
- 示例 33
- 示例 34
- 示例 35
- 示例 36
- 示例 37
- 示例 38
- 示例 39
- 示例 40
- 示例 41
- 示例 42
- 示例 43
- 示例 44
- 示例 45
- 示例 46
- 示例 47
- 示例 48
- 示例 49
Seaborn 简介
Seaborn 是一个基于 Python 的数据可视化库,它建立在 matplotlib 之上,并与 pandas 数据结构密切集成。Seaborn 的主要目的是通过使用更高级的界面来制作有吸引力的统计图形,从而使可视化变得更简单。
Seaborn 的主要特点包括:
- 高级界面: Seaborn 提供了更高级的界面来绘制有吸引力的统计图形,例如散点图、条形图、箱线图等。这些图形可以通过几行代码快速生成,而不需要手动调整每个细节。
- 内置主题: Seaborn 包括几个预定义的主题,可以用于改变图形的外观。这使得它更容易创建美观且专业的图形。
- 与 pandas 集成: Seaborn 与 pandas 数据结构紧密集成,这意味着你可以直接在 pandas 的 DataFrame 上调用 Seaborn 的函数,从而方便地进行数据可视化。
- 统计绘图: Seaborn 不仅提供了用于绘制基本图形的函数,还提供了用于绘制更复杂的统计图形的函数,例如 Pairplot(用于显示数据集中的成对关系)、Violinplot(用于显示分组的分布)等。
- 颜色控制: Seaborn 允许用户通过参数控制图形的颜色,使其更易于创建颜色协调的图形。
- 面板绘图: Seaborn 支持面板绘图,可以方便地在一个图形中显示多个不同的视图。
Seaborn 安装
Seaborn 可以通过 pip 安装:
pip install seaborn
Seaborn 使用
要使用 Seaborn,必须先导入 Seaborn 库。通常,Seaborn 会与 numpy、pandas 和 matplotlib 一起导入:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
Seaborn 样例数据集
Seaborn 中提供了多种样例数据集,可以用于练习和测试。可以通过以下命令查看所有可用的数据集:
print(sns.get_dataset_names())
得到以下输出:
['anagrams', 'anscombe', 'attention', 'brain_networks', 'car_crashes', 'diamonds', 'dots', 'exercise', 'flights', 'fmri', 'gammas', 'geyser', 'iris', 'mpg', 'penguins', 'planets', 'taxis', 'tips', 'titanic']
Seaborn 中的数据集可以通过 load_dataset() 函数加载,该函数返回一个 pandas 的 DataFrame 对象。例如,要加载 Seaborn 中的 anscombe 数据集,可以使用以下命令:
df = sns.load_dataset("anscombe")
print(df.head())
得到以下输出:
dataset x y
0 I 10.0 8.04
1 I 8.0 6.95
2 I 13.0 7.58
3 I 9.0 8.81
4 I 11.0 8.33
Seaborn 样式设置
Seaborn 中的样式可以通过 set_style() 函数设置。Seaborn 中有五种不同的样式,可以通过 set_style() 函数的 style 参数设置:
darkgrid:默认样式,带有灰色网格。whitegrid:带有白色网格的样式。dark:不带网格的黑色背景样式。white:不带网格的白色背景样式。ticks:不带网格的样式,但带有刻度。
例如,要将样式设置为 whitegrid,可以使用以下命令:
sns.set_style("whitegrid")
Seaborn 颜色设置
Seaborn 中的颜色可以通过 set_palette() 函数设置。Seaborn 中有六种不同的调色板,可以通过 set_palette() 函数的 palette 参数设置:
deep:默认调色板muted:较柔和的颜色pastel:柔和的颜色bright:明亮的颜色dark:暗色调colorblind:适合色盲的颜色
除此之外,还可以使用任何 matplotlib 调色板或者自定义调色盘。
要将颜色设置为 pastel,可以使用以下命令:
sns.set_palette("pastel")
Seaborn 绘图函数
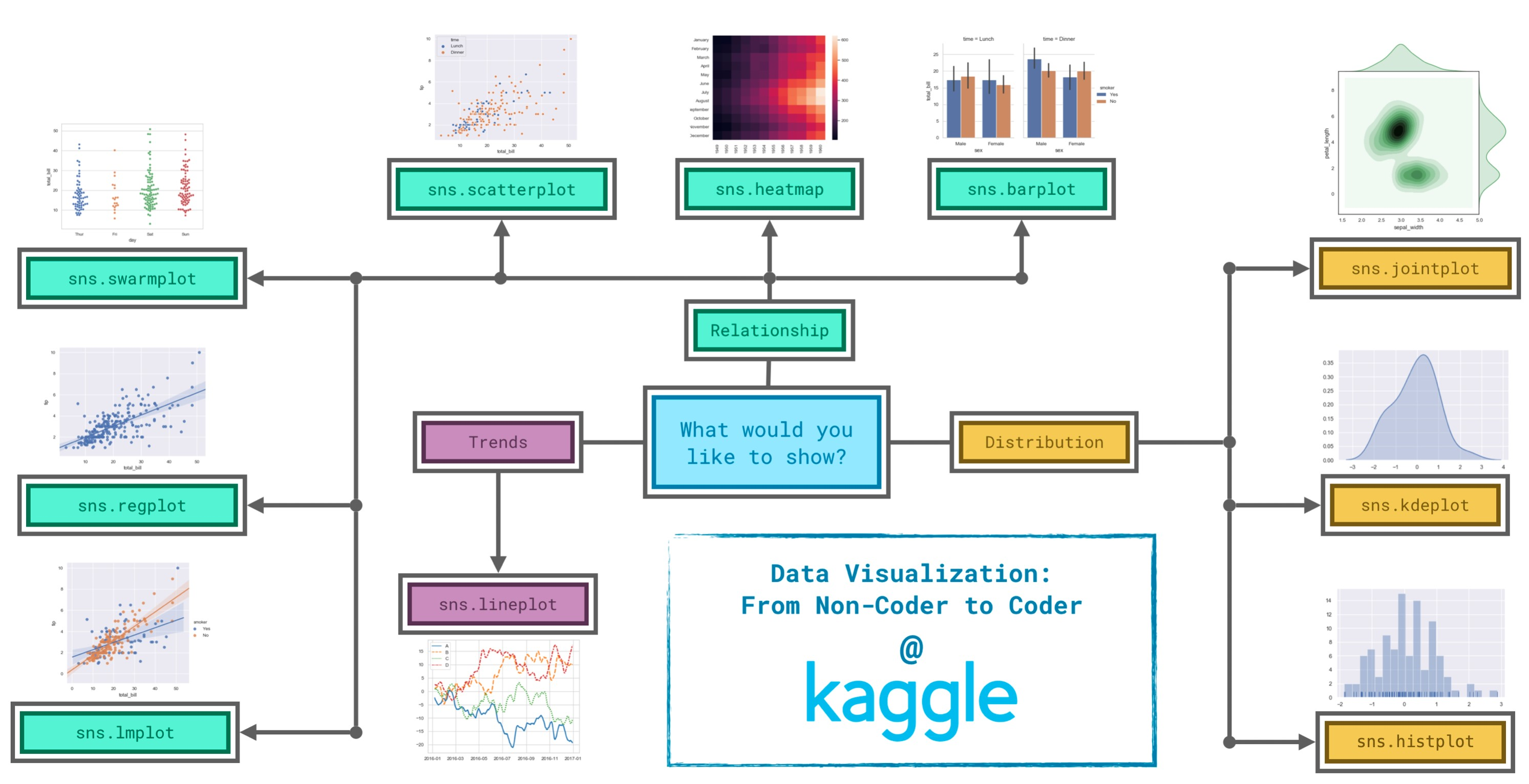
Seaborn 支持绘制超多种不同的图表。下面列出了 Seaborn 支持的所有图表:
- 关系图表
relplot()- 散点图
scatterplot() - 折线图
lineplot()
- 散点图
- 分布图表
displot()- 直方图
histplot() - 核密度估计图
kdeplot() - 累积分布图
ecdfplot() - 地毯图
rugplot()
- 直方图
- 分类图表
catplot()- 分类散点图
stripplot()、swarmplot() - 分类分布图
boxplot()、violinplot()、boxenplot() - 分类估计图
pointplot()、barplot()、countplot()
- 分类散点图
- 回归图表
- 回归模型图
lmplot()- 简单回归图
regplot() - 多图网格
FacetGrid
- 简单回归图
- 回归残差图
residplot()
- 回归模型图
- 其他图表
- 热力图
heatmap() - 聚类图
clustermap() - 成对关系图
pairplot()- 成对网格
PairGrid
- 成对网格
- 联合分布图
jointplot()- 联合网格
JointGrid
- 联合网格
- 热力图
绘图示例
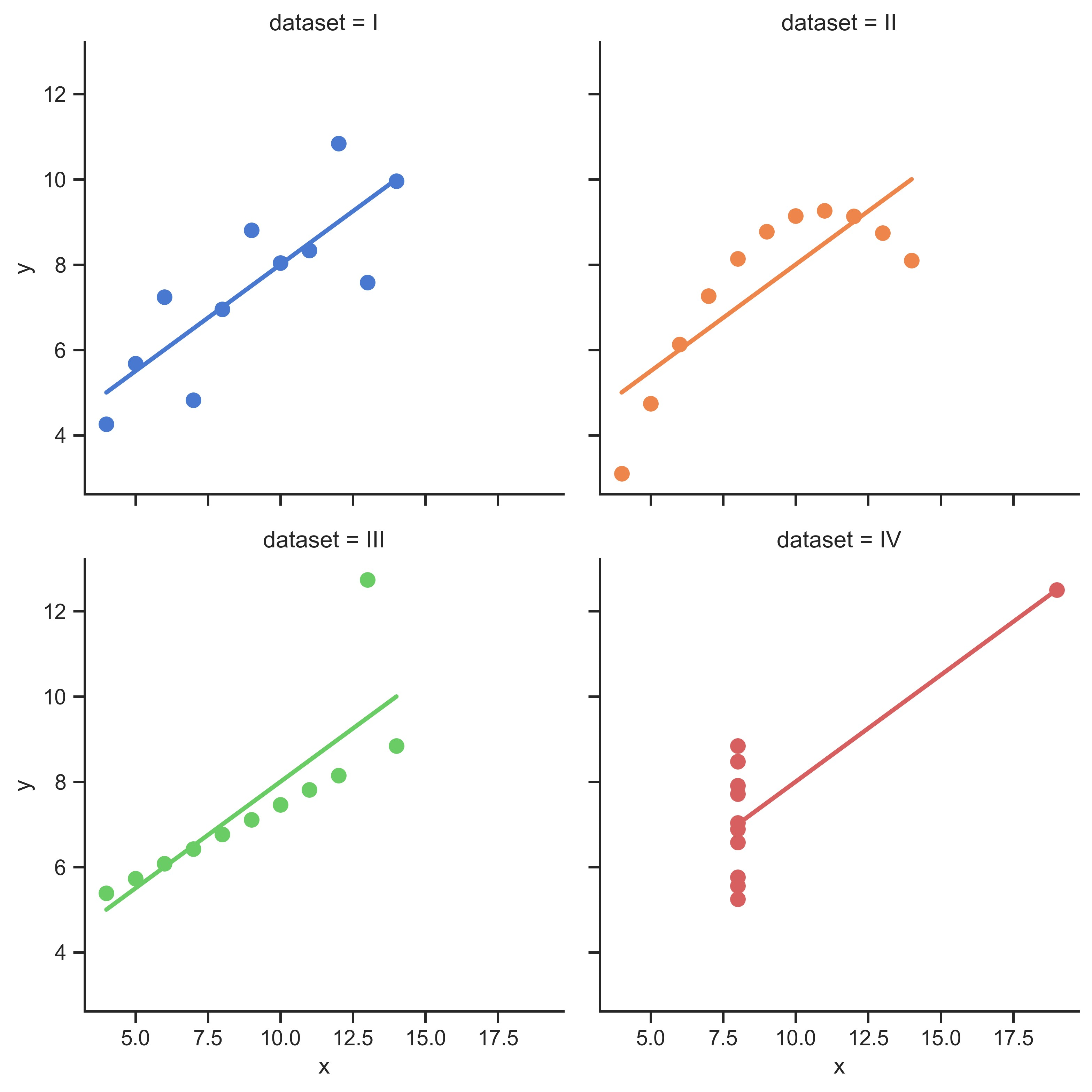
示例 1
sns.set_theme(style="ticks")
# Load the example dataset for Anscombe's quartet
df = sns.load_dataset("anscombe")
# Show the results of a linear regression within each dataset
sns.lmplot(
data=df,
x="x",
y="y",
col="dataset",
hue="dataset",
col_wrap=2,
palette="muted",
ci=None,
height=4,
scatter_kws={"s": 50, "alpha": 1},
)
plt.show()
示例 2
sns.set_theme(style="whitegrid")
# Load the example diamonds dataset
diamonds = sns.load_dataset("diamonds")
# Draw a scatter plot while assigning point colors and sizes to different
# variables in the dataset
f, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6.5, 6.5))
sns.despine(f, left=True, bottom=True)
clarity_ranking = ["I1", "SI2", "SI1", "VS2", "VS1", "VVS2", "VVS1", "IF"]
sns.scatterplot(
x="carat",
y="price",
hue="clarity",
size="depth",
palette="ch:r=-.2,d=.3_r",
hue_order=clarity_ranking,
sizes=(1, 8),
linewidth=0,
data=diamonds,
ax=ax,
)
plt.show()

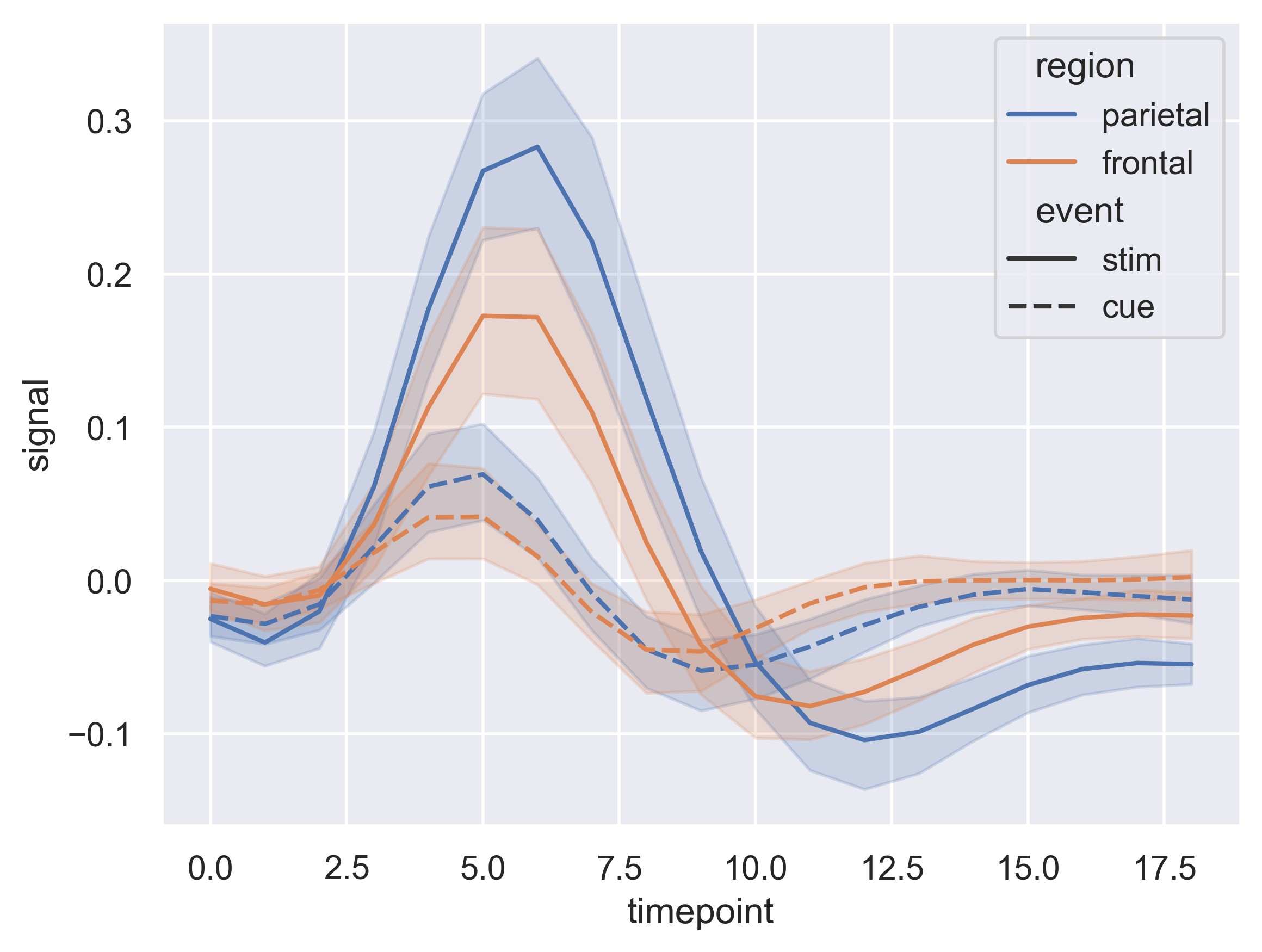
示例 3
sns.set_theme(style="darkgrid")
# Load an example dataset with long-form data
fmri = sns.load_dataset("fmri")
# Plot the responses for different events and regions
sns.lineplot(x="timepoint", y="signal", hue="region", style="event", data=fmri)
plt.show()
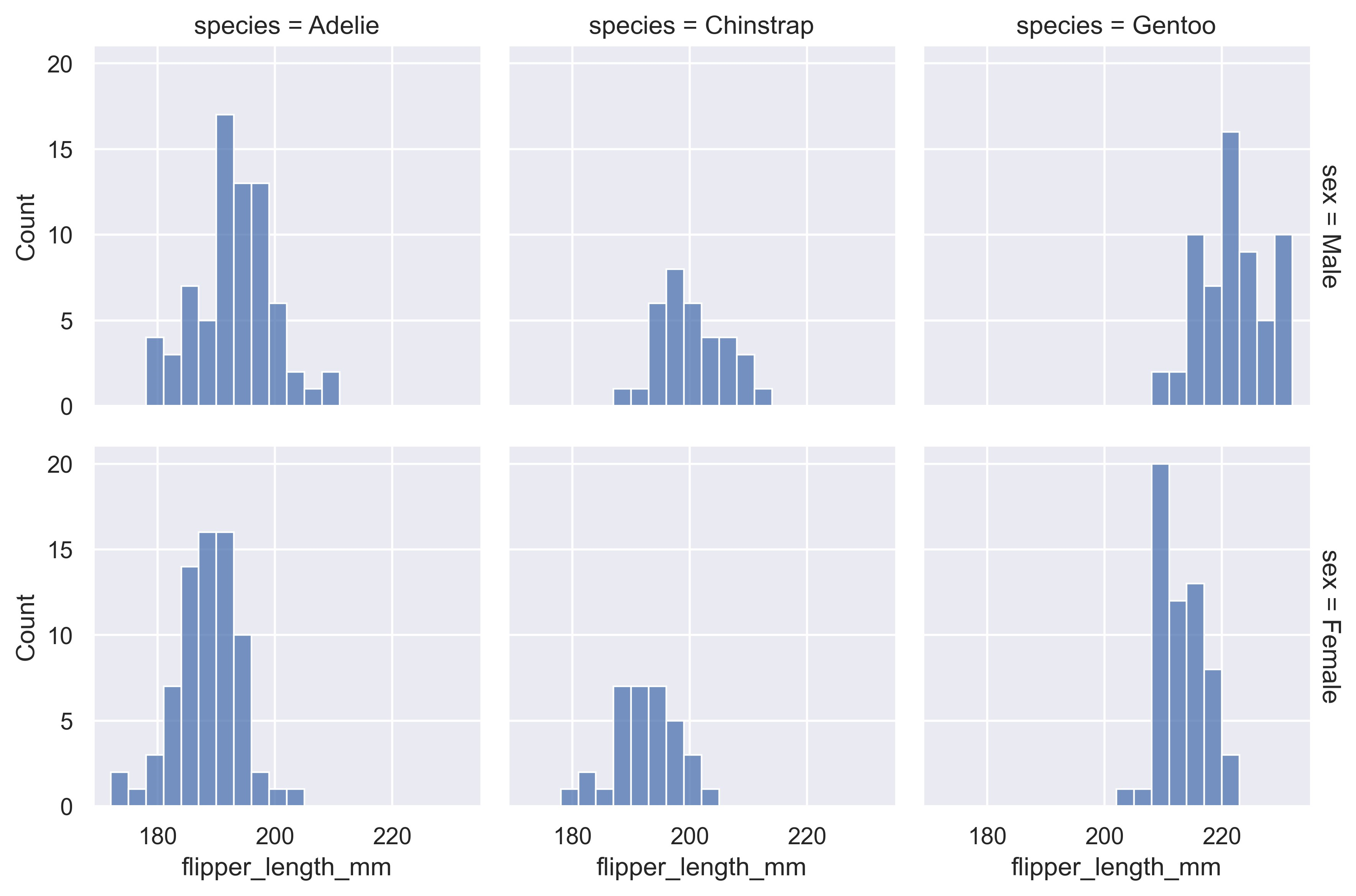
示例 4
sns.set_theme(style="darkgrid")
df = sns.load_dataset("penguins")
sns.displot(
df,
x="flipper_length_mm",
col="species",
row="sex",
binwidth=3,
height=3,
facet_kws=dict(margin_titles=True),
)
plt.show()
示例 5
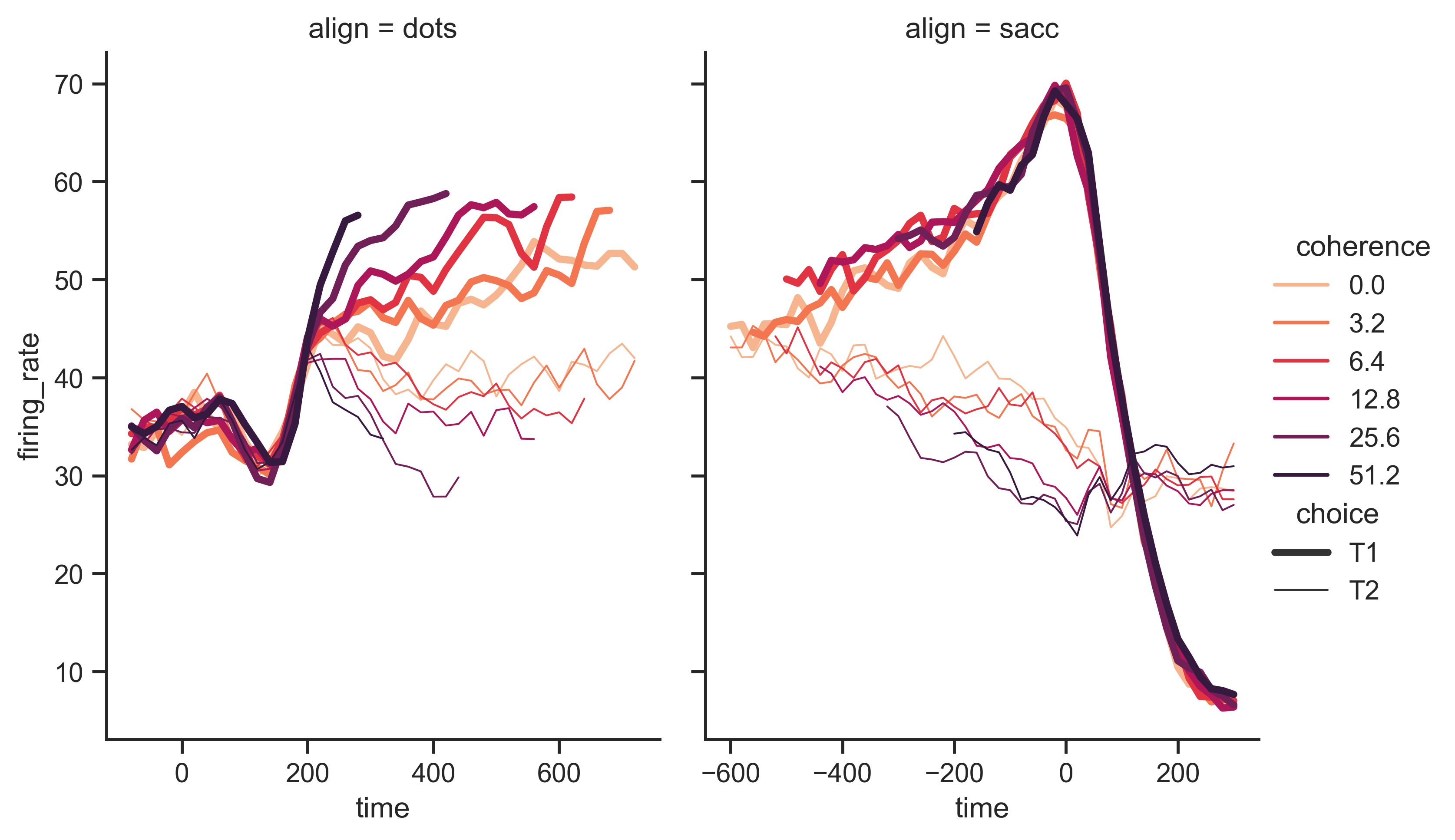
sns.set_theme(style="ticks")
dots = sns.load_dataset("dots")
# Define the palette as a list to specify exact values
palette = sns.color_palette("rocket_r")
# Plot the lines on two facets
sns.relplot(
data=dots,
x="time",
y="firing_rate",
hue="coherence",
size="choice",
col="align",
kind="line",
size_order=["T1", "T2"],
palette=palette,
height=5,
aspect=0.75,
facet_kws=dict(sharex=False),
)
plt.show()
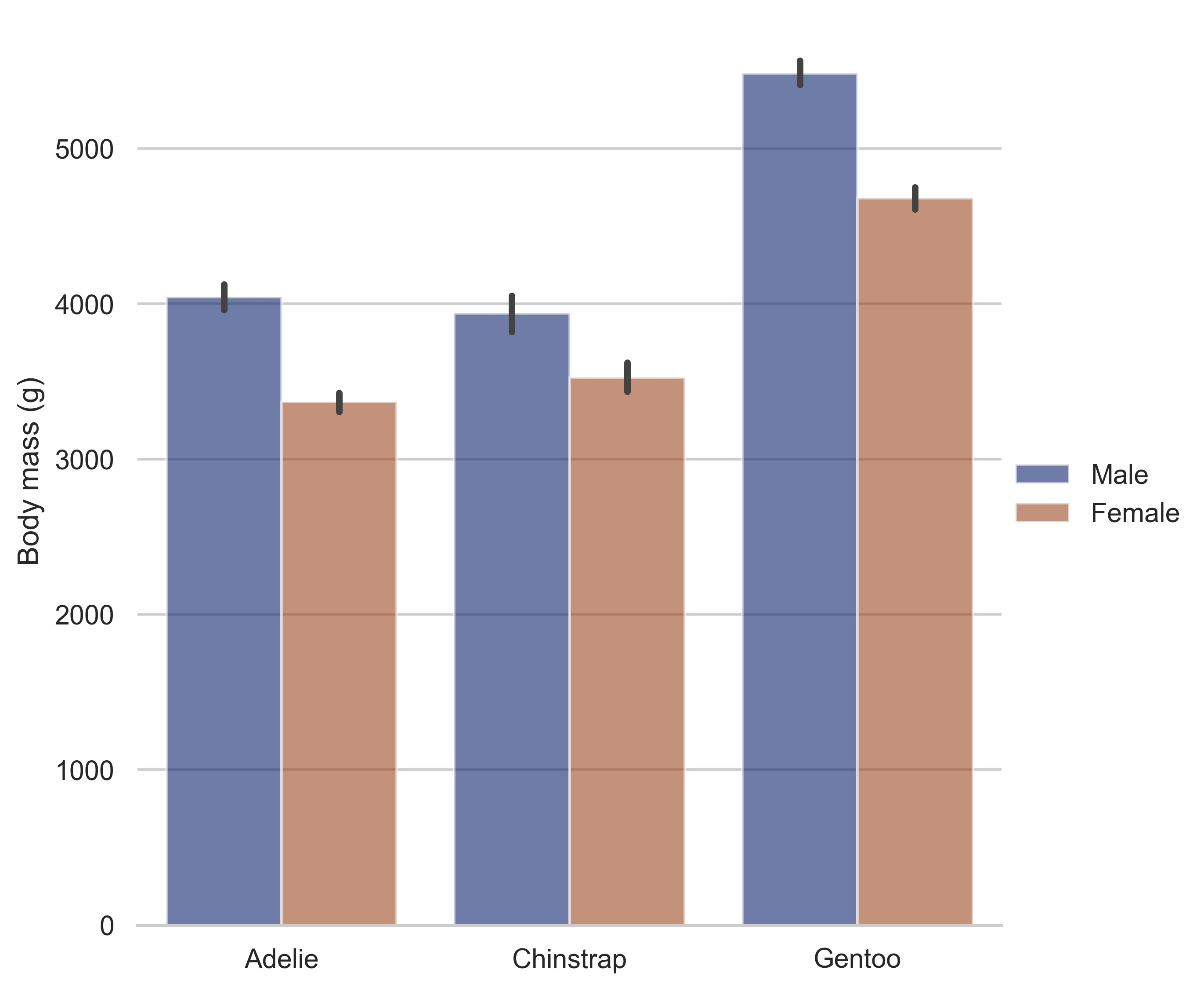
示例 6
sns.set_theme(style="whitegrid")
penguins = sns.load_dataset("penguins")
# Draw a nested barplot by species and sex
g = sns.catplot(
data=penguins,
kind="bar",
x="species",
y="body_mass_g",
hue="sex",
palette="dark",
alpha=0.6,
height=6,
)
g.despine(left=True)
g.set_axis_labels("", "Body mass (g)")
g.legend.set_title("")
plt.show()
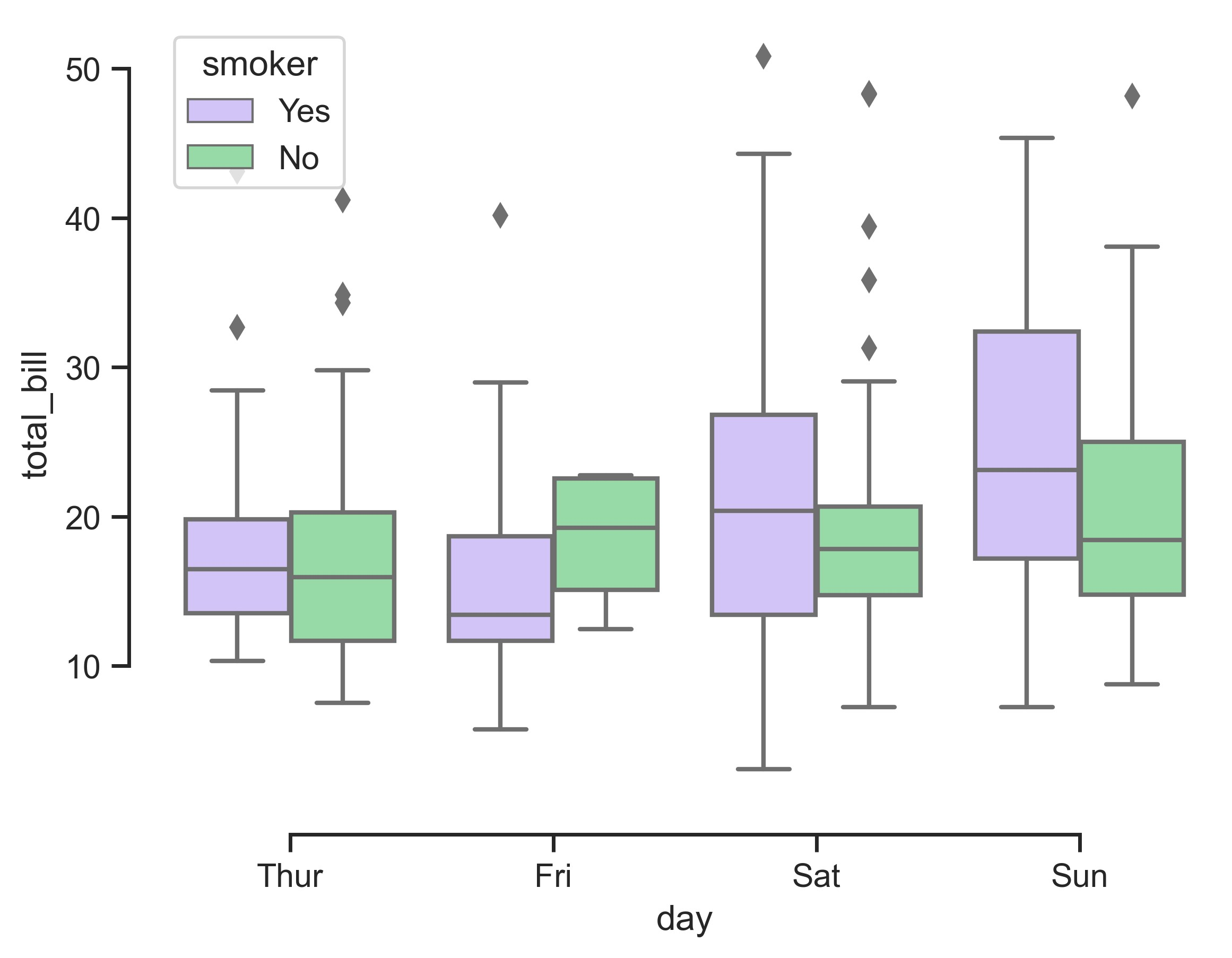
示例 7
sns.set_theme(style="ticks", palette="pastel")
# Load the example tips dataset
tips = sns.load_dataset("tips")
# Draw a nested boxplot to show bills by day and time
sns.boxplot(x="day", y="total_bill", hue="smoker", palette=["m", "g"], data=tips)
sns.despine(offset=10, trim=True)
plt.show()
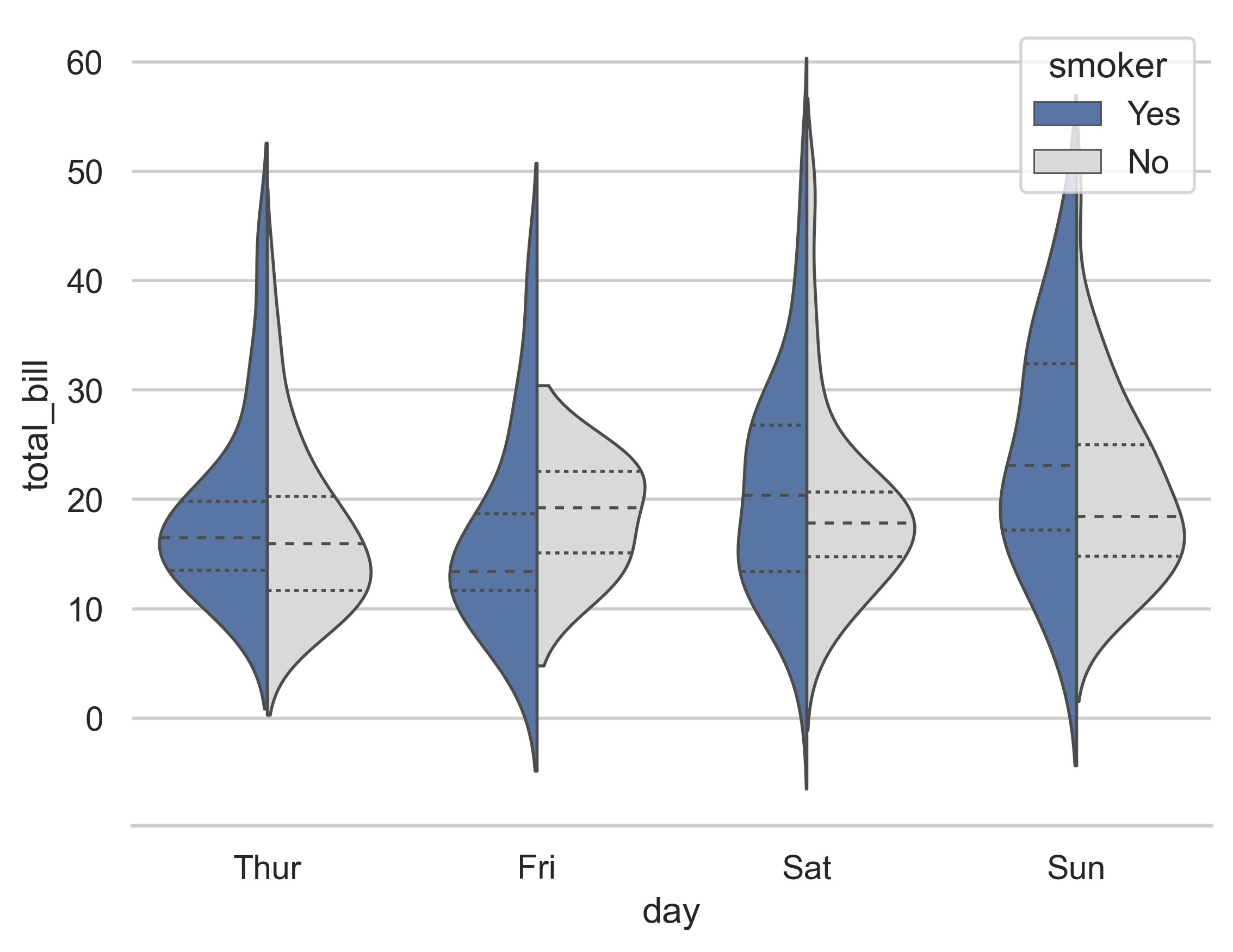
示例 8
sns.set_theme(style="whitegrid")
# Load the example tips dataset
tips = sns.load_dataset("tips")
# Draw a nested violinplot and split the violins for easier comparison
sns.violinplot(
data=tips,
x="day",
y="total_bill",
hue="smoker",
split=True,
inner="quart",
linewidth=1,
palette={"Yes": "b", "No": ".85"},
)
sns.despine(left=True)
plt.show()
示例 9
sns.set_theme(style="whitegrid")
# Load the brain networks dataset, select subset, and collapse the multi-index
df = sns.load_dataset("brain_networks", header=[0, 1, 2], index_col=0)
used_networks = [1, 5, 6, 7, 8, 12, 13, 17]
used_columns = df.columns.get_level_values("network").astype(int).isin(used_networks)
df = df.loc[:, used_columns]
df.columns = df.columns.map("-".join)
# Compute a correlation matrix and convert to long-form
corr_mat = df.corr().stack().reset_index(name="correlation")
# Draw each cell as a scatter point with varying size and color
g = sns.relplot(
data=corr_mat,
x="level_0",
y="level_1",
hue="correlation",
size="correlation",
palette="vlag",
hue_norm=(-1, 1),
edgecolor=".7",
height=10,
sizes=(50, 250),
size_norm=(-0.2, 0.8),
)
# Tweak the figure to finalize
g.set(xlabel="", ylabel="", aspect="equal")
g.despine(left=True, bottom=True)
g.ax.margins(0.02)
for label in g.ax.get_xticklabels():
label.set_rotation(90)
for artist in g.legend.legendHandles:
artist.set_edgecolor(".7")
plt.show()

示例 10
sns.set_theme(style="ticks")
rs = np.random.RandomState(11)
x = rs.gamma(2, size=1000)
y = -0.5 * x + rs.normal(size=1000)
sns.jointplot(x=x, y=y, kind="hex", color="#4CB391")
plt.show()
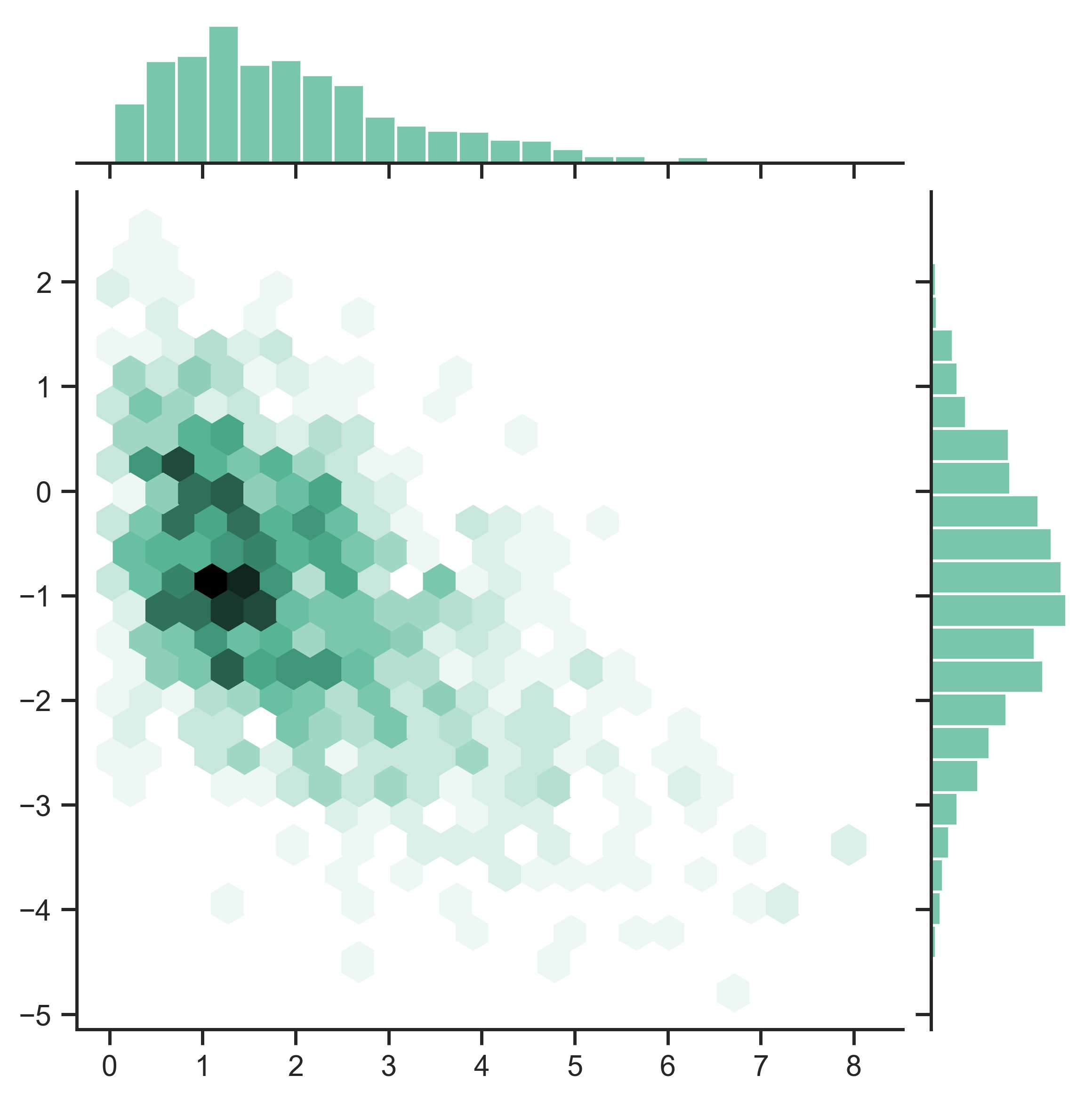
示例 11
sns.set_theme(style="ticks")
diamonds = sns.load_dataset("diamonds")
f, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(7, 5))
sns.despine(f)
sns.histplot(
diamonds,
x="price",
hue="cut",
multiple="stack",
palette="light:m_r",
edgecolor=".3",
linewidth=0.5,
log_scale=True,
)
ax.set_xticks([500, 1000, 2000, 5000, 10000])
plt.show()
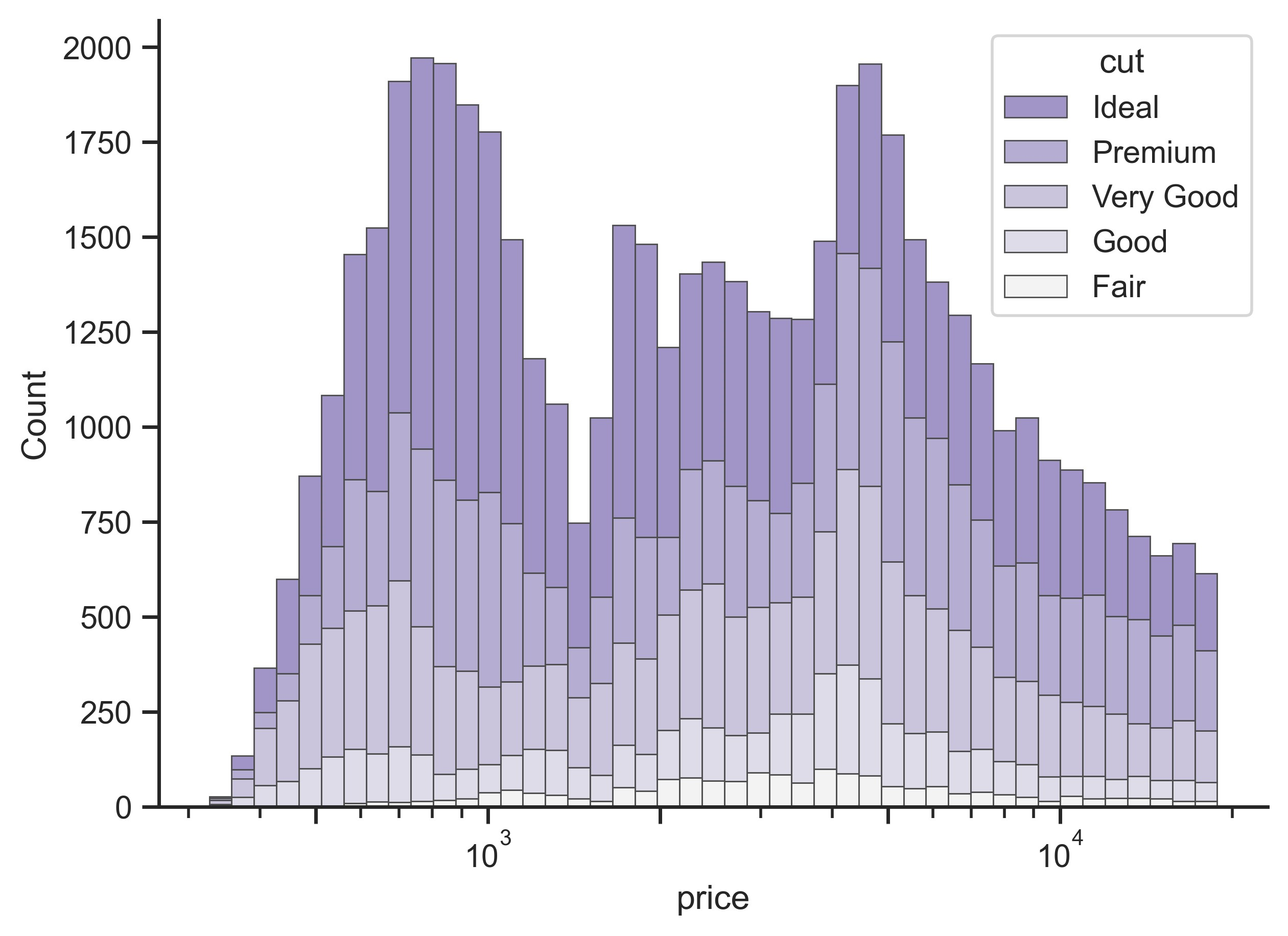
示例 12
sns.set_theme(style="ticks")
# Initialize the figure with a logarithmic x axis
f, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(7, 6))
ax.set_xscale("log")
# Load the example planets dataset
planets = sns.load_dataset("planets")
# Plot the orbital period with horizontal boxes
sns.boxplot(
x="distance", y="method", data=planets, whis=[0, 100], width=0.6, palette="vlag"
)
# Add in points to show each observation
sns.stripplot(x="distance", y="method", data=planets, size=4, color=".3", linewidth=0)
# Tweak the visual presentation
ax.xaxis.grid(True)
ax.set(ylabel="")
sns.despine(trim=True, left=True)
plt.show()
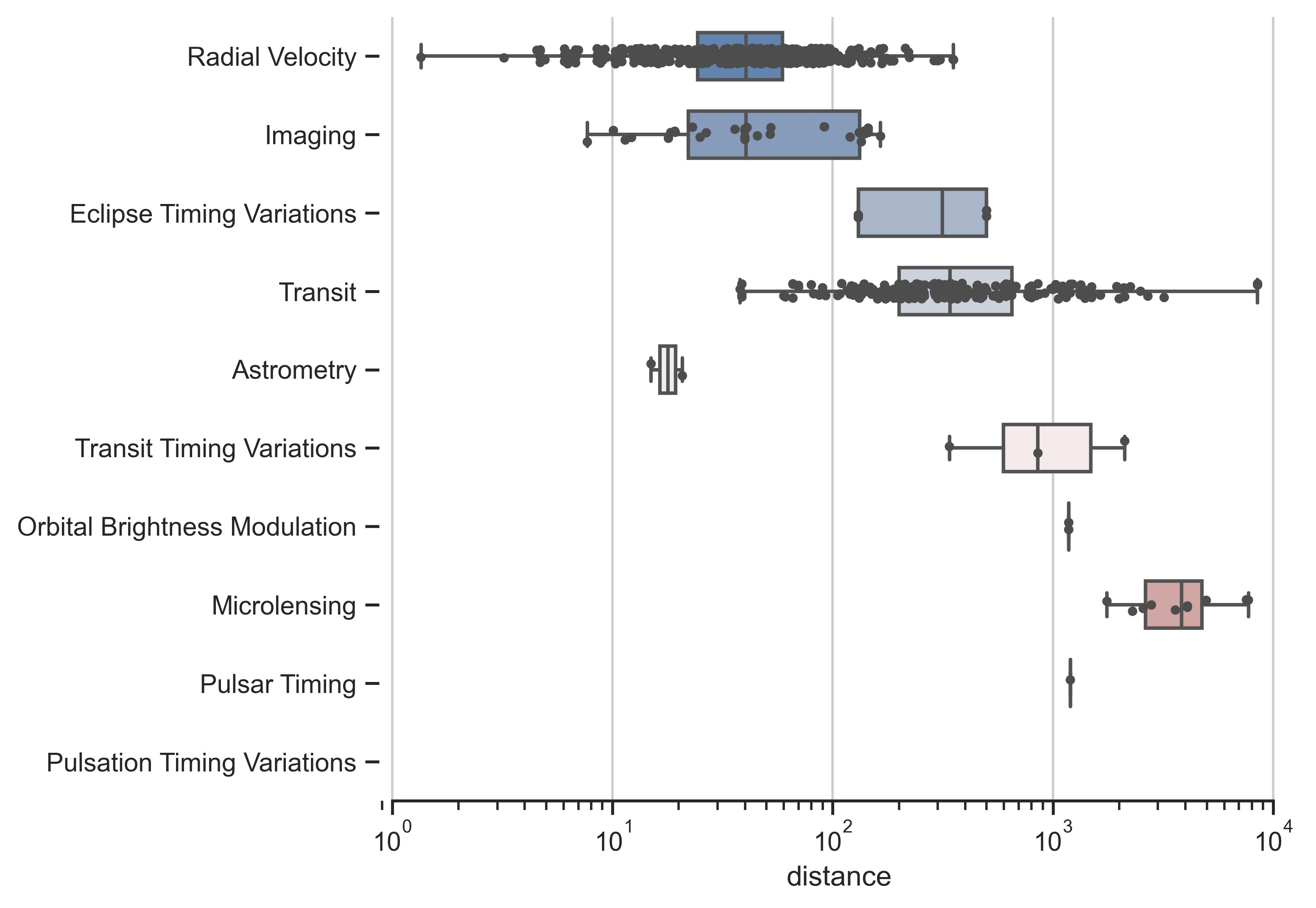
示例 13
sns.set_theme(style="whitegrid")
iris = sns.load_dataset("iris")
# "Melt" the dataset to "long-form" or "tidy" representation
iris = pd.melt(iris, "species", var_name="measurement")
# Initialize the figure
f, ax = plt.subplots()
sns.despine(bottom=True, left=True)
# Show each observation with a scatterplot
sns.stripplot(
data=iris,
x="value",
y="measurement",
hue="species",
dodge=True,
alpha=0.25,
zorder=1,
)
# Show the conditional means, aligning each pointplot in the
# center of the strips by adjusting the width allotted to each
# category (.8 by default) by the number of hue levels
sns.pointplot(
data=iris,
x="value",
y="measurement",
hue="species",
join=False,
dodge=0.8 - 0.8 / 3,
palette="dark",
markers="d",
scale=0.75,
errorbar=None,
)
# Improve the legend
sns.move_legend(
ax, loc="lower right", ncol=3, frameon=True, columnspacing=1, handletextpad=0
)
plt.show()
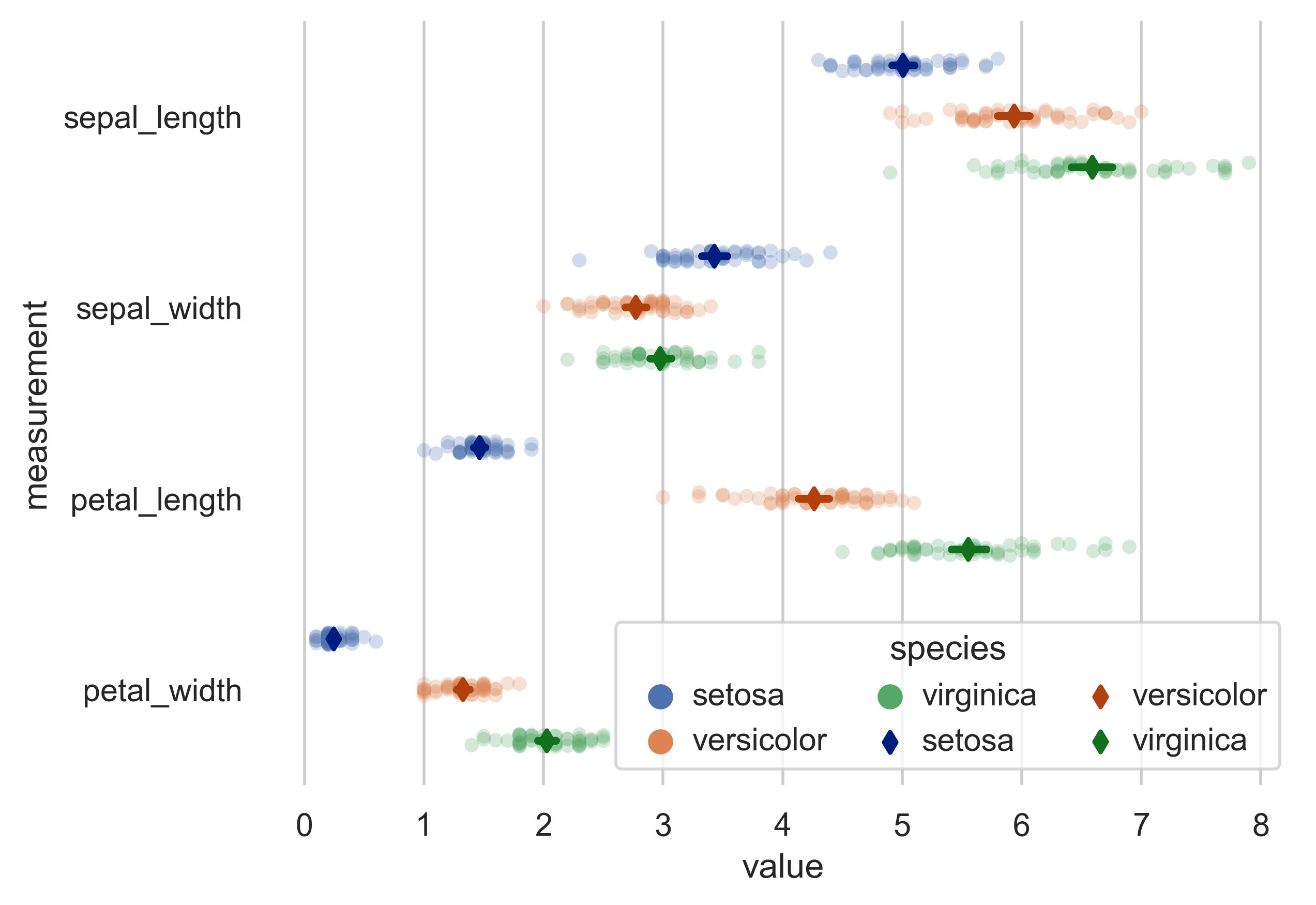
示例 14
sns.set_theme(style="ticks")
# Load the planets dataset and initialize the figure
planets = sns.load_dataset("planets")
g = sns.JointGrid(data=planets, x="year", y="distance", marginal_ticks=True)
# Set a log scaling on the y axis
g.ax_joint.set(yscale="log")
# Create an inset legend for the histogram colorbar
cax = g.figure.add_axes([0.15, 0.55, 0.02, 0.2])
# Add the joint and marginal histogram plots
g.plot_joint(
sns.histplot,
discrete=(True, False),
cmap="light:#03012d",
pmax=0.8,
cbar=True,
cbar_ax=cax,
)
g.plot_marginals(sns.histplot, element="step", color="#03012d")
plt.show()
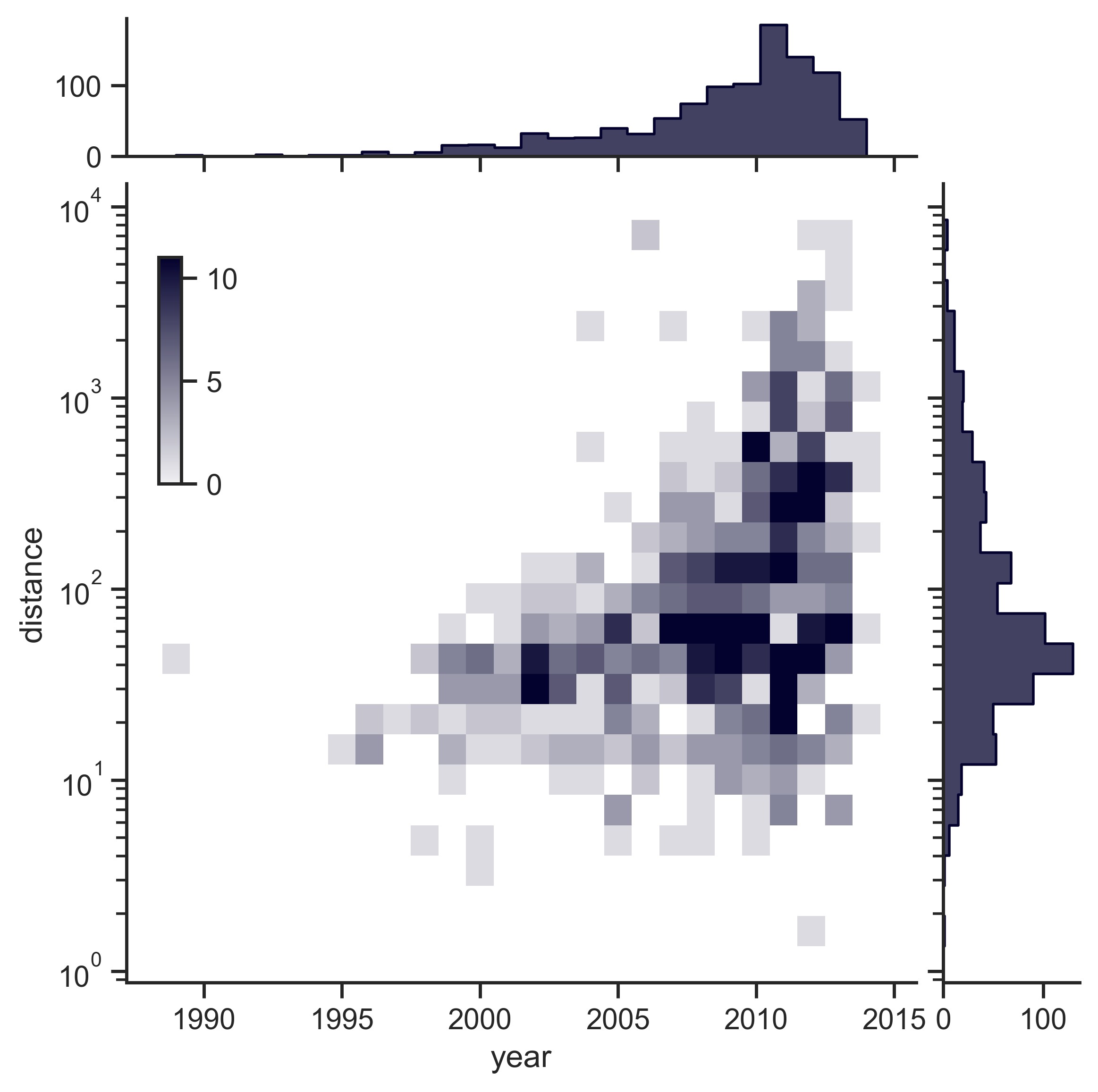
示例 15
sns.set_theme(style="ticks")
# Load the penguins dataset
penguins = sns.load_dataset("penguins")
# Show the joint distribution using kernel density estimation
g = sns.jointplot(
data=penguins,
x="bill_length_mm",
y="bill_depth_mm",
hue="species",
kind="kde",
)
plt.show()
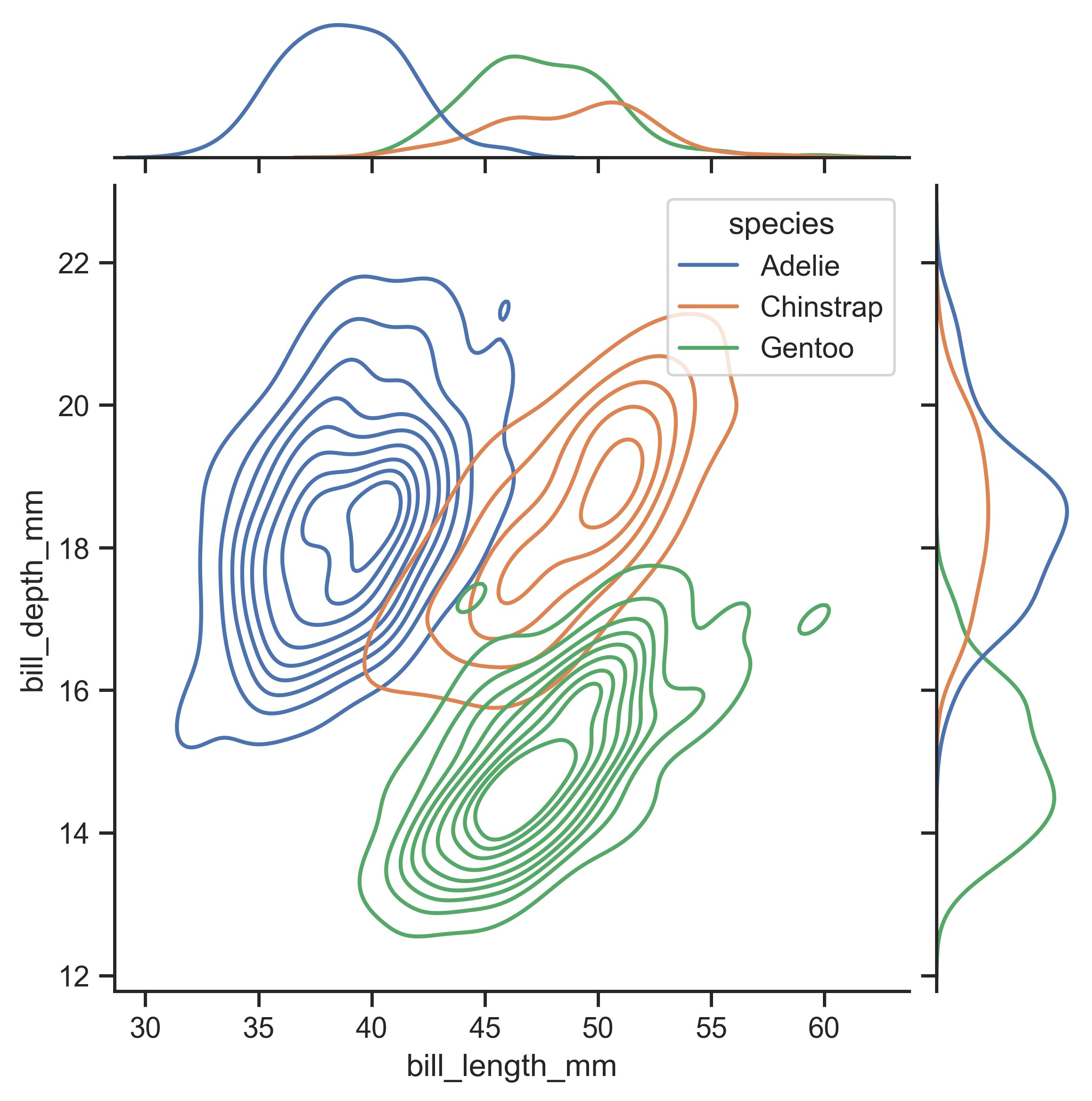
示例 16
sns.set_theme(style="white", rc={"axes.facecolor": (0, 0, 0, 0)})
# Create the data
rs = np.random.RandomState(1979)
x = rs.randn(500)
g = np.tile(list("ABCDEFGHIJ"), 50)
df = pd.DataFrame(dict(x=x, g=g))
m = df.g.map(ord)
df["x"] += m
# Initialize the FacetGrid object
pal = sns.cubehelix_palette(10, rot=-0.25, light=0.7)
g = sns.FacetGrid(df, row="g", hue="g", aspect=15, height=0.5, palette=pal)
# Draw the densities in a few steps
g.map(sns.kdeplot, "x", bw_adjust=0.5, clip_on=False, fill=True, alpha=1, linewidth=1.5)
g.map(sns.kdeplot, "x", clip_on=False, color="w", lw=2, bw_adjust=0.5)
# passing color=None to refline() uses the hue mapping
g.refline(y=0, linewidth=2, linestyle="-", color=None, clip_on=False)
# Define and use a simple function to label the plot in axes coordinates
def label(x, color, label):
ax = plt.gca()
ax.text(
0,
0.2,
label,
fontweight="bold",
color=color,
ha="left",
va="center",
transform=ax.transAxes,
)
g.map(label, "x")
# Set the subplots to overlap
g.figure.subplots_adjust(hspace=-0.25)
# Remove axes details that don't play well with overlap
g.set_titles("")
g.set(yticks=[], ylabel="")
g.despine(bottom=True, left=True)
plt.show()
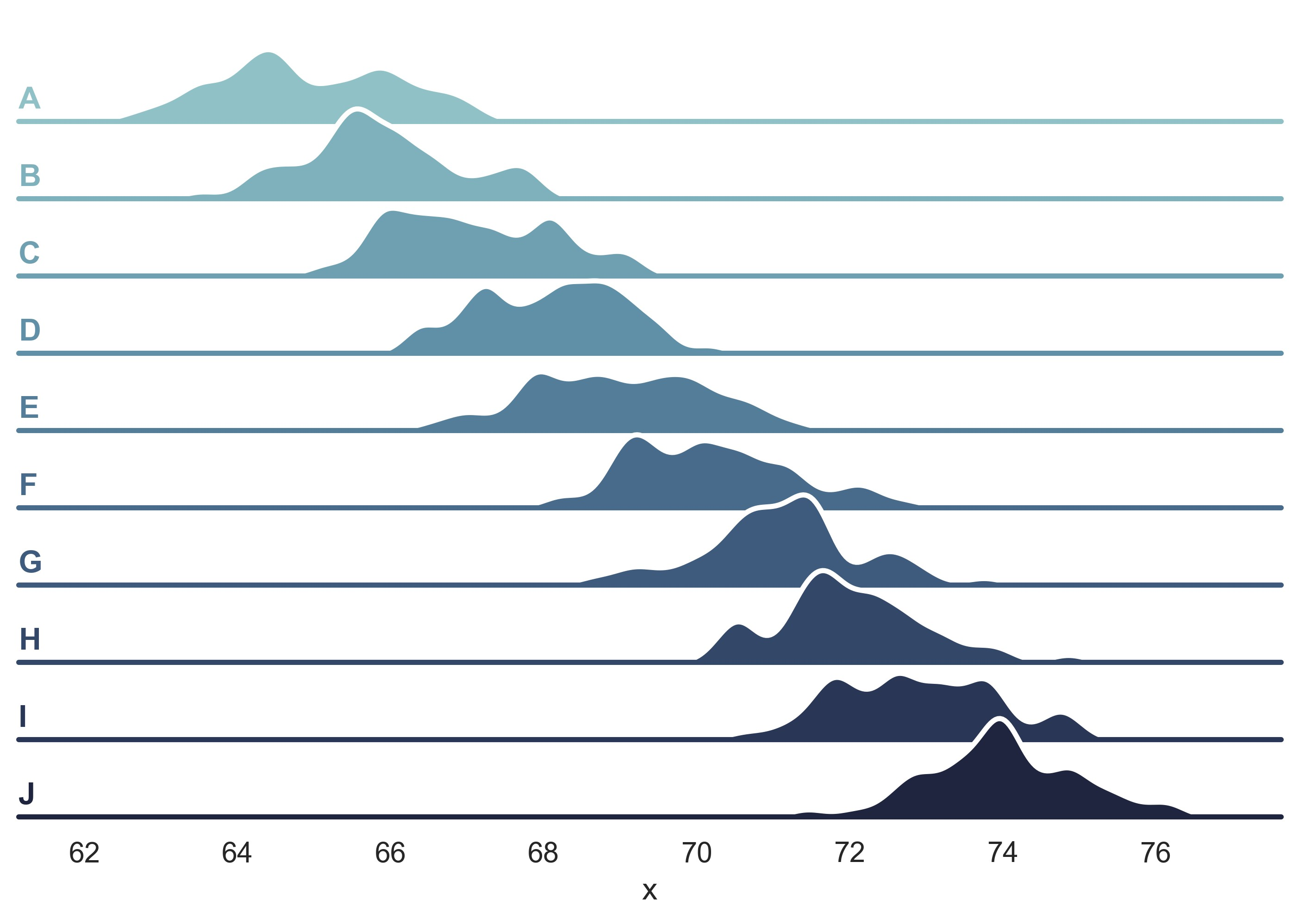
示例 17
sns.set_theme(style="whitegrid")
diamonds = sns.load_dataset("diamonds")
clarity_ranking = ["I1", "SI2", "SI1", "VS2", "VS1", "VVS2", "VVS1", "IF"]
sns.boxenplot(
x="clarity",
y="carat",
color="b",
order=clarity_ranking,
scale="linear",
data=diamonds,
)
plt.show()
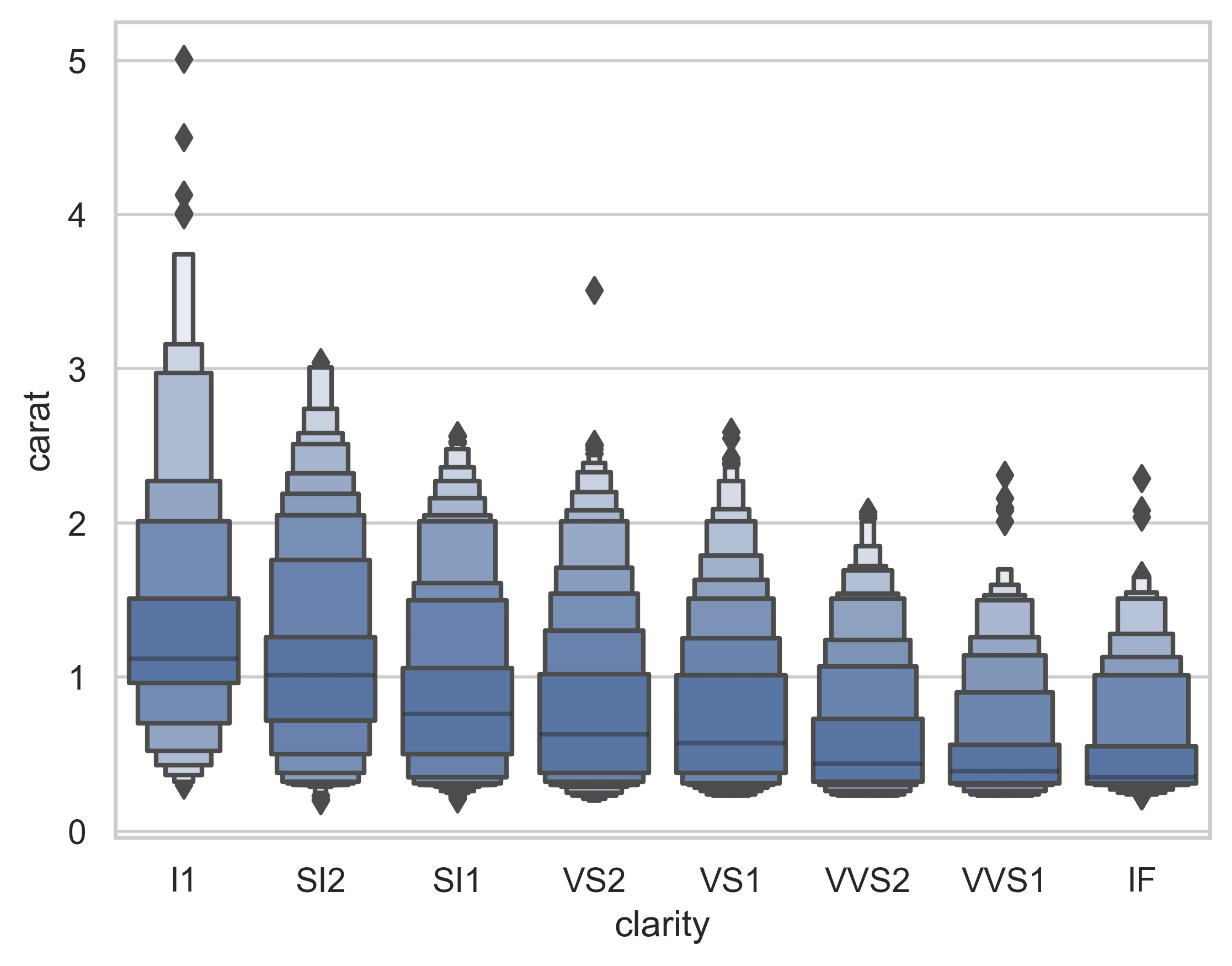
示例 18
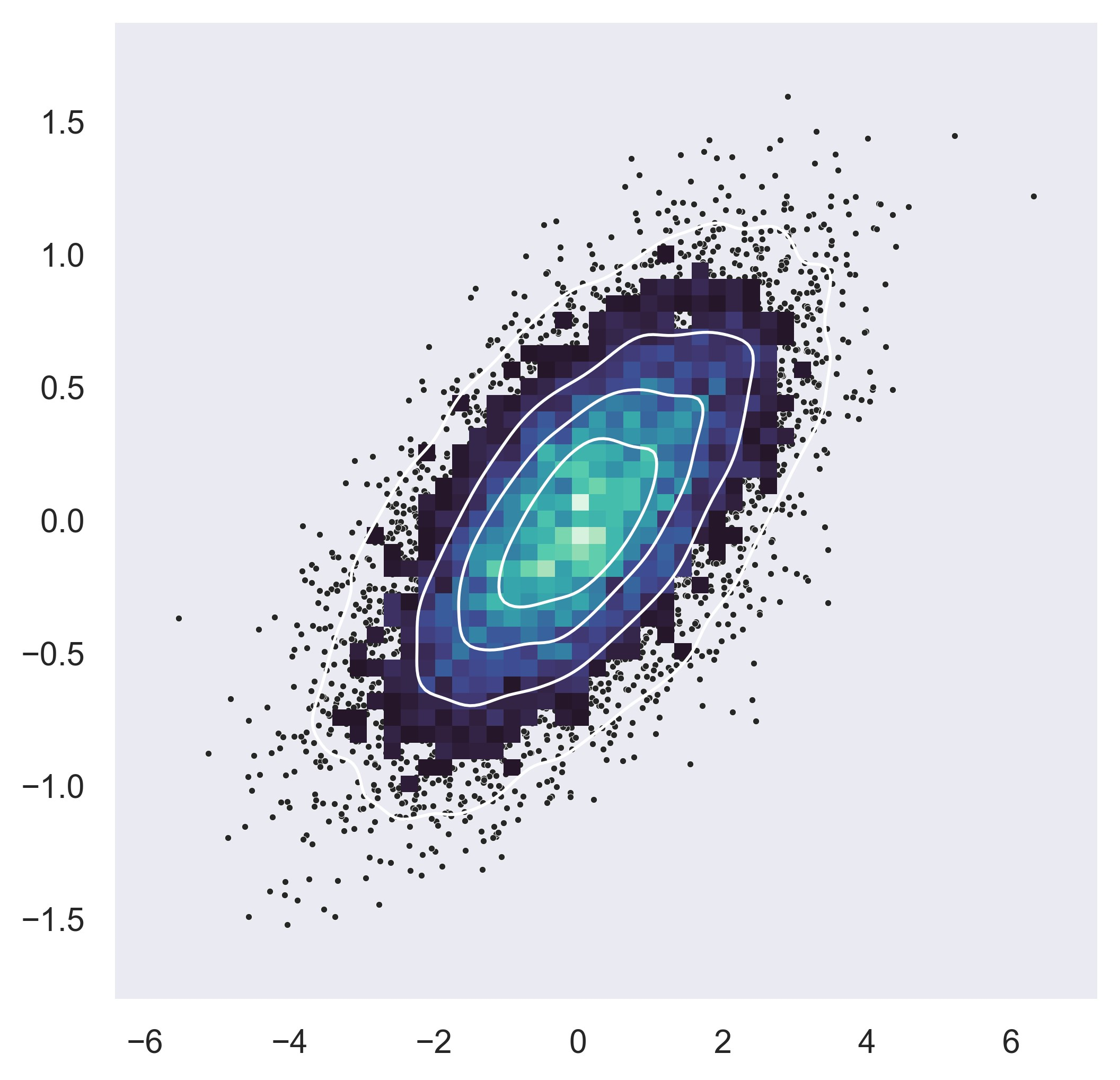
sns.set_theme(style="dark")
# Simulate data from a bivariate Gaussian
n = 10000
mean = [0, 0]
cov = [(2, 0.4), (0.4, 0.2)]
rng = np.random.RandomState(0)
x, y = rng.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, n).T
# Draw a combo histogram and scatterplot with density contours
f, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6, 6))
sns.scatterplot(x=x, y=y, s=5, color=".15")
sns.histplot(x=x, y=y, bins=50, pthresh=0.1, cmap="mako")
sns.kdeplot(x=x, y=y, levels=5, color="w", linewidths=1)
plt.show()
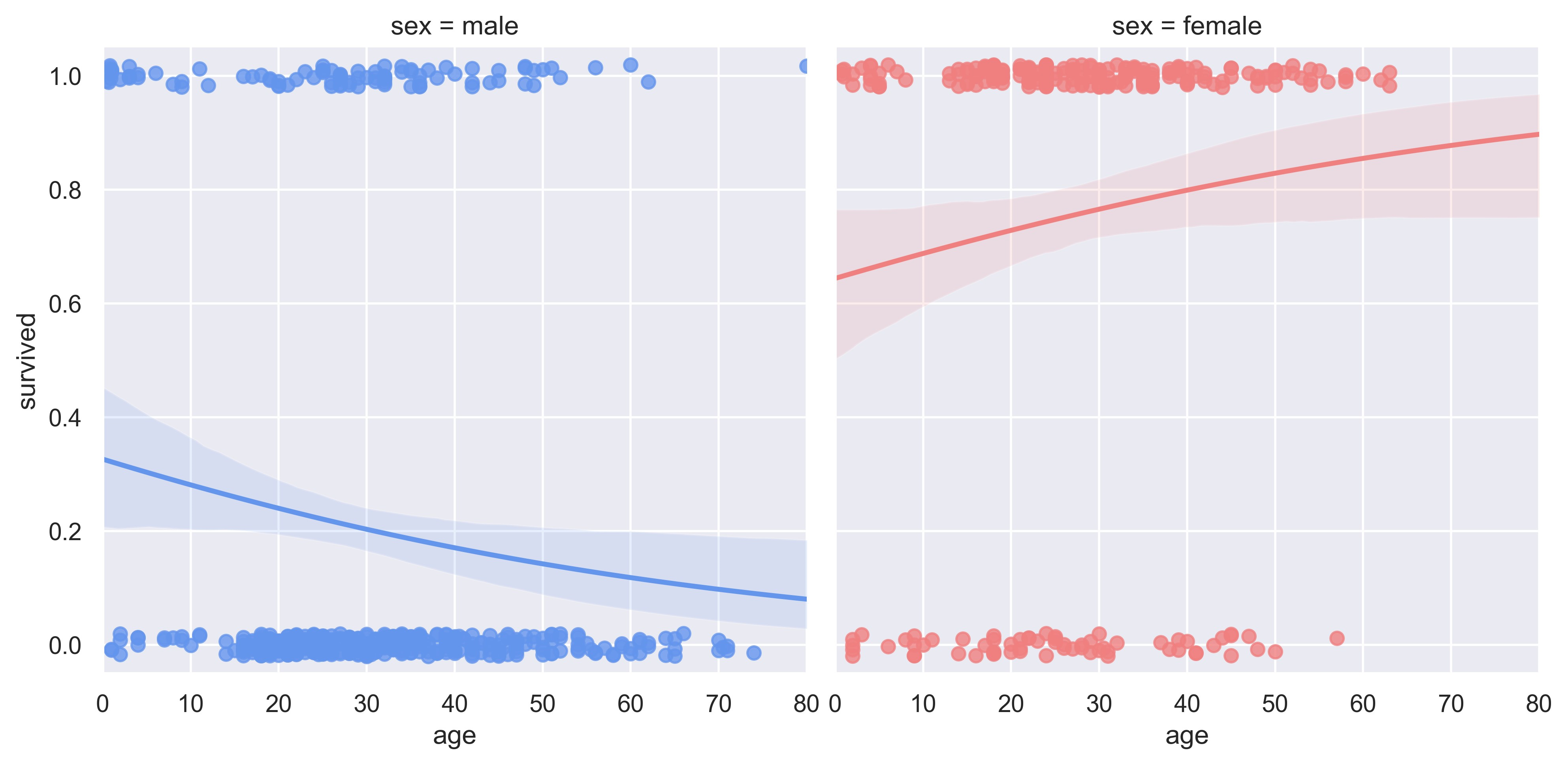
示例 19
sns.set_theme(style="darkgrid")
# Load the example Titanic dataset
df = sns.load_dataset("titanic")
# Make a custom palette with gendered colors
pal = dict(male="#6495ED", female="#F08080")
# Show the survival probability as a function of age and sex
g = sns.lmplot(
x="age",
y="survived",
col="sex",
hue="sex",
data=df,
palette=pal,
y_jitter=0.02,
logistic=True,
truncate=False,
)
g.set(xlim=(0, 80), ylim=(-0.05, 1.05))
plt.show()
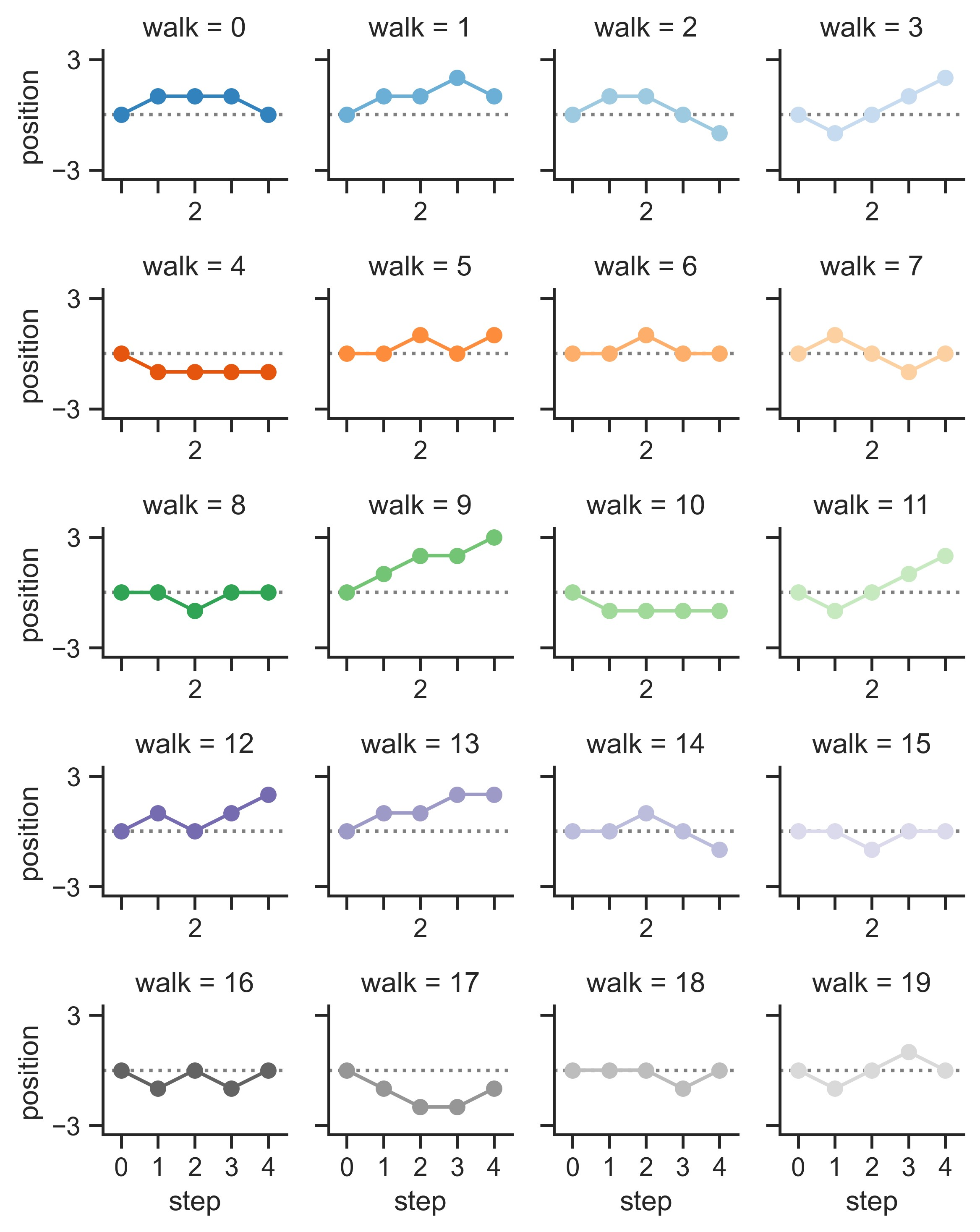
示例 20
sns.set_theme(style="ticks")
# Create a dataset with many short random walks
rs = np.random.RandomState(4)
pos = rs.randint(-1, 2, (20, 5)).cumsum(axis=1)
pos -= pos[:, 0, np.newaxis]
step = np.tile(range(5), 20)
walk = np.repeat(range(20), 5)
df = pd.DataFrame(np.c_[pos.flat, step, walk], columns=["position", "step", "walk"])
# Initialize a grid of plots with an Axes for each walk
grid = sns.FacetGrid(
df, col="walk", hue="walk", palette="tab20c", col_wrap=4, height=1.5
)
# Draw a horizontal line to show the starting point
grid.refline(y=0, linestyle=":")
# Draw a line plot to show the trajectory of each random walk
grid.map(plt.plot, "step", "position", marker="o")
# Adjust the tick positions and labels
grid.set(xticks=np.arange(5), yticks=[-3, 3], xlim=(-0.5, 4.5), ylim=(-3.5, 3.5))
# Adjust the arrangement of the plots
grid.fig.tight_layout(w_pad=1)
plt.show()
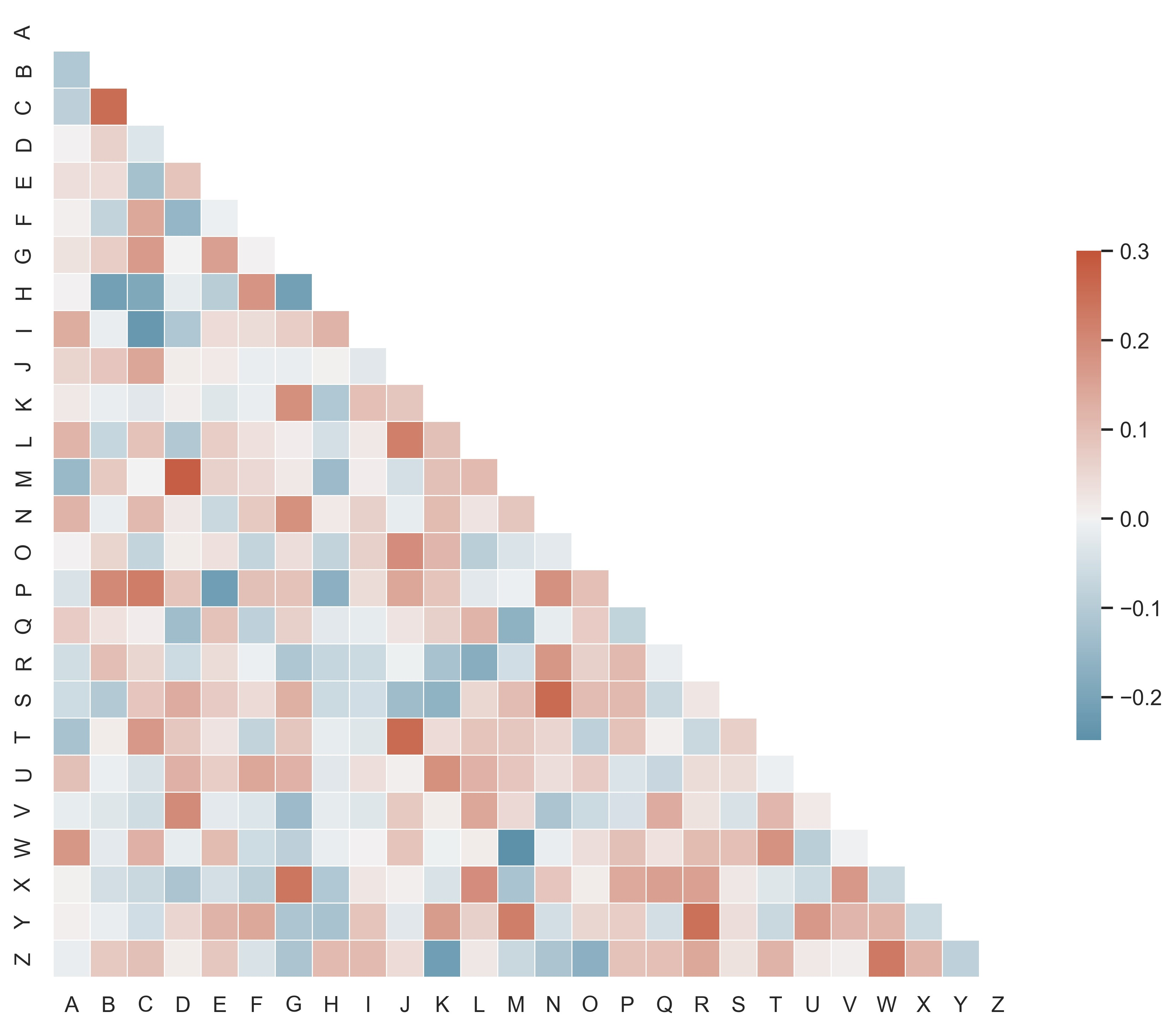
示例 21
from string import ascii_letters
sns.set_theme(style="white")
# Generate a large random dataset
rs = np.random.RandomState(33)
d = pd.DataFrame(data=rs.normal(size=(100, 26)), columns=list(ascii_letters[26:]))
# Compute the correlation matrix
corr = d.corr()
# Generate a mask for the upper triangle
mask = np.triu(np.ones_like(corr, dtype=bool))
# Set up the matplotlib figure
f, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(11, 9))
# Generate a custom diverging colormap
cmap = sns.diverging_palette(230, 20, as_cmap=True)
# Draw the heatmap with the mask and correct aspect ratio
sns.heatmap(
corr,
mask=mask,
cmap=cmap,
vmax=0.3,
center=0,
square=True,
linewidths=0.5,
cbar_kws={"shrink": 0.5},
)
plt.show()
示例 22
sns.set_theme(style="white", color_codes=True)
mpg = sns.load_dataset("mpg")
# Use JointGrid directly to draw a custom plot
g = sns.JointGrid(data=mpg, x="mpg", y="acceleration", space=0, ratio=17)
g.plot_joint(
sns.scatterplot,
size=mpg["horsepower"],
sizes=(30, 120),
color="g",
alpha=0.6,
legend=False,
)
g.plot_marginals(sns.rugplot, height=1, color="g", alpha=0.6)
plt.show()
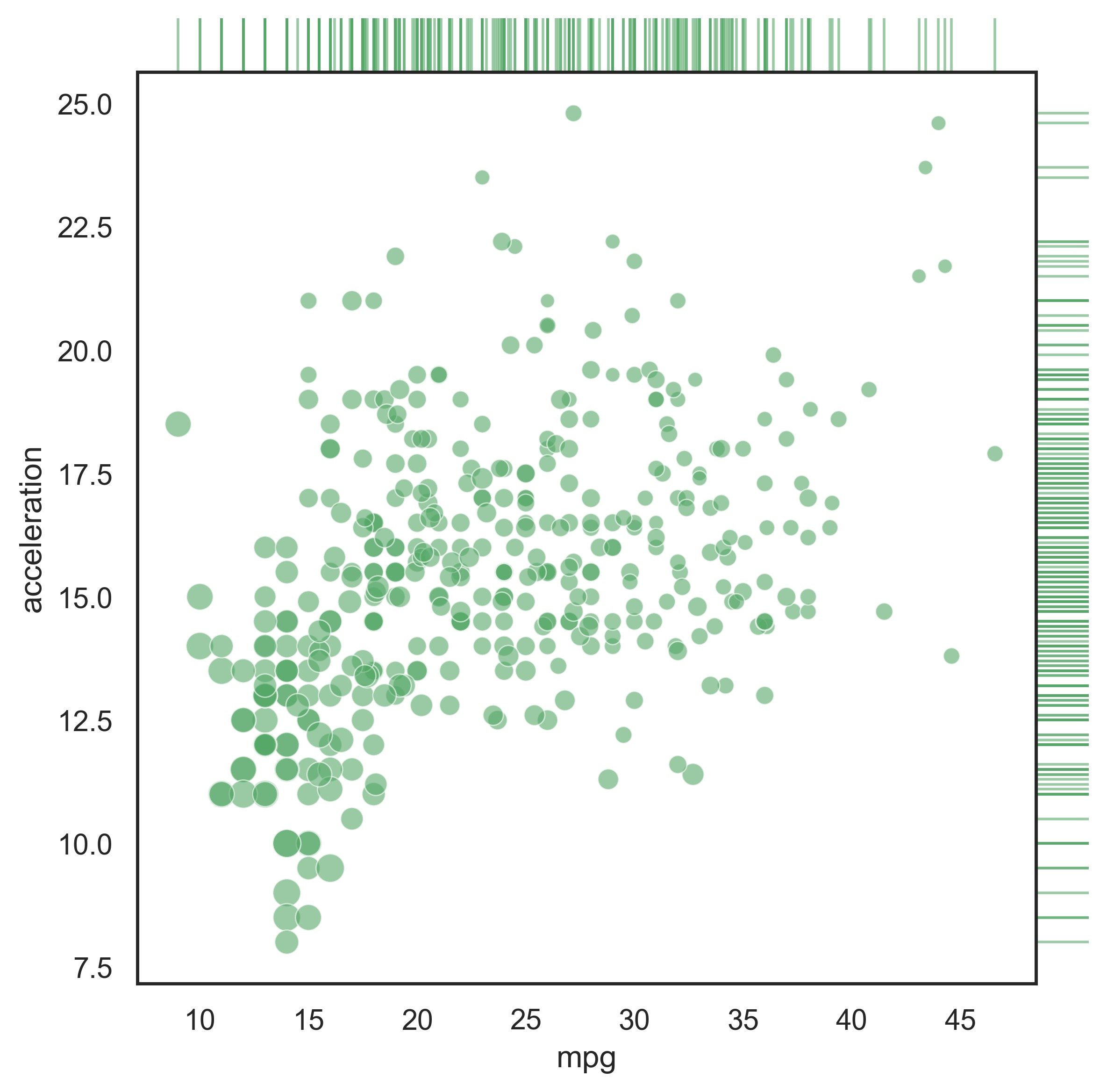
示例 23
sns.set_theme(style="darkgrid")
iris = sns.load_dataset("iris")
# Set up the figure
f, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8, 8))
ax.set_aspect("equal")
# Draw a contour plot to represent each bivariate density
sns.kdeplot(
data=iris.query("species != 'versicolor'"),
x="sepal_width",
y="sepal_length",
hue="species",
thresh=0.1,
)
plt.show()
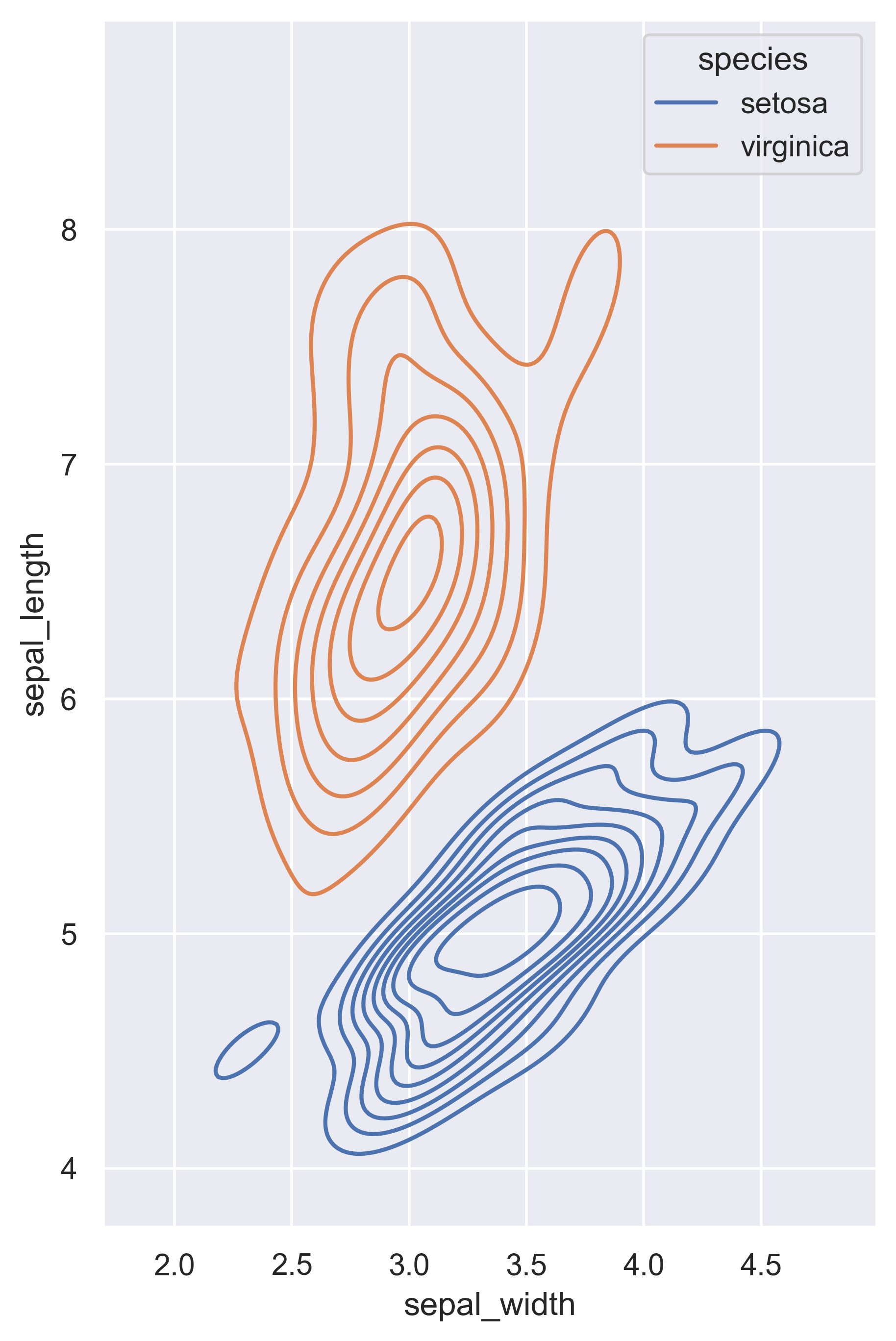
示例 24
sns.set_theme(style="whitegrid")
# Load the diamonds dataset
diamonds = sns.load_dataset("diamonds")
# Plot the distribution of clarity ratings, conditional on carat
sns.displot(
data=diamonds,
x="carat",
hue="cut",
kind="kde",
height=6,
multiple="fill",
clip=(0, None),
palette="ch:rot=-.25,hue=1,light=.75",
)
plt.show()
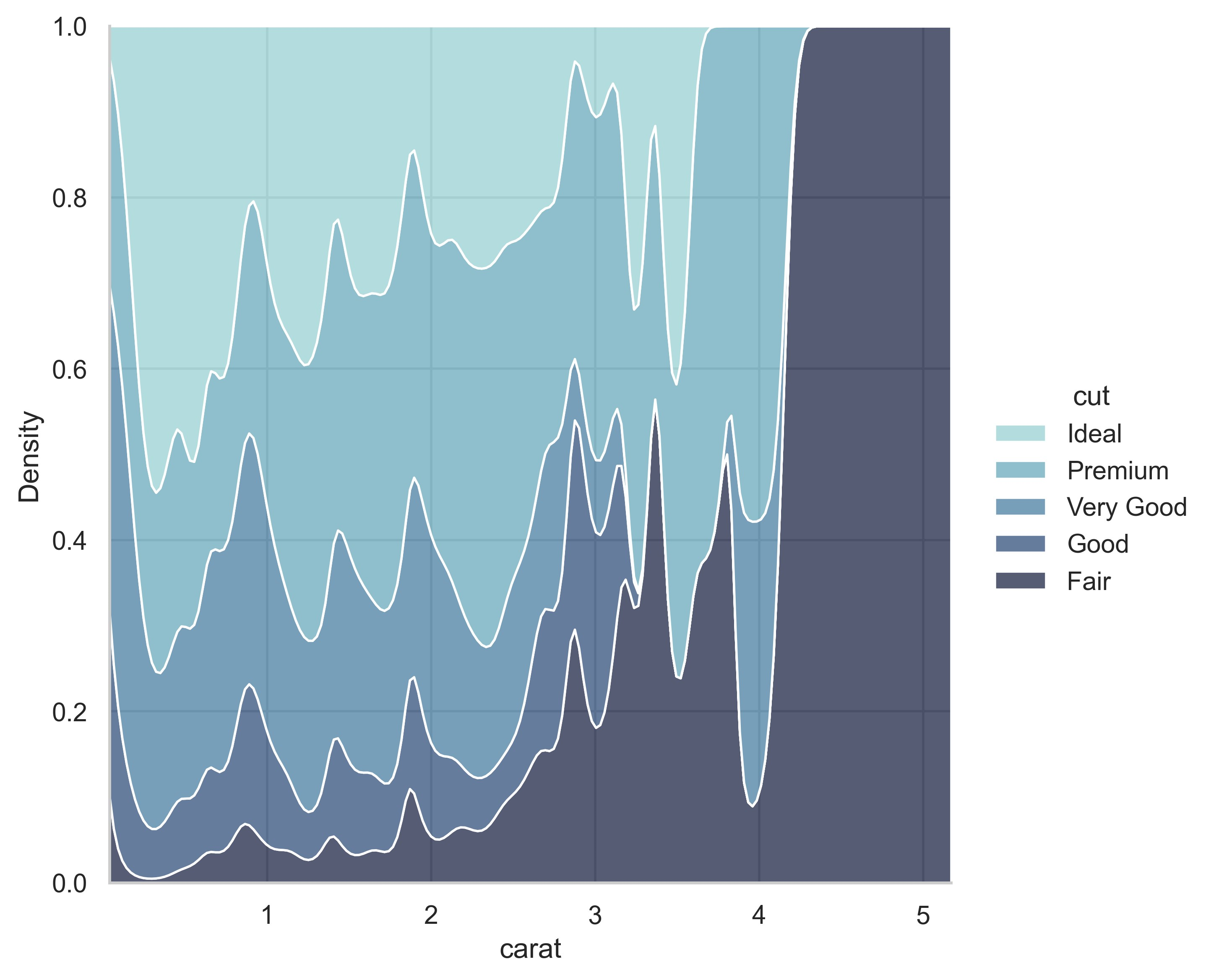
示例 25
sns.set_theme(style="ticks")
mpg = sns.load_dataset("mpg")
colors = (250, 70, 50), (350, 70, 50)
cmap = sns.blend_palette(colors, input="husl", as_cmap=True)
sns.displot(
mpg,
x="displacement",
col="origin",
hue="model_year",
kind="ecdf",
aspect=0.75,
linewidth=2,
palette=cmap,
)
plt.show()
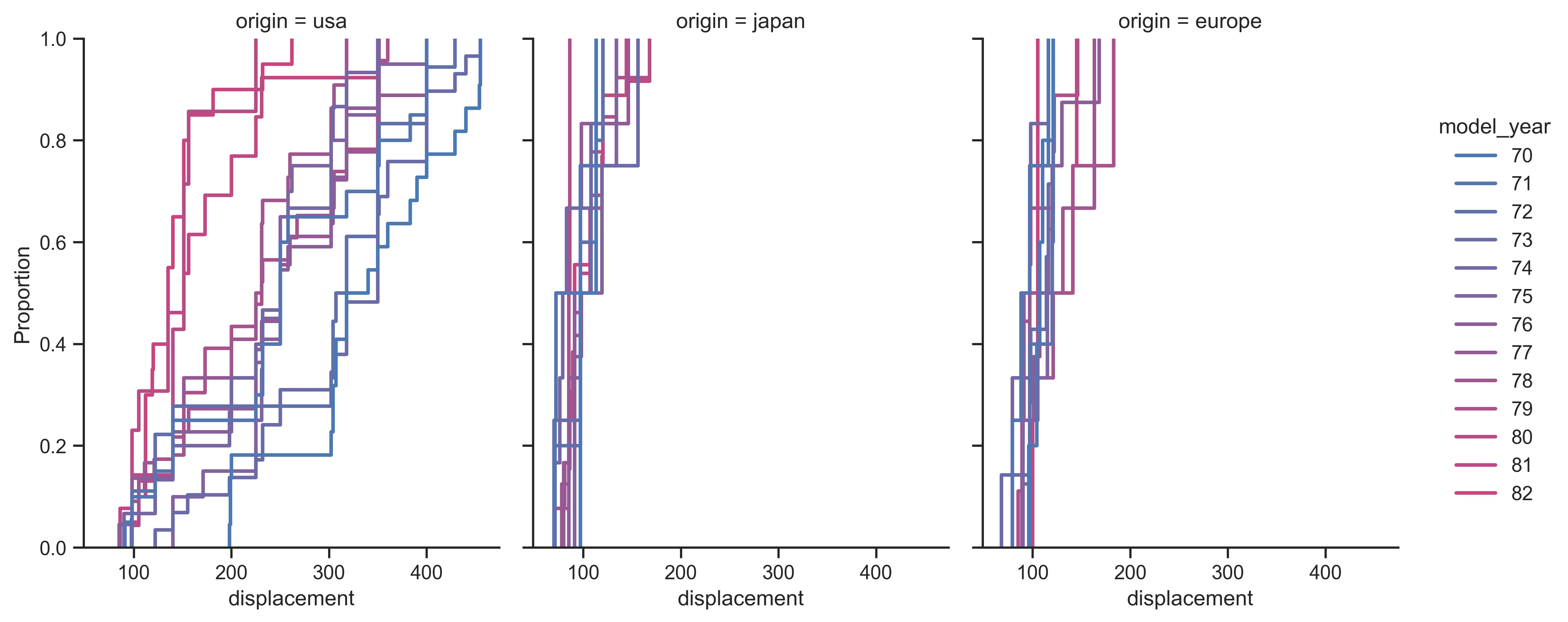
示例 26
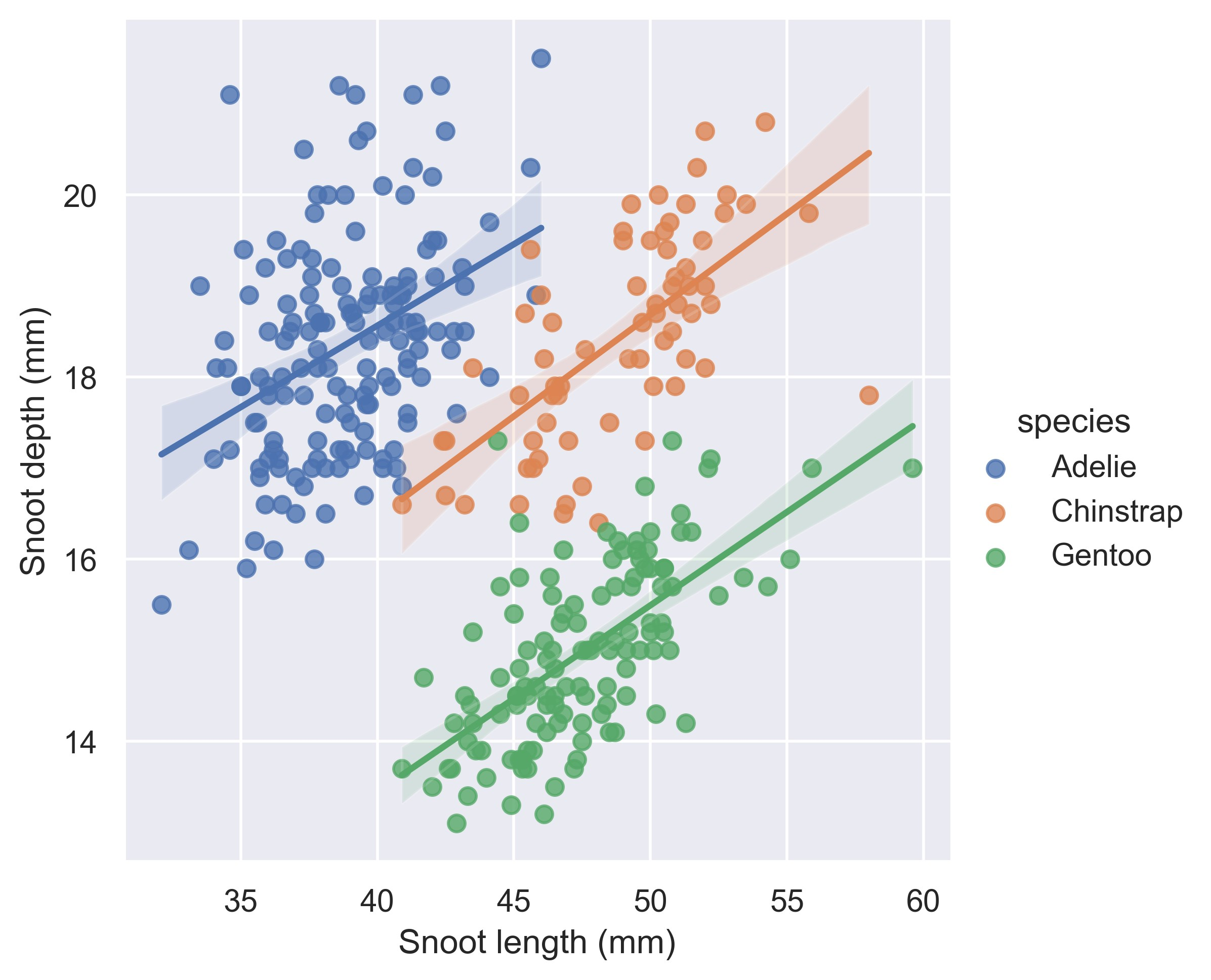
sns.set_theme()
# Load the penguins dataset
penguins = sns.load_dataset("penguins")
# Plot sepal width as a function of sepal_length across days
g = sns.lmplot(
data=penguins, x="bill_length_mm", y="bill_depth_mm", hue="species", height=5
)
# Use more informative axis labels than are provided by default
g.set_axis_labels("Snoot length (mm)", "Snoot depth (mm)")
plt.show()
示例 27
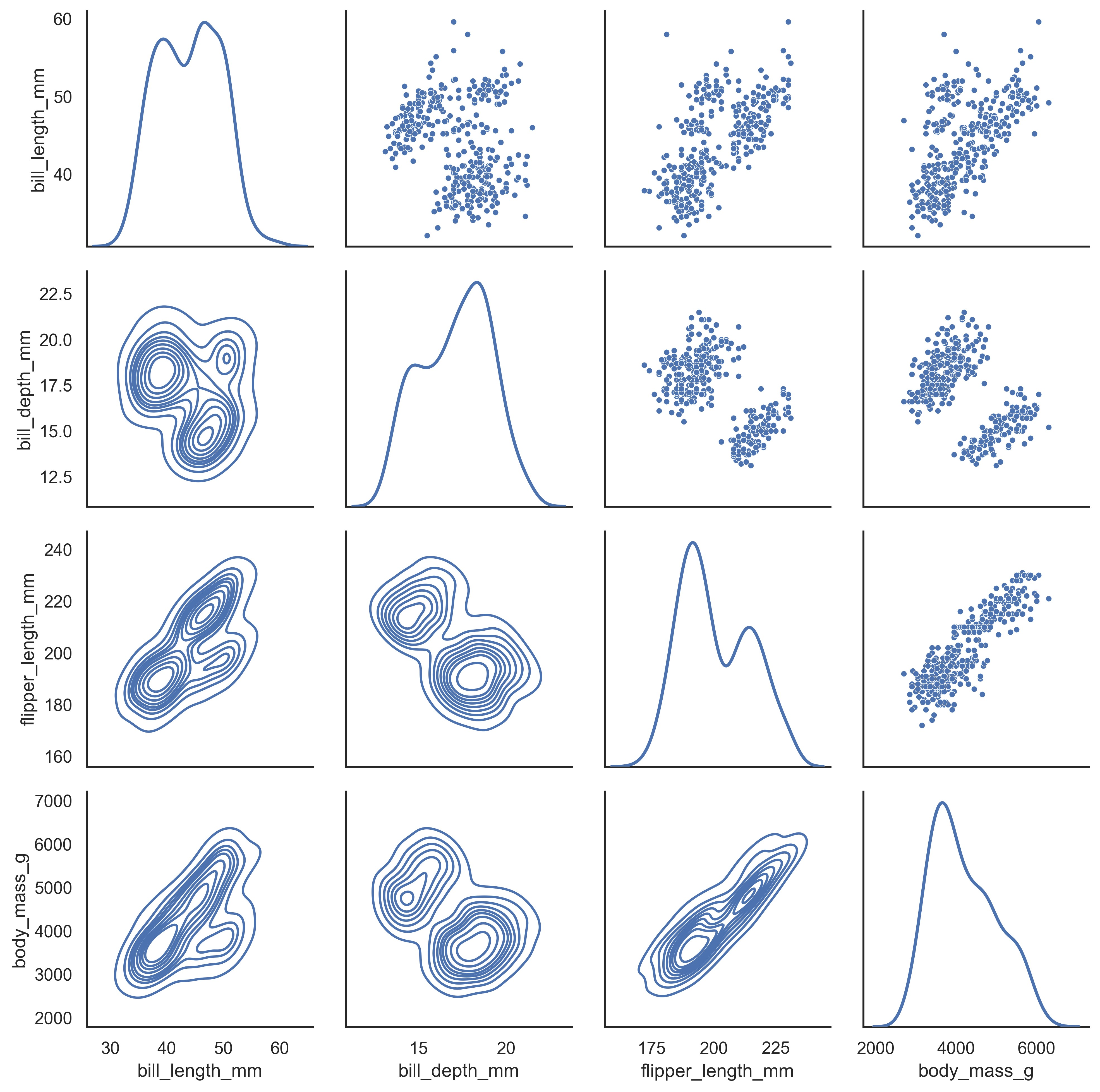
sns.set_theme(style="white")
df = sns.load_dataset("penguins")
g = sns.PairGrid(df, diag_sharey=False)
g.map_upper(sns.scatterplot, s=15)
g.map_lower(sns.kdeplot)
g.map_diag(sns.kdeplot, lw=2)
plt.show()
示例 28
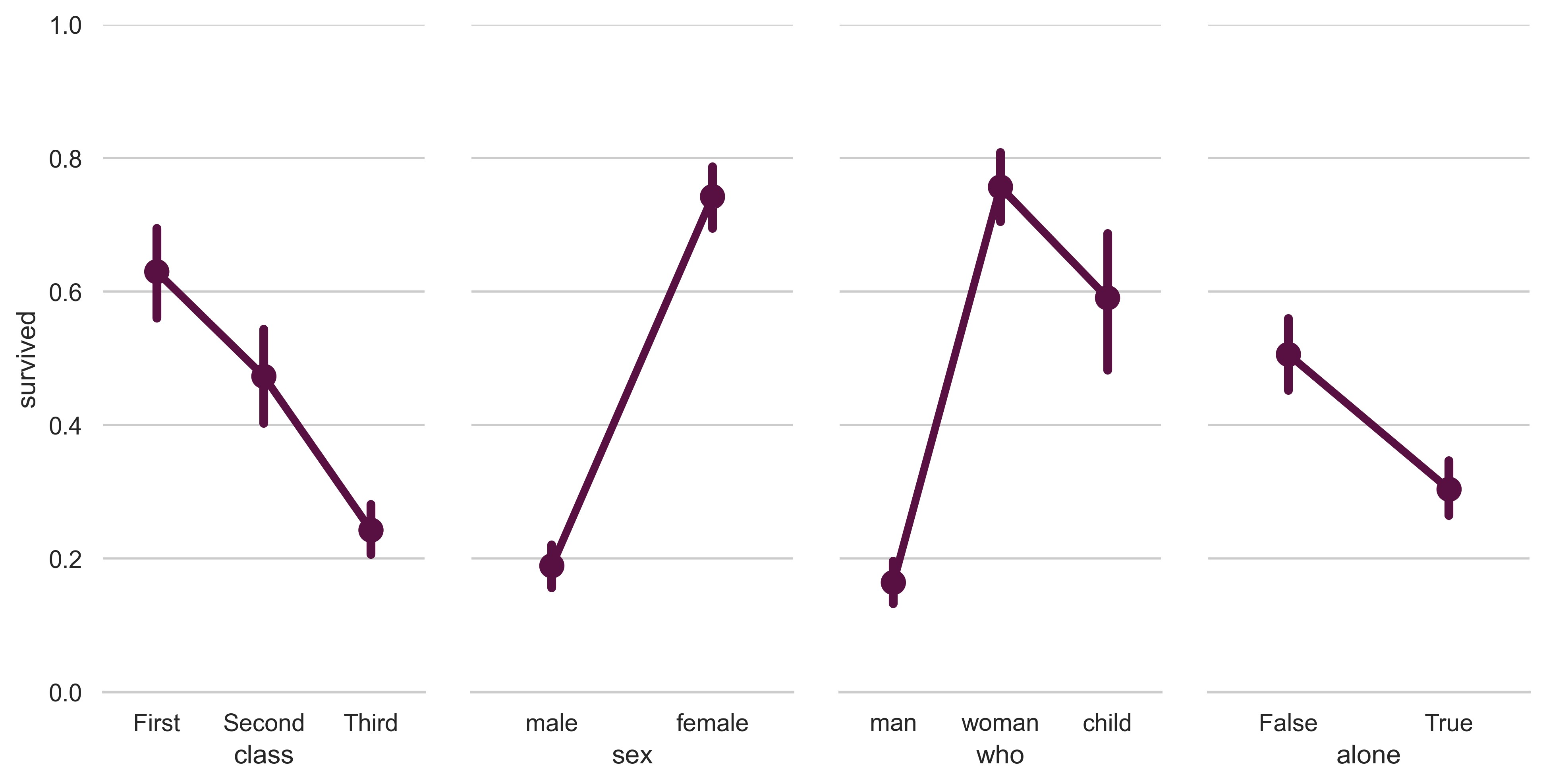
sns.set_theme(style="whitegrid")
# Load the example Titanic dataset
titanic = sns.load_dataset("titanic")
# Set up a grid to plot survival probability against several variables
g = sns.PairGrid(
titanic,
y_vars="survived",
x_vars=["class", "sex", "who", "alone"],
height=5,
aspect=0.5,
)
# Draw a seaborn pointplot onto each Axes
g.map(sns.pointplot, scale=1.3, errwidth=4, color="xkcd:plum")
g.set(ylim=(0, 1))
sns.despine(fig=g.fig, left=True)
plt.show()
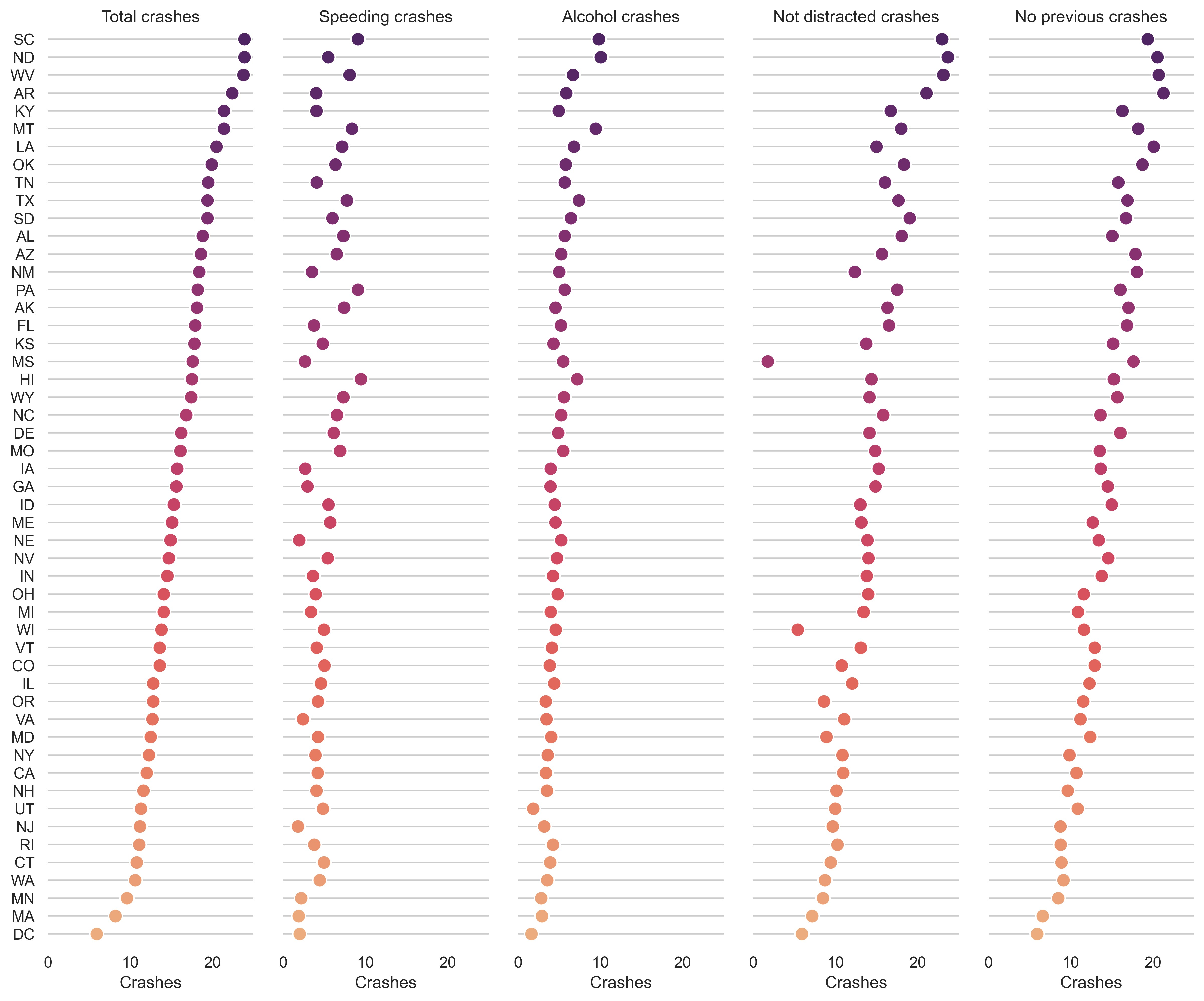
示例 29
sns.set_theme(style="whitegrid")
# Load the dataset
crashes = sns.load_dataset("car_crashes")
# Make the PairGrid
g = sns.PairGrid(
crashes.sort_values("total", ascending=False),
x_vars=crashes.columns[:-3],
y_vars=["abbrev"],
height=10,
aspect=0.25,
)
# Draw a dot plot using the stripplot function
g.map(
sns.stripplot,
size=10,
orient="h",
jitter=False,
palette="flare_r",
linewidth=1,
edgecolor="w",
)
# Use the same x axis limits on all columns and add better labels
g.set(xlim=(0, 25), xlabel="Crashes", ylabel="")
# Use semantically meaningful titles for the columns
titles = [
"Total crashes",
"Speeding crashes",
"Alcohol crashes",
"Not distracted crashes",
"No previous crashes",
]
for ax, title in zip(g.axes.flat, titles):
# Set a different title for each axes
ax.set(title=title)
# Make the grid horizontal instead of vertical
ax.xaxis.grid(False)
ax.yaxis.grid(True)
sns.despine(left=True, bottom=True)
plt.show()
示例 30
sns.set_theme(style="white", context="talk")
rs = np.random.RandomState(8)
# Set up the matplotlib figure
f, (ax1, ax2, ax3) = plt.subplots(3, 1, figsize=(7, 5), sharex=True)
# Generate some sequential data
x = np.array(list("ABCDEFGHIJ"))
y1 = np.arange(1, 11)
sns.barplot(x=x, y=y1, palette="rocket", ax=ax1)
ax1.axhline(0, color="k", clip_on=False)
ax1.set_ylabel("Sequential")
# Center the data to make it diverging
y2 = y1 - 5.5
sns.barplot(x=x, y=y2, palette="vlag", ax=ax2)
ax2.axhline(0, color="k", clip_on=False)
ax2.set_ylabel("Diverging")
# Randomly reorder the data to make it qualitative
y3 = rs.choice(y1, len(y1), replace=False)
sns.barplot(x=x, y=y3, palette="deep", ax=ax3)
ax3.axhline(0, color="k", clip_on=False)
ax3.set_ylabel("Qualitative")
# Finalize the plot
sns.despine(bottom=True)
plt.setp(f.axes, yticks=[])
plt.tight_layout(h_pad=2)
plt.show()
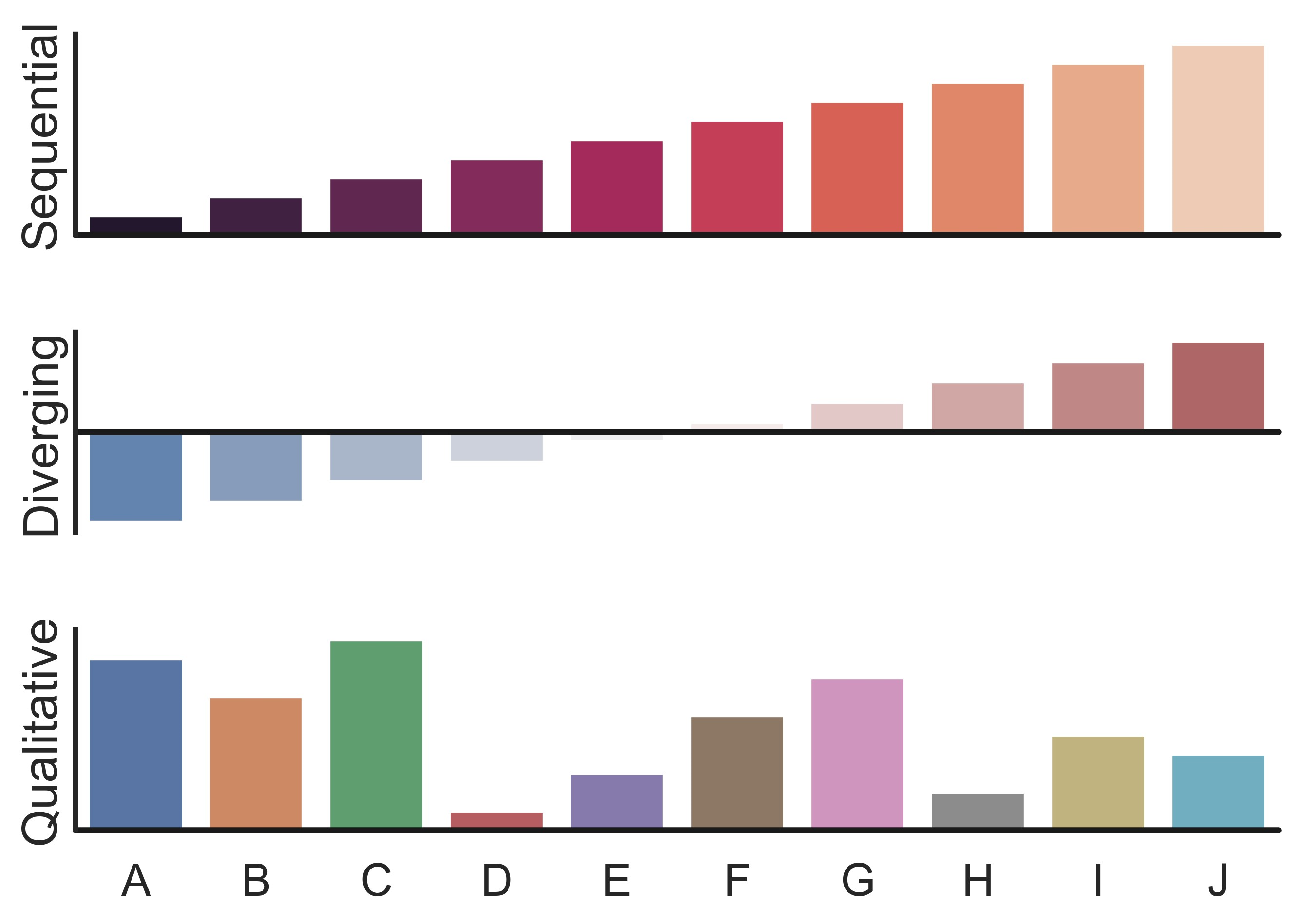
示例 31
sns.set_theme(style="white")
rs = np.random.RandomState(50)
# Set up the matplotlib figure
f, axes = plt.subplots(3, 3, figsize=(9, 9), sharex=True, sharey=True)
# Rotate the starting point around the cubehelix hue circle
for ax, s in zip(axes.flat, np.linspace(0, 3, 10)):
# Create a cubehelix colormap to use with kdeplot
cmap = sns.cubehelix_palette(start=s, light=1, as_cmap=True)
# Generate and plot a random bivariate dataset
x, y = rs.normal(size=(2, 50))
sns.kdeplot(
x=x,
y=y,
cmap=cmap,
fill=True,
clip=(-5, 5),
cut=10,
thresh=0,
levels=15,
ax=ax,
)
ax.set_axis_off()
ax.set(xlim=(-3.5, 3.5), ylim=(-3.5, 3.5))
f.subplots_adjust(0, 0, 1, 1, 0.08, 0.08)
plt.show()
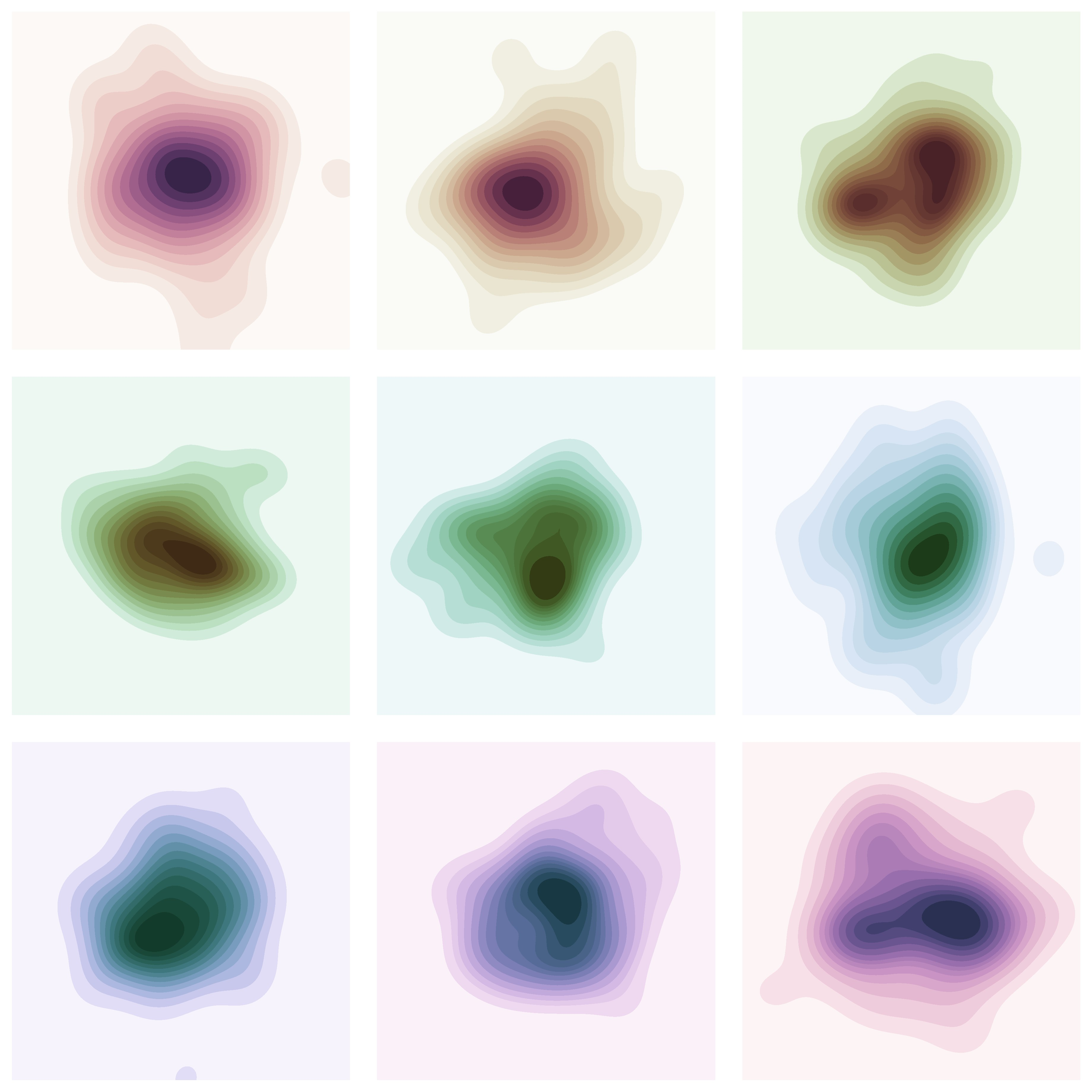
示例 32
sns.set_theme(style="whitegrid")
# Initialize the matplotlib figure
f, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6, 15))
# Load the example car crash dataset
crashes = sns.load_dataset("car_crashes").sort_values("total", ascending=False)
# Plot the total crashes
sns.set_color_codes("pastel")
sns.barplot(x="total", y="abbrev", data=crashes, label="Total", color="b")
# Plot the crashes where alcohol was involved
sns.set_color_codes("muted")
sns.barplot(x="alcohol", y="abbrev", data=crashes, label="Alcohol-involved", color="b")
# Add a legend and informative axis label
ax.legend(ncol=2, loc="lower right", frameon=True)
ax.set(xlim=(0, 24), ylabel="", xlabel="Automobile collisions per billion miles")
sns.despine(left=True, bottom=True)
plt.show()
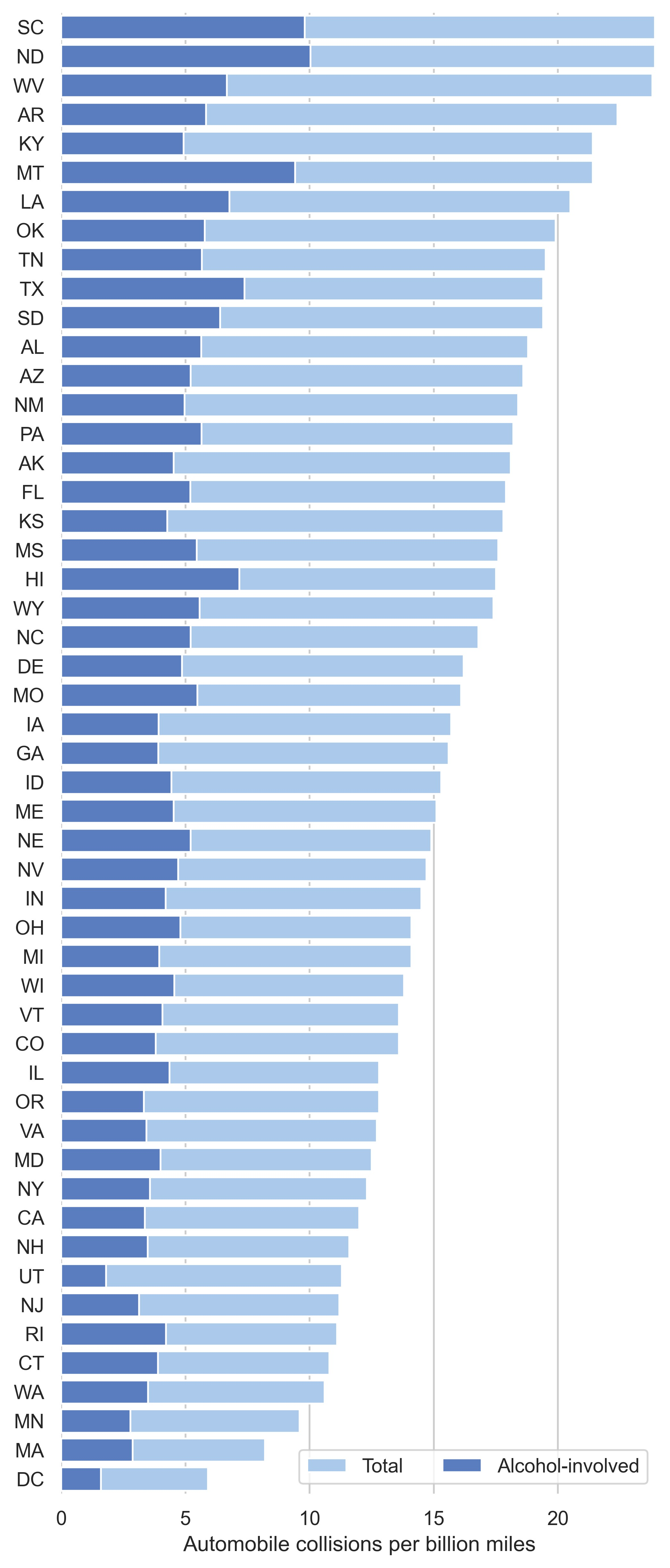
示例 33
sns.set_theme(style="whitegrid")
# Load the example exercise dataset
exercise = sns.load_dataset("exercise")
# Draw a pointplot to show pulse as a function of three categorical factors
g = sns.catplot(
data=exercise,
x="time",
y="pulse",
hue="kind",
col="diet",
capsize=0.2,
palette="YlGnBu_d",
errorbar="se",
kind="point",
height=6,
aspect=0.75,
)
g.despine(left=True)
plt.show()
示例 34
sns.set_theme()
# Generate an example radial datast
r = np.linspace(0, 10, num=100)
df = pd.DataFrame({"r": r, "slow": r, "medium": 2 * r, "fast": 4 * r})
# Convert the dataframe to long-form or "tidy" format
df = pd.melt(df, id_vars=["r"], var_name="speed", value_name="theta")
# Set up a grid of axes with a polar projection
g = sns.FacetGrid(
df,
col="speed",
hue="speed",
subplot_kws=dict(projection="polar"),
height=4.5,
sharex=False,
sharey=False,
despine=False,
)
# Draw a scatterplot onto each axes in the grid
g.map(sns.scatterplot, "theta", "r")
plt.show()
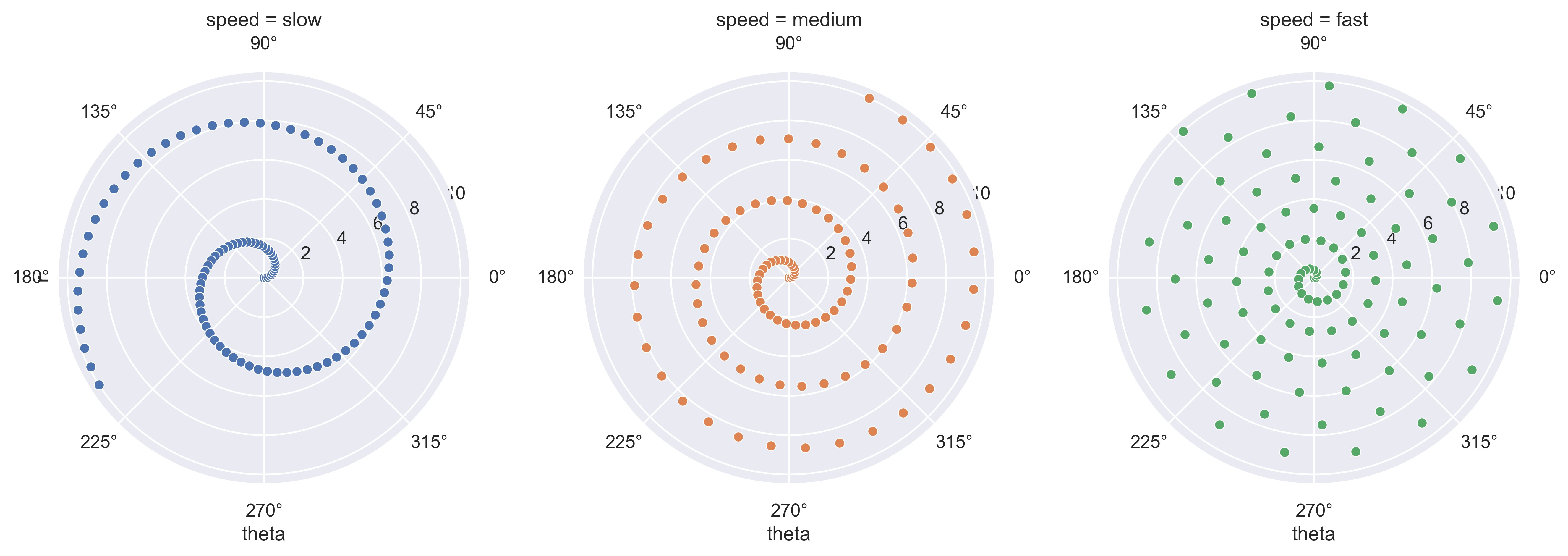
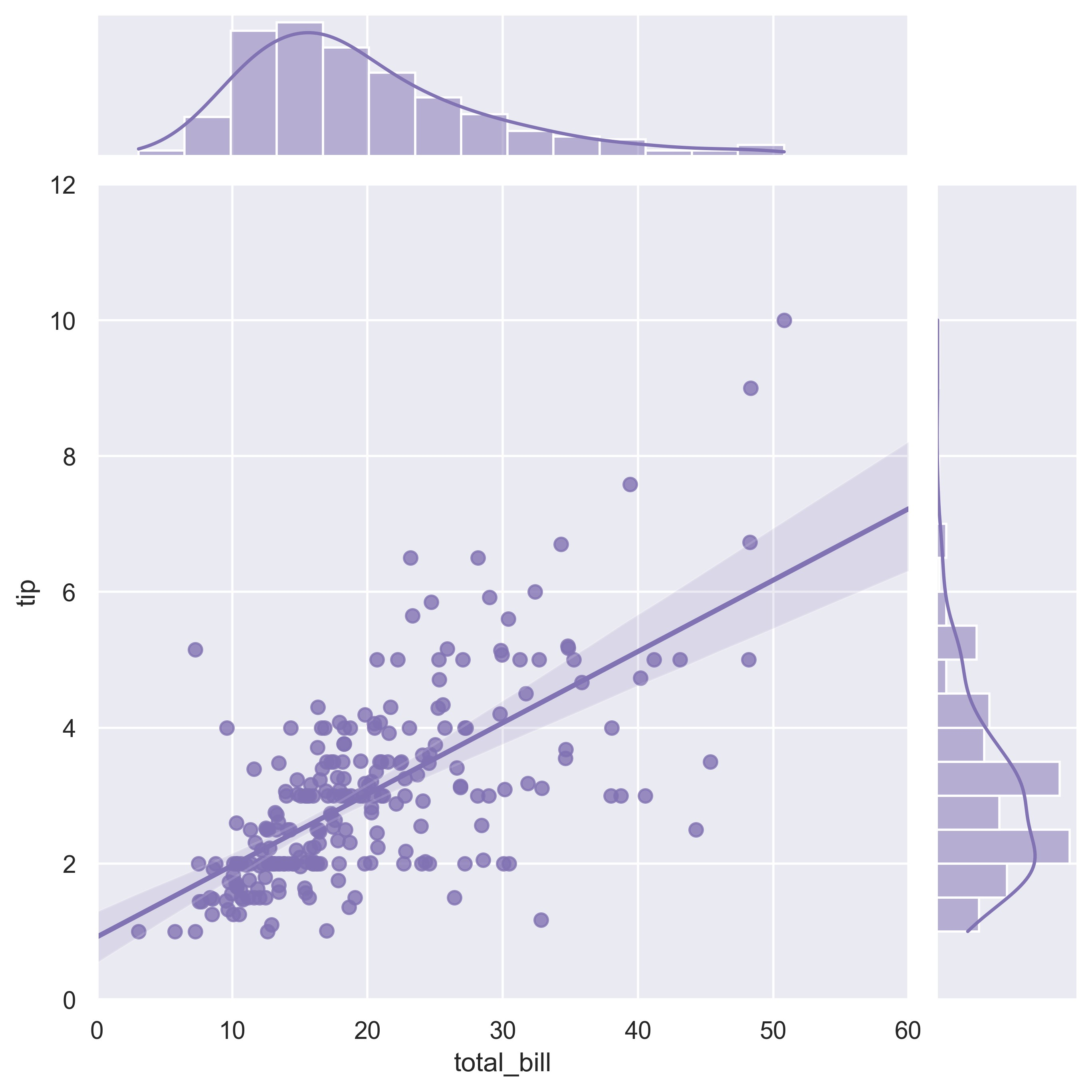
示例 35
sns.set_theme(style="darkgrid")
tips = sns.load_dataset("tips")
g = sns.jointplot(
x="total_bill",
y="tip",
data=tips,
kind="reg",
truncate=False,
xlim=(0, 60),
ylim=(0, 12),
color="m",
height=7,
)
plt.show()
示例 36
sns.set_theme(style="whitegrid")
# Make an example dataset with y ~ x
rs = np.random.RandomState(7)
x = rs.normal(2, 1, 75)
y = 2 + 1.5 * x + rs.normal(0, 2, 75)
# Plot the residuals after fitting a linear model
sns.residplot(x=x, y=y, lowess=True, color="g")
plt.show()
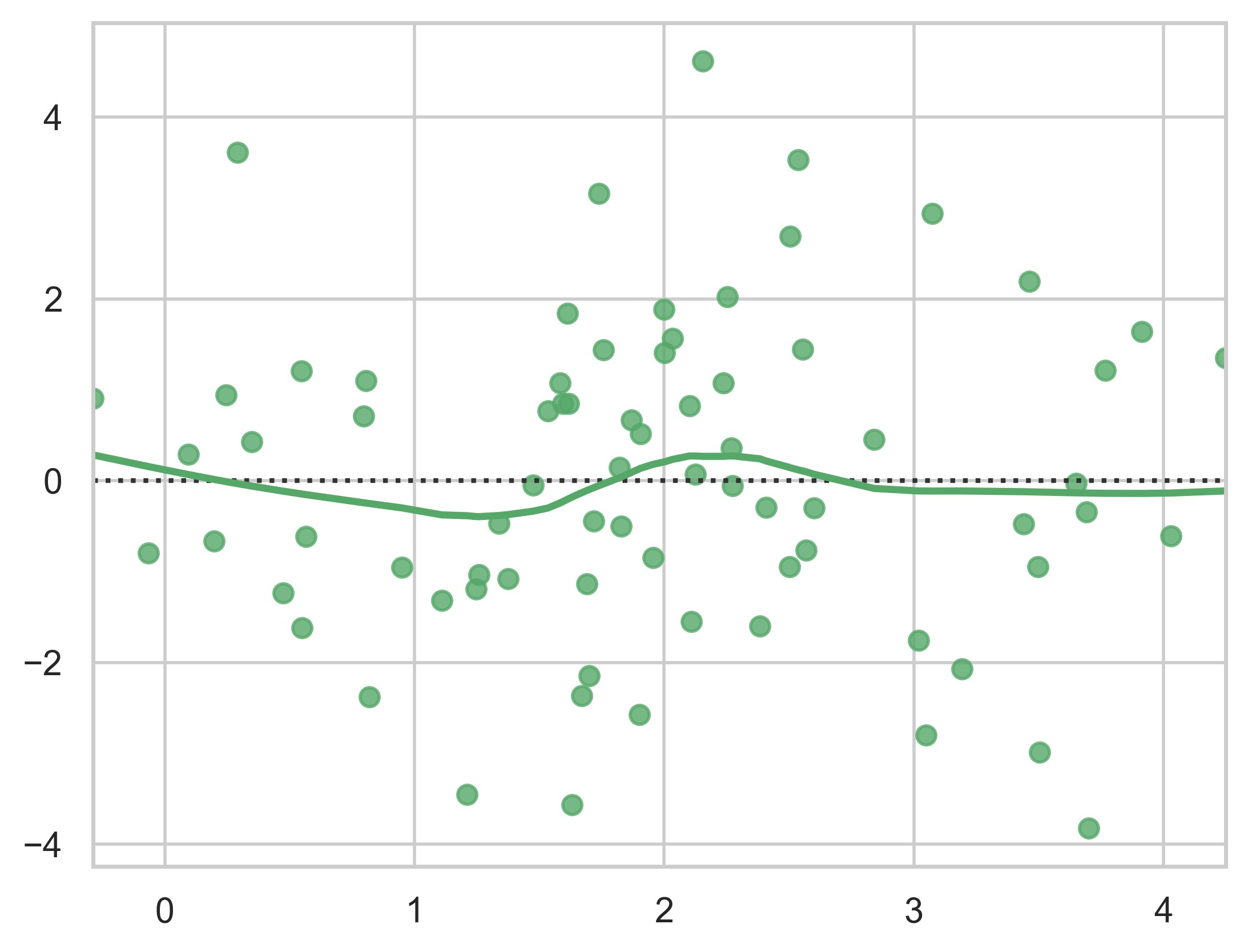
示例 37
sns.set_theme(style="white")
# Load the example mpg dataset
mpg = sns.load_dataset("mpg")
# Plot miles per gallon against horsepower with other semantics
sns.relplot(
x="horsepower",
y="mpg",
hue="origin",
size="weight",
sizes=(40, 400),
alpha=0.5,
palette="muted",
height=6,
data=mpg,
)
plt.show()
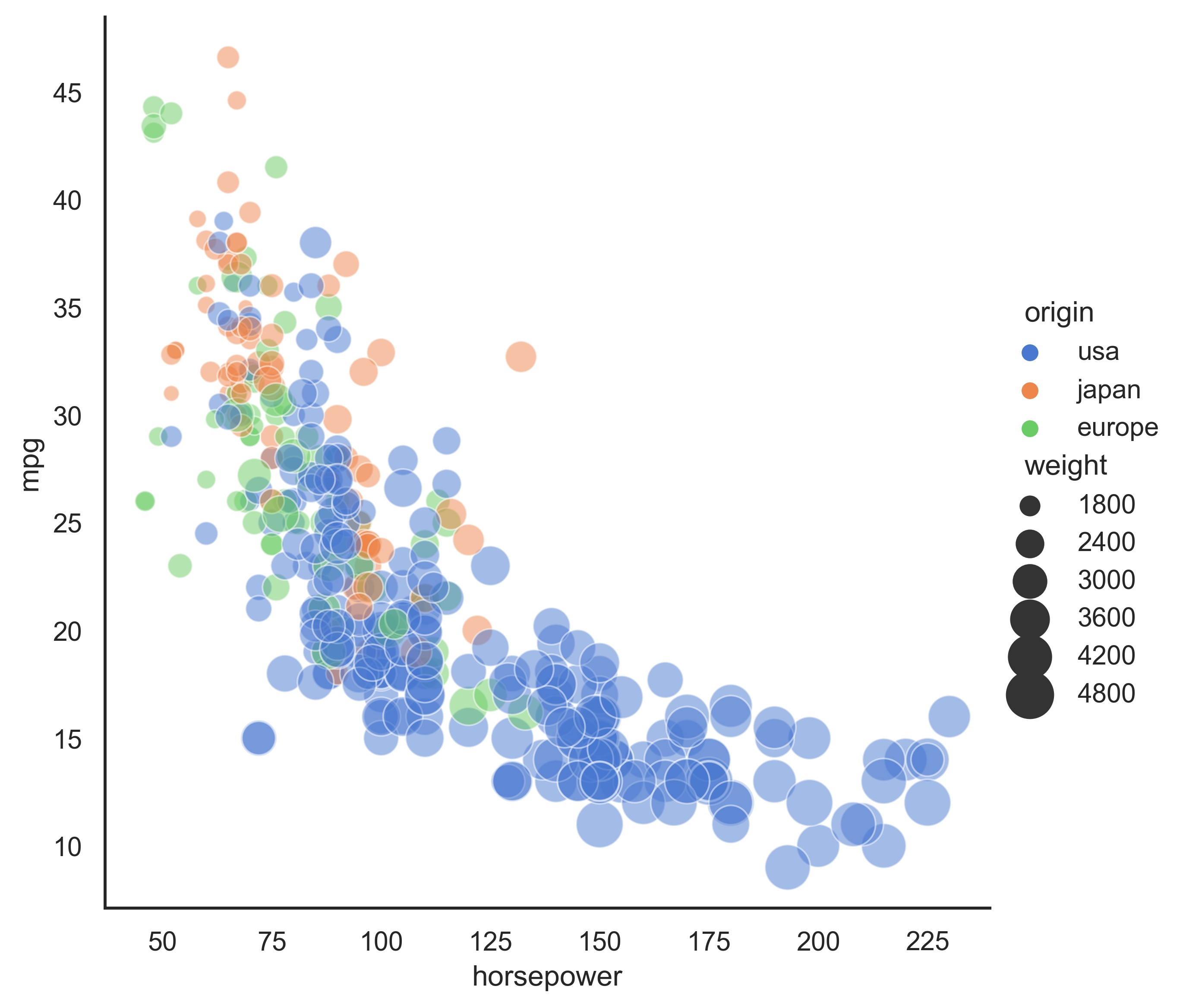
示例 38
sns.set_theme(style="whitegrid", palette="muted")
# Load the penguins dataset
df = sns.load_dataset("penguins")
# Draw a categorical scatterplot to show each observation
ax = sns.swarmplot(data=df, x="body_mass_g", y="sex", hue="species")
ax.set(ylabel="")
plt.show()
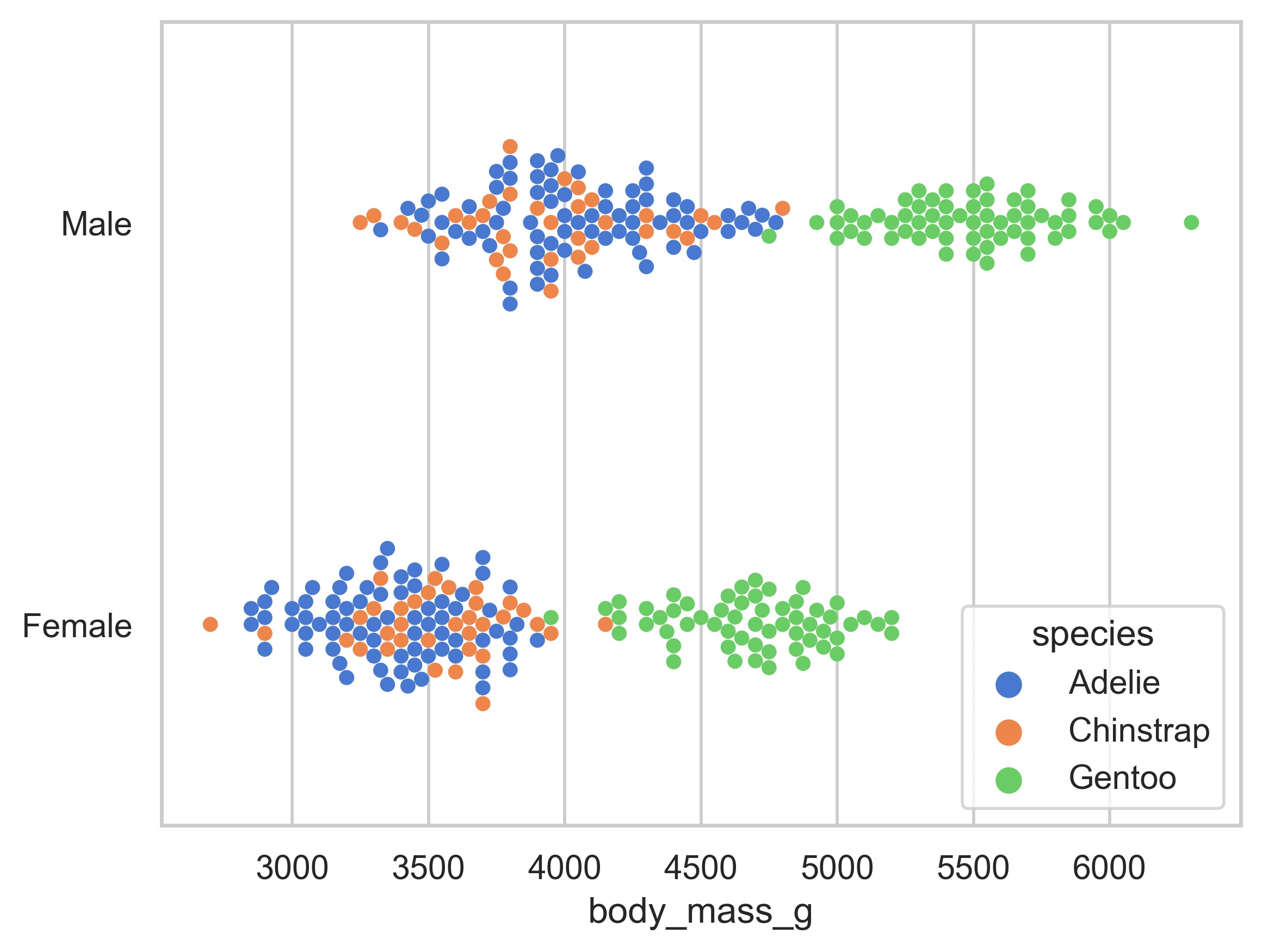
示例 39
sns.set_theme(style="ticks")
df = sns.load_dataset("penguins")
sns.pairplot(df, hue="species")
plt.show()
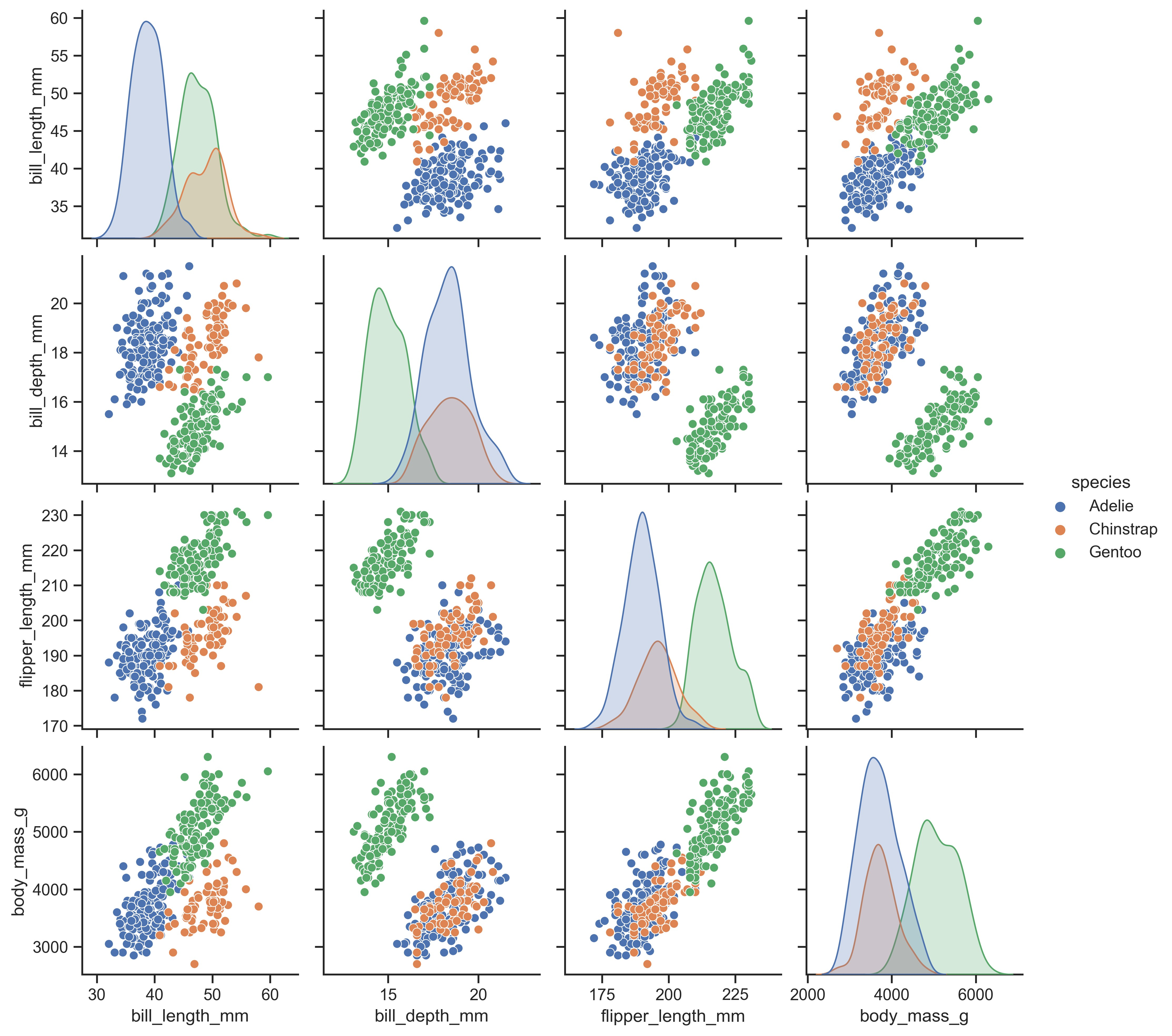
示例 40
sns.set_theme(style="whitegrid")
# Load the example planets dataset
planets = sns.load_dataset("planets")
cmap = sns.cubehelix_palette(rot=-0.2, as_cmap=True)
g = sns.relplot(
data=planets,
x="distance",
y="orbital_period",
hue="year",
size="mass",
palette=cmap,
sizes=(10, 200),
)
g.set(xscale="log", yscale="log")
g.ax.xaxis.grid(True, "minor", linewidth=0.25)
g.ax.yaxis.grid(True, "minor", linewidth=0.25)
g.despine(left=True, bottom=True)
plt.show()
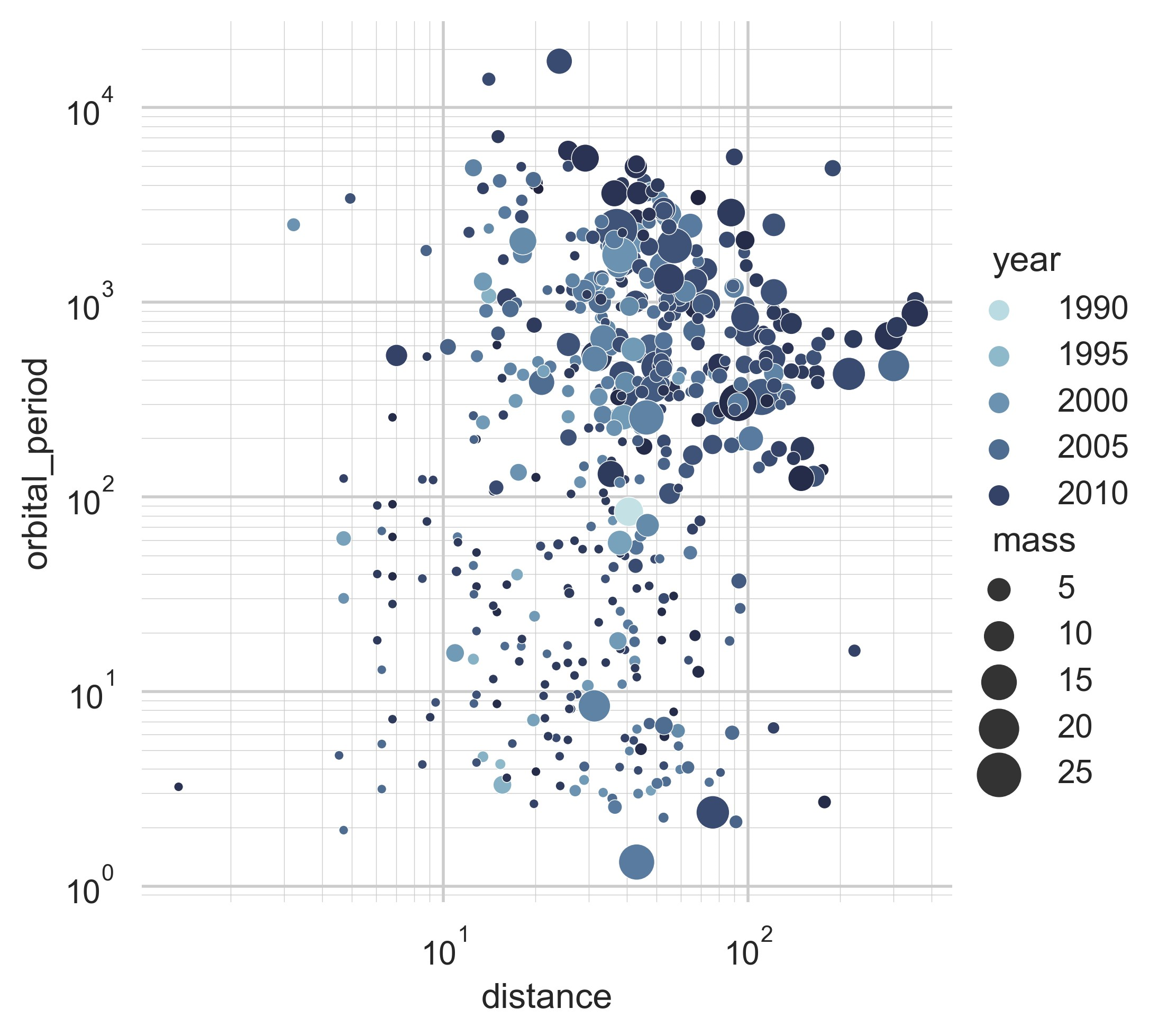
示例 41
sns.set_theme()
# Create a random dataset across several variables
rs = np.random.default_rng(0)
n, p = 40, 8
d = rs.normal(0, 2, (n, p))
d += np.log(np.arange(1, p + 1)) * -5 + 10
# Show each distribution with both violins and points
sns.violinplot(data=d, palette="light:g", inner="points", orient="h")
plt.show()
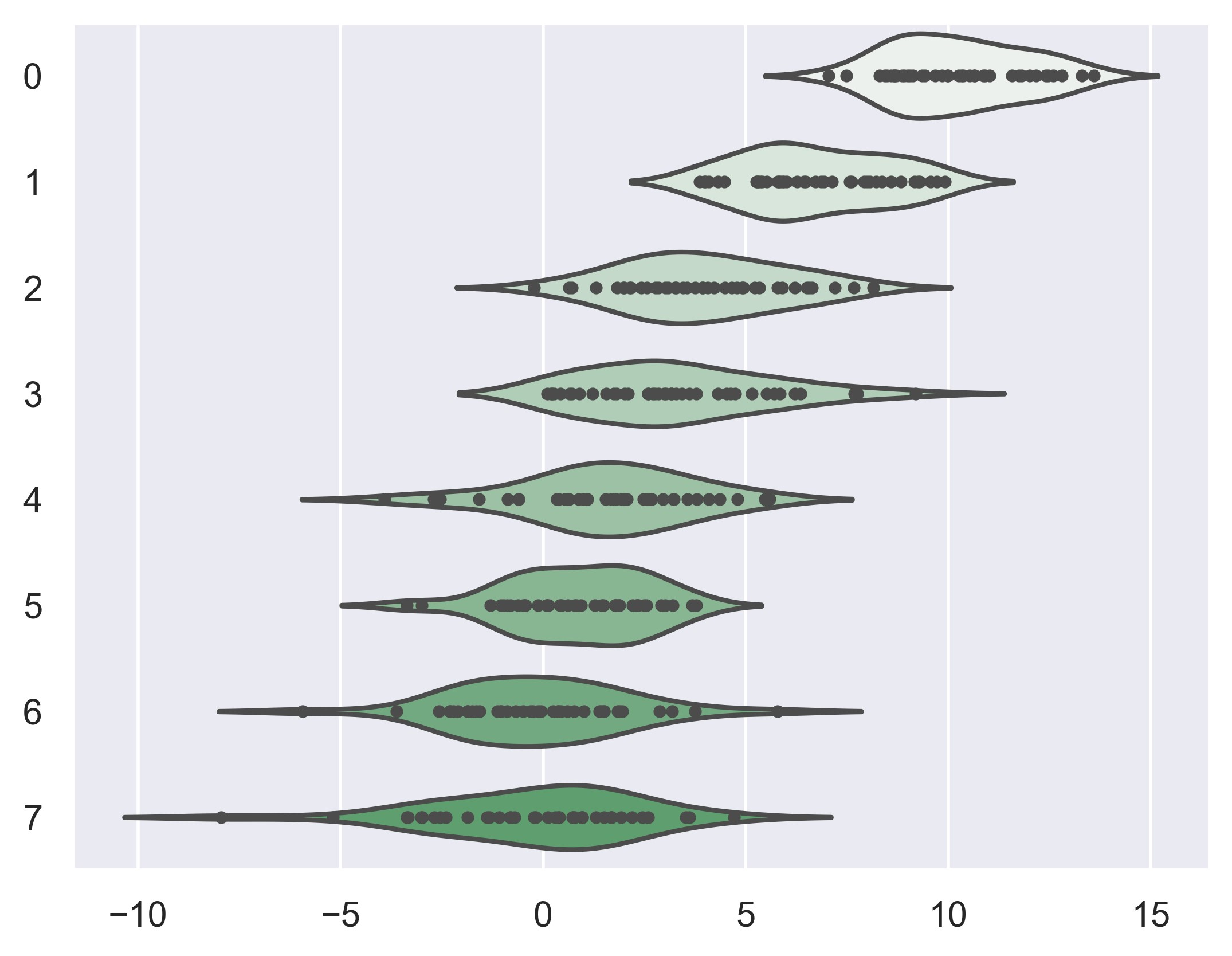
示例 42
sns.set_theme(style="white")
df = sns.load_dataset("penguins")
g = sns.JointGrid(data=df, x="body_mass_g", y="bill_depth_mm", space=0)
g.plot_joint(
sns.kdeplot,
fill=True,
clip=((2200, 6800), (10, 25)),
thresh=0,
levels=100,
cmap="rocket",
)
g.plot_marginals(sns.histplot, color="#03051A", alpha=1, bins=25)
plt.show()
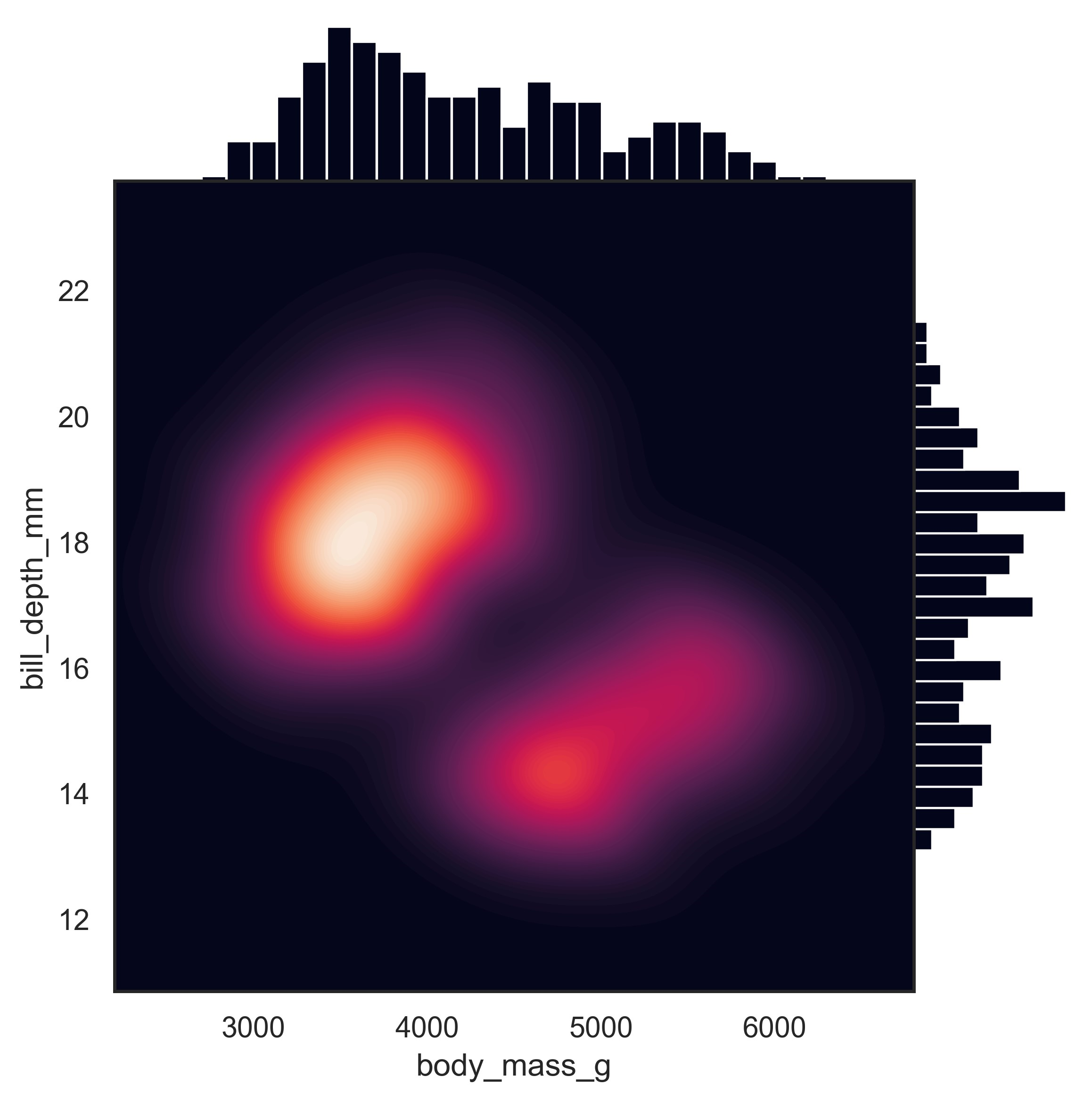
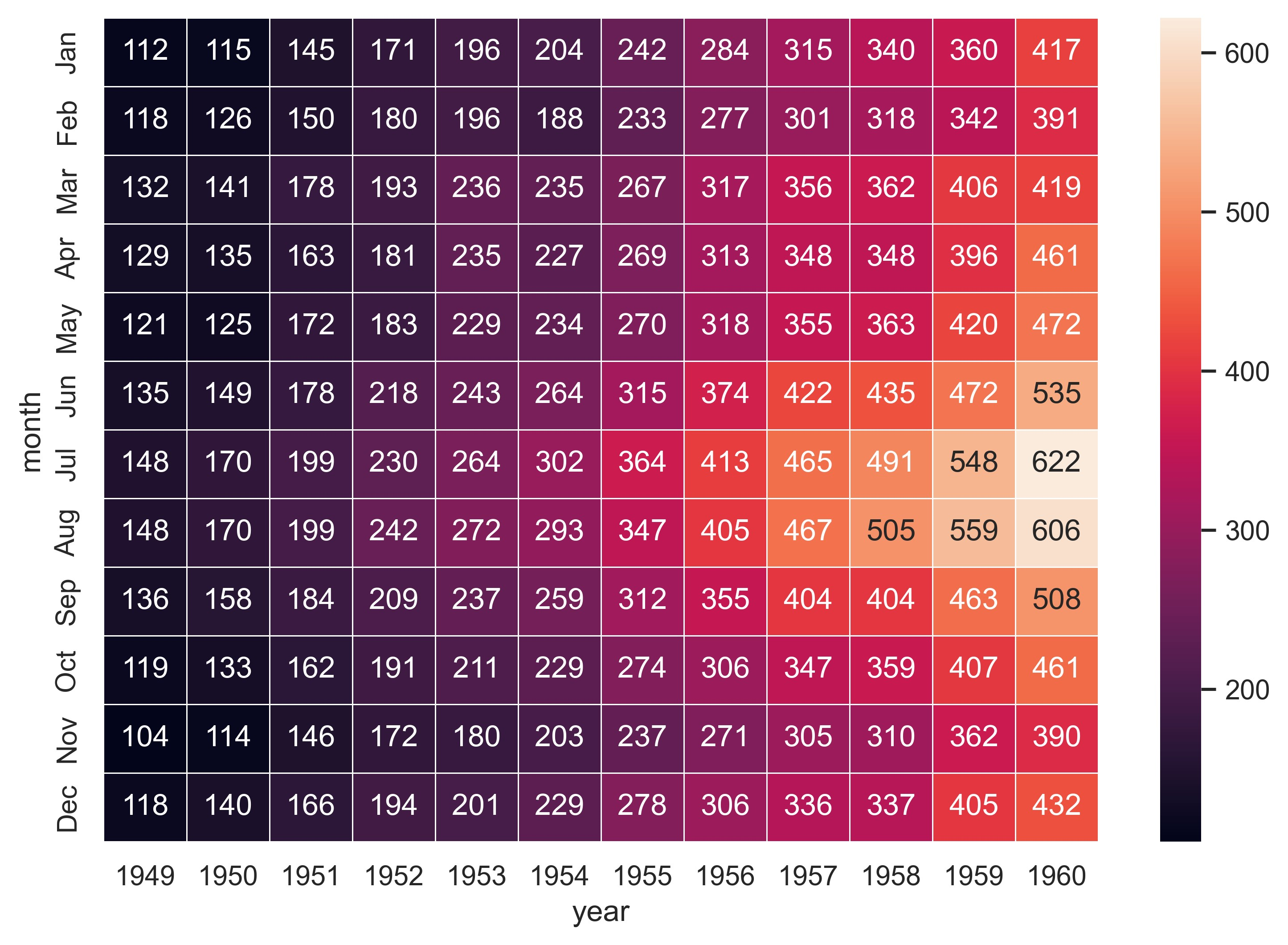
示例 43
sns.set_theme()
# Load the example flights dataset and convert to long-form
flights_long = sns.load_dataset("flights")
flights = flights_long.pivot("month", "year", "passengers")
# Draw a heatmap with the numeric values in each cell
f, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(9, 6))
sns.heatmap(flights, annot=True, fmt="d", linewidths=0.5, ax=ax)
plt.show()
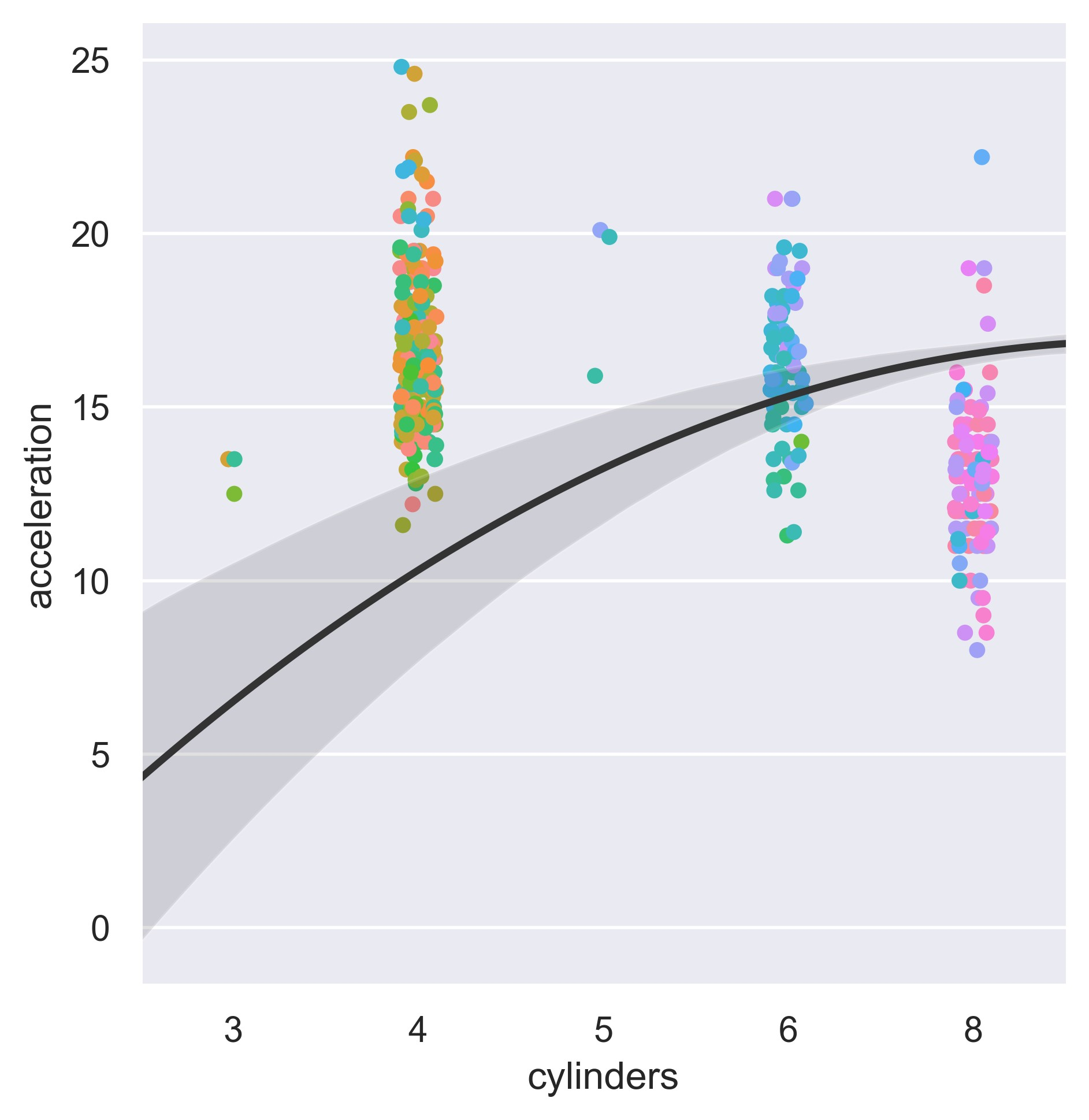
示例 44
sns.set_theme()
mpg = sns.load_dataset("mpg")
sns.catplot(
data=mpg, x="cylinders", y="acceleration", hue="weight", zorder=1, legend=False
)
sns.regplot(
data=mpg,
x="cylinders",
y="acceleration",
scatter=False,
truncate=False,
order=2,
color=".2",
)
plt.show()
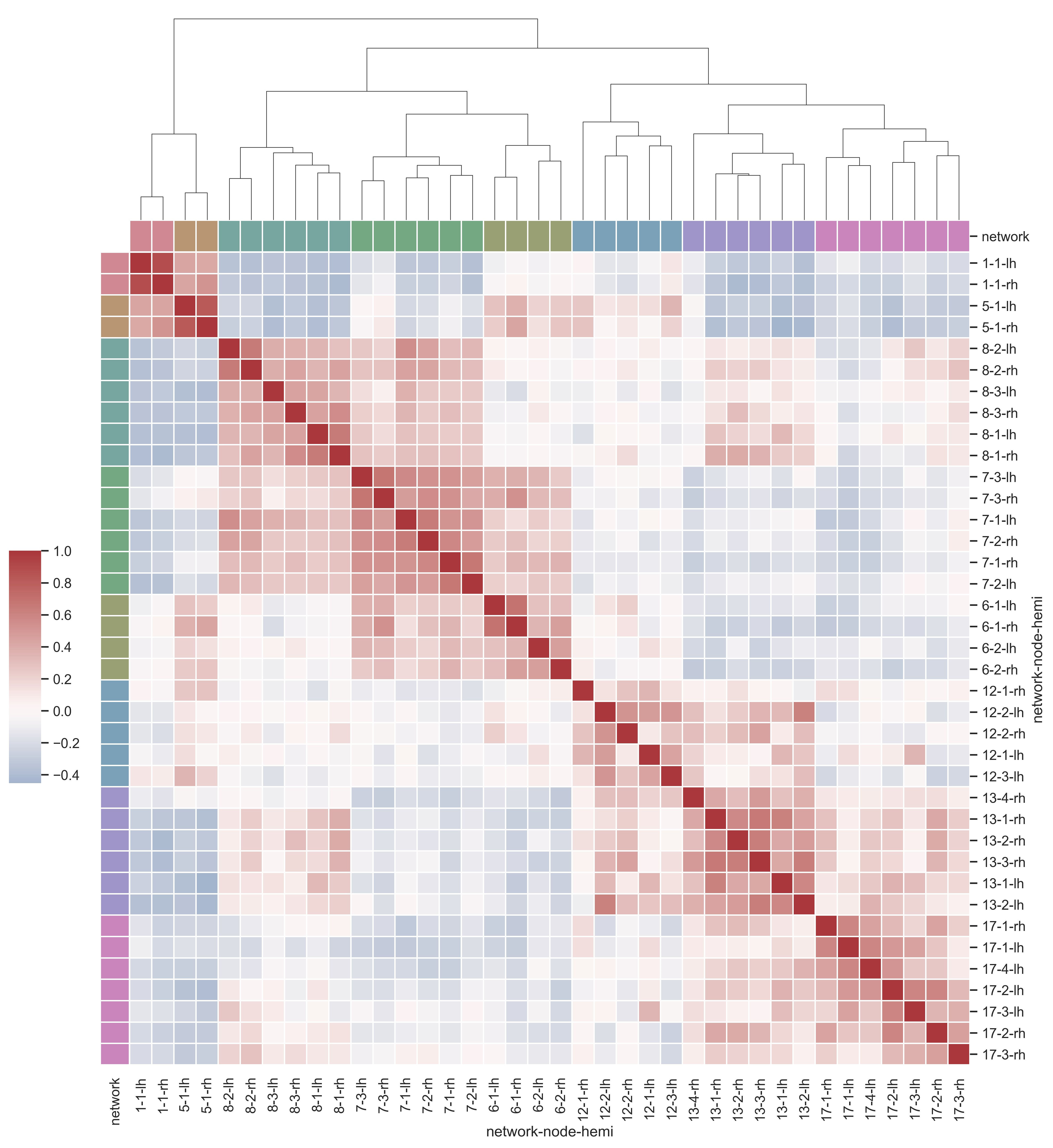
示例 45
sns.set_theme()
# Load the brain networks example dataset
df = sns.load_dataset("brain_networks", header=[0, 1, 2], index_col=0)
# Select a subset of the networks
used_networks = [1, 5, 6, 7, 8, 12, 13, 17]
used_columns = df.columns.get_level_values("network").astype(int).isin(used_networks)
df = df.loc[:, used_columns]
# Create a categorical palette to identify the networks
network_pal = sns.husl_palette(8, s=0.45)
network_lut = dict(zip(map(str, used_networks), network_pal))
# Convert the palette to vectors that will be drawn on the side of the matrix
networks = df.columns.get_level_values("network")
network_colors = pd.Series(networks, index=df.columns).map(network_lut)
# Draw the full plot
g = sns.clustermap(
df.corr(),
center=0,
cmap="vlag",
row_colors=network_colors,
col_colors=network_colors,
dendrogram_ratio=(0.1, 0.2),
cbar_pos=(0.02, 0.32, 0.03, 0.2),
linewidths=0.75,
figsize=(12, 13),
)
g.ax_row_dendrogram.remove()
plt.show()
示例 46
sns.set_theme(style="dark")
diamonds = sns.load_dataset("diamonds")
sns.displot(
data=diamonds,
x="price",
y="color",
col="clarity",
log_scale=(True, False),
col_wrap=4,
height=4,
aspect=0.7,
)
plt.show()
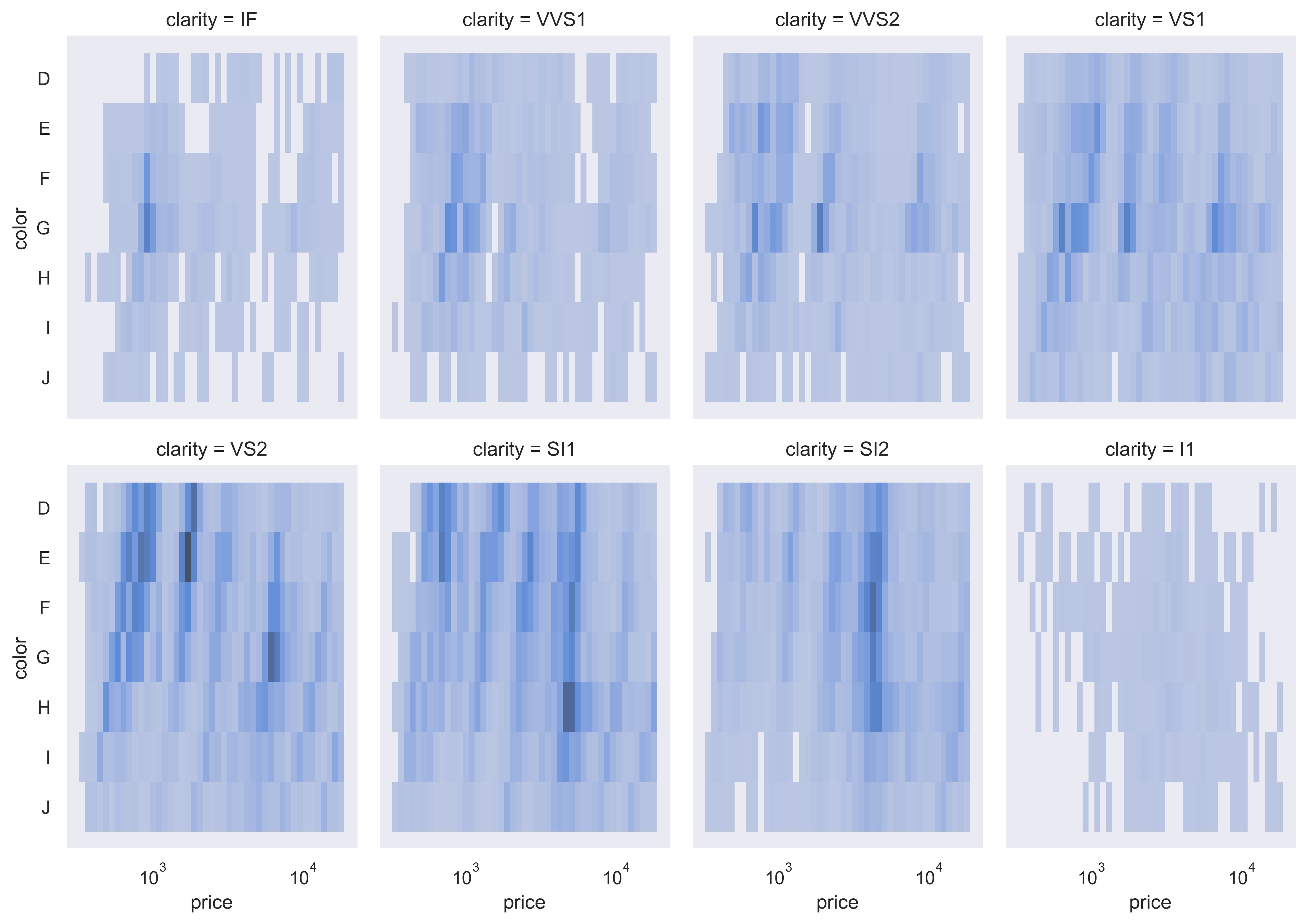
示例 47
sns.set_theme(style="dark")
flights = sns.load_dataset("flights")
# Plot each year's time series in its own facet
g = sns.relplot(
data=flights,
x="month",
y="passengers",
col="year",
hue="year",
kind="line",
palette="crest",
linewidth=4,
zorder=5,
col_wrap=3,
height=2,
aspect=1.5,
legend=False,
)
# Iterate over each subplot to customize further
for year, ax in g.axes_dict.items():
# Add the title as an annotation within the plot
ax.text(0.8, 0.85, year, transform=ax.transAxes, fontweight="bold")
# Plot every year's time series in the background
sns.lineplot(
data=flights,
x="month",
y="passengers",
units="year",
estimator=None,
color=".7",
linewidth=1,
ax=ax,
)
# Reduce the frequency of the x axis ticks
ax.set_xticks(ax.get_xticks()[::2])
# Tweak the supporting aspects of the plot
g.set_titles("")
g.set_axis_labels("", "Passengers")
g.tight_layout()
plt.show()
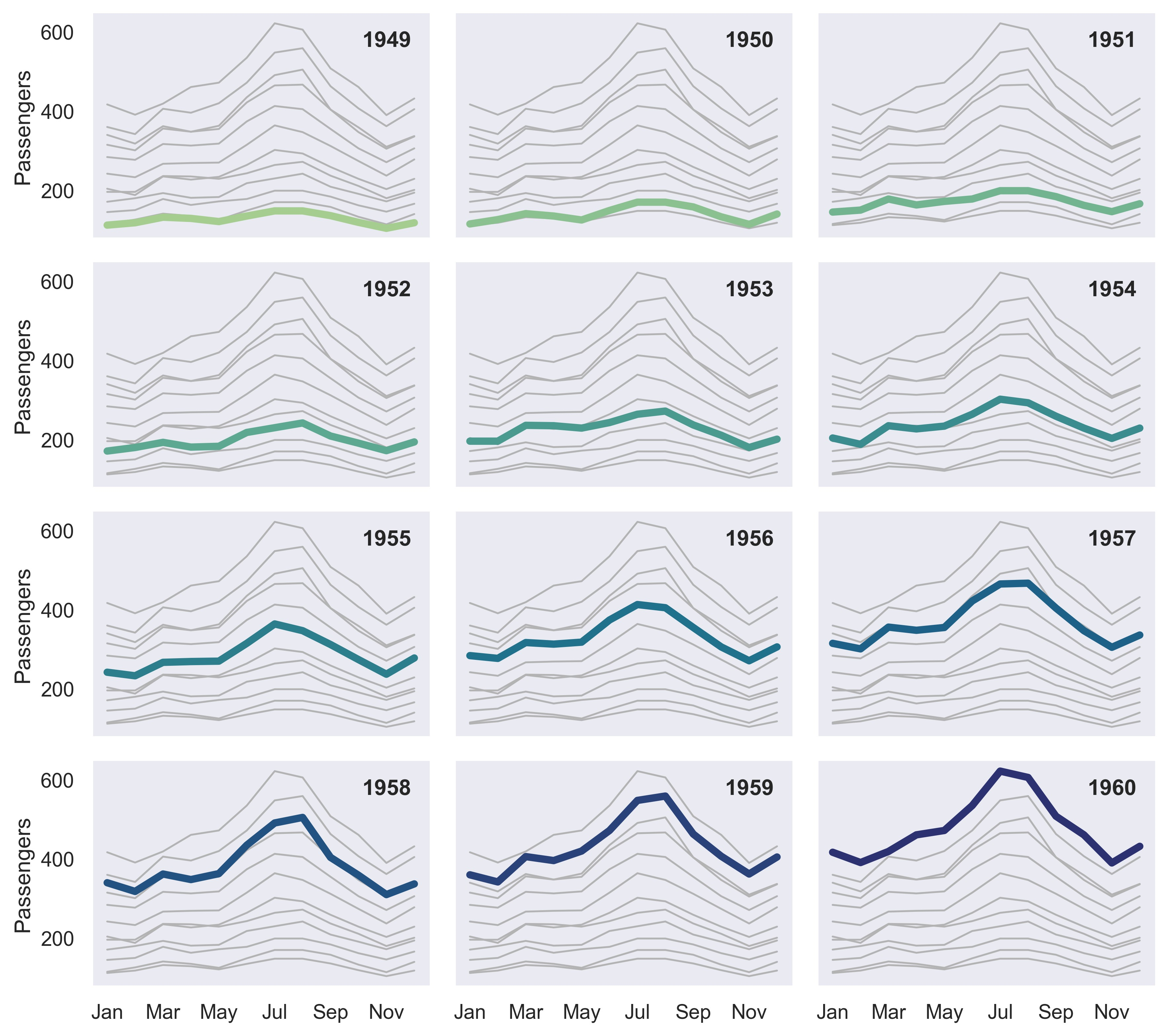
示例 48
sns.set_theme(style="whitegrid")
rs = np.random.RandomState(365)
values = rs.randn(365, 4).cumsum(axis=0)
dates = pd.date_range("1 1 2016", periods=365, freq="D")
data = pd.DataFrame(values, dates, columns=["A", "B", "C", "D"])
data = data.rolling(7).mean()
sns.lineplot(data=data, palette="tab10", linewidth=2.5)
plt.show()
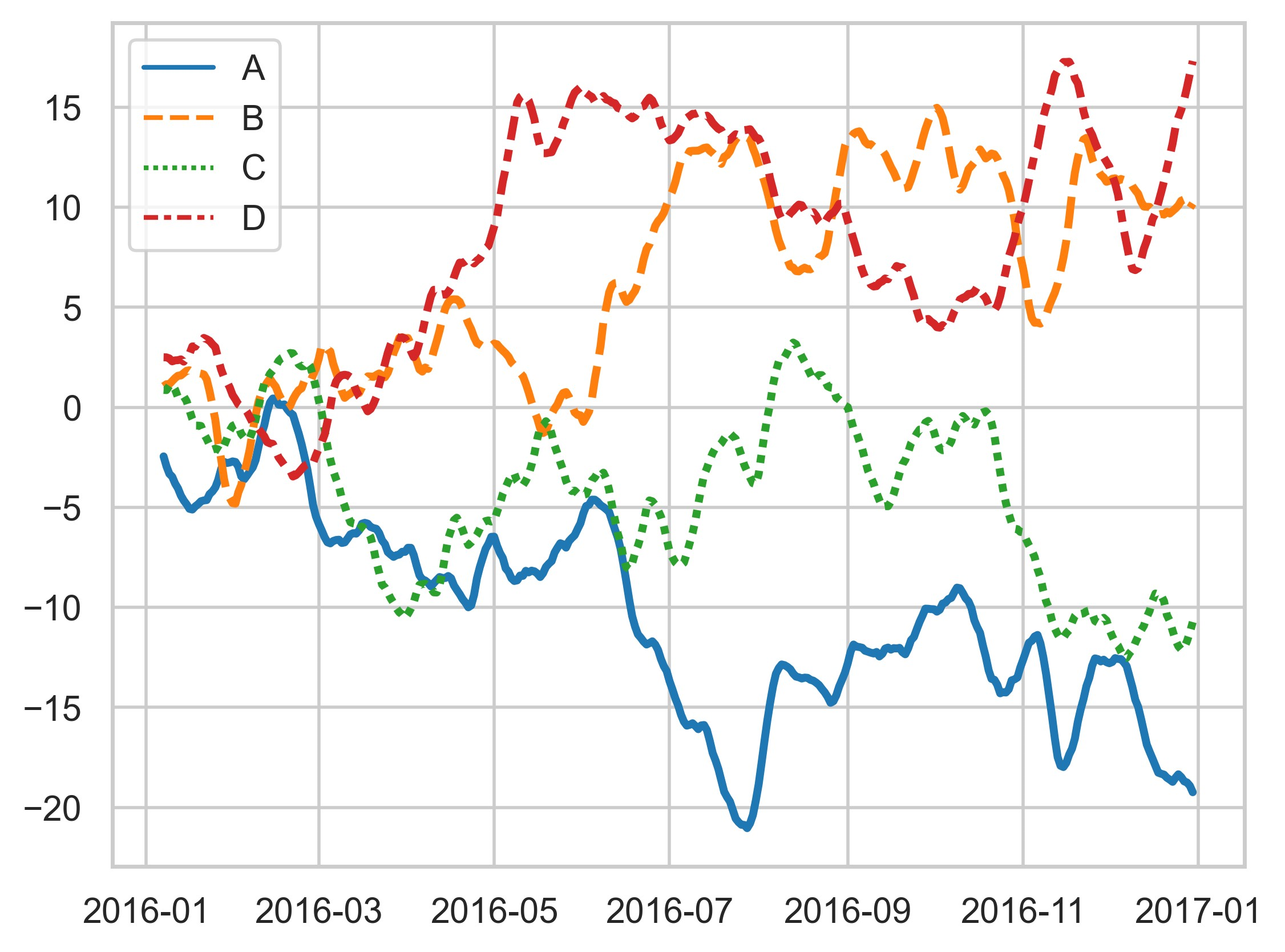
示例 49
sns.set_theme(style="whitegrid")
# Load the example dataset of brain network correlations
df = sns.load_dataset("brain_networks", header=[0, 1, 2], index_col=0)
# Pull out a specific subset of networks
used_networks = [1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 11, 12, 13, 16, 17]
used_columns = df.columns.get_level_values("network").astype(int).isin(used_networks)
df = df.loc[:, used_columns]
# Compute the correlation matrix and average over networks
corr_df = df.corr().groupby(level="network").mean()
corr_df.index = corr_df.index.astype(int)
corr_df = corr_df.sort_index().T
# Set up the matplotlib figure
f, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(11, 6))
# Draw a violinplot with a narrower bandwidth than the default
sns.violinplot(data=corr_df, palette="Set3", bw=0.2, cut=1, linewidth=1)
# Finalize the figure
ax.set(ylim=(-0.7, 1.05))
sns.despine(left=True, bottom=True)
plt.show()