谷歌Material Design推出了许多非常好用的控件,所以我决定写一个专题来讲述MaterialDesign,今天带来Material Design系列的第一弹 LinearLayoutCompat。
以前要在LinearLayout布局之间的子View之间添加分割线,还需要自己去自定义控件进行添加或者就是在子View之间写很多个TextView,但是谷歌已经给我们提供了这样一个组件,可以很轻松的解决分割线的问题,妈妈再也不用担心分割线问题啦,这个组件就是Material Design中的 LinearLayoutCompat。本篇博客将会从以下两个方面来对LinearLayoutCompat进行介绍:
\1. LinearLayoutCompat的使用
\2. LinearLayoutCompat的源码分析
LinearLayoutCompat的使用
LinearLayoutCompat位于support-v7包中,LinearLayoutCompat其实就是LinerLayout组件,只是为了兼容低版本,所以你必须的引用 V7包下面的LinearLayoutCompat。 LinearLayoutCompat除了拥有LinerLayout原本的属性之外,主要有如下几种属性来实现间隔线效果。
当然使用LinearLayoutCompat需要自定义命名空间xmlns:app=”http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto”
app:divider=”@drawable/line”给分隔线设置自定义的drawable,这里你需要在drawable在定义shape资源,否则将没有效果。
app:dividerPadding 给分隔线设置距离左右边距的距离。
app:showDividers="beginning|middle|end"属性。 beginning,middle,end属性值分别指明将在何处添加分割线。 beginning表示从该LinearLayoutCompat布局的最顶一个子view的顶部开始。 middle表示在此LinearLayoutCompat布局内的子view之间添加。 end表示在此LinearLayoutCompat最后一个子view的底部添加分割线。
none表示不设置间隔线。
使用LinearLayoutCompat可以很方便的就做出微信的发现界面:
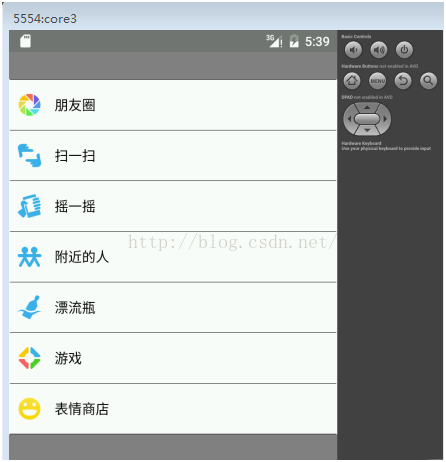
布局的代码如下:
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="@color/gray"
android:gravity="top"
tools:context="com.example.linearlayoutcompatdemo.MainActivity" >
<!-- <android.support.v7.widget.LinearLayoutCompat -->
<android.support.v7.widget.LinearLayoutCompat
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="30dp"
android:background="@color/white"
android:gravity="center"
android:orientation="vertical"
app:divider="@drawable/line"
app:dividerPadding="1dp"
app:showDividers="middle|beginning|end" >
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:paddingBottom="10dip"
android:paddingLeft="5dip"
android:paddingTop="10dip" >
<ImageView
android:layout_width="35dp"
android:layout_height="35dp"
android:scaleType="fitCenter"
android:src="@drawable/find_more_friend_photograph_icon" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dp"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="朋友圈"
android:textColor="@color/black"
android:textSize="15dip" />
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:paddingBottom="10dip"
android:paddingLeft="5dip"
android:paddingTop="10dip" >
<ImageView
android:layout_width="35dp"
android:layout_height="35dp"
android:scaleType="fitCenter"
android:src="@drawable/find_more_friend_scan" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dp"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="扫一扫"
android:textColor="@color/black"
android:textSize="15dip" />
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:paddingBottom="10dip"
android:paddingLeft="5dip"
android:paddingTop="10dip" >
<ImageView
android:layout_width="35dp"
android:layout_height="35dp"
android:scaleType="fitCenter"
android:src="@drawable/find_more_friend_shake" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dp"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="摇一摇"
android:textColor="@color/black"
android:textSize="15dip" />
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:paddingBottom="10dip"
android:paddingLeft="5dip"
android:paddingTop="10dip" >
<ImageView
android:layout_width="35dp"
android:layout_height="35dp"
android:scaleType="fitCenter"
android:src="@drawable/find_more_friend_near_icon" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dp"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="附近的人"
android:textColor="@color/black"
android:textSize="15dip" />
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:paddingBottom="10dip"
android:paddingLeft="5dip"
android:paddingTop="10dip" >
<ImageView
android:layout_width="35dp"
android:layout_height="35dp"
android:scaleType="fitCenter"
android:src="@drawable/find_more_friend_bottle" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dp"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="漂流瓶"
android:textColor="@color/black"
android:textSize="15dip" />
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:paddingBottom="10dip"
android:paddingLeft="5dip"
android:paddingTop="10dip" >
<ImageView
android:layout_width="35dp"
android:layout_height="35dp"
android:scaleType="fitCenter"
android:src="@drawable/more_game" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dp"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="游戏"
android:textColor="@color/black"
android:textSize="15dip" />
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:paddingBottom="10dip"
android:paddingLeft="5dip"
android:paddingTop="10dip" >
<ImageView
android:layout_width="35dp"
android:layout_height="35dp"
android:scaleType="fitCenter"
android:src="@drawable/more_emoji_store" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dp"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="表情商店"
android:textColor="@color/black"
android:textSize="15dip" />
</LinearLayout>
</android.support.v7.widget.LinearLayoutCompat>
</RelativeLayout>
当然和真正微信里的界面还是不一样的,还需要处理很多细节,这里就不过分纠结于细节了,主要还是了解LinearLayoutCompat的用法。
LinearLayoutCompat的源码分析
在使用完LinearLayoutCompat之后,我们会很好奇它内部是如何实现添加分割线的,那我们就看一下LinearLayoutCompat的源码进行分析。
\1. 观看源码,首先可以知道 LinearLayoutCompat继承了ViewGroup,然后我们查看它的构造函数
public LinearLayoutCompat(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
final TintTypedArray a = TintTypedArray.obtainStyledAttributes(context, attrs,
R.styleable.LinearLayoutCompat, defStyleAttr, 0);
int index = a.getInt(R.styleable.LinearLayoutCompat_android_orientation, -1);
if (index >= 0) {
setOrientation(index);
}
index = a.getInt(R.styleable.LinearLayoutCompat_android_gravity, -1);
if (index >= 0) {
setGravity(index);
}
boolean baselineAligned = a.getBoolean(R.styleable.LinearLayoutCompat_android_baselineAligned, true);
if (!baselineAligned) {
setBaselineAligned(baselineAligned);
}
mWeightSum = a.getFloat(R.styleable.LinearLayoutCompat_android_weightSum, -1.0f);
mBaselineAlignedChildIndex =
a.getInt(R.styleable.LinearLayoutCompat_android_baselineAlignedChildIndex, -1);
mUseLargestChild = a.getBoolean(R.styleable.LinearLayoutCompat_measureWithLargestChild, false);
setDividerDrawable(a.getDrawable(R.styleable.LinearLayoutCompat_divider));
mShowDividers = a.getInt(R.styleable.LinearLayoutCompat_showDividers, SHOW_DIVIDER_NONE);
mDividerPadding = a.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.LinearLayoutCompat_dividerPadding, 0);
a.recycle();
}
从构造函数中,首先会把LinearLayoutCompat的所有风格属性的值保存到一个TintTypedArray数组中,然后从中取出用户给LinearLayoutCompat设置的orientation, gravity,baselineAligned的值,如果这些值存在,就给LinearLayoutCompat设置这些值。当然还会从TintTypedArray中取出weightSum,baselineAlignedChildIndex,measureWithLargestChild等属性,然后在构造函数的最低部,会发现这一段代码:
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>setDividerDrawable(a.getDrawable(R.styleable.LinearLayoutCompat_divider));
mShowDividers = a.getInt(R.styleable.LinearLayoutCompat_showDividers, SHOW_DIVIDER_NONE);
mDividerPadding = a.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.LinearLayoutCompat_dividerPadding, 0);
可以发现setDividerDrawable方法,看名字意思是设置分割线的Drawable,非常明显和分割线有关系,接着是从TintTypedArray中继续获取mShowDividers和mDividerPadding的值,分别用于判断显示分割线的模式和分割线的Padding值为多少。我们查看setDividerDrawable方法的内部实现:
public void setDividerDrawable(Drawable divider) {
if (divider == mDivider) {
return;
}
mDivider = divider;
if (divider != null) {
mDividerWidth = divider.getIntrinsicWidth();
mDividerHeight = divider.getIntrinsicHeight();
} else {
mDividerWidth = 0;
mDividerHeight = 0;
}
setWillNotDraw(divider == null);
requestLayout();
}
可以看到,该方法中传进来一个Drawable,然后会进行if判断,是否和原有的Drawable相等,如果为true则return,不执行下面的语句,如果不是,则将该Drawable设置给全局的mDivider,又是if判断,如果传进来的divider!= null,则获取它的固有宽高并设置给mDivider,否则mDivider的宽高设为0,然后会执行setWillNotDraw和requestLayout方法。
我们都知道每一个ViewGroup都会拥有onDraw,onLayout和onMeasure方法,下面我们就查看一下这几个方法的源码进行分析,看看分割线是如何进行绘制的。从源码往下看,首先会看到onDraw方法。
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
if (mDivider == null) {
return;
}
if (mOrientation == VERTICAL) {
drawDividersVertical(canvas);
} else {
drawDividersHorizontal(canvas);
}
}
onDraw方法内部逻辑很简单,判断mDivider是否为空,然后是根据mOrientation的属性,来调用不同的方法进行横或者竖的分割线绘制。查看drawDividersVertical方法内部:
void drawDividersVertical(Canvas canvas) {
final int count = getVirtualChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = getVirtualChildAt(i);
if (child != null && child.getVisibility() != GONE) {
if (hasDividerBeforeChildAt(i)) {
final LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
final int top = child.getTop() - lp.topMargin - mDividerHeight;
drawHorizontalDivider(canvas, top);
}
}
}
循环遍历所有子孩子,进行是否为空和是否为不可见的判断,然后调用hasDividerBeforeChildAt(i),如果为true,则通过获取child的LayoutParams进行计算,然后就可以计算出分割线的top距离,然后调用drawHorizontalDivider(canvas,top)方法,查看一下hasDividerBeforeChildAt方法的内部逻辑:
protected boolean hasDividerBeforeChildAt(int childIndex) {
if (childIndex == 0) {
return (mShowDividers & SHOW_DIVIDER_BEGINNING) != 0;
} else if (childIndex == getChildCount()) {
return (mShowDividers & SHOW_DIVIDER_END) != 0;
} else if ((mShowDividers & SHOW_DIVIDER_MIDDLE) != 0) {
boolean hasVisibleViewBefore = false;
for (int i = childIndex - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (getChildAt(i).getVisibility() != GONE) {
hasVisibleViewBefore = true;
break;
}
}
return hasVisibleViewBefore;
}
return false;
}
基本就是根据子孩子的位置进行相应的判断,第一个位置,最后一个位置,还有中间所有位置,返回一个boolean值,会根据这个值来判断是否画分割线。然后回到drawDividersVertical方法中,它会在遍历子View的最后调用drawHorizontalDivider方法,查看一下这个方法:
void drawHorizontalDivider(Canvas canvas, int top) {
mDivider.setBounds(getPaddingLeft() + mDividerPadding, top,
getWidth() - getPaddingRight() - mDividerPadding, top + mDividerHeight);
mDivider.draw(canvas);
}
发现分割线其实是通过Drawable的setBounds方法进行设置的,然后会调用 Drawable的draw方法对分割线进行绘制。drawDividersHorizontal方法的逻辑跟drawDividersVertical方法差不多,它最后调用的是drawVerticalDivider方法。
void drawDividersHorizontal(Canvas canvas) {
final int count = getVirtualChildCount();
final boolean isLayoutRtl = ViewUtils.isLayoutRtl(this);
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = getVirtualChildAt(i);
if (child != null && child.getVisibility() != GONE) {
if (hasDividerBeforeChildAt(i)) {
final LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
final int position;
if (isLayoutRtl) {
position = child.getRight() + lp.rightMargin;
} else {
position = child.getLeft() - lp.leftMargin - mDividerWidth;
}
drawVerticalDivider(canvas, position);
}
}
}
然后我们查看一下onMeasure方法,内部就是根据Orientation的不同,调用不同的方法:
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
if (mOrientation == VERTICAL) {
measureVertical(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
} else {
measureHorizontal(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
}
查看measureVertical方法,内容较多,我们一点点分析,下面这段代码会循环遍历所有的子View,然后做出相应的判断,如果hasDividerBeforeChildAt方法返回true,mTotalLength会加上分割线的高度,这个方法我们前面已经看过他内部的逻辑,然后会获取子view的LayoutParams,totalWeight用于记录Weight的总和:
for (int i = 0; i < count; ++i) {
final View child = getVirtualChildAt(i);
if (child == null) {
mTotalLength += measureNullChild(i);
continue;
}
if (child.getVisibility() == View.GONE) {
i += getChildrenSkipCount(child, i);
continue;
}
if (hasDividerBeforeChildAt(i)) {
mTotalLength += mDividerHeight;
}
LinearLayoutCompat.LayoutParams lp = (LinearLayoutCompat.LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
totalWeight += lp.weight;
接下来会对heightMode进行判断,跟MeasureSpec.EXACTLY等属性进行比较,还会判断是否使用了权重,根据heightMode的值不同会有不同的处理方式,mTotalLength的值的处理是不同的,同时如果不满足if语句的条件,会调用 measureChildBeforeLayout方法进行一次测量:
<pre name="code" class="java"> if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY && lp.height == 0 && lp.weight > 0) {
// Optimization: don't bother measuring children who are going to use
// leftover space. These views will get measured again down below if
// there is any leftover space.
final int totalLength = mTotalLength;
mTotalLength = Math.max(totalLength, totalLength + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin);
skippedMeasure = true;
} else {
int oldHeight = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
if (lp.height == 0 && lp.weight > 0) {
// heightMode is either UNSPECIFIED or AT_MOST, and this
// child wanted to stretch to fill available space.
// Translate that to WRAP_CONTENT so that it does not end up
// with a height of 0
oldHeight = 0;
lp.height = LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT;
}
// Determine how big this child would like to be. If this or
// previous children have given a weight, then we allow it to
// use all available space (and we will shrink things later
// if needed).
measureChildBeforeLayout(
child, i, widthMeasureSpec, 0, heightMeasureSpec,
totalWeight == 0 ? mTotalLength : 0);
if (oldHeight != Integer.MIN_VALUE) {
lp.height = oldHeight;
}
final int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
final int totalLength = mTotalLength;
mTotalLength = Math.max(totalLength, totalLength + childHeight + lp.topMargin +
lp.bottomMargin + getNextLocationOffset(child));
if (useLargestChild) {
largestChildHeight = Math.max(childHeight, largestChildHeight);
}
}
<pre name="code" class="java">void measureChildBeforeLayout(View child, int childIndex,
int widthMeasureSpec, int totalWidth, int heightMeasureSpec,
int totalHeight) {
measureChildWithMargins(child, widthMeasureSpec, totalWidth,
heightMeasureSpec, totalHeight);
}
当heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST || heightMode == MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED时,mTotalLength值的计算方式是不同的
if (mTotalLength > 0 && hasDividerBeforeChildAt(count)) {
mTotalLength += mDividerHeight;
}
if (useLargestChild &&
(heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST || heightMode == MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED)) {
mTotalLength = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < count; ++i) {
final View child = getVirtualChildAt(i);
if (child == null) {
mTotalLength += measureNullChild(i);
continue;
}
if (child.getVisibility() == GONE) {
i += getChildrenSkipCount(child, i);
continue;
}
final LinearLayoutCompat.LayoutParams lp = (LinearLayoutCompat.LayoutParams)
child.getLayoutParams();
// Account for negative margins
final int totalLength = mTotalLength;
mTotalLength = Math.max(totalLength, totalLength + largestChildHeight +
lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin + getNextLocationOffset(child));
}
}
到最后有下面一段代码:
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>maxWidth += getPaddingLeft() + getPaddingRight();
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>
// Check against our minimum width
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, getSuggestedMinimumWidth());
setMeasuredDimension(ViewCompat.resolveSizeAndState(maxWidth, widthMeasureSpec, childState),
heightSizeAndState);
measureVertical方法最后是通过setMeasuredDimension方法对测量的值进行设置的,至于 maxWidth的值在源码的前面有相应的判断进行赋值,所以整个measure的方法基本围绕 maxWidth和mTotalLength值的确定展开的,其中如果hasDividerBeforeChildAt返回的值为true,mTotalLength会加上分割线的高度,最后通过setMeasuredDimension赋值。
最后我们看看onLayout方法
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
if (mOrientation == VERTICAL) {
layoutVertical(l, t, r, b);
} else {
layoutHorizontal(l, t, r, b);
}
}
看一下layoutVertical的逻辑,里面基本围绕以下两个值展开的:
int childTop;
int childLeft;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = getVirtualChildAt(i);
if (child == null) {
childTop += measureNullChild(i);
} else if (child.getVisibility() != GONE) {
final int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();
final int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
final LinearLayoutCompat.LayoutParams lp =
(LinearLayoutCompat.LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
int gravity = lp.gravity;
if (gravity < 0) {
gravity = minorGravity;
}
final int layoutDirection = ViewCompat.getLayoutDirection(this);
final int absoluteGravity = GravityCompat.getAbsoluteGravity(gravity,
layoutDirection);
switch (absoluteGravity & Gravity.HORIZONTAL_GRAVITY_MASK) {
case Gravity.CENTER_HORIZONTAL:
childLeft = paddingLeft + ((childSpace - childWidth) / 2)
+ lp.leftMargin - lp.rightMargin;
break;
case Gravity.RIGHT:
childLeft = childRight - childWidth - lp.rightMargin;
break;
case Gravity.LEFT:
default:
childLeft = paddingLeft + lp.leftMargin;
break;
}
if (hasDividerBeforeChildAt(i)) {
childTop += mDividerHeight;
}
childTop += lp.topMargin;
setChildFrame(child, childLeft, childTop + getLocationOffset(child),
childWidth, childHeight);
childTop += childHeight + lp.bottomMargin + getNextLocationOffset(child);
i += getChildrenSkipCount(child, i);
}
}
循环遍历子View,根据不同的gravity对childLeft和childTop进行赋值,如果存在分割线childTop会加上分割线的高度mDividerHeight,最后是通过setChildFrame方法进行layout的完成的,可以查看这个方法内部,调用了child的layout方法
private void setChildFrame(View child, int left, int top, int width, int height) {
child.layout(left, top, left + width, top + height);
}
到这里,所有的LinearLayoutCompat的源码分析,就结束了,为什么要看分割线绘制的源码,因为在很多控件中并没有分割线,我们可以通过学习谷歌的源码,仿照着进行分割线的绘制,比如recyclerView就没有分割线,但我们可以自己写一个分割线,对于 recyclerView分割线设置,有很多大神的博客都有描述,这里就不在赘述了,以后的博文会陆续给大家带来Material Design其他控件的博客。
更多Android进阶指南 可以扫码 解锁 《Android十大板块文档》

1.Android车载应用开发系统学习指南(附项目实战)
2.Android Framework学习指南,助力成为系统级开发高手
3.2023最新Android中高级面试题汇总+解析,告别零offer
4.企业级Android音视频开发学习路线+项目实战(附源码)
5.Android Jetpack从入门到精通,构建高质量UI界面
6.Flutter技术解析与实战,跨平台首要之选
7.Kotlin从入门到实战,全方面提升架构基础
8.高级Android插件化与组件化(含实战教程和源码)
9.Android 性能优化实战+360°全方面性能调优
10.Android零基础入门到精通,高手进阶之路
敲代码不易,关注一下吧。ღ( ´・ᴗ・` ) 🤔