文章目录
- 前言
- 一.类的设计
- 书籍类
- 书架类
- 用户类
- 二.行为的规范
- 2.1 增加书籍
- 2.2展示所有书籍
- 2.3查找书籍
- 2.4 删除书籍
- 2.5 归还书籍
- 2.6 借阅书籍
- 2.7 退出系统
- 三.测试类的方法
- 四.项目的目录
前言
在我们学习完面向对象的知识之后,我们就要运用相关知识去实现一个图书管理系统,不要紧张,这个东西还是很简单的,我们一定要用面向对象的观点,去思考问题。其他的就没什么注意的了。
一.类的设计
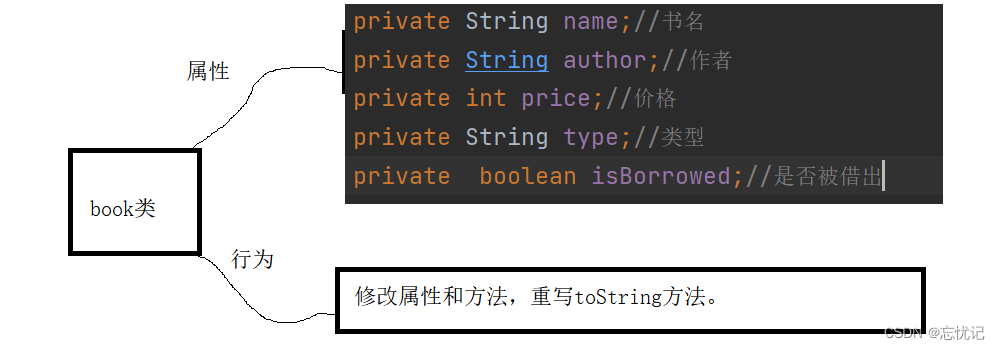
书籍类
package book;
//设计一个图书类
public class Book {
private String name;//书名
private String author;//作者
private int price;//价格
private String type;//类型
private boolean isBorrowed;//是否被借出
public Book(String name, String author, int price, String type) {
this.name = name;
this.author = author;
this.price = price;
this.type = type;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getAuthor() {
return author;
}
public void setAuthor(String author) {
this.author = author;
}
public int getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(int price) {
this.price = price;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
public boolean isBorrowed() {
return isBorrowed;
}
public void setBorrowed(boolean borrowed) {
isBorrowed = borrowed;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Book{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", author='" + author + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
", type='" + type + '\'' +
// ", isBorrowed=" + isBorrowed +
(isBorrowed ? "已经被借出" : "未被借出")+
'}';
}
}
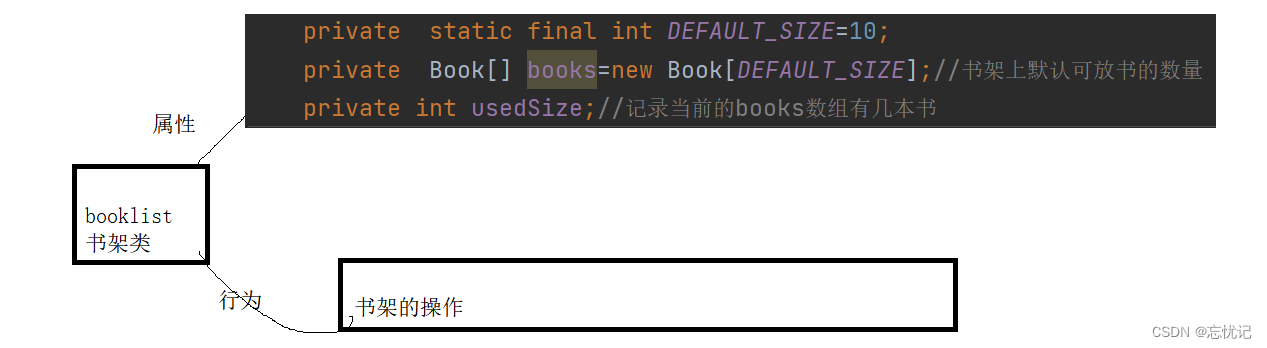
书架类
package book;
//我们把书架看做一个对象,我们针对书架所看到的内容,我们会有对书架上的书有拿出来的操作和放回去的操作。
public class BookList {
private static final int DEFAULT_SIZE=10;
private Book[] books=new Book[DEFAULT_SIZE];//书架上默认可放书的数量
private int usedSize;//记录当前的books数组有几本书
//声明一个构造方法,在启动图书管理之前,我们就去初始化系统,初始化图书馆里系统后,里面就有几本书。
public BookList(){
books[0] = new Book("三国演义","罗贯中",89,"小说");
books[1] = new Book("西游记","吴承恩",78,"小说");
books[2] = new Book("红楼梦","曹雪芹",49,"小说");
books[3]=new Book("七龙珠","鸟山明",89,"漫画");
this.usedSize=4;
}
//下面就是我们针对书架的书的取操作和存操作
public Book getBook(int pos){
return this.books[pos];
}
public void setBook(Book book){
this.books[usedSize]=book;
}
public void setBook(int pos,Book book){
this.books[pos]=book;
}
public int getUsedSize() {
return usedSize;
}
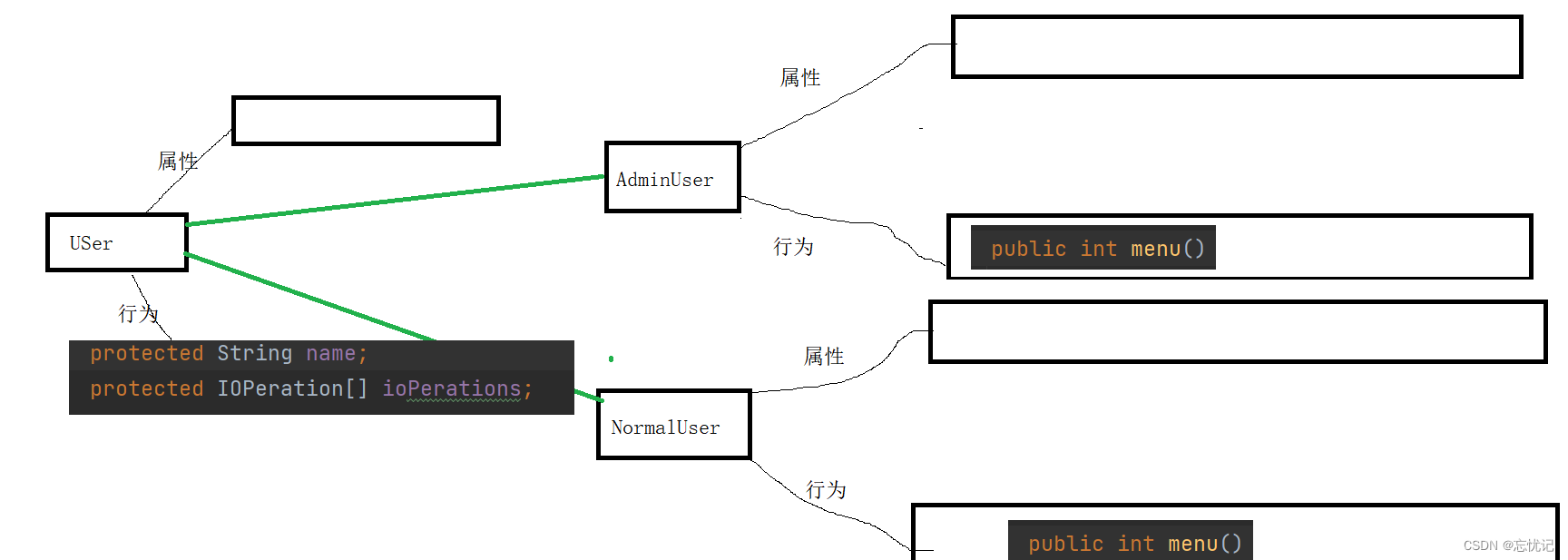
用户类
package user;
import book.BookList;
import opera.IOPeration;
/*
针对用户来说,我们有不同的用户对象,也有不同的用户对象,也对应了不同的操作。
我们在接受到不同的用户对象的时候,我们就要去实现不同用户对象的动作。
因此我们就要存储不同用户对象的操作。
再根据不同用户的操作,进行不同的功能。
*/
public abstract class User {
protected String name;
protected IOPeration[] ioPerations;
public User(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
//用户类的打印菜单功能
public abstract int menu();
//根据不同的对象去调用不同的动作
public void dowork(int choice, BookList bookList){
this.ioPerations[choice].work(bookList);
}
}
package user;
import opera.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
//我们在进入方法之前,用构造方法初始化。
public class AdminUser extends User{
public AdminUser(String name) {
super(name);
this.ioPerations=new IOPeration[]{
new ExitOperation(),
new FindOperation(),
new AddOperation(),
new DelOperation(),
new ShowOperation(),
};
}
@Override
public int menu() {
System.out.println("****************************");
System.out.println("hello "+name+" 欢迎来到图书小练习");
System.out.println("1.查找图书!");
System.out.println("2.新增图书!");
System.out.println("3.删除图书!");
System.out.println("4.显示图书!");
System.out.println("0.退出系统!");
System.out.println("****************************");
System.out.println("请输入你的操作:");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int choice = scanner.nextInt();
return choice;
}
}
package user;
import opera.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class NormalUser extends User {
public NormalUser(String name){
super(name);
this.ioPerations = new IOPeration[] {
new ExitOperation(),
new FindOperation(),
new BrrowOperation(),
new ReturnOperation(),
};
}
@Override
public int menu() {
System.out.println("****************************");
System.out.println("hello "+name+" 欢迎来到图书小练习");
System.out.println("1.查找图书!");
System.out.println("2.借阅图书!");
System.out.println("3.归还图书!");
System.out.println("0.退出系统!");
System.out.println("****************************");
System.out.println("请输入你的操作:");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int choice = scanner.nextInt();
return choice;
}
}
我来解释一下为什么要设计这几个类,我们设计Book这里就是用来表示一本书应该有的属性。设计一个书架类,书架可以放书,也有书架的操作,取书,存书,所以我们设计了一个类。
用户类的话,既然是一个系统就有普通用户身份和管理员身份。当然也有管理员身份的相关操作。
二.行为的规范
行为的规范,大家自然而然就想到的是接口,因为我们不同的管理员要做不同的操作,那么我们就要定好相应的规范,用一个接口去表明,让类去实现。
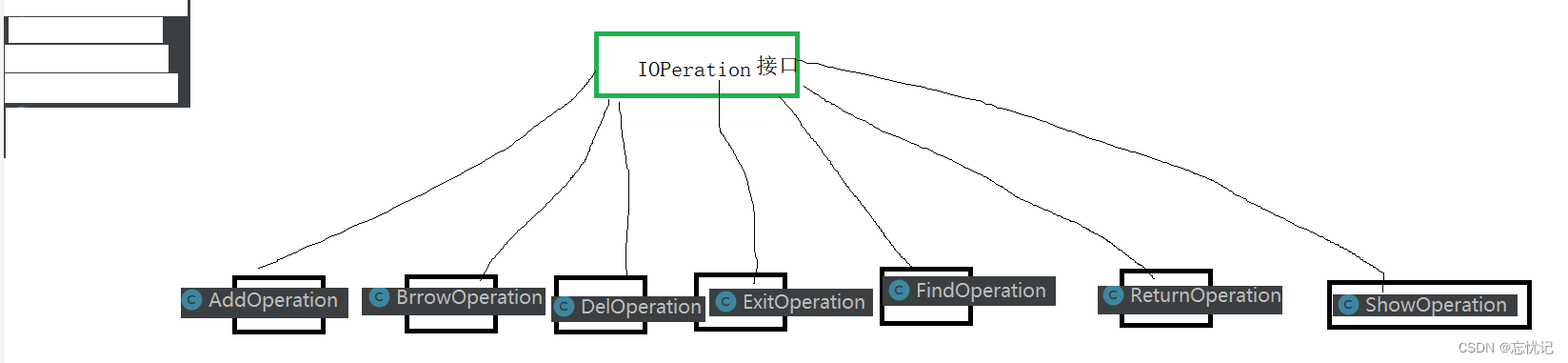
IOperation接口代码:
//对书架进行操作
public interface IOPeration {
void work(BookList bookList);
}
我们进行下面所有的的操作,都是在实现IOperation的基础上进行的。你在进行以下的功能实现中,你只需要注意怎么去实现这个功能,不必在意其他的类是怎么写的,牢记面向对象的思想。
2.1 增加书籍
增加书籍,顾名思义我们是要往书架上放东西,在定义书架的时候,我们已经有了操作相关书架的方法,这个时候我们就要调用书架的相关方法去实现我们增加书籍的功能。
怎么去增加书籍呢?
1.首先遍历这个书架
2.判断书籍是否存在
3.如果不存在放入书籍
代码如下:
public class AddOperation implements IOPeration{
public void work(BookList bookList) {
System.out.println("新增图书!");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("输入书名:");
String name = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println("输入作者:");
String author = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println("输入类型:");
String type = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println("输入价格:");
int price = scanner.nextInt();
Book book = new Book(name,author,price,type);
int currentSize=bookList.getUsedSize();
for (int i = 0; i < currentSize; i++) {
Book tmp=bookList.getBook(i);
if (tmp.getName().equals(name)) {
System.out.println("书已经存在了,不能再放入了!");
return;
}
}
//书架的相关操作,放入书籍即可
bookList.setBook(book);
bookList.setUsedSize(currentSize+1);
}
}
2.2展示所有书籍
这个东西也别想的太复杂,就跟遍历数组一样,遍历完结果,逐个打印出来即可。
public class ShowOperation implements IOPeration{
@Override
public void work(BookList bookList) {
int currentSize = bookList.getUsedSize();
for (int i = 0; i < currentSize; i++) {
Book book=bookList.getBook(i);
System.out.println(book);
}
System.out.println("打印所有图书!");
}
}
2.3查找书籍
查找书籍,自然就是根据名字查找,当然这也别想的太复杂,具体的步骤如下:
1.遍历数据
2.逐个比对
3.查找成功
public class FindOperation implements IOPeration{
@Override
public void work(BookList bookList) {
System.out.println("查找图书!");
System.out.println("请输入书名!");
Scanner scanner=new Scanner(System.in);
String name=scanner.nextLine();
//获取当前书的数量
int currentSize=bookList.getUsedSize();
//因为book数据是由private属性修饰的,因此我们要调用booklist里面要用的get和set方法
for (int i = 0; i < currentSize; i++) {
Book book=bookList.getBook(i);
if (book.getName().equals(name)){
System.out.println("找到了这本书!");
System.out.println(book);
return;
}
}
System.out.println("没有这本书!");
}
}
2.4 删除书籍
删除书籍,大家可能觉得有些麻烦,但是我说一句话你就明白了,好比我把书架上的书比作我们正在排队,突然你中间有一个人走了,你跟你后面的人都要向前挪动一步。换到这儿就是数组的删除,把后面的值赋值给前面,依次进行,当然还是少不了循环遍历。
public class DelOperation implements IOPeration {
@Override
public void work(BookList bookList) {
System.out.println("删除图书!");
System.out.println("请输入你要删除图书的名字:");
Scanner scanner =new Scanner(System.in);
String name=scanner.nextLine();
int currentSize=bookList.getUsedSize();
int index=-1;
for (int i = 0; i < currentSize; i++) {
Book tmp=bookList.getBook(i);
index=i;
break;
}
//挪动数据
for (int j = index; j < currentSize-1; j++) {
Book book=bookList.getBook(j+1);
bookList.setBook(j,book);
}
//修改size的值
bookList.setUsedSize(currentSize-1);
//因为删除的是对象,要把最后一个置为null
bookList.setBook(currentSize-1,null);
System.out.println("删除成功!");
}
}
2.5 归还书籍
归还书籍,是个很简单操作,我们Book类的属性里面有一个借阅标志属性,所谓的归还,就是给书打上归还的标记。
public class ReturnOperation implements IOPeration{
@Override
public void work(BookList bookList) {
System.out.println("归还图书!");
System.out.println("输入你要归还的图书:");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String name = scanner.nextLine();
int currentSize = bookList.getUsedSize();
for (int i = 0; i < currentSize; i++) {
Book book = bookList.getBook(i);
if(book.getName().equals(name) &&
book.isBorrowed()) {
book.setBorrowed(false);
System.out.println("归还成功");
return;
}
}
}
}
2.6 借阅书籍
借阅与归还很相似。
public class BrrowOperation implements IOPeration {
@Override
public void work(BookList bookList) {
System.out.println("借阅图书!");
System.out.println("请输入你要借阅的图书");
Scanner scanner =new Scanner(System.in);
String name=scanner.nextLine();
int currentSize=bookList.getUsedSize();
for (int i = 0; i < currentSize; i++) {
Book book=bookList.getBook(i);
if (book.getName().equals(name)
&& !book.isBorrowed()) {
book.setBorrowed(true);
System.out.println("借阅成功!");
return;
}
}
}
}
2.7 退出系统
我们这里退出系统就是退出控制台。
public class ExitOperation implements IOPeration{
@Override
public void work(BookList bookList) {
System.out.println("退出系统操作!");
System.exit(0);
}
}
三.测试类的方法
public class Main {
//函数主入口
public static User login(){
System.out.println("请输入你的姓名");
Scanner scanner=new Scanner(System.in);
String name=scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入你的身份:1 管理员 ,2 普通用户");
int choice=scanner.nextInt();
if(choice == 1) {
return new AdminUser(name);
}else {
return new NormalUser(name);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BookList bookList=new BookList();
//向上转型
User user=login();
while (true) {
int choice = user.menu();
//根据 choice 和 user 来确定 我到底 调用哪个对象的哪个操作?
user.dowork(choice, bookList);
}
}
//根据 choice 和 user 来确定 我到底 调用哪个对象的哪个操作?
}
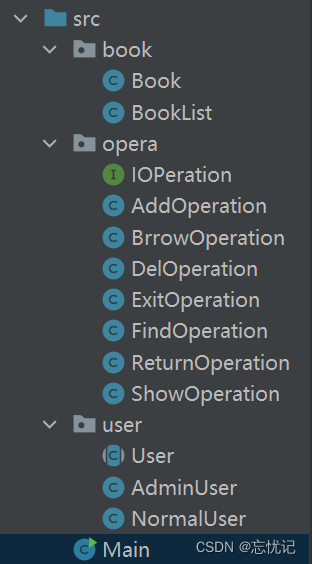
四.项目的目录
我给大家看看我项目的目录,大家运用我的代码,也会更清晰一点。






![[附源码]Node.js计算机毕业设计河南美丽乡村旅游信息网Express](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/37aaa2f439de4713bcd20e715e0625bf.png)
![[附源码]Nodejs计算机毕业设计基于远程协作的汽车故障诊断系统Express(程序+LW)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/fff55294a4f74894921b682db8a7f52a.png)