文章目录
- 第四讲
- 第五讲
- 第六讲
第四讲
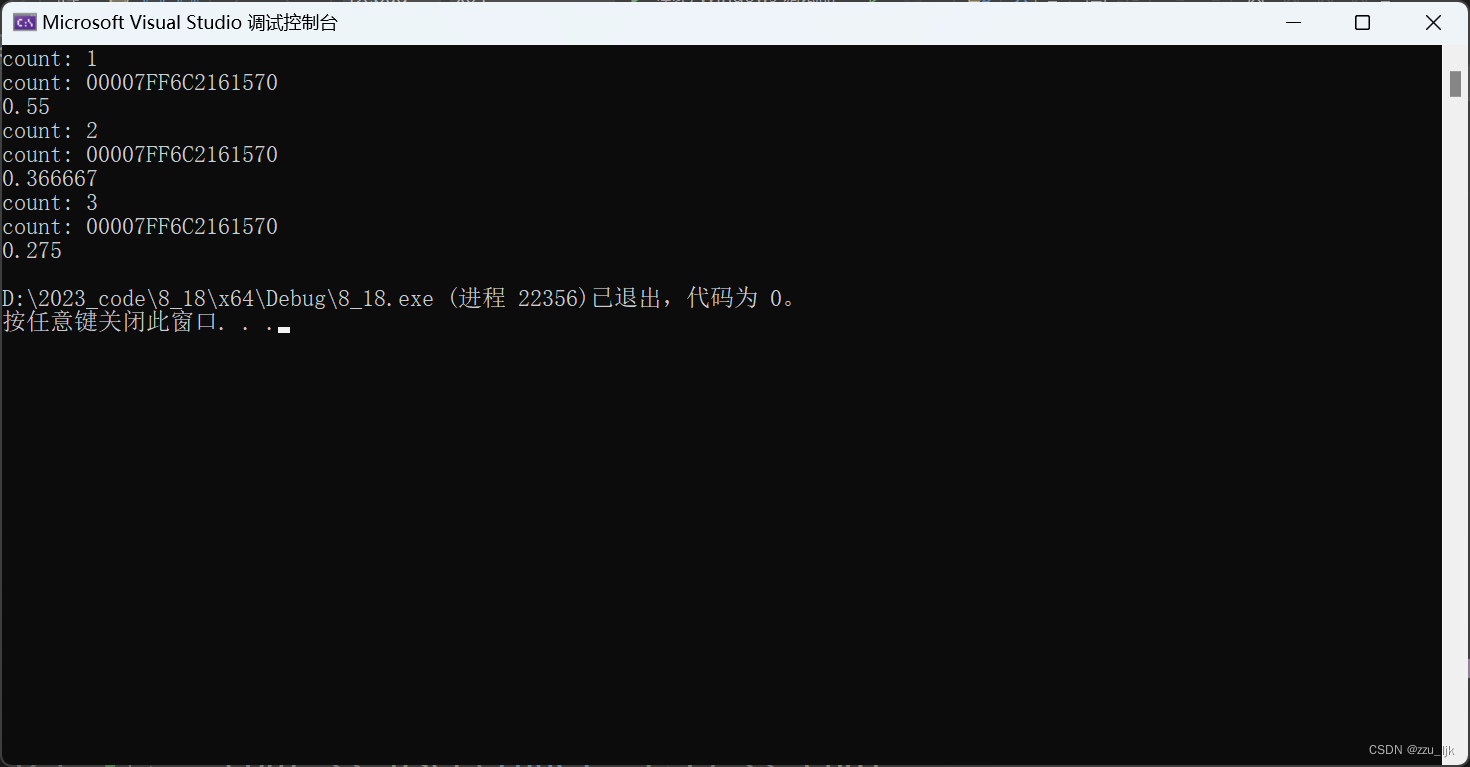
1、计数器
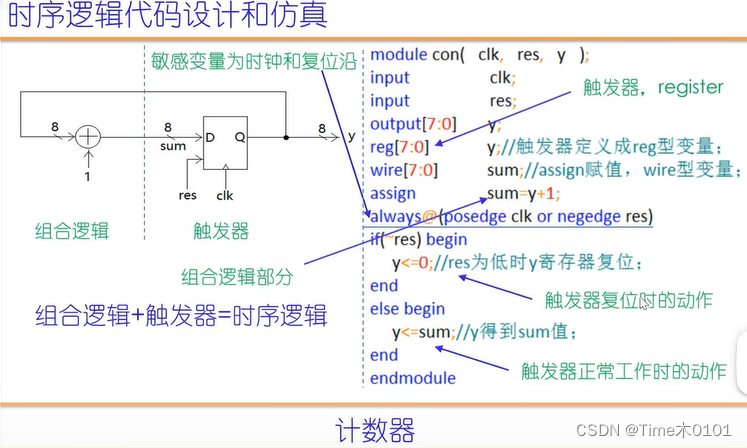
代码:
//计数器
`timescale 1ns/10ps
module counter(
clk,
res,
y
);
input clk;
input res;
output[7:0] y;
reg[7:0] y;
wire[7:0] sum;//+1运算的结果(1)
assign sum=y+1;//组合逻辑部分(2)
always@(posedge clk or negedge res)
if(~res) begin
y<=0;
end
else begin
y<=sum; //可省略上面(1)(2)语句,y<=y+1;
end
endmodule
//--------testbench of counter------
module counter_tb;
reg clk,res;
wire[7:0] y;
counter counter(
.clk(clk),
.res(res),
.y(y)
);
initial begin
clk<=0;res<=0;
#17 res<=1;
#6000 $stop;
end
always #5 clk<=~clk;
endmodule
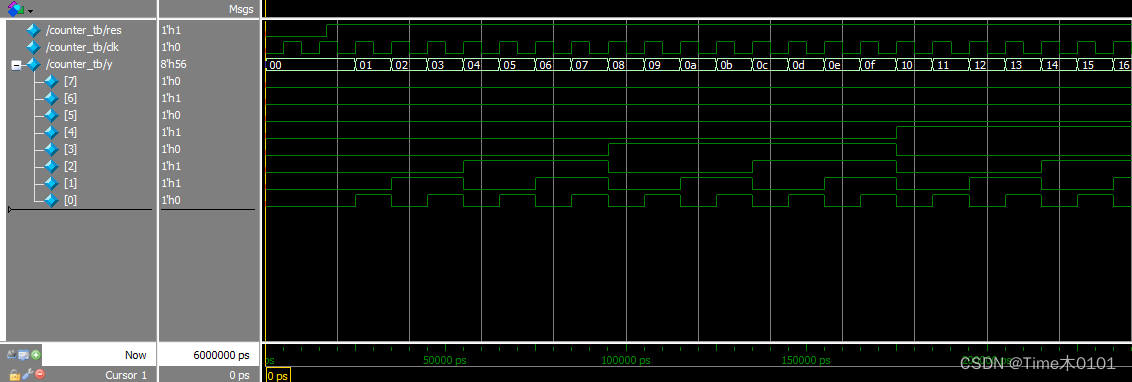
仿真结果:
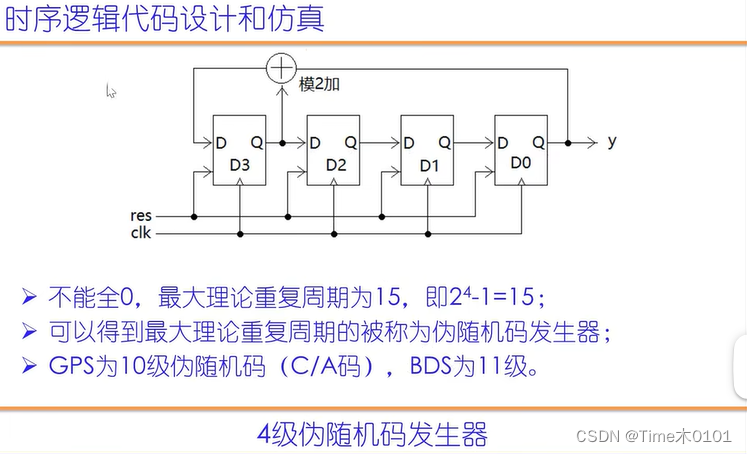
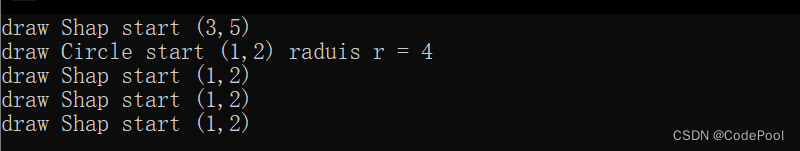
2、4级伪随机码发生器
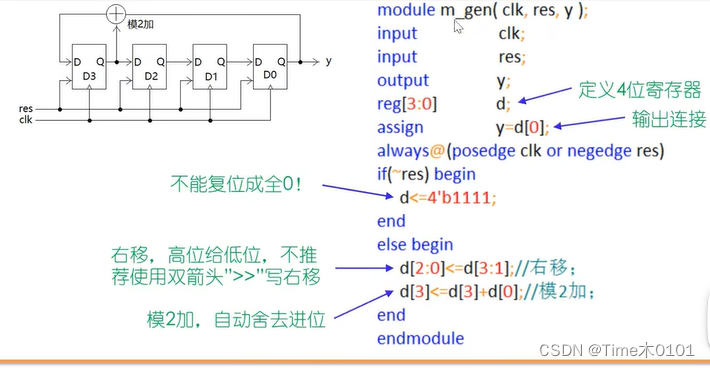
代码:
//四级伪随机码发生器
`timescale 1ns/10ps
module m_gen(
clk,
res,
y
);
input clk;
input res;
output y;
reg[3:0] d;
assign y=d[0];
always@(posedge clk or negedge res)
if(~res)begin
d<=4'b1111;
end
else begin
d[2:0]<=d[3:1]; //右移一位
d[3]<=d[3]+d[0]; //模二加
end
endmodule
//-------testbench of m_gen-------
module m_gen_tb;
reg clk,res;
wire y;
m_gen m_gen(
.clk(clk),
.res(res),
.y(y)
);
initial begin
clk=0;res=0;
#17 res=1;
#600 $stop;
end
always #5 clk=~clk;
endmodule
仿真波形图:
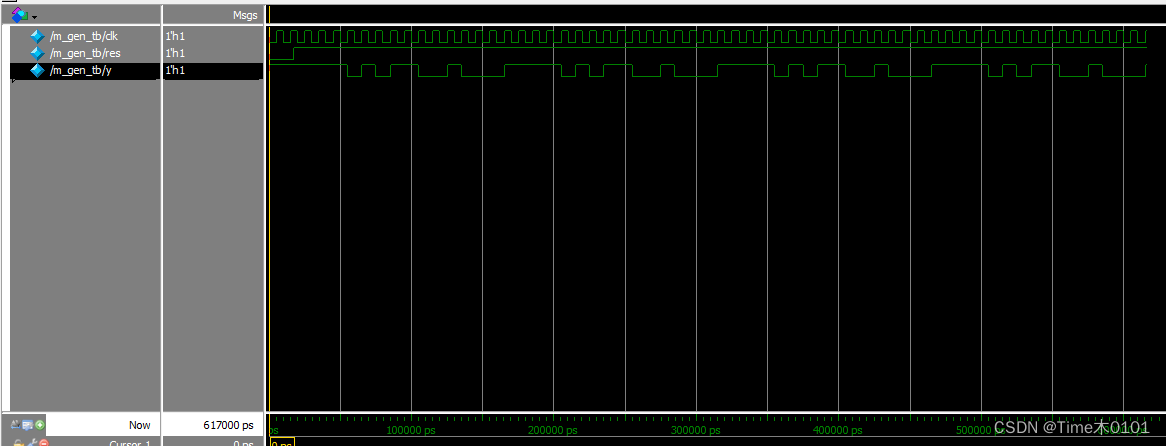
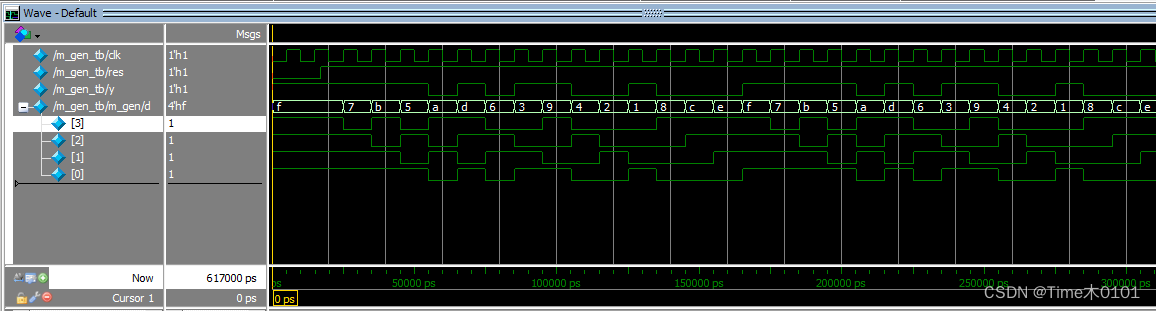
小结:

第五讲
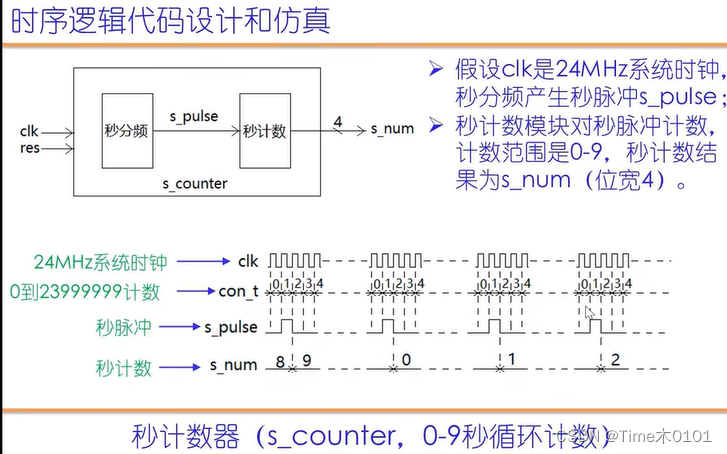
1、秒计数器(s_counter, 0-9秒循环计数)
代码:
//2023-09-07,time
//秒计数器,0-9循环;
`timescale 1ns/10ps
module s_counter(
clk,
res,
s_num
);
input clk;
input res;
output[3:0] s_num;
parameter frequency_clk=24;//24MHz
reg[24:0] con_t; //秒脉冲分频计数器;
reg s_pulse; //秒脉冲尖;
reg[3:0] s_num;
always@(posedge clk or negedge res)
if(~res)begin
con_t<=0;s_pulse<=0;s_num<=0;
end
else begin
//if( con_t==frequency_clk*1000000-1)begin
if( con_t==frequency_clk*1000-1)begin//为了仿真方便观察,数值改小了
con_t<=0;
end
else begin
con_t<= con_t+1;
end
if( con_t==0)begin
s_pulse<=1;
end
else begin
s_pulse<=0;
end
if(s_pulse)begin
if(s_num==9)begin
s_num<=0;
end
else begin
s_num<=s_num+1;
end
end
end
endmodule
//-------testbench of s_counter------
module s_counter_tb;
reg clk,res;
wire[3:0] s_num;
s_counter s_counter(
.clk(clk),
.res(res),
.s_num(s_num)
);
initial begin
clk<=0;res<=0;
#17 res<=1;
#300000 $stop;
end
always#5 clk=~clk;
endmodule
仿真图:
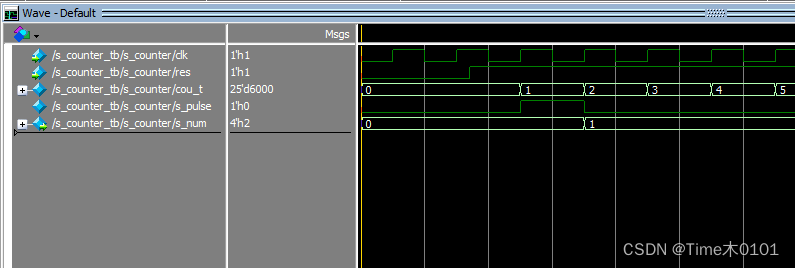 2、秒计数器加数码管显示
2、秒计数器加数码管显示
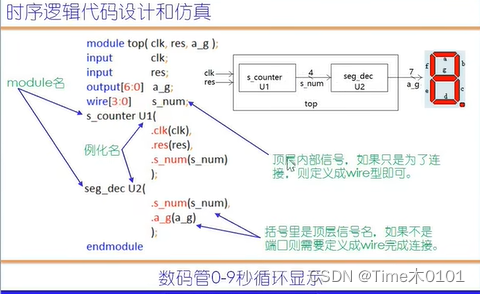
3、0-59秒显示
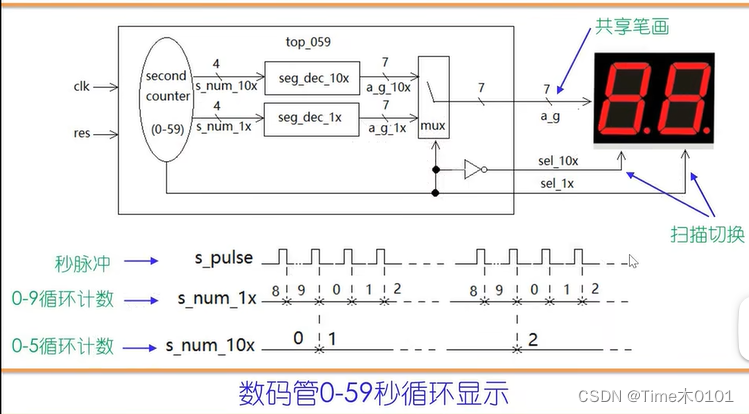
小结:

第六讲
1、相邻点累加
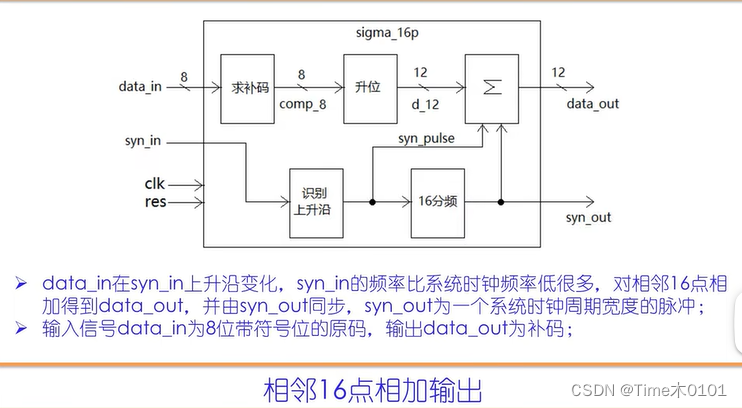
构想:
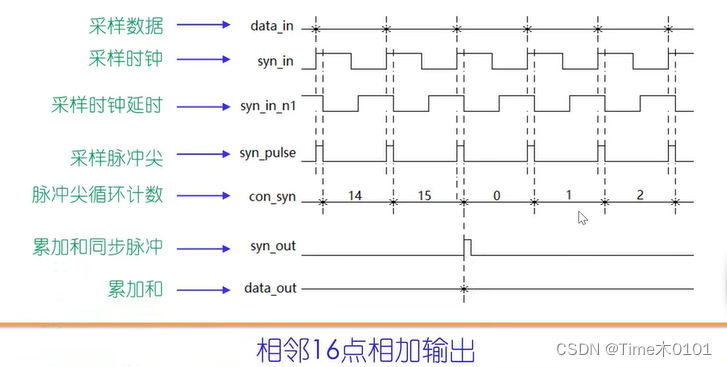
代码:
//2023-09-11,time
//相邻16点相加;
`timescale 1ns/10ps
module sigma_16p(
clk,
res,
data_in,
syn_in,
data_out,
syn_out
);
input clk;
input res;
input[7:0] data_in;//采样信号
input syn_in;//采样时钟
output[11:0] data_out;//累加结果输出
output syn_out;//累加结果同步脉冲
reg syn_in_n1;//syn_in的反向延时;
wire syn_pulse;//采样时钟上升沿识别脉冲;
assign syn_pulse=syn_in&syn_in_n1;
reg[3:0] con_syn;//采样时钟循环计数器
wire[7:0] comp_8;//补码
wire[11:0] d_12;//升位结果
assign comp_8=data_in[7]?{data_in[7],~data_in[6:0]+1}:data_in;//补码运算;
assign d_12={comp_8[7],comp_8[7],comp_8[7],comp_8[7],comp_8};
reg[11:0] sigma;//累加计算;
reg[11:0] data_out;
reg syn_out;
always@(posedge clk or negedge res)
if(~res)begin
syn_in_n1<=0;con_syn<=0;sigma<=0;data_out<=0;
syn_out<=0;
end
else begin
syn_in_n1<=~syn_in;
if(syn_pulse)begin
con_syn<=con_syn+1;
end
if(syn_pulse)begin
if(con_syn==15)begin
sigma<=d_12;
data_out<=sigma;
syn_out<=1;
end
else begin
sigma<=sigma+d_12;
end
end
else begin
syn_out<=0;
end
end
endmodule
//---------testbench of sigma_16p_tb-------
module sigma_16p_tb;
reg clk,res;
reg[7:0] data_in;
reg syn_in;
wire[11:0] data_out;
wire syn_out;
sigma_16p sigma_16p(
.clk(clk),
.res(res),
.data_in(data_in),
.syn_in(syn_in),
.data_out(data_out),
.syn_out(syn_out)
);
initial begin
clk<=0;res<=0;data_in=1;syn_in<=0;
#17 res<=1;
#25000 $stop;
end
always #5 clk<=~clk;
always #100 syn_in<=~syn_in;
endmodule
仿真结果:
data_in=1:
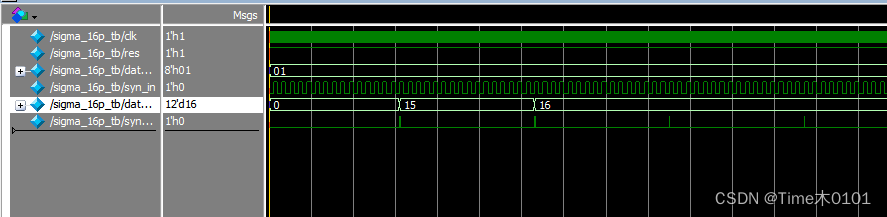
data_in=8’b1000_0001 //data_in=-1
小结:



![[每周一更]-(第60期):15种MySQL索引失效场景](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/d83b7135730245aebd12e005c49e851f.jpeg#pic_center)