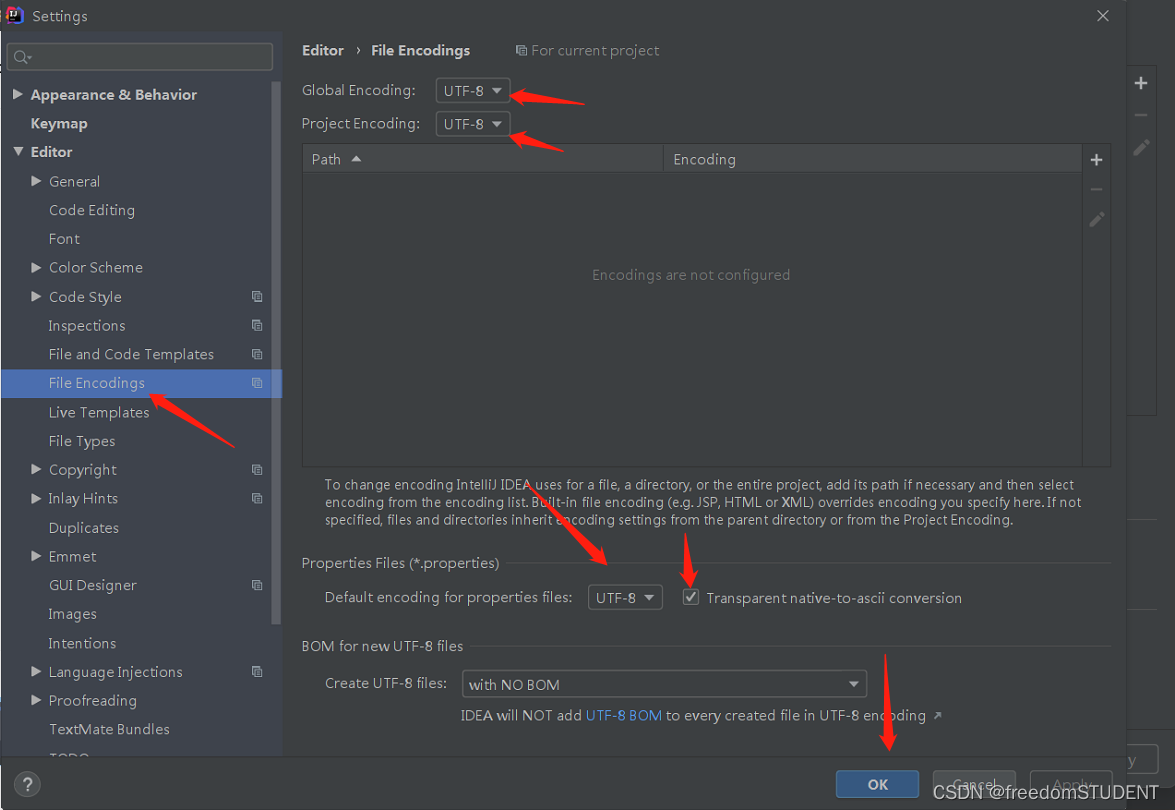
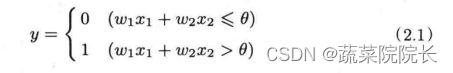1.C++ 编程简介 & 目标
- 培养代码正规编范
- class 分为 带pointer 和 不带pointer的
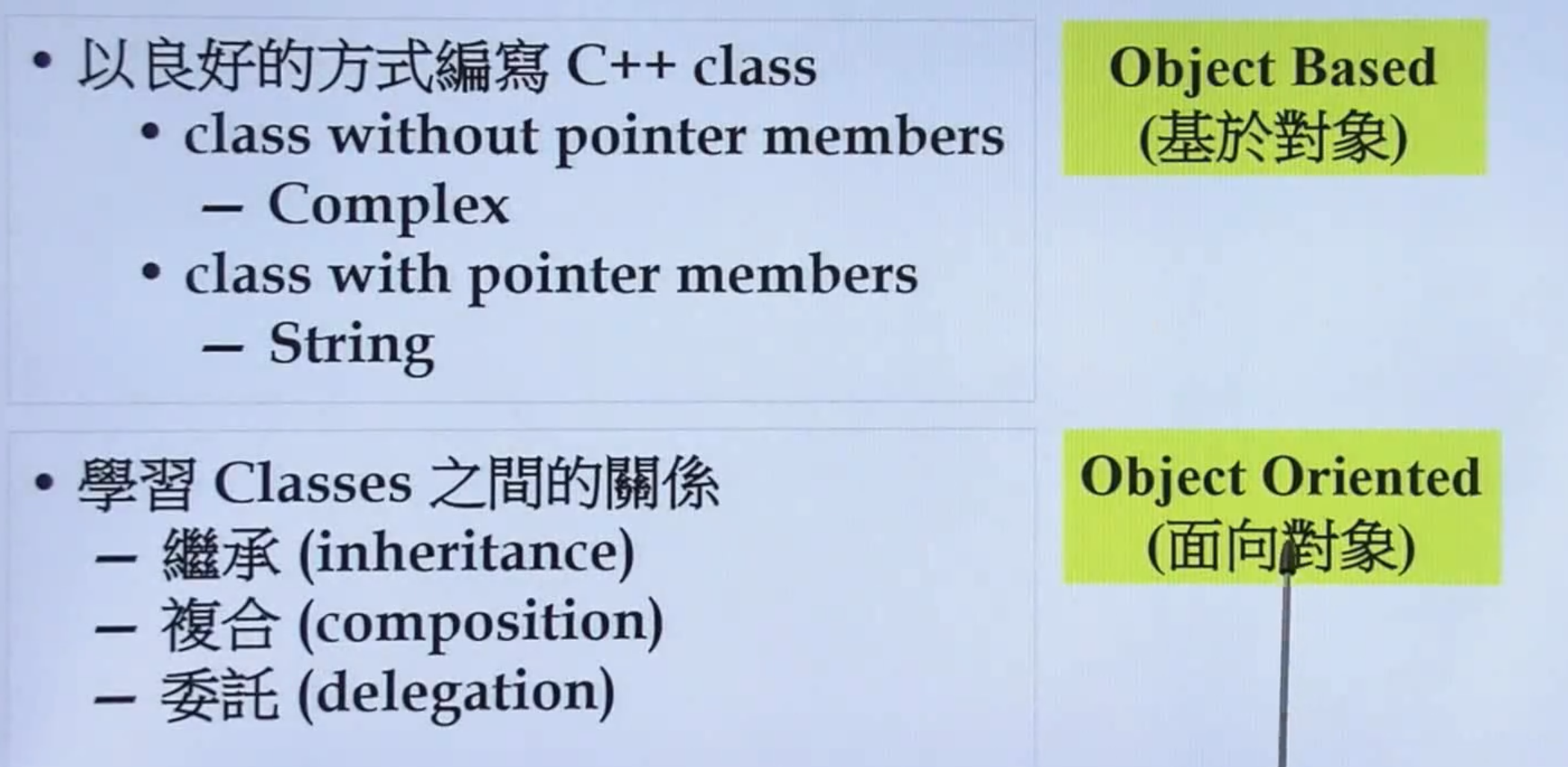
- 学习C++ : 语言 + 标准库
2.C vs C++
- C语言 : (type)数据 + 函数 —create—》 数据s
- C++ : (class ) 数据 + 成员 —create—》 对象
- 不带指针的类 :complex 复数
- 带指针的类 : string 字符串
- 如果是自己写的头文件 那就必须加上防卫式的声明
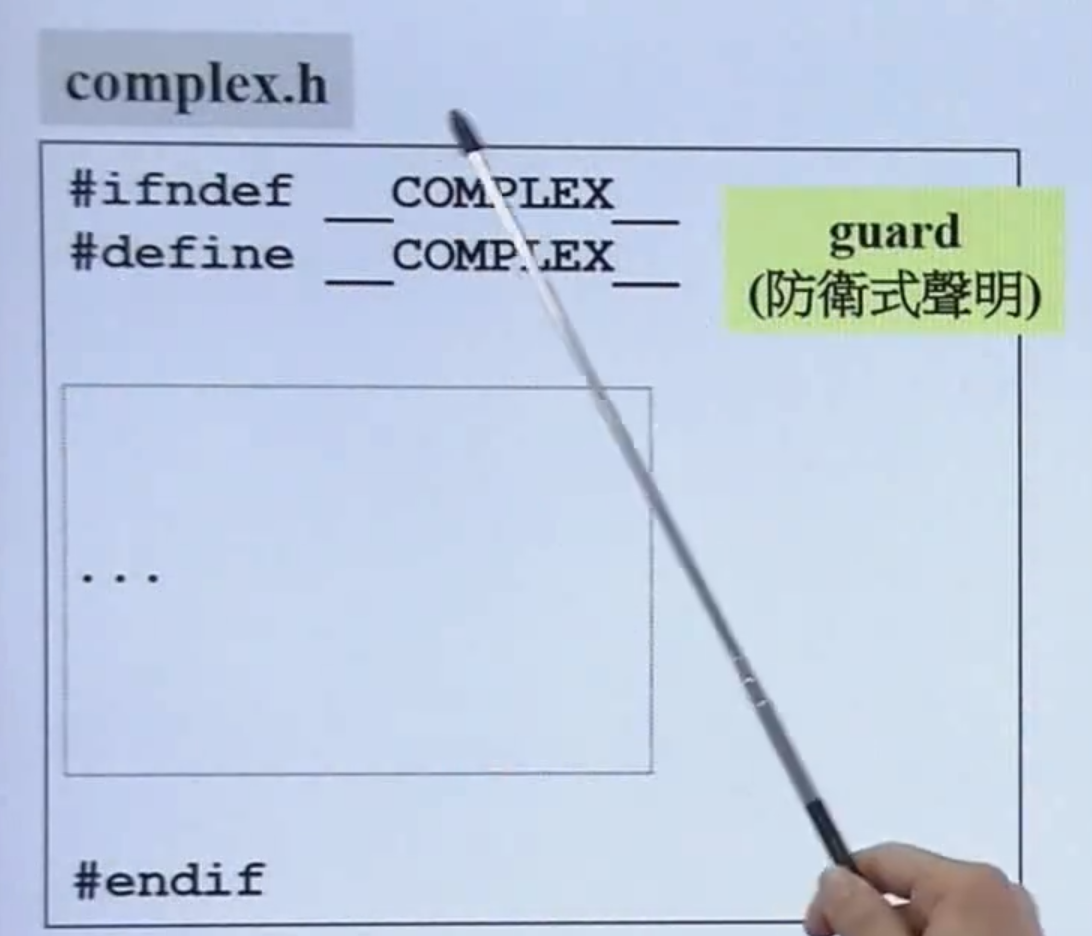
- 头文件布局:
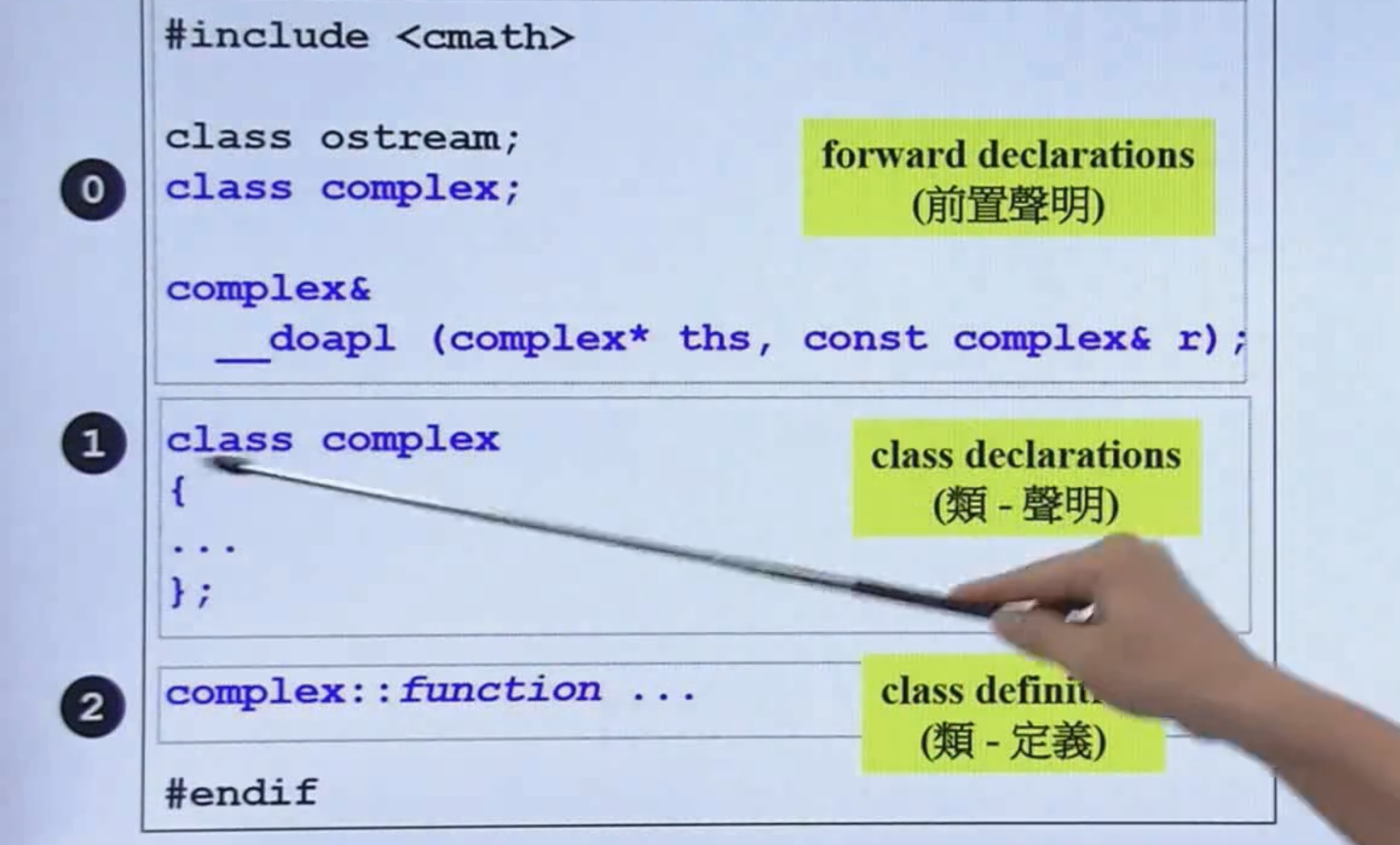
- 然后就是body/ 函数设计
- 函数可以直接在body定义 (inline 函数) 或者 在外部定义
- inline 函数 :比较快 比较好 并不是什么函数都可以是 inline 如果函数太复杂就不行, 能否inline 仍然又编译器决定。
- private : 数据部分 写函数调用获取 prublic 俩部分可以分很多段写
3.构造函数
- C++ 如果创建一个对象 ,自动调用的函数 就是构造函数
- 函数名称 与 类名称一样
- 初值列表 : 构造函数独有的 , 不适用 赋值的方式 先执行初值列表,再执行body里面的, 如果使用赋值 就会影响效率 比较差

- 构造函数不需要写类型 不带指针的类多半不需要写虚构函数
- 构造函数可以有很多个 overloading(重载)
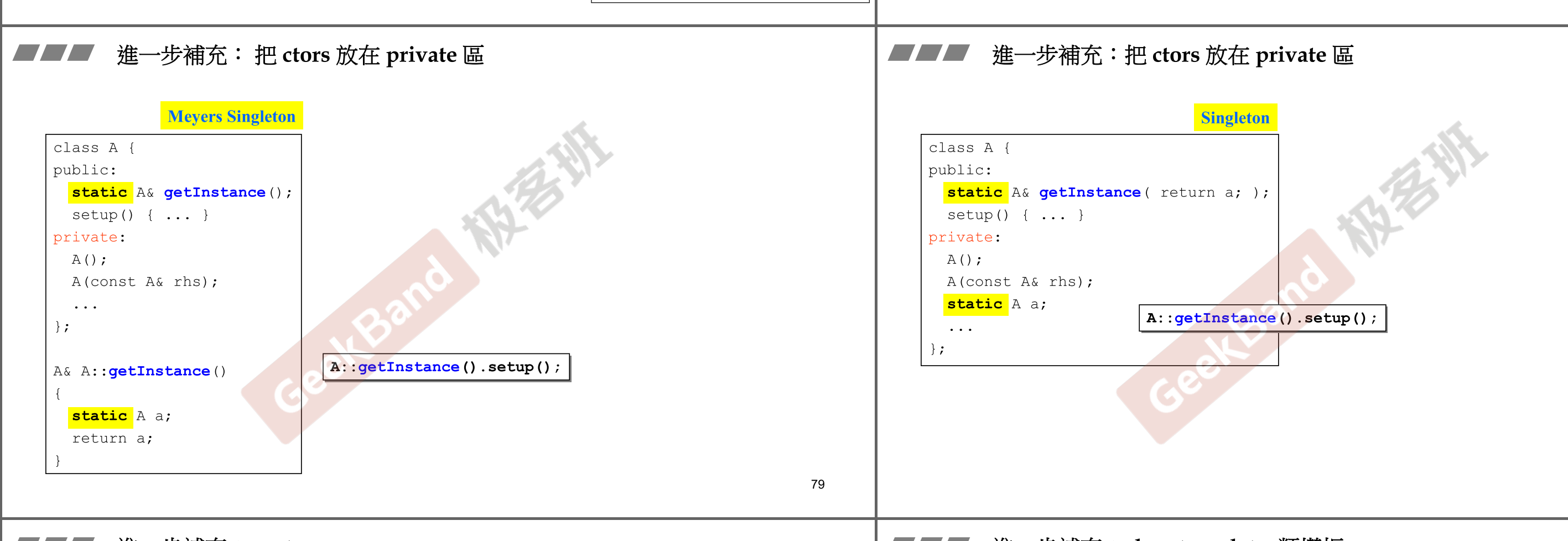
- 构造函数如果放在private 区 将无法被外界调用 但可以使用单例模式 进行设计

- 凡是对不会改变的变量 通通加上const 变成常量成员函数
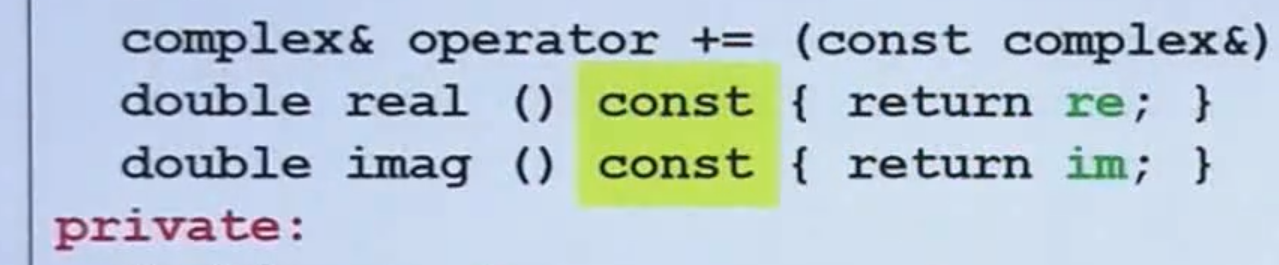
- 如果定义是const 但是 real 和imag、函数都没加const 则会报错

传参 or 传引用?
- 传值的话,值多大 就传多大,传的动作加上压到函数的栈里面去, 多少个byte就穿多少, 传指针 == 传地址 4byte
- 传引用 0 byte , 比指针更好 , 相当于传指针, 快, 最好都是传引用 , 如果传过去的变量,不希望对方修改,那么就必须加上const
返回传递 return by value vs return by reference(to const)
- 如果在可以的情况下 必须 return by reference(to const)
- 如果不是(局部)local object 就可以传引用
- 比如在函数中创建一个变量, 然后对这啊 v f个变量进行return by referenbce, 变量脱离函数就会销毁, 所以不能 return by referenbce
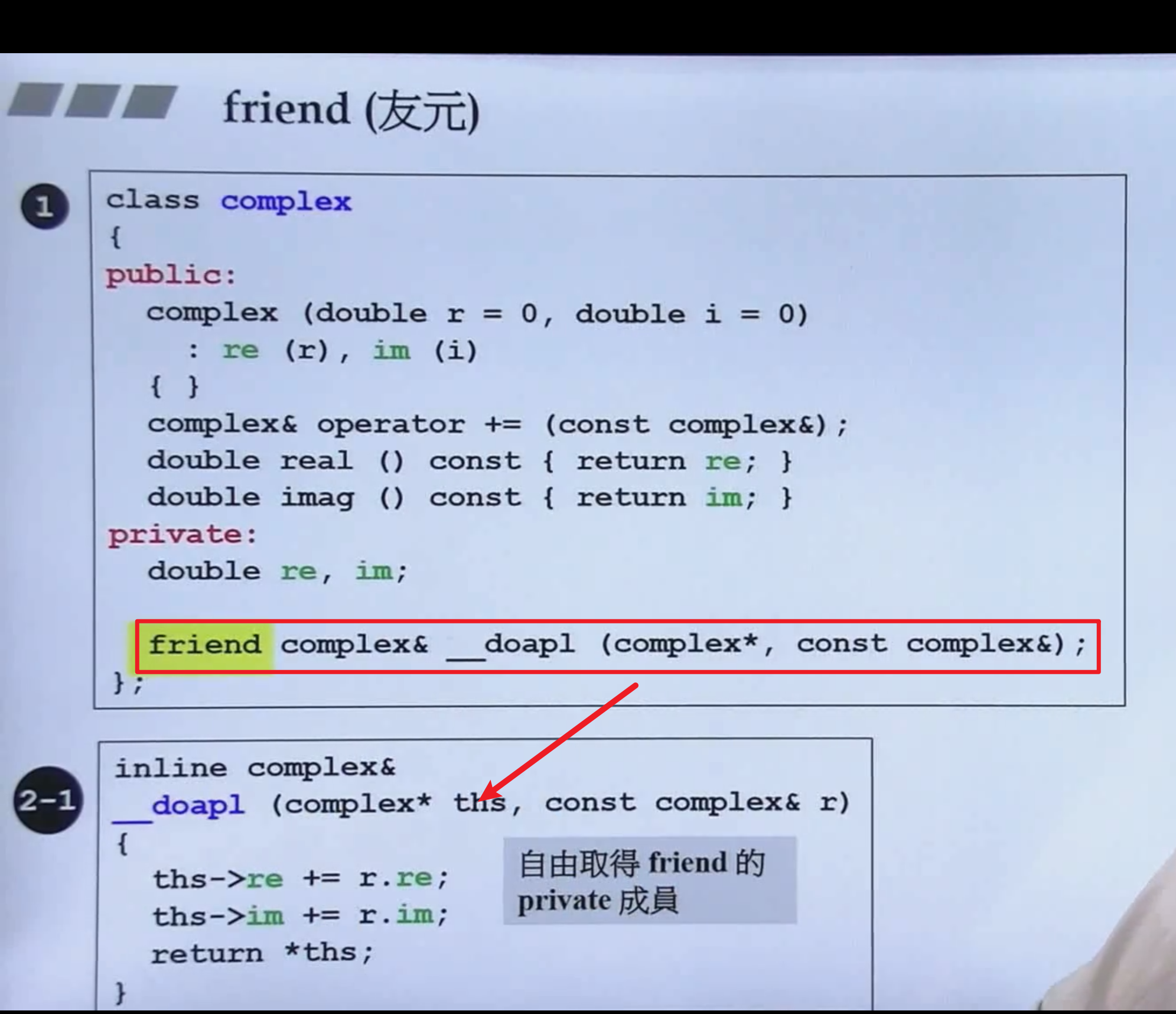
友元 friend
-
设置friend 就可以直接获取 和public一样, 但是不写friend 获取就只能通过函数,效率会下降.
-
05 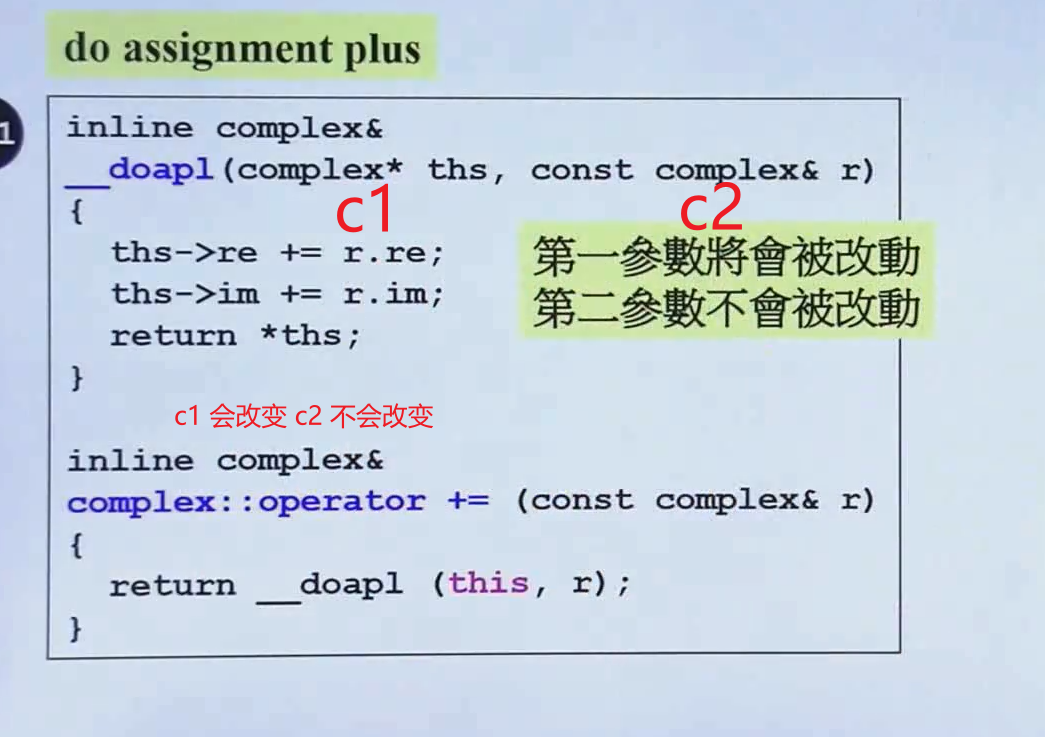
- 首要考虑 & 然后再看 , 使用 & 会不会出错,如果会就改80
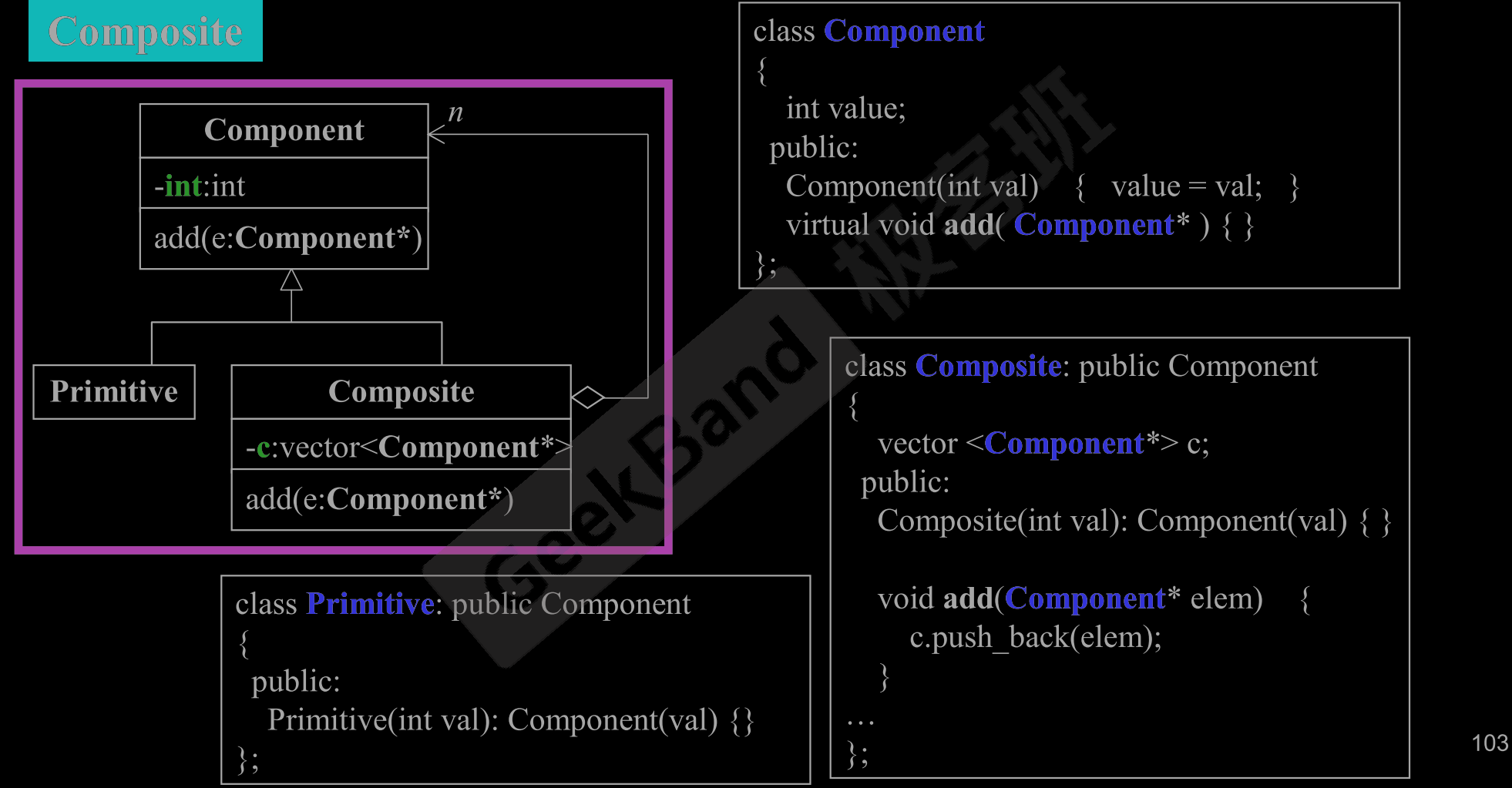
4.操作符重载
complex.h
#ifndef __MYCOMPLEX__
#define __MYCOMPLEX__
class complex;
complex&
__doapl (complex* ths, const complex& r);
complex&
__doami (complex* ths, const complex& r);
complex&
__doaml (complex* ths, const complex& r);
class complex
{
public:
complex (double r = 0, double i = 0): re (r), im (i) { }
complex& operator += (const complex&);
complex& operator -= (const complex&);
complex& operator *= (const complex&);
complex& operator /= (const complex&);
double real () const { return re; }
double imag () const { return im; }
private:
double re, im;
friend complex& __doapl (complex *, const complex&);
friend complex& __doami (complex *, const complex&);
friend complex& __doaml (complex *, const complex&);
};
inline complex&
__doapl (complex* ths, const complex& r)
{
ths->re += r.re;
ths->im += r.im;
return *ths;
}
inline complex&
complex::operator += (const complex& r)
{
return __doapl (this, r);
}
inline complex&
__doami (complex* ths, const complex& r)
{
ths->re -= r.re;
ths->im -= r.im;
return *ths;
}
inline complex&
complex::operator -= (const complex& r)
{
return __doami (this, r);
}
inline complex&
__doaml (complex* ths, const complex& r)
{
double f = ths->re * r.re - ths->im * r.im;
ths->im = ths->re * r.im + ths->im * r.re;
ths->re = f;
return *ths;
}
inline complex&
complex::operator *= (const complex& r)
{
return __doaml (this, r);
}
inline double
imag (const complex& x)
{
return x.imag ();
}
inline double
real (const complex& x)
{
return x.real ();
}
inline complex
operator + (const complex& x, const complex& y)
{
return complex (real (x) + real (y), imag (x) + imag (y));
}
inline complex
operator + (const complex& x, double y)
{
return complex (real (x) + y, imag (x));
}
inline complex
operator + (double x, const complex& y)
{
return complex (x + real (y), imag (y));
}
inline complex
operator - (const complex& x, const complex& y)
{
return complex (real (x) - real (y), imag (x) - imag (y));
}
inline complex
operator - (const complex& x, double y)
{
return complex (real (x) - y, imag (x)); // 被减数
}
inline complex
operator - (double x, const complex& y)
{
return complex (x - real (y), - imag (y)); // 减数
}
inline complex
operator + (const complex& x) // 正值
{
return x;
}
inline complex
operator - (const complex& x) // 负值
{
return complex (-real (x), -imag (x));
}
inline complex
operator * (const complex& x, const complex& y)
{
return complex (real (x) * real (y) - imag (x) * imag (y),
real (x) * imag (y) + imag (x) * real (y));
}
inline complex
operator * (const complex& x, double y)
{
return complex (real (x) * y, imag (x) * y);
}
inline complex
operator * (double x, const complex& y)
{
return complex (x * real (y), x * imag (y));
}
complex
operator / (const complex& x, double y)
{
return complex (real (x) / y, imag (x) / y);
}
inline bool
operator == (const complex& x, const complex& y)
{
return real (x) == real (y) && imag (x) == imag (y);
}
inline bool
operator == (const complex& x, double y)
{
return real (x) == y && imag (x) == 0;
}
inline bool
operator == (double x, const complex& y)
{
return x == real (y) && imag (y) == 0;
}
inline bool
operator != (const complex& x, const complex& y)
{
return real (x) != real (y) || imag (x) != imag (y);
}
inline bool
operator != (const complex& x, double y)
{
return real (x) != y || imag (x) != 0;
}
inline bool
operator != (double x, const complex& y)
{
return x != real (y) || imag (y) != 0;
}
#include <cmath>
inline complex
polar (double r, double t)
{
return complex (r * cos (t), r * sin (t));
}
inline complex
conj (const complex& x) //鍏辫江澶嶆暟
{
return complex (real (x), -imag (x));
}
inline double
norm (const complex& x)
{
return real (x) * real (x) + imag (x) * imag (x);
}
#endif //__MYCOMPLEX__
5.类的区分

就是成员函数是否带指针
6.浅拷贝 & 深拷贝
在 C++ 中,浅拷贝和深拷贝是两种不同的复制对象的方法。浅拷贝是通过简单地复制原始对象的所有变量的数据来创建一个对象。这种方法适用于对象的变量没有在堆内存区域定义的情况。如果某些变量是从堆内存区域动态分配的内存,则复制的对象变量也将引用相同的内存位置。这将导致歧义和运行时错误,悬空指针。由于两个对象都将引用相同的内存位置,因此一个对象所做的更改也会反映在另一个对象上。由于我们希望创建一个对象的副本,因此浅拷贝无法实现这一目的。
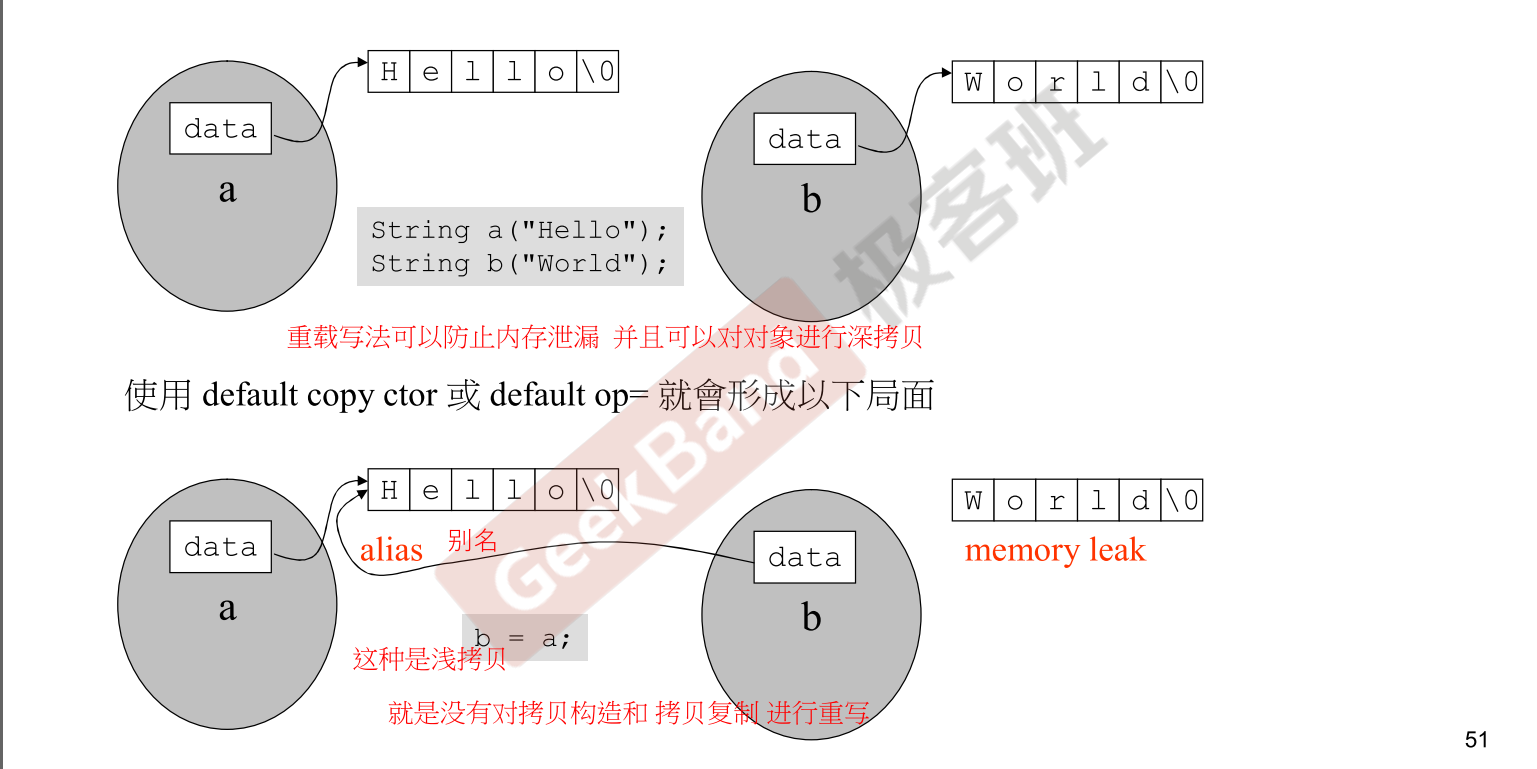
深拷贝是通过复制所有变量的数据并为对象分配相同值的类似内存资源来创建一个对象。为了执行深拷贝,我们需要显式地定义复制构造函数并根据需要分配动态内存。此外,还需要在其他构造函数中为变量动态分配内存 。
inline
String::String(const String& str) // 拷贝本身 收到的参数就是它本身
{
m_data = new char[ strlen(str.m_data) + 1 ];
strcpy(m_data, str.m_data);
}

准确性 !!

7.stack和heap
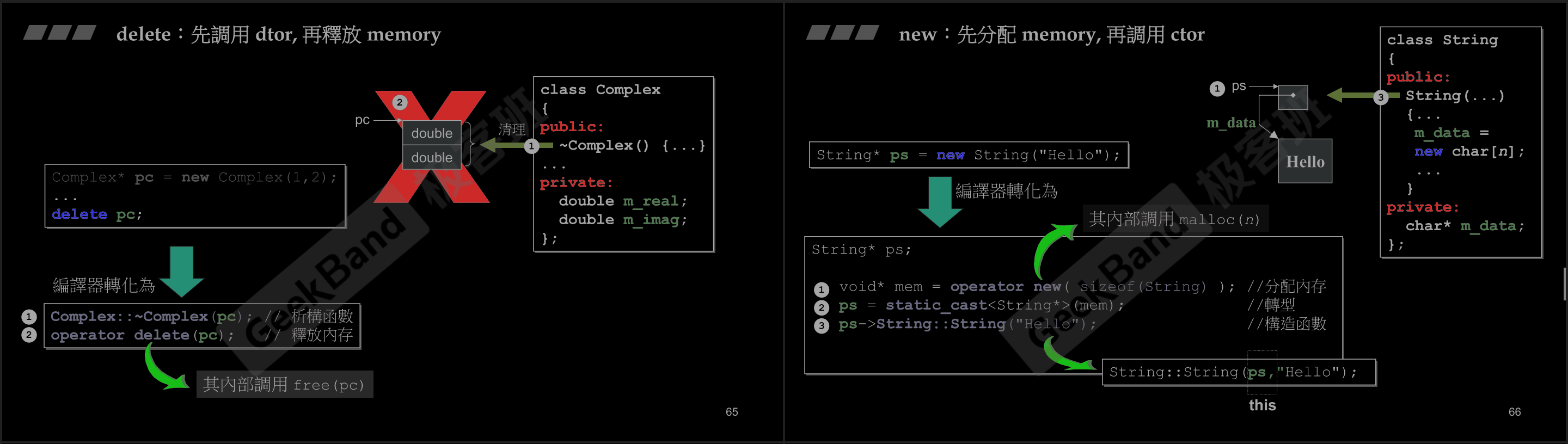
Stack是存在于某作用域 (scope) 的一块内存空间 (memory space)。例如当你调用函数,函数本身即会形成一个 stack 用来放置它所接收的参数,以及返回地址。在函数本体 (function body) 内声明的任何变量,其所使用的内存块都取自上述 stack。Heap,或谓 system heap,是指由操作系统提供的一块 global 内存空间,程序可动态分配 (dynamic allocated)从某中获得若干区块 (blocks)。希望这些信息对您有所帮助!如果您有其他问题,请随时告诉我。- 你可以在程序的任何地方
new它, 但是你就必须要有delete它的职责。


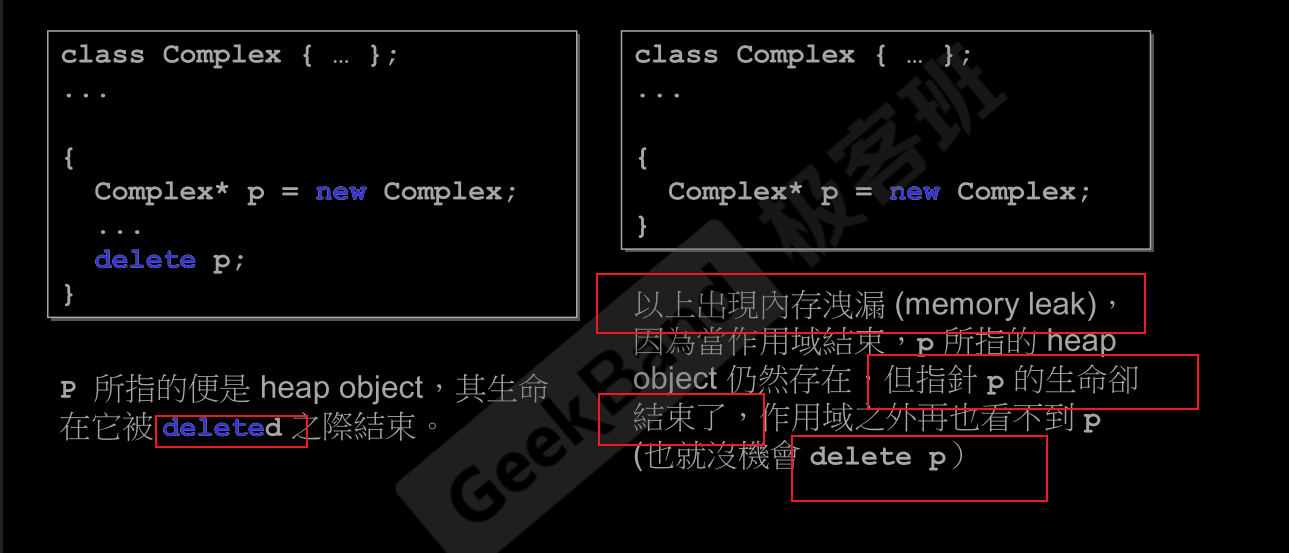
new & delete操作
new和delete都会调用C语言中的malloc和free函数
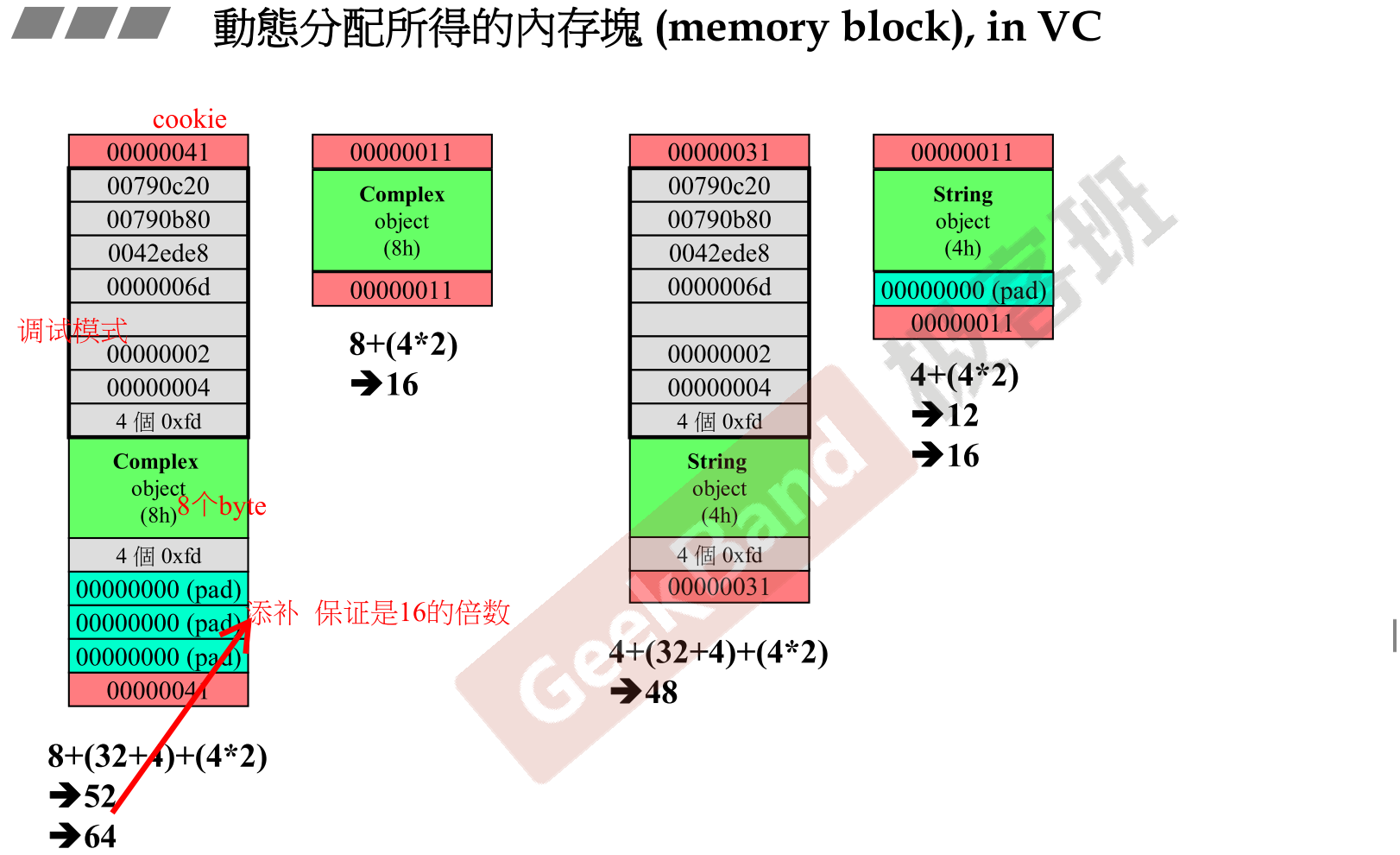
memory block
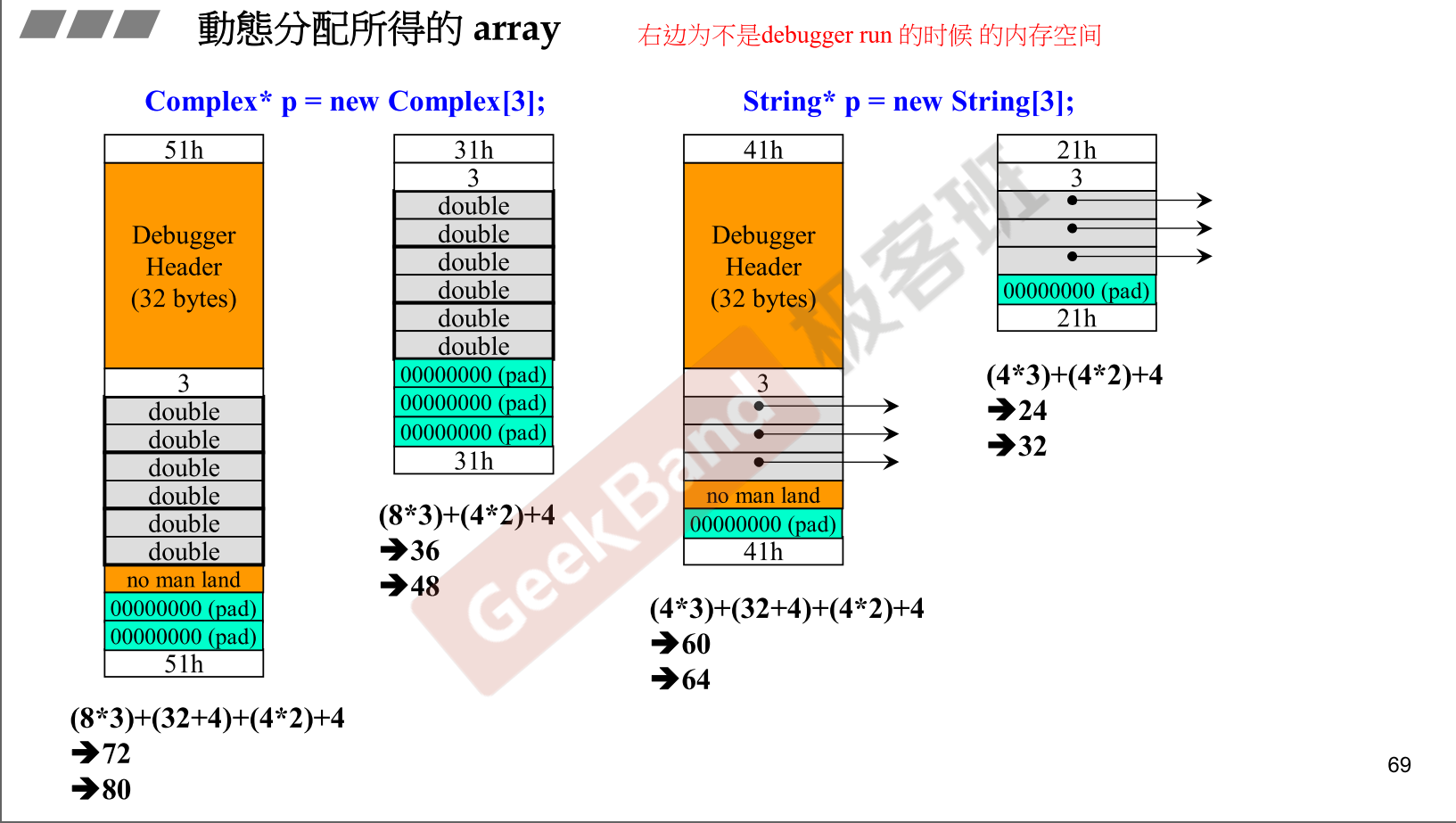
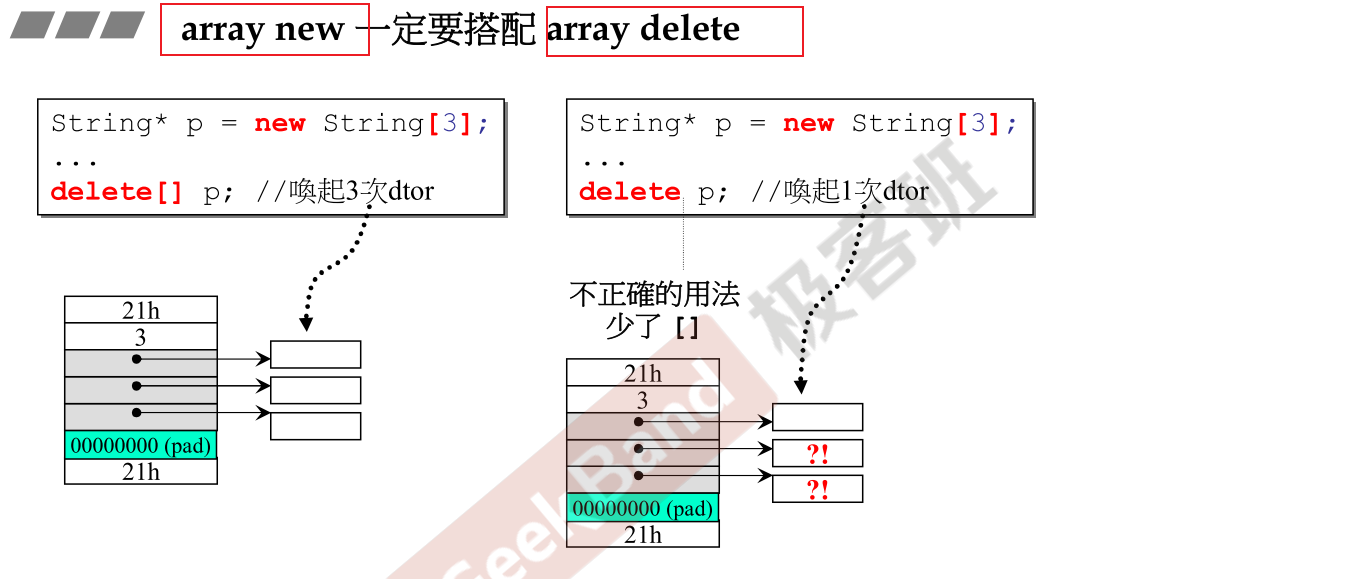
- 保证万无一失
string类
#ifndef __MYSTRING__
#define __MYSTRING__
class String
{
public:
// 如果成员函数为指针 , 必须重写拷贝构造 和 拷贝复制 ,
// 不然系统会 一个字节一个字节复制
String(const char* cstr=0); //拷贝构造
String(const String& str); //拷贝构造 拷贝本身()
String& operator=(const String& str); // 拷贝复制
~String();
char* get_c_str() const { return m_data; } // 获取c风格的 str
private:
char* m_data;
};
#include <cstring>
inline
String::String(const char* cstr)
{
if (cstr) {
m_data = new char[strlen(cstr)+1];
strcpy(m_data, cstr);
}
else {
m_data = new char[1];
*m_data = '\0';
}
}
inline
String::~String()
{
delete[] m_data;
}
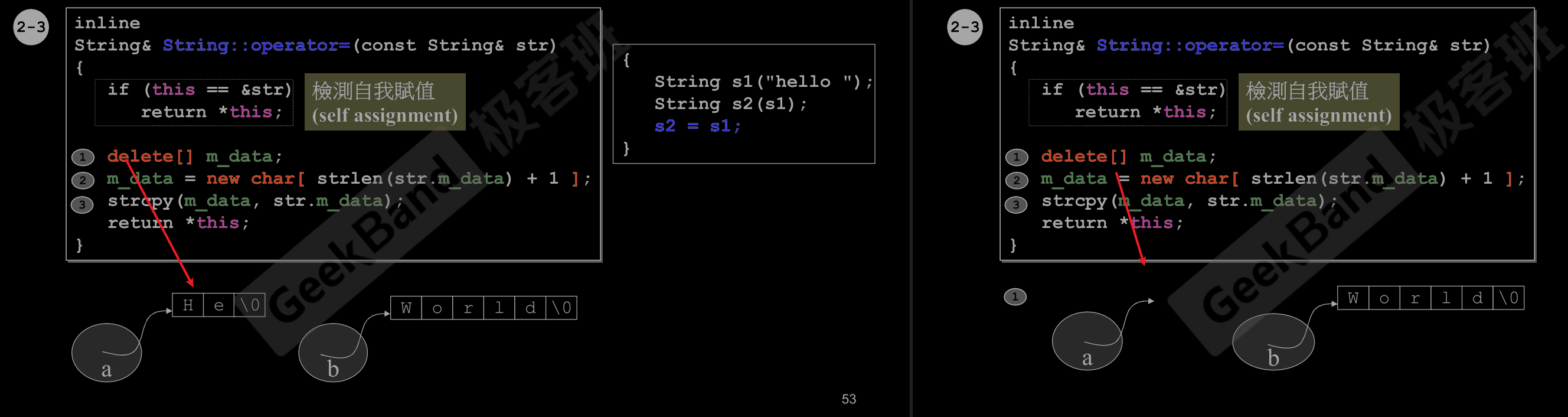
inline
String& String::operator=(const String& str) //
{
if (this == &str) // 检测自我赋值
return *this;
delete[] m_data;
m_data = new char[ strlen(str.m_data) + 1 ];
strcpy(m_data, str.m_data);
return *this;
}
inline
String::String(const String& str) // 拷贝本身
{
m_data = new char[ strlen(str.m_data) + 1 ];
strcpy(m_data, str.m_data);
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const String& str)
{
os << str.get_c_str();
return os;
}
#endif
8.Static
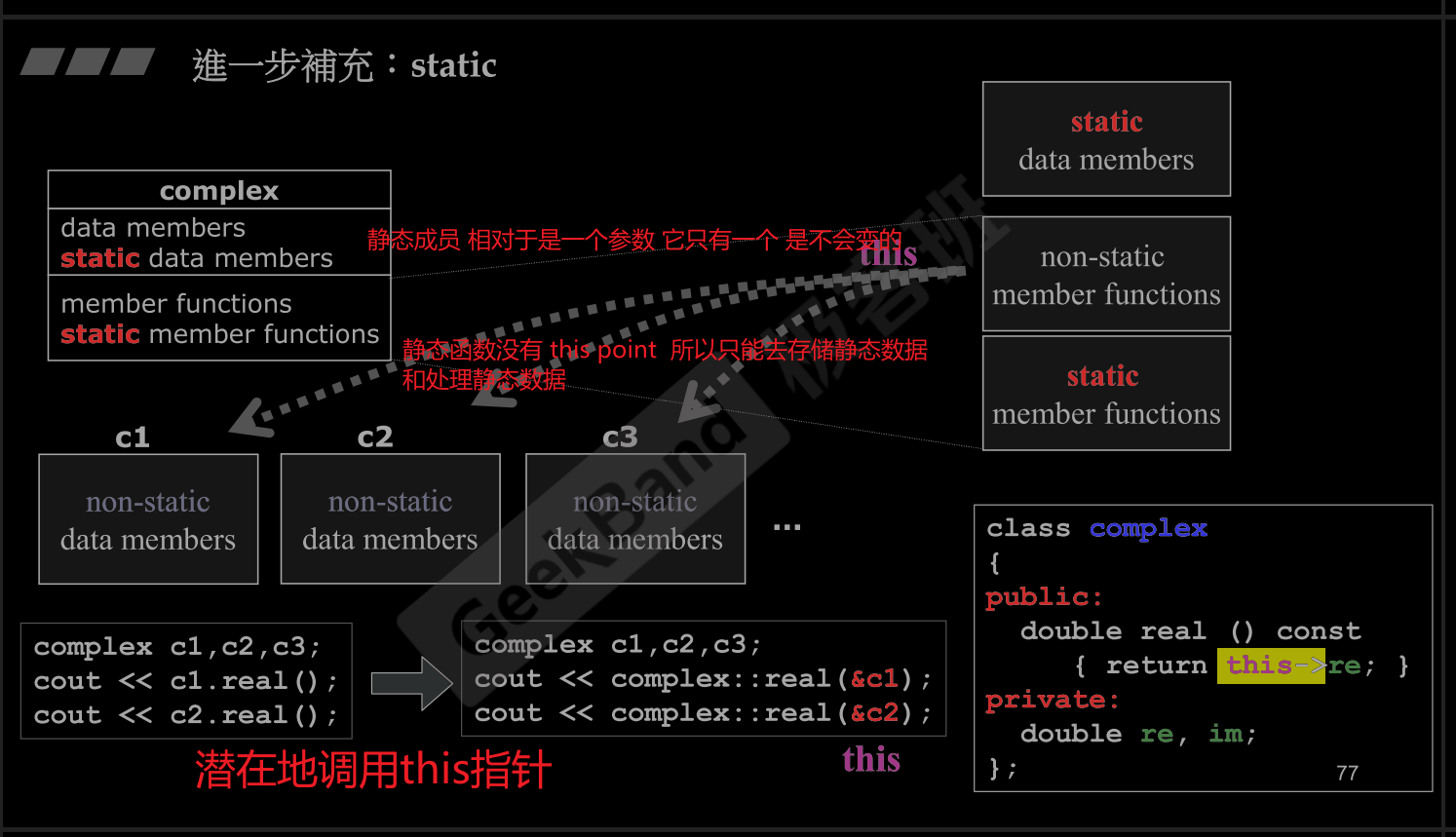
- static example : 利率 每个人都一样
- static 控制static 变量
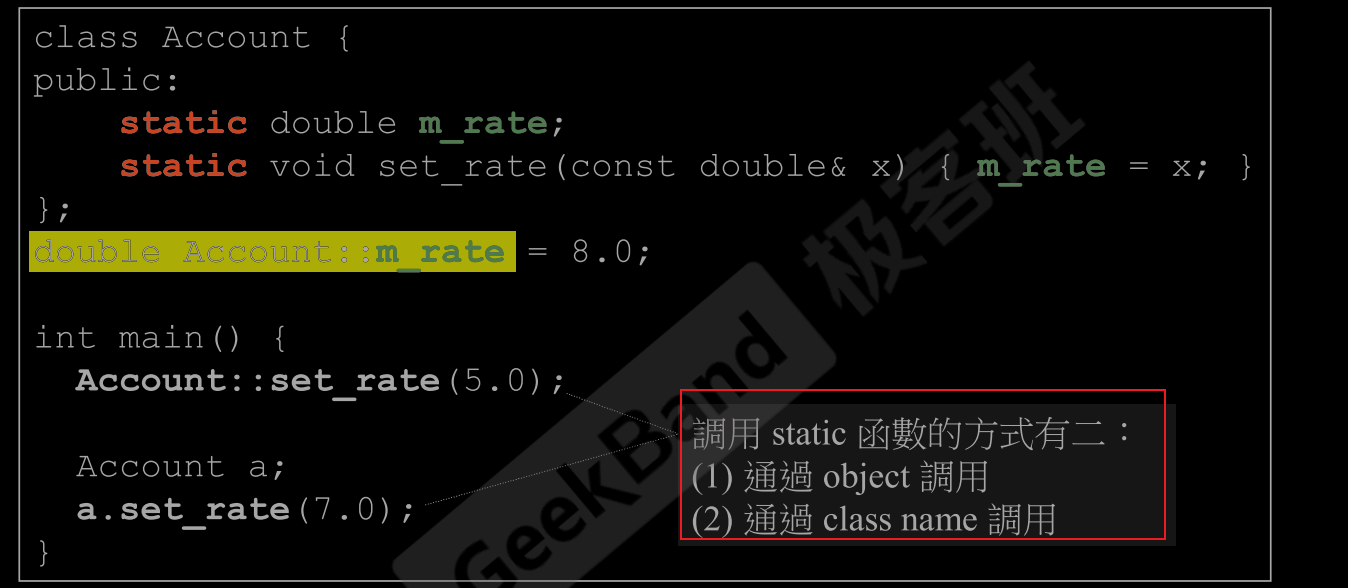
- static 变量只有定义后才会出现
- 一种设计模式 : 将构造函数 放在
private里面
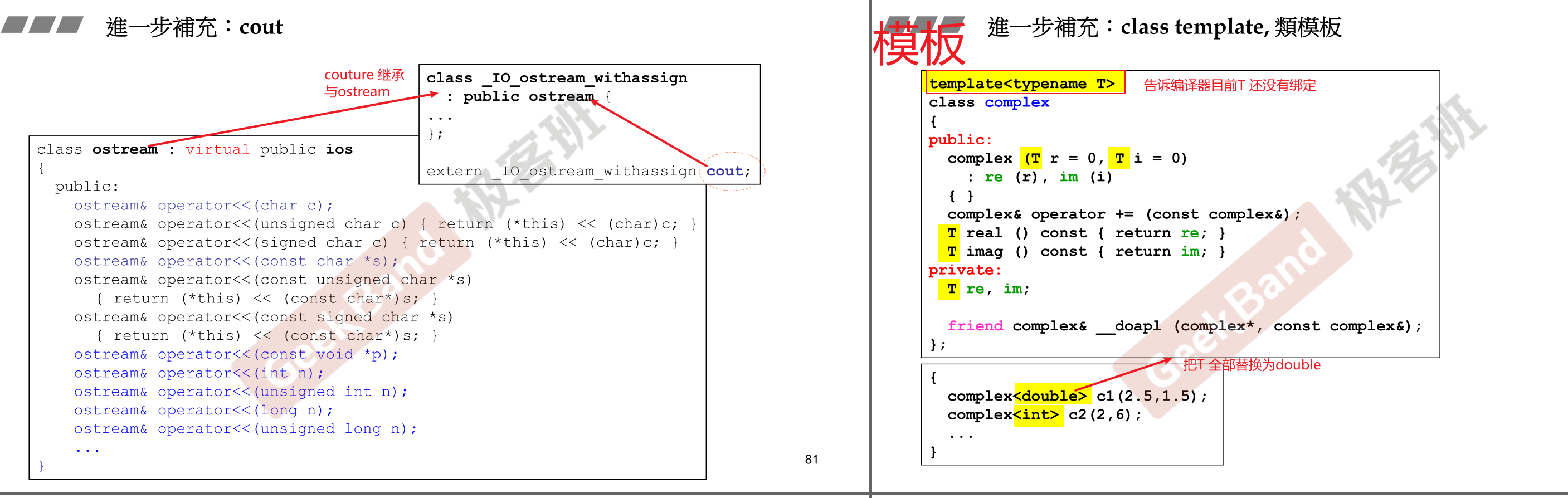
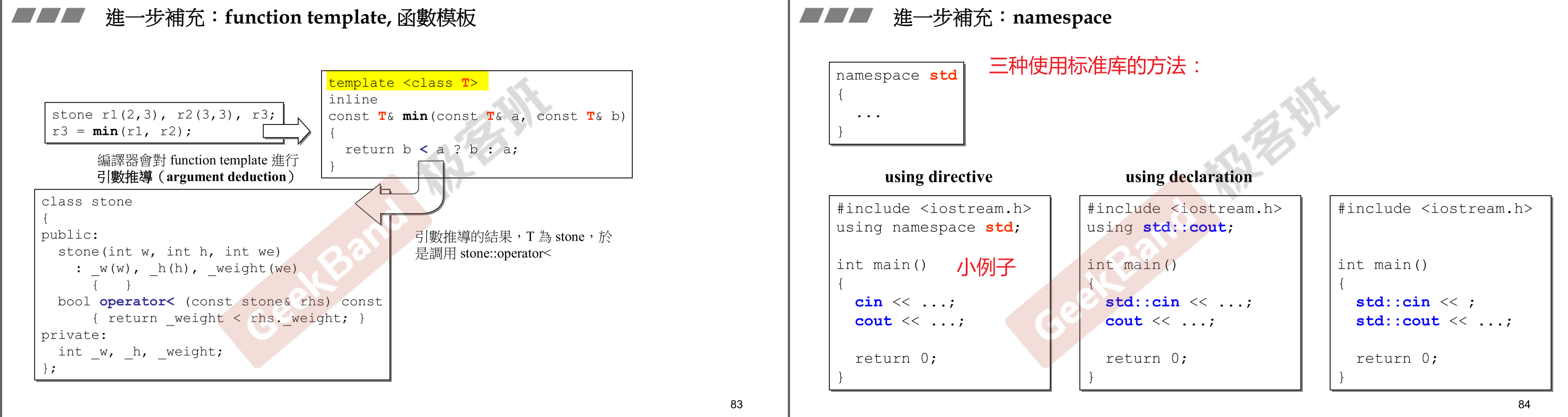
cout和 模板
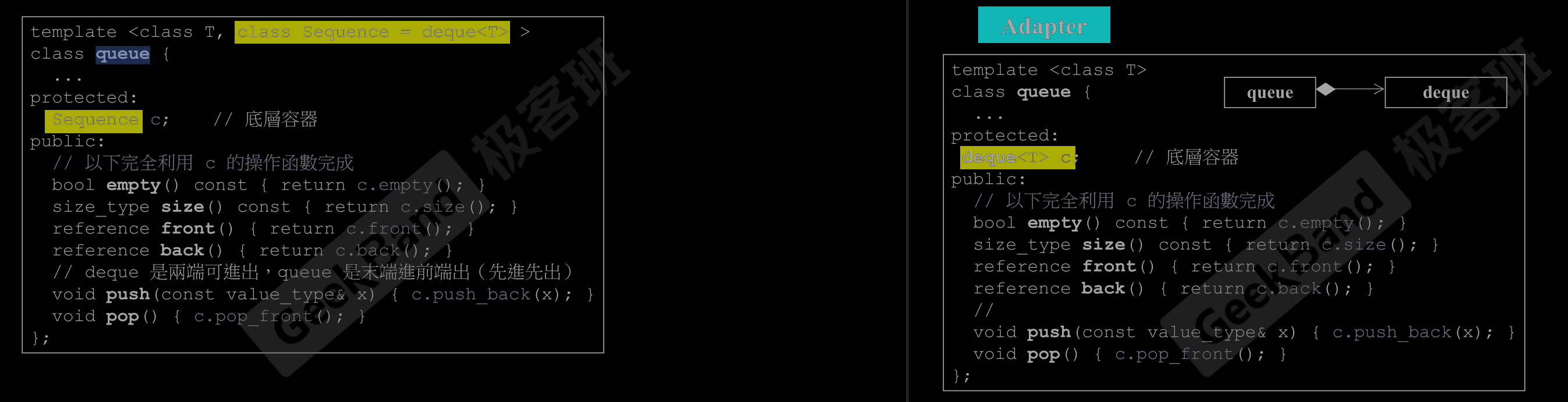
9.继承、符合、委托
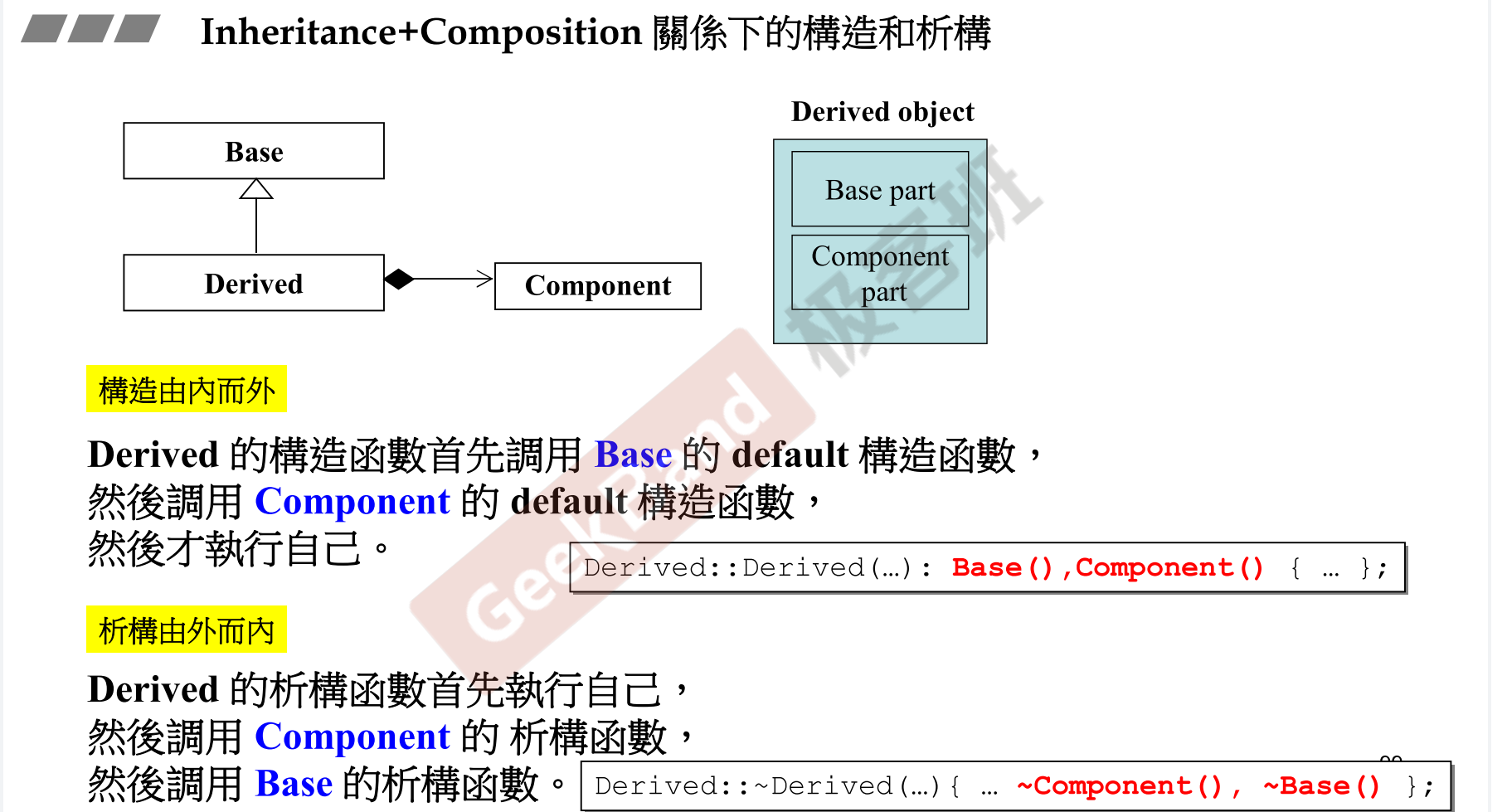
Composition (複合)
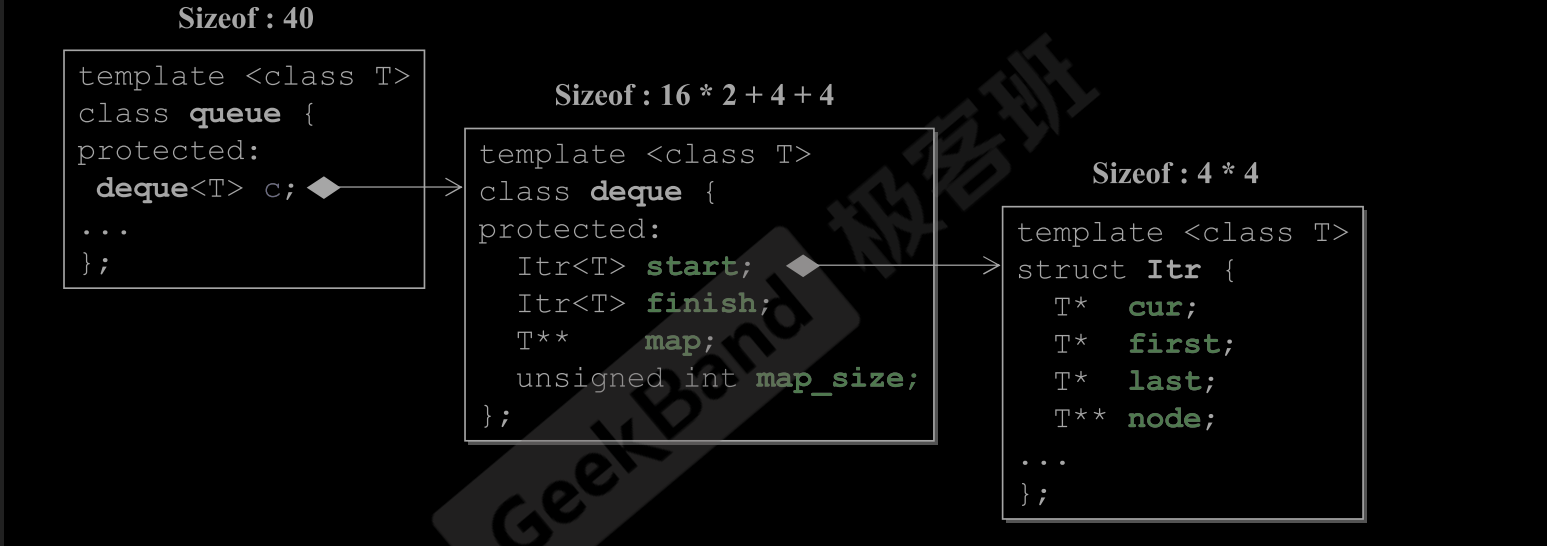
- 内存部分 : 内存空间
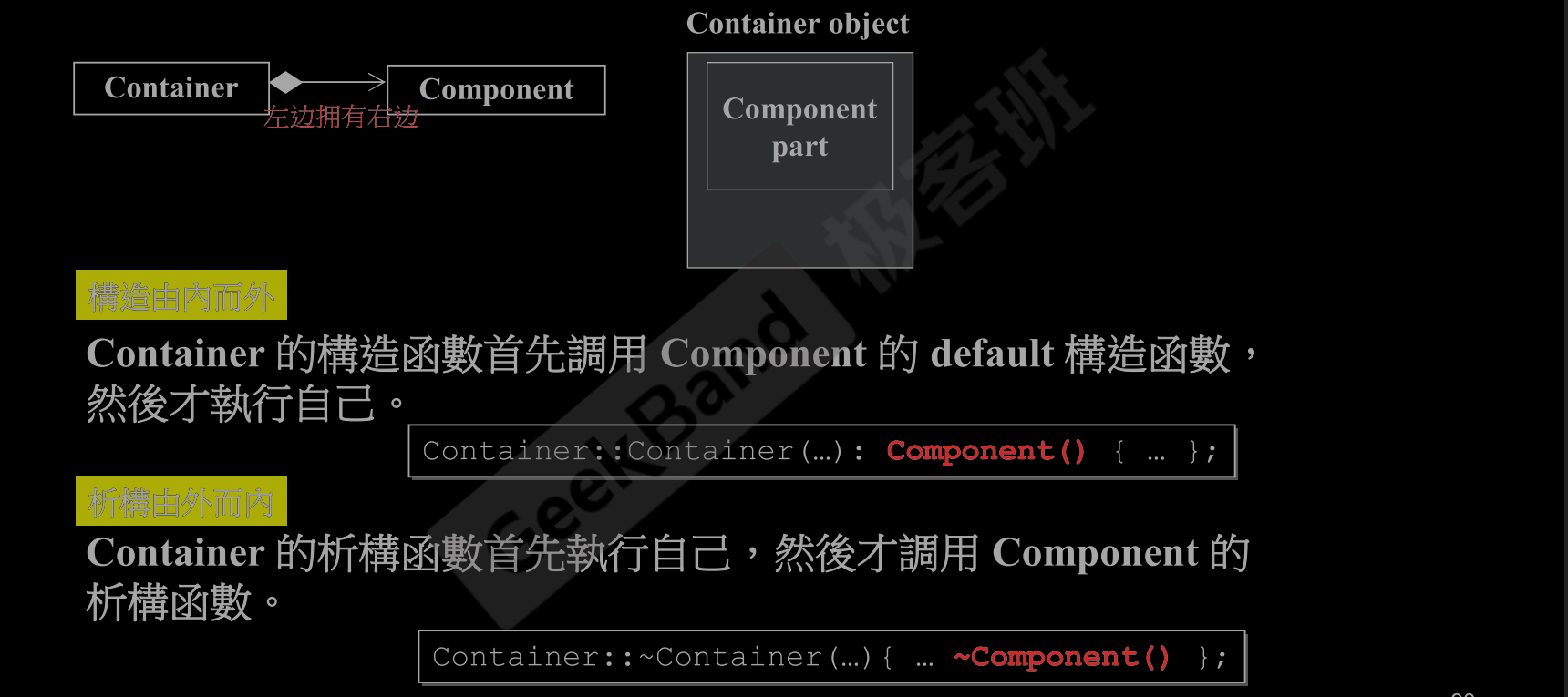
- 调用顺序
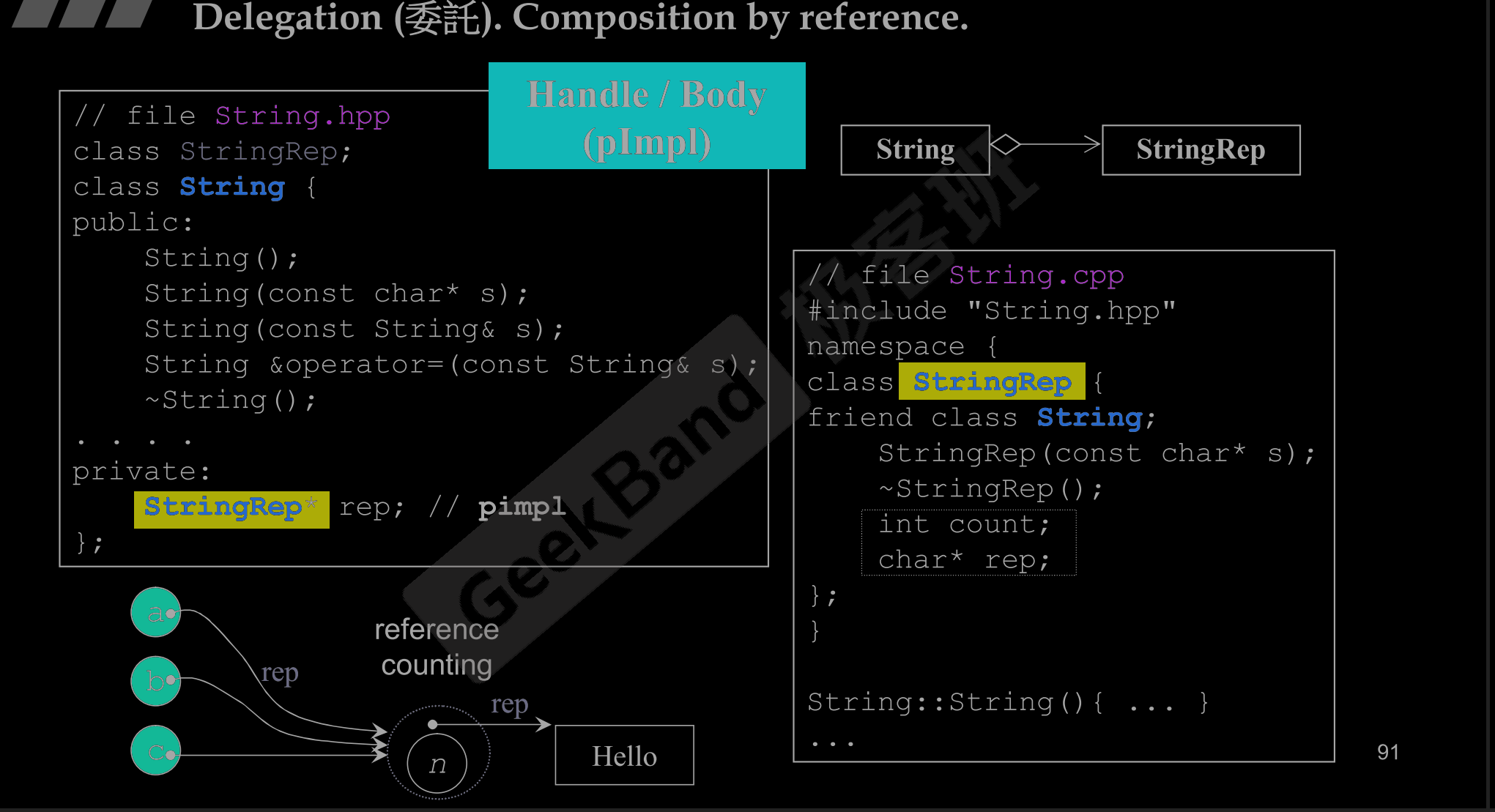
Delegation (委托 ). Composition by reference.
- 用指针相连 , 字符串怎么设计 , 怎么实现,都在另一个类来实现 。
- pImpl : point to implement 可实现 引用计数 & 共享
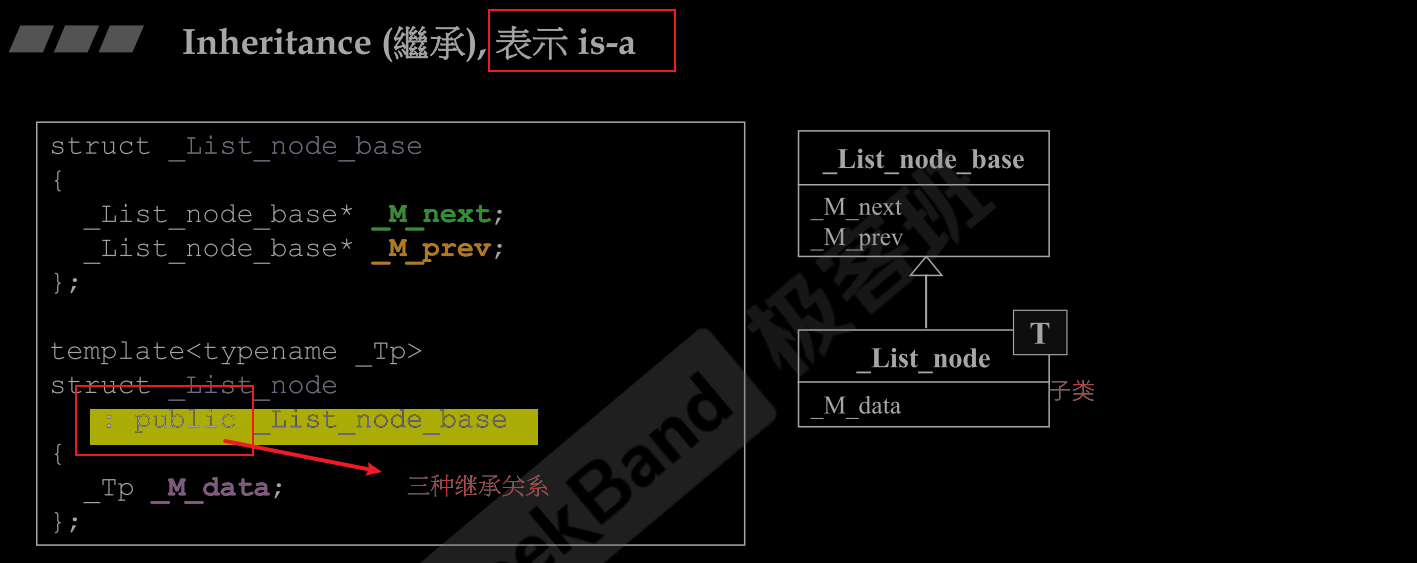
Inheritance (繼承), 表示 is-a
- 内存关系 :

10.虚函数与多态
- override 重写 这个名词是针对于继承设计的
- non-virtual 非虚函数:你不希望派生类重写 (override, 覆盖) 它。
- virtual虚函数:你希望派生类重写 (override, 覆盖) 它,且你对它已有默认定义。
- pure virtual 纯虚函数:你希望派生类一定要重写 (override 覆盖) 它,你对它没有默认定义
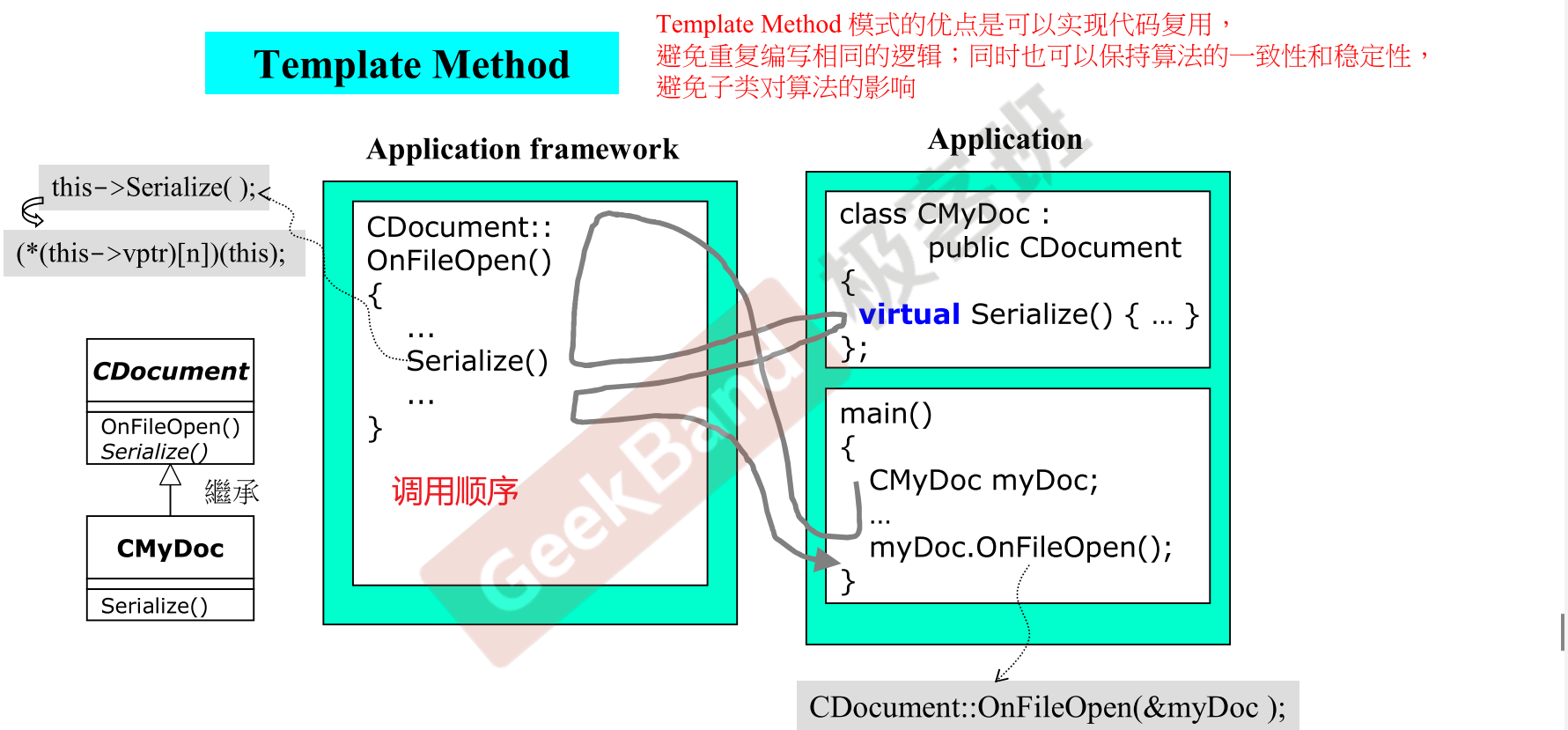
Delegation (委託) + Inheritance (繼承)
如何设计几个窗口, 内容是共享的, 一个改变 另外的类也会改变 ?
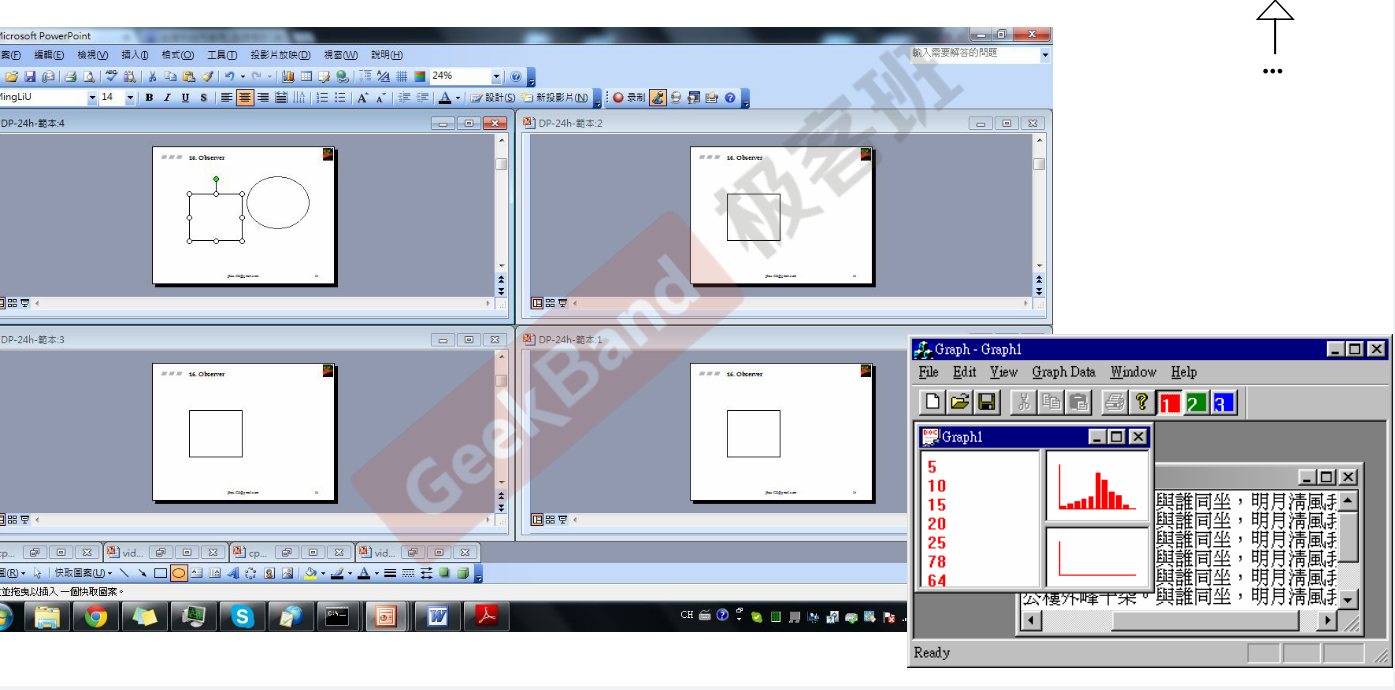
- Observer 设计模式 :
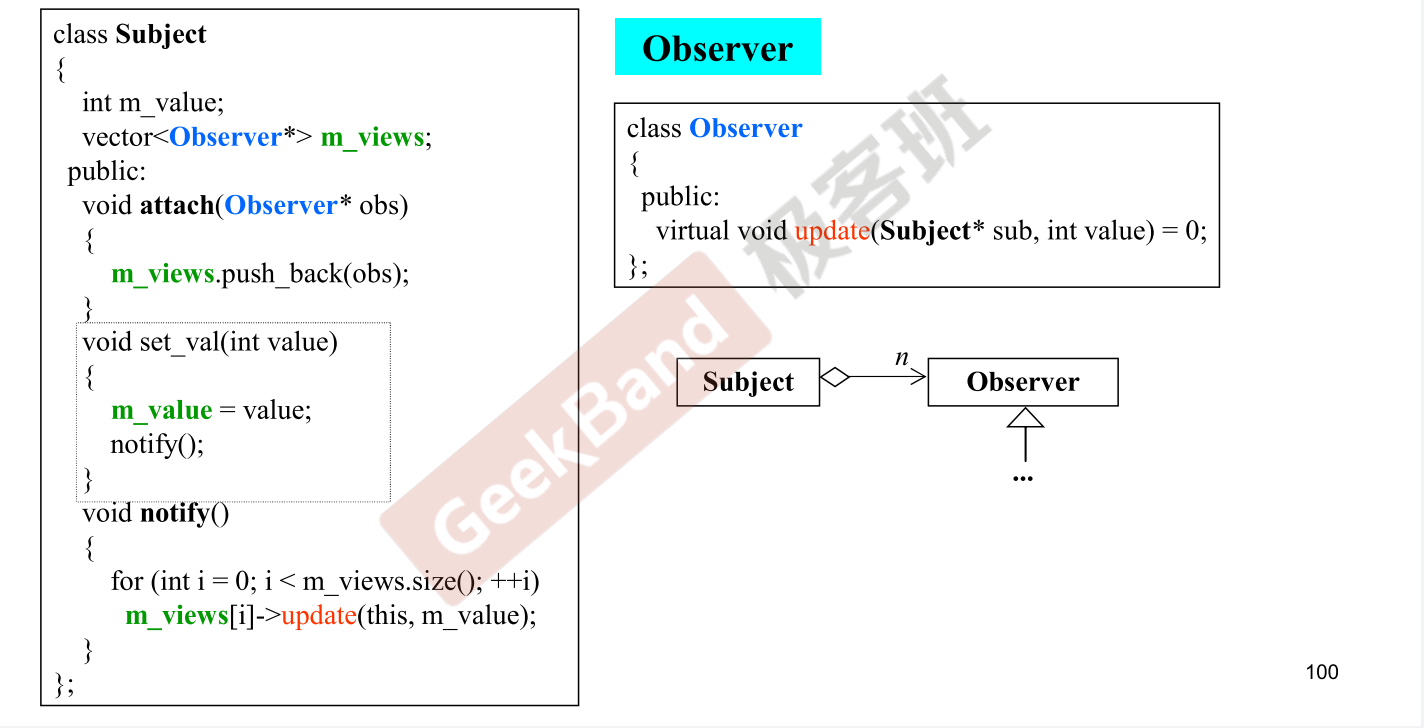
11.委托相关设计