平台
RK3288 + Android 8.1
显示: 1920x1080 @ 160 dpi
概述
碰到一个问题: 弹出的输入法会覆盖文本输入框。
原因:输入框使用了setTranslationY() 位置偏移后, 输入法无法正确获取焦点的位置。
分析
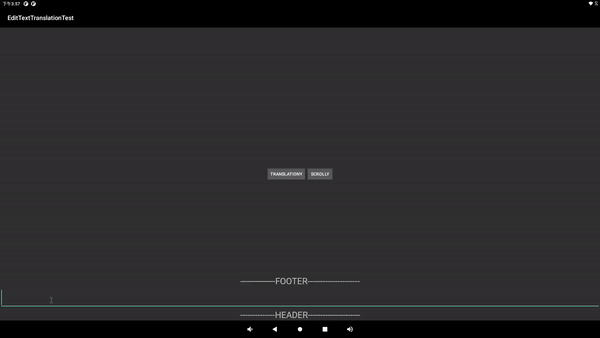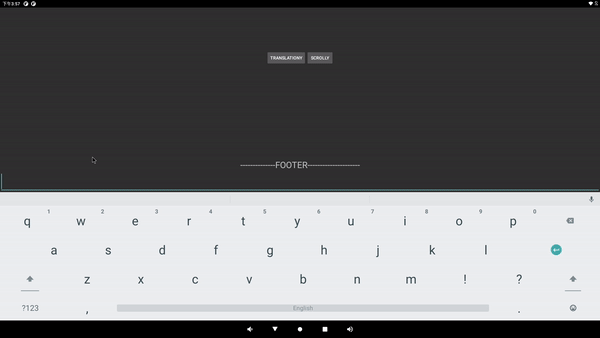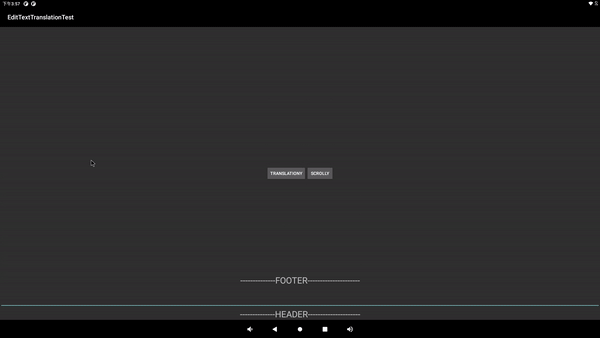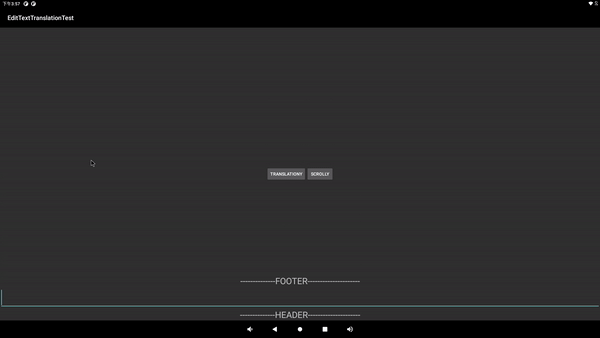
先上图: 初始布局

调用etTranslationY(700);

弹出输入法

最后一张图中, 输入框大概在红框的位置, 也是本文所描述的问题: 输入法遮挡了输入框控件
- 布局
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<LinearLayout android:id="@+id/llEdit"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv"
android:textSize="28sp"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="--------------FOOTER---------------------"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
<EditText android:id="@+id/et"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textSize="36sp"
/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv2"
android:textSize="28sp"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="--------------HEADER---------------------"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
</LinearLayout>
<Button android:id="@+id/btTy"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:text="TranslationY"/>
</RelativeLayout>
- java
package com.android.apitester.test;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.EditText;
import com.android.apitester.R;
public class EditTextTranslationTest extends Activity {
EditText et;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.test_edittext_translation);
et = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.et);
findViewById(R.id.btTy).setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
et.setTranslationY(et.getTranslationY() != 0 ? 0 : 700);
}
});
}
}
稍微改下代码,把输入框放到界面底部


输入法正常弹出,并把整体UI往上顶。
后续做了一些数据, getTranslationY不同的大小以作比对
| 位移大小 | 展示效果 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| -300 | 被覆盖 | - |
| -70 | 被覆盖 | - |
| -69 | 第一次后正常 | 第一次被覆盖 |
| -50 | 第一次后正常 | 第一次被覆盖 |
| >0 | 被覆盖 | - |
70 是控件的高度!
输入法是怎么把布局顶上去的? 答案在ViewRootImpl中。
frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java
public void dump(String prefix, FileDescriptor fd, PrintWriter writer, String[] args) {
String innerPrefix = prefix + " ";
//..... 省略 .....
writer.print(innerPrefix);
writer.print("getCurrY=");writer.print(mScroller != null ? mScroller.getCurrY():0);
writer.print("mScrollY=");writer.print(mScrollY);
writer.print("mCurScrollY=");writer.print(mCurScrollY);
}
dumpsys activity name
//未打开输入法
getCurrY=0,mScrollY=0,mCurScrollY=0
//打开输入法
getCurrY=372,mScrollY=372,mCurScrollY=372
准确地说,是滚上去的
boolean scrollToRectOrFocus(Rect rectangle, boolean immediate) {
final Rect ci = getWindowInsets(false).getSystemWindowInsetsAsRect();
final Rect vi = mAttachInfo.mVisibleInsets;
int scrollY = 0;
boolean handled = false;
if (vi.left > ci.left || vi.top > ci.top
|| vi.right > ci.right || vi.bottom > ci.bottom) {
// We'll assume that we aren't going to change the scroll
// offset, since we want to avoid that unless it is actually
// going to make the focus visible... otherwise we scroll
// all over the place.
scrollY = mScrollY;
// We can be called for two different situations: during a draw,
// to update the scroll position if the focus has changed (in which
// case 'rectangle' is null), or in response to a
// requestChildRectangleOnScreen() call (in which case 'rectangle'
// is non-null and we just want to scroll to whatever that
// rectangle is).
final View focus = mView.findFocus();
if (focus == null) {
return false;
}
View lastScrolledFocus = (mLastScrolledFocus != null) ? mLastScrolledFocus.get() : null;
if (focus != lastScrolledFocus) {
// If the focus has changed, then ignore any requests to scroll
// to a rectangle; first we want to make sure the entire focus
// view is visible.
rectangle = null;
}
if (DEBUG_INPUT_RESIZE) Log.v(mTag, "Eval scroll: focus=" + focus
+ " rectangle=" + rectangle + " ci=" + ci
+ " vi=" + vi);
if (focus == lastScrolledFocus && !mScrollMayChange && rectangle == null) {
// Optimization: if the focus hasn't changed since last
// time, and no layout has happened, then just leave things
// as they are.
if (DEBUG_INPUT_RESIZE) Log.v(mTag, "Keeping scroll y="
+ mScrollY + " vi=" + vi.toShortString());
} else {
// We need to determine if the currently focused view is
// within the visible part of the window and, if not, apply
// a pan so it can be seen.
mLastScrolledFocus = new WeakReference<View>(focus);
mScrollMayChange = false;
if (DEBUG_INPUT_RESIZE) Log.v(mTag, "Need to scroll?");
// Try to find the rectangle from the focus view.
if (focus.getGlobalVisibleRect(mVisRect, null)) {
if (DEBUG_INPUT_RESIZE) Log.v(mTag, "Root w="
+ mView.getWidth() + " h=" + mView.getHeight()
+ " ci=" + ci.toShortString()
+ " vi=" + vi.toShortString());
if (rectangle == null) {
focus.getFocusedRect(mTempRect);
if (DEBUG_INPUT_RESIZE) Log.v(mTag, "Focus " + focus
+ ": focusRect=" + mTempRect.toShortString());
if (mView instanceof ViewGroup) {
((ViewGroup) mView).offsetDescendantRectToMyCoords(
focus, mTempRect);
}
if (DEBUG_INPUT_RESIZE) Log.v(mTag,
"Focus in window: focusRect="
+ mTempRect.toShortString()
+ " visRect=" + mVisRect.toShortString());
} else {
mTempRect.set(rectangle);
if (DEBUG_INPUT_RESIZE) Log.v(mTag,
"Request scroll to rect: "
+ mTempRect.toShortString()
+ " visRect=" + mVisRect.toShortString());
}
if (mTempRect.intersect(mVisRect)) {
if (DEBUG_INPUT_RESIZE) Log.v(mTag,
"Focus window visible rect: "
+ mTempRect.toShortString());
if (mTempRect.height() >
(mView.getHeight()-vi.top-vi.bottom)) {
// If the focus simply is not going to fit, then
// best is probably just to leave things as-is.
if (DEBUG_INPUT_RESIZE) Log.v(mTag,
"Too tall; leaving scrollY=" + scrollY);
}
// Next, check whether top or bottom is covered based on the non-scrolled
// position, and calculate new scrollY (or set it to 0).
// We can't keep using mScrollY here. For example mScrollY is non-zero
// due to IME, then IME goes away. The current value of mScrollY leaves top
// and bottom both visible, but we still need to scroll it back to 0.
else if (mTempRect.top < vi.top) {
scrollY = mTempRect.top - vi.top;
if (DEBUG_INPUT_RESIZE) Log.v(mTag,
"Top covered; scrollY=" + scrollY);
} else if (mTempRect.bottom > (mView.getHeight()-vi.bottom)) {
scrollY = mTempRect.bottom - (mView.getHeight()-vi.bottom);
if (DEBUG_INPUT_RESIZE) Log.v(mTag,
"Bottom covered; scrollY=" + scrollY);
} else {
scrollY = 0;
}
handled = true;
}
}
}
}
if (scrollY != mScrollY) {
if (DEBUG_INPUT_RESIZE) Log.v(mTag, "Pan scroll changed: old="
+ mScrollY + " , new=" + scrollY);
if (!immediate) {
if (mScroller == null) {
mScroller = new Scroller(mView.getContext());
}
mScroller.startScroll(0, mScrollY, 0, scrollY-mScrollY);
} else if (mScroller != null) {
mScroller.abortAnimation();
}
mScrollY = scrollY;
}
return handled;
}
frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/View.java
public void getDrawingRect(Rect outRect) {
outRect.left = mScrollX;
outRect.top = mScrollY;
outRect.right = mScrollX + (mRight - mLeft);
outRect.bottom = mScrollY + (mBottom - mTop);
}
public void getFocusedRect(Rect r) {
getDrawingRect(r);
}
获取当前聚焦的控件的位置信息与当前ViewRootImpl的可见区域进行比对计算出滚动距离。
在绘制的过程中不断更新并计算滚动位置
通过修改mScroller的动画时长,可以清晰看到滚动的过程效果
mScroller.startScroll(0, mScrollY, 0, scrollY-mScrollY);
//改为
mScroller.startScroll(0, mScrollY, 0, scrollY-mScrollY, 1000);
为什么刚好位移 setTranslationY(70) 无法滚动主窗口
if (mTempRect.intersect(mVisRect)) {
if (DEBUG_INPUT_RESIZE) Log.v(mTag,
"Focus window visible rect: "
+ mTempRect.toShortString());
if (mTempRect.height() >
(mView.getHeight()-vi.top-vi.bottom)) {
// If the focus simply is not going to fit, then
// best is probably just to leave things as-is.
if (DEBUG_INPUT_RESIZE) Log.v(mTag,
"Too tall; leaving scrollY=" + scrollY);
}
// Next, check whether top or bottom is covered based on the non-scrolled
// position, and calculate new scrollY (or set it to 0).
// We can't keep using mScrollY here. For example mScrollY is non-zero
// due to IME, then IME goes away. The current value of mScrollY leaves top
// and bottom both visible, but we still need to scroll it back to 0.
else if (mTempRect.top < vi.top) {
scrollY = mTempRect.top - vi.top;
if (DEBUG_INPUT_RESIZE) Log.v(mTag,
"Top covered; scrollY=" + scrollY);
} else if (mTempRect.bottom > (mView.getHeight()-vi.bottom)) {
scrollY = mTempRect.bottom - (mView.getHeight()-vi.bottom);
if (DEBUG_INPUT_RESIZE) Log.v(mTag,
"Bottom covered; scrollY=" + scrollY);
} else {
scrollY = 0;
}
handled = true;
}
获取的控件的焦点区域和可视区域不存在交集, 导致后续的mScroller部分的代码没有执行。
在TextView中重写了 getFocusedRect,返回的是 光标的坐标,在测试的DEMO中输出如下 [2,10][6,70] 的坐标。
/**
//弹
Need to scroll?
Root w=1920 h=1080 ci=[0,24][0,56] vi=[0,24][0,466]
Focus android.widget.EditText{4146188 VFED..CL. .F..H.I. 0,828-1920,898 #7f03000a app:id/et aid=1073741824}: focusRect=[2,10][6,70]
Focus in window: focusRect=[2,926][6,986] visRect=[0,916][1920,986]
Focus window visible rect: [2,926][6,986]
Bottom covered; scrollY=372
Pan scroll changed: old=0 , new=372
//不弹
Eval scroll: focus=android.widget.EditText{40fcecd VFED..CL. .F..H.I. 0,828-1920,898 #7f03000a app:id/et aid=1073741824} rectangle=null ci=Rect(0, 24 -
Need to scroll?
Root w=1920 h=1080 ci=[0,24][0,56] vi=[0,24][0,466]
Focus android.widget.EditText{40fcecd VFED..CL. .F..H.I. 0,828-1920,898 #7f03000a app:id/et aid=1073741824}: focusRect=[2,10][6,70]
Focus in window: focusRect=[2,926][6,986] visRect=[0,846][1920,916]
if (mTempRect.intersect(mVisRect)) 对应的两个矩形:
- focusRect=[2,926][6,986] visRect=[0,916][1920,986] <- 弹
- focusRect=[2,926][6,986] visRect=[0,846][1920,916] <- 不弹,无交集
参考
Android软键盘弹出时把布局顶上去的解决方法
Android EditText默认不弹出输入法的实现方法
5种方法完美解决android软键盘挡住输入框方法详解
Android输入法弹出流程