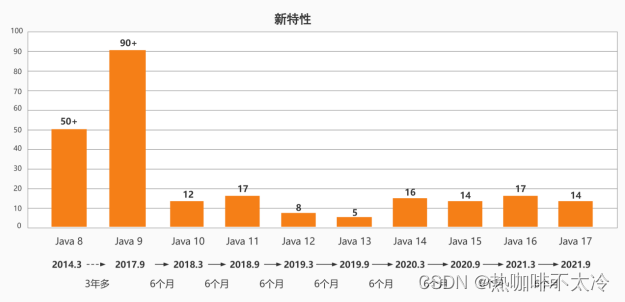
一、Java版本迭代概述
1.1发布特点(小步快跑,快速迭代)
| 发行版本 | 发行时间 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| Java 1.0 | 1996.01.23 | Sun公司发布了Java的第一个开发工具包 |
| Java 5.0 | 2004.09.30 | ①版本号从1.4直接更新至5.0;②平台更名为JavaSE、JavaEE、JavaME |
| Java 8.0 | 2014.03.18 | 此版本是继Java 5.0以来变化最大的版本。是长期支持版本(LTS) |
| Java 9.0 | 2017.09.22 | 此版本开始,每半年更新一次 |
| Java 10.0 | 2018.03.21 | |
| Java 11.0 | 2018.09.25 | JDK安装包取消独立JRE安装包,是长期支持版本(LTS) |
| Java 12.0 | 2019.03.19 | |
| … | … | |
| Java17.0 | 2021.09 | 发布Java 17.0,版本号也称为21.9,是长期支持版本(LTS) |
| … | … | |
| Java19.0 | 2022.09 | 发布Java19.0,版本号也称为22.9。 |
1.2各版本介绍
1.3如何学习新特性
- 对于新特性,我们应该从哪几个角度学习新特性呢?
- 语法层面:
- 比如JDK5中的自动拆箱、自动装箱、enum、泛型
- 比如JDK8中的lambda表达式、接口中的默认方法、静态方法
- 比如JDK10中局部变量的类型推断
- 比如JDK12中的switch
- 比如JDK13中的文本块
- API 层面:
- 比如JDK8中的Stream、Optional、新的日期时间、HashMap的底层结构
- 比如JDK9中String的底层结构
- 新的/过时的API
- 底层优化
- 比如 JDK8中永久代被元空间替代、新的JS执行引擎
- 比如新的垃圾回收器、GC 参数、JVM的优化
- 语法层面:
二、Java 8新特性:Lambda表达式
2.1关于Java 8新特性简介
- 速度更快
- 代码更少(增加了新的语法:Lambda表达式)
- 强大的Stream API
- 便于并行
- 最大化减少空指针异常:Optional
- Nashorn引擎
2.2 Lambda语法及其使用举例
- Lambda是一个匿名函数,我们可以把Lambda表达式理解为一段可以传递的代码。使用它可以写出更简洁、更灵活的代码。作为一种更紧凑的代码风格,使Java的语言表达能力得到了提升。语法如下:
->的左边:lambda形参列表,参数的类型都可以省略。如果形参只有一个,则一对()也可以省略。
->的右边:lambda体,对应者重写的方法的方法体。如果方法体中只有一行执行语句,则一对{}可以省略。如果有return关键字,则必须将return关键字也省略。
使用方式
- 前提:必须是函数式接口
public class LambdaTest1 {
//语法格式一:无参,无返回值
@Test
public void test1(){
Runnable r1 = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("我爱北京天安门");
}
};
r1.run();
System.out.println("***********************");
Runnable r2 = () -> {
System.out.println("我爱北京天安门");
};
r2.run();
}
//语法格式二:Lambda 需要一个参数,但是没有返回值。
@Test
public void test2(){
Consumer<String> con = new Consumer<String>() {
@Override
public void accept(String s) {
System.out.println(s);
}
};
con.accept("谎言和誓言的区别是什么?");
System.out.println("*******************");
Consumer<String> con1 = (String s) -> {
System.out.println(s);
};
con1.accept("一个是说的人当真了,一个是听的人当真了。");
}
//语法格式三:数据类型可以省略,因为可由编译器推断得出,称为“类型推断”
@Test
public void test3(){
Consumer<String> con1 = (String s) -> {
System.out.println(s);
};
con1.accept("如果大学可以重来,你最想重来的事是啥?");
System.out.println("*******************");
Consumer<String> con2 = (s) -> {
System.out.println(s);
};
con1.accept("谈一场轰轰烈烈的爱情");
}
@Test
public void test3_1(){
int[] arr = {1,2,3,4}; //类型推断
HashMap<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();//类型推断
var entrySet = map.entrySet(); //类型推断 ,在jdk10及之后可以用。
}
//语法格式四:Lambda 若只需要一个参数时,参数的小括号可以省略
@Test
public void test4(){
Consumer<String> con1 = (s) -> {
System.out.println(s);
};
con1.accept("世界那么大,我想去看看");
System.out.println("*******************");
Consumer<String> con2 = s -> {
System.out.println(s);
};
con2.accept("世界那么大,我想去看看");
}
//语法格式五:Lambda 需要两个或以上的参数,多条执行语句,并且可以有返回值
@Test
public void test5(){
Comparator<Integer> com1 = new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
System.out.println(o1);
System.out.println(o2);
return o1.compareTo(o2);
}
};
System.out.println(com1.compare(12,21));
System.out.println("*****************************");
Comparator<Integer> com2 = (o1, o2) -> {
System.out.println(o1);
System.out.println(o2);
return o1.compareTo(o2);
};
System.out.println(com2.compare(12,21));
}
//语法格式六:当 Lambda 体只有一条语句时,return 与大括号若有,都可以省略
@Test
public void test6(){
Comparator<Integer> com1 = (o1,o2) -> {
return o1.compareTo(o2);
};
System.out.println(com1.compare(12,6));
System.out.println("*****************************");
Comparator<Integer> com2 = (o1,o2) -> o1.compareTo(o2);
System.out.println(com2.compare(12,16));
}
}
2.3四大核心函数式接口
| 函数式接口 | 称谓 | 参数类型 | 用途 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Consumer | 消费型接口 | T | 对类型为T的对象应用操作,包含方法: void accept(T t) |
| Supplier | 供给型接口 | 无 | 返回类型为T的对象,包含方法:T get() |
| Function<T, R> | 函数型接口 | T | 对类型为T的对象应用操作,并返回结果。结果是R类型的对象。包含方法:R apply(T t) |
| Predicate | 判断型接口 | T | 确定类型为T的对象是否满足某约束,并返回 boolean 值。包含方法:boolean test(T t) |
三、Java 8新特性:方法引用与构造器引用
- Lambda表达式是为了简化函数式接口的变量或形参赋值的语法。而方法引用和构造器引用是为了简化Lambda表达式的。
3.1方法引用
- 当要传递给Lambda体的操作已经有实现的方法了,可以使用方法引用。
- 方法引用可以看做是Lambda表达式深层次的表达。换而言之,方法引用就是Lambda表达式的一个实例,通过方法的名字来指向一个方法,可以认为是Lambda表达式的一个增强。
3.1.1方法引用格式
情况一: 对象 :: 实例方法
情况二:类 :: 静态方法名
情况三: 类 :: 实例方法名
3.1.2方法引用实例
public class MethodRefTest {
// 情况一:对象 :: 实例方法
//Consumer中的void accept(T t)
//PrintStream中的void println(T t)
@Test
public void test1() {
Consumer<String> con1 = new Consumer<String>() {
@Override
public void accept(String s) {
System.out.println(s);
}
};
con1.accept("hello");
//lambda表达式
Consumer<String> con2 = s -> {
System.out.println(s);
};
con2.accept("hello2");
//方法引用
Consumer<String> con3 = System.out::println;
con3.accept("hello3");
}
//Supplier中的T get()
//Employee中的String getName()
@Test
public void test2() {
Employee emp = new Employee(1001, "马化腾", 34, 6000.38);
Supplier<String> sup1 = new Supplier<String>() {
@Override
public String get() {
return emp.getName();
}
};
System.out.println(sup1.get());
//lambda表达式
Supplier<String> sup2 = () -> emp.getName();
System.out.println(sup2.get());
//方法引用
Supplier<String> sup3 = emp::getName;
System.out.println(sup3.get());
}
// 情况二:类 :: 静态方法
//Comparator中的int compare(T t1,T t2)
//Integer中的int compare(T t1,T t2)
@Test
public void test3() {
Comparator<Integer> com1 = new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return Integer.compare(o1, o2);
}
};
System.out.println(com1.compare(12, 34));
//lambda表达式
Comparator<Integer> com2 = (o1, o2) -> Integer.compare(o1, o2);
System.out.println(com2.compare(3, 2));
//方法引用
Comparator<Integer> com3 = Integer::compare;
System.out.println(com3.compare(6, 6));
}
//Function中的R apply(T t)
//Math中的Long round(Double d)
@Test
public void test4() {
Function<Double, Long> fun1 = new Function<Double, Long>() {
@Override
public Long apply(Double aDouble) {
return Math.round(aDouble);
}
};
Function<Double, Long> fun2 = aDouble -> Math.round(aDouble);
Function<Double, Long> fun3 = Math::round;
}
// 情况三:类 :: 实例方法
// Comparator中的int comapre(T t1,T t2)
// String中的int t1.compareTo(t2)
@Test
public void test5() {
Comparator<String> com1 = (o1, o2) -> o1.compareTo(o2);
System.out.println(com1.compare("abc", "abd"));
Comparator<String> com2 = String::compareTo;
System.out.println(com2.compare("abc", "abb"));
}
//BiPredicate中的boolean test(T t1, T t2);
//String中的boolean t1.equals(t2)
@Test
public void test6() {
BiPredicate<String, String> b1 = new BiPredicate<String, String>() {
@Override
public boolean test(String s1, String s2) {
return s1.equals(s2);
}
};
BiPredicate<String, String> b2 = (s1, s2) -> s1.equals(s2);
BiPredicate<String, String> b3 = String::equals;
}
// Function中的R apply(T t)
// Employee中的String getName();
@Test
public void test7() {
Employee emp = new Employee(1001, "马化腾", 34, 6000.38);
Function<Employee, String> fun1 = new Function<Employee, String>() {
@Override
public String apply(Employee employee) {
return emp.getName();
}
};
System.out.println(fun1.apply(emp));
Function<Employee, String> fun2 = employee -> emp.getName();
System.out.println(fun2.apply(emp));
Function<Employee, String> fun3 = Employee::getName;
System.out.println(fun3.apply(emp));
}
}
3.2构造器引用
- 当Lambda表达式是创建一个对象,并且满足Lambda表达式形参,正好是给创建这个对象的构造器的实参列表,就可以使用构造器引用。
格式
类名 :: new
实例
public class ConstructorRefTest {
//构造器引用
//Supplier中的T get()
@Test
public void test1() {
Supplier<Employee> sup1 = new Supplier<Employee>() {
@Override
public Employee get() {
return new Employee();
}
};
System.out.println(sup1.get());
Supplier<Employee> sup2 = Employee::new;
System.out.println(sup2.get());
}
//Function中的R apply(T t)
@Test
public void test2() {
Function<Integer, Employee> fun1 = new Function<Integer, Employee>() {
@Override
public Employee apply(Integer id) {
return new Employee(id);
}
};
System.out.println(fun1.apply(12));
Function<Integer, Employee> fun2 = Employee::new;
System.out.println(fun2.apply(11));
}
//BiFunction中的R apply(T t,U u)
@Test
public void test3() {
BiFunction<Integer, String, Employee> b1 = new BiFunction<Integer, String, Employee>() {
@Override
public Employee apply(Integer id, String name) {
return new Employee(id, name);
}
};
System.out.println(b1.apply(10, "tom"));
BiFunction<Integer, String, Employee> b2 = Employee::new;
System.out.println(b2.apply(20, "jerry"));
}
//数组引用
//Function中的R apply(T t)
@Test
public void test4() {
Function<Integer, Employee[]> fun1 = new Function<Integer, Employee[]>() {
@Override
public Employee[] apply(Integer length) {
return new Employee[length];
}
};
System.out.println(fun1.apply(10).length);
Function<Integer, Employee[]> fun2 = Employee[]::new;
System.out.println(fun2.apply(20).length);
}
}
四、API的变化
4.1 Optional类
- 为什么需要Optional类?为了避免代码中出现空指针异常。
实例
public class OptionalTest {
@Test
public void test(){
String star="张三";
//star=null;
//使用Optional避免空指针的问题
//1.实例化
//ofNullable(T value)用来创建一个Optional实例,value可能是空,也可能非空
Optional<String> optional = Optional.ofNullable(star);
//orElse(T other)如果Optional实例内部的value属性不为null,则返回value。如果value为空,则返回other。
String otherStar="李四";
String finalStar = optional.orElse(otherStar);
System.out.println(finalStar.toString());
}
@Test
public void test2() {
String star="张三";
//star=null;
Optional<String> optional = Optional.ofNullable(star);
//get()取出内部的value值
System.out.println(optional.get());
}
}
4.2 StringBuilder、StringBuffer
- String为不可变的字符序列,虽然可以共享常量对象,但是对于频繁字符串的修改和拼接操作,效率极低,空间消耗也比较高。因此,JDK又在java.lang包提供了可变字符序列StringBuffer和StringBuilder。
- StringBuffer:JDK1.0声明,可以对字符串内容进行增删,此时不会产生新的对象,线程安全的,效率低。
- StringBuilder:JDK5.0声明,可以对字符串内容进行增删,此时不会产生新的对象,线程不安全的,效率高。
常用API
- StringBuilder、StringBuffer的API是完全一致的,并且很多方法与String相同。
public class StringBufferBuilderTest {
/*
* (1)StringBuffer append(xx):提供了很多的append()方法,用于进行字符串追加的方式拼接
(2)StringBuffer delete(int start, int end):删除[start,end)之间字符
(3)StringBuffer deleteCharAt(int index):删除[index]位置字符
(4)StringBuffer replace(int start, int end, String str):替换[start,end)范围的字符序列为str
(5)void setCharAt(int index, char c):替换[index]位置字符
(6)char charAt(int index):查找指定index位置上的字符
(7)StringBuffer insert(int index, xx):在[index]位置插入xx
(8)int length():返回存储的字符数据的长度
(9)StringBuffer reverse():反转
* */
@Test
public void test1(){
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
stringBuilder.append("abc").append("123").append("def");
System.out.println(stringBuilder);
}
@Test
public void test2() {
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder("hello");
stringBuilder.insert(2,1);
stringBuilder.insert(2,"abc");
System.out.println(stringBuilder);
stringBuilder.reverse();
System.out.println(stringBuilder);
System.out.println(stringBuilder.length());
}
@Test
public void test3() {
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder("hello");
stringBuilder.setLength(2);
System.out.println(stringBuilder);//he
stringBuilder.append("c");
System.out.println(stringBuilder);//hec
stringBuilder.setLength(10);
System.out.println(stringBuilder);//hec0000000
}
}
4.3本地日期时间:LocalDate、LocalTime、LocalDateTime
| 方法 | *描述* |
|---|---|
| now()/ now(ZoneId zone) | 静态方法,根据当前时间创建对象/指定时区的对象 |
| of(xx,xx,xx,xx,xx,xxx) | 静态方法,根据指定日期/时间创建对象 |
| getDayOfMonth()/getDayOfYear() | 获得月份天数(1-31) /获得年份天数(1-366) |
| getDayOfWeek() | 获得星期几(返回一个 DayOfWeek 枚举值) |
| getMonth() | 获得月份, 返回一个 Month 枚举值 |
| getMonthValue() / getYear() | 获得月份(1-12) /获得年份 |
| getHours()/getMinute()/getSecond() | 获得当前对象对应的小时、分钟、秒 |
| withDayOfMonth()/withDayOfYear()/withMonth()/withYear() | 将月份天数、年份天数、月份、年份修改为指定的值并返回新的对象 |
| with(TemporalAdjuster t) | 将当前日期时间设置为校对器指定的日期时间 |
| plusDays(), plusWeeks(), plusMonths(), plusYears(),plusHours() | 向当前对象添加几天、几周、几个月、几年、几小时 |
| minusMonths() / minusWeeks()/minusDays()/minusYears()/minusHours() | 从当前对象减去几月、几周、几天、几年、几小时 |
| plus(TemporalAmount t)/minus(TemporalAmount t) | 添加或减少一个 Duration 或 Period |
| isBefore()/isAfter() | 比较两个 LocalDate |
| isLeapYear() | 判断是否是闰年(在LocalDate类中声明) |
| format(DateTimeFormatter t) | 格式化本地日期、时间,返回一个字符串 |
| parse(Charsequence text) | 将指定格式的字符串解析为日期、时间 |
实例
@Test
public void test(){
//now():获取当前日期和时间对应的实例
LocalDate localDate = LocalDate.now();
LocalTime localTime = LocalTime.now();
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.now();
System.out.println(localDate);//2022-12-05
System.out.println(localTime);//15:43:51.474
System.out.println(localDateTime); //2022-12-05T15:43:51.475
//of():获取指定的日期、时间对应的实例
LocalDate localDate1 = LocalDate.of(2021, 5, 23);
LocalDateTime localDateTime1 = LocalDateTime.of(2022, 12, 5, 11, 23, 45);
System.out.println(localDate1);
System.out.println(localDateTime1);
//getXXX()
LocalDateTime localDateTime2 = LocalDateTime.now();
System.out.println(localDateTime2.getDayOfMonth());
//体现不可变性
//withXxx()
LocalDateTime localDateTime3 = localDateTime2.withDayOfMonth(15);
System.out.println(localDateTime2);//2022-12-05T15:48:48.399
System.out.println(localDateTime3);//2022-12-15T15:48:48.399
//plusXxx()
LocalDateTime localDateTime4 = localDateTime2.plusDays(5);
System.out.println(localDateTime2);//2022-12-05T15:50:21.864
System.out.println(localDateTime4);//2022-12-10T15:50:21.864
}
五、Stream API
5.1说明
- Stream API把真正的函数式编程风格引入到Java中。
- 使用Stream API对集合数据进行操作,就类似于使用SQL执行的数据库查询。
- Stream API提供了一种高效且易于使用的处理数据的方式。
5.2什么是Stream
- Collection是一种静态的内存数据结构,讲的是数据,主要面向内存,存储再内存中。
- Stream是有关计算的,讲的是计算,主要是面向CPU的,通过CPU实现计算。
- 注意:
- Stream自己不会存储元素。
- Stream不会改变源对象。相反,他们会返回一个持有结果的新的Stream。
- Stream操作是延迟执行的。这意味着他们会等到需要结果的时候才执行。
- Stream一旦执行了终止操作,就不能再调用其它中间操作或终止操作了。
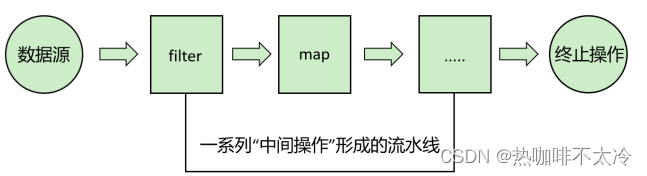
5.3 Stream的操作的三个步骤
1.创建Stream
- Stream是一个数据源(如:集合、数组),获取一个流。
2.中间操作
- 每次处理都会返回一个持有结果的新Stream,即中间操作的方法返回值仍然是Stream类型的对象。
3.终止操作
- 终止操作的方法返回值类型就不再是Stream了,因此一旦执行终止操作,就结束整个Stream操作了。一旦执行终止操作,就执行中间操作链,最终产生结果并结束Stream。
5.4实例
1.创建Stream实例
public class StreamAPITest {
//创建 Stream方式一:通过集合
@Test
public void test1(){
List<Employee> list = EmployeeData.getEmployees();
// default Stream<E> stream() : 返回一个顺序流
Stream<Employee> stream = list.stream();
// default Stream<E> parallelStream() : 返回一个并行流
Stream<Employee> stream1 = list.parallelStream();
System.out.println(stream);
System.out.println(stream1);
}
//创建 Stream方式二:通过数组
@Test
public void test2(){
//调用Arrays类的static <T> Stream<T> stream(T[] array): 返回一个流
Integer[] arr = new Integer[]{1,2,3,4,5};
Stream<Integer> stream = Arrays.stream(arr);
int[] arr1 = new int[]{1,2,3,4,5};
IntStream stream1 = Arrays.stream(arr1);
}
//创建 Stream方式三:通过Stream的of()
@Test
public void test3(){
Stream<String> stream = Stream.of("AA", "BB", "CC", "SS", "DD");
}
}
2.一系列中间操作
public class StreamAPITest1 {
//1-筛选与切片
@Test
public void test1() {
// filter(Predicate p)——接收 Lambda,从流中排除某些元素。
//练习:查询员工表中薪资大于7000的员工信息
List<Employee> list = EmployeeData.getEmployees();
Stream<Employee> stream = list.stream();
stream.filter(emp -> emp.getSalary() > 7000).forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println();
// limit(n)——截断流,使其元素不超过给定数量。
//错误的。因为stream已经执行了终止操作,就不可以再调用其它的中间操作或终止操作了。
// stream.limit(2).forEach(System.out::println);
list.stream().filter(emp -> emp.getSalary() > 7000).limit(2).forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println();
// skip(n) —— 跳过元素,返回一个扔掉了前 n 个元素的流。若流中元素不足 n 个,则返回一个空流。与 limit(n) 互补
list.stream().skip(5).forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println();
// distinct()——筛选,通过流所生成元素的 hashCode() 和 equals() 去除重复元素
list.add(new Employee(1009, "马斯克", 40, 12500.32));
list.add(new Employee(1009, "马斯克", 40, 12500.32));
list.add(new Employee(1009, "马斯克", 40, 12500.32));
list.add(new Employee(1009, "马斯克", 40, 12500.32));
list.stream().distinct().forEach(System.out::println);
}
//2-映射
@Test
public void test2() {
//map(Function f)——接收一个函数作为参数,将元素转换成其他形式或提取信息,该函数会被应用到每个元素上,并将其映射成一个新的元素。
//练习:转换为大写
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("aa", "bb", "cc", "dd");
//方式1:
list.stream().map(str -> str.toUpperCase()).forEach(System.out::println);
//方式2:
list.stream().map(String :: toUpperCase).forEach(System.out::println);
//练习:获取员工姓名长度大于3的员工。
List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployees();
employees.stream().filter(emp -> emp.getName().length() > 3).forEach(System.out::println);
//练习:获取员工姓名长度大于3的员工的姓名。
//方式1:
employees.stream().filter(emp -> emp.getName().length() > 3).map(emp -> emp.getName()).forEach(System.out::println);
//方式2:
employees.stream().map(emp -> emp.getName()).filter(name -> name.length() > 3).forEach(System.out::println);
//方式3:
employees.stream().map(Employee::getName).filter(name -> name.length() > 3).forEach(System.out::println);
}
//3-排序
@Test
public void test3() {
//sorted()——自然排序
Integer[] arr = new Integer[]{345,3,64,3,46,7,3,34,65,68};
String[] arr1 = new String[]{"GG","DD","MM","SS","JJ"};
Arrays.stream(arr).sorted().forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));//arr数组并没有因为升序,做调整。
Arrays.stream(arr1).sorted().forEach(System.out::println);
//因为Employee没有实现Comparable接口,所以报错!
// List<Employee> list = EmployeeData.getEmployees();
// list.stream().sorted().forEach(System.out::println);
//sorted(Comparator com)——定制排序
List<Employee> list = EmployeeData.getEmployees();
list.stream().sorted((e1,e2) -> e1.getAge() - e2.getAge()).forEach(System.out::println);
//针对于字符串从大大小排列
Arrays.stream(arr1).sorted((s1,s2) -> -s1.compareTo(s2)).forEach(System.out::println);
// Arrays.stream(arr1).sorted(String :: compareTo).forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
3.终止操作
public class StreamAPITest2 {
//1-匹配与查找
@Test
public void test1(){
// allMatch(Predicate p)——检查是否匹配所有元素。
// 练习:是否所有的员工的年龄都大于18
List<Employee> list = EmployeeData.getEmployees();
System.out.println(list.stream().allMatch(emp -> emp.getAge() > 18));
// anyMatch(Predicate p)——检查是否至少匹配一个元素。
//练习:是否存在年龄大于18岁的员工
System.out.println(list.stream().anyMatch(emp -> emp.getAge() > 18));
// 练习:是否存在员工的工资大于 10000
System.out.println(list.stream().anyMatch(emp -> emp.getSalary() > 10000));
// findFirst——返回第一个元素
System.out.println(list.stream().findFirst().get());
}
@Test
public void test2(){
// count——返回流中元素的总个数
List<Employee> list = EmployeeData.getEmployees();
System.out.println(list.stream().filter(emp -> emp.getSalary() > 7000).count());
// max(Comparator c)——返回流中最大值
//练习:返回最高工资的员工
System.out.println(list.stream().max((e1, e2) -> Double.compare(e1.getSalary(), e2.getSalary())));
// 练习:返回最高的工资:
//方式1:
System.out.println(list.stream().max((e1, e2) -> Double.compare(e1.getSalary(), e2.getSalary())).get().getSalary());
//方式2:
System.out.println(list.stream().map(emp -> emp.getSalary()).max((salary1, salary2) -> Double.compare(salary1, salary2)).get());
System.out.println(list.stream().map(emp -> emp.getSalary()).max(Double::compare).get());
// min(Comparator c)——返回流中最小值
// 练习:返回最低工资的员工
System.out.println(list.stream().min((e1, e2) -> Double.compare(e1.getSalary(), e2.getSalary())));
// forEach(Consumer c)——内部迭代
list.stream().forEach(System.out::println);
//针对于集合,jdk8中增加了一个遍历的方法
list.forEach(System.out::println);
//针对于List来说,遍历的方式:① 使用Iterator ② 增强for ③ 一般for ④ forEach()
}
//2-归约
@Test
public void test3(){
// reduce(T identity, BinaryOperator)——可以将流中元素反复结合起来,得到一个值。返回 T
// 练习1:计算1-10的自然数的和
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10);
System.out.println(list.stream().reduce(0, (x1, x2) -> x1 + x2));
System.out.println(list.stream().reduce(0, (x1, x2) -> Integer.sum(x1,x2)));
System.out.println(list.stream().reduce(0, Integer::sum));
System.out.println(list.stream().reduce(10, (x1, x2) -> x1 + x2));
// reduce(BinaryOperator) ——可以将流中元素反复结合起来,得到一个值。返回 Optional<T>
// 练习2:计算公司所有员工工资的总和
List<Employee> employeeList = EmployeeData.getEmployees();
System.out.println(employeeList.stream().map(emp -> emp.getSalary()).reduce((salary1, salary2) -> Double.sum(salary1, salary2)));
System.out.println(employeeList.stream().map(emp -> emp.getSalary()).reduce(Double::sum));
}
//3-收集
@Test
public void test4(){
List<Employee> list = EmployeeData.getEmployees();
// collect(Collector c)——将流转换为其他形式。接收一个 Collector接口的实现,用于给Stream中元素做汇总的方法
// 练习1:查找工资大于6000的员工,结果返回为一个List或Set
List<Employee> list1 = list.stream().filter(emp -> emp.getSalary() > 6000).collect(Collectors.toList());
list1.forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println();
list.forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println();
// 练习2:按照员工的年龄进行排序,返回到一个新的List中
List<Employee> list2 = list.stream().sorted((e1, e2) -> e1.getAge() - e2.getAge()).collect(Collectors.toList());
list2.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}