ARTS 2023.8.28-2023.9.03 (第二周)
💡ARTS:
A:至少每周完成一道Leecode的算法题;
R:阅读并点评至少一篇英文技术文章;
T:学习至少一个技术技巧;
S:分享一篇有观点和思考的技术文章;
Algorithm🤦♀️
题目:28.找出字符串中第一个匹配项的下标
给你两个字符串 haystack 和 needle ,请你在 haystack 字符串中找出 needle 字符串的第一个匹配项的下标(下标从 0 开始)。如果 needle 不是 haystack 的一部分,则返回 -1 。
示例 1:
输入:haystack = “sadbutsad”, needle = “sad” 输出:0 解释:“sad” 在下标 0 和 6 处匹配。 第一个匹配项的下标是 0 ,所以返回 0 。
示例 2:
输入:haystack = “leetcode”, needle = “leeto” 输出:-1 解释:“leeto” 没有在 “leetcode” 中出现,所以返回 -1 。
解题思路:
1.先获取needle 字符串的一个字符 A(任意字符,这里使用A来代替),然后在haystack 里遍历寻找出现A的位置i;然后在截取字符串i 到 i + needle .length() 的字符串与needle 比较,如果相等则i就是下标;
public static int strStr(String haystack, String needle) {
if (haystack == null || needle == null || !haystack.contains(needle)) {
return -1;
}
//记录needle的长度,方便后续在haystack进行截串
int needleLength = needle.length();
//获取要比较的第一个字符
char needleFirst = needle.charAt(0);
for (int i = 0, strLen = haystack.length(); i < strLen; i++) {
char c = haystack.charAt(i);
if(c == needleFirst){
String substring = haystack.substring(i, needleLength + i);
if(substring.equals(needle)){
return i;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
上述代码复杂度为 m*n,以下KMP解法才是「原字符串」中找到「匹配字符串」的最佳解法;下面代码来自chatgpt所写。
KMP 解法 https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/KMP%E7%AE%97%E6%B3%95
KMP 算法是一个快速查找匹配串的算法,它的作用其实就是本题问题:如何快速在「原字符串」中找到「匹配字符串」。上述的朴素解法,不考虑剪枝的话复杂度是 O(m∗n) 的,而 KMP 算法的复杂度为 O(m+n)。
KMP 之所以能够在 O(m+n) 复杂度内完成查找,是因为其能在「非完全匹配」的过程中提取到有效信息进行复用,以减少「重复匹配」的消耗。
public static int strStr2(String haystack, String needle) {
if (needle.isEmpty()) {
return 0;
}
int[] next = computeNext(needle);
int i = 0, j = 0;
while (i < haystack.length()) {
if (haystack.charAt(i) == needle.charAt(j)) {
i++;
j++;
if (j == needle.length()) {
return i - j;
}
} else {
if (j > 0) {
j = next[j - 1];
} else {
i++;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
private static int[] computeNext(String pattern) {
int[] next = new int[pattern.length()];
int i = 1, j = 0;
while (i < pattern.length()) {
if (pattern.charAt(i) == pattern.charAt(j)) {
j++;
next[i] = j;
i++;
} else {
if (j > 0) {
j = next[j - 1];
} else {
next[i] = 0;
i++;
}
}
}
return next;
}
Review📝
Basic Memory-Saving Techniques for Java Programming https://medium.com/javarevisited/basic-memory-saving-techniques-for-java-programming-6677a7237a69
1.本篇文章主要是举例子在Java在编写中减少内存开销的常用技巧,主要包括如下几个点:
-
使用基础数据类型,而不是包装类; 减少对象创建内存开销
-
避免创建不必要的对象;
-
- Strings=“Hello” + " World"; // use StringBuilder instead
-
使用懒加载模式 (use lazy initializetion), 减少在类加载时创建,在使用时候在创建;
-
如果知道数据大小范围时使用数组来代替集合类 ; Use arrays instead of collections
-
重复使用对象
-
- List tempList = newArrayList<>();
for (inti=0; i < 1000; i++) {
tempList.add("Item " + i);
// do something with tempList
}
tempList.clear(); // clear the list for reuse
for (inti=0; i < 1000; i++) {
tempList.add("Another item " + i);
// do something with tempList
}
- List tempList = newArrayList<>();
-
使用static工程方法来创建我们所需要的对象;
-
- 例如: 使用工程方法创建一个指定大小的ArrayList, 这样可以减少添加元素时需要调整 ArrayList 大小的次数,从而节省内存。
-
使用享元模式
-
使用字符串的intern方法 Use the intern() method
-
避免使用自动装箱;
-
- inti=42;
Integerj= Integer.valueOf(i); // use Integer.valueOf() instead of autoboxing
- inti=42;
it is important to note that memory optimization should not come at the expense of code readability or maintainability. 值得注意的是,内存优化不应该牺牲代码的可读性与维护性为代价;
keep exploring, keep learning, keep coding.
Tip🐾
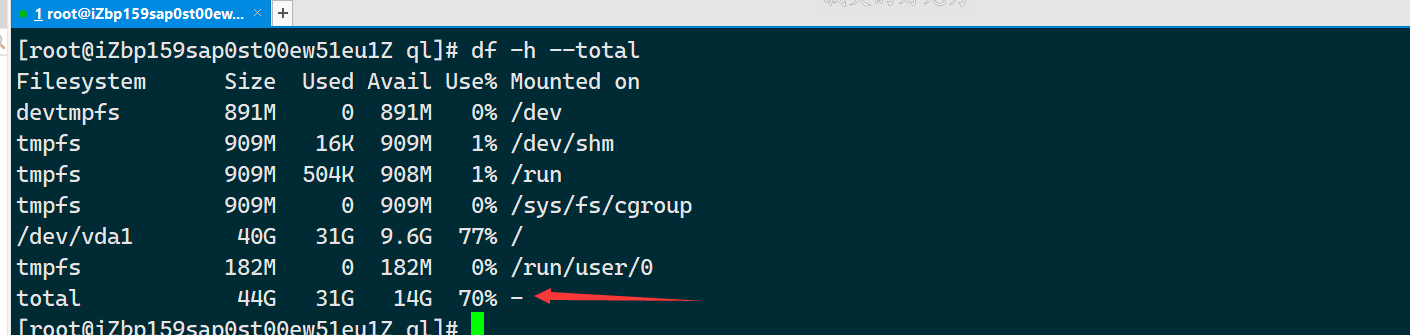
本周主要是学习Linux里的 du与df两个命令;
du 是 disk usage 的缩写,主要用于查看文件在磁盘中占用的空间大小;
df 是 disk free 的缩写,用于显示磁盘分区的可用和已用空间。它会列出系统中每个分区的总空间、已用空间和可用空间。
1.du的使用 du [opinions] [file]
- du -h [-- human-readable] 人类可读的格式打印大小输出;
- du -s [–summarize] 汇总显示大小

- du -a:显示所有文件和目录的磁盘使用情况,包括隐藏文件。
2.df的使用 命令与du类似
- df -h:以人类可读的格式显示磁盘使用情况。
- df -h --total
Share🎨
- Java线程池的创建方式
在平时在Java开发中,我们创建线程池的方式有哪些呢? 通过 Executors工具类方法? 或者是自动new 一个出来呢? Executors工具类创建出来的线程池可能造成计算机资源内存不足的情况,因为它创建的任务队列是LinkedBlockingQueue() { this(Integer.MAX_VALUE); }MAX_VALUE的无尽队列,如果一直往队列里添加任务,而线程没有及时处理掉的话就会导致OOM;
我们在开发中都会使用 new ThreadPoolExecutor 方式进行创建线程池的;其中构造方法具有7大参数,也是面试常问的面试题;在这次分享中介绍一下这7个参数;
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
}
- corePoolSize 核心线程数
- maximunPoolSize 最大线程数 (核心线程数+x)
- keepAliveTime 线程空闲时间 核心线程数不会销毁,销毁的是非核心线程数
- unit 空闲单位
- workQueue 任务队列
- threadFactory 线程工厂 一般可以自定义线程名等
- handler 拒绝策略 任务拒绝策是当线程池无法接受新任务时应该采取的行动。当线程池的任务队列已满,并且线程池中的线程数已达到最大线程数时;
- AbortPolicy 任务队列满了就报错
- CallerRunsPolicy 调用者运行策略 当线程池的任务队列已满时,新提交的任务会由提交该任务的线程执行,而不是交给线程池中的线程来执行。
- DiscardPolicy 丢弃策略
- DiscardOldPolicy 线程池会丢弃队列中最早(最老)的任务,然后尝试将新提交的任务添加到队列中。