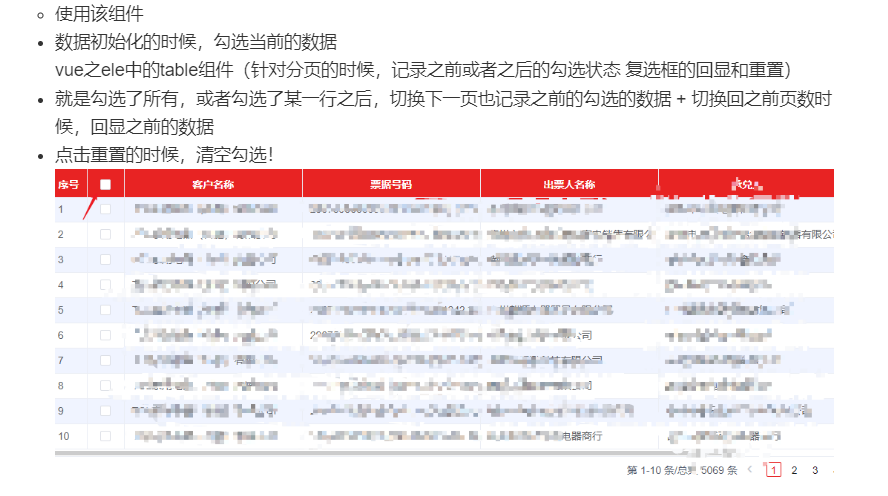
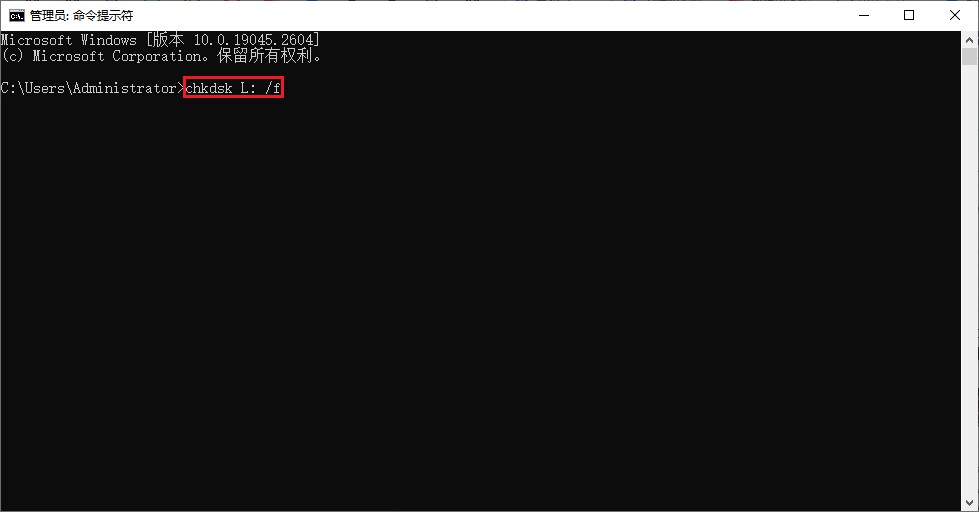
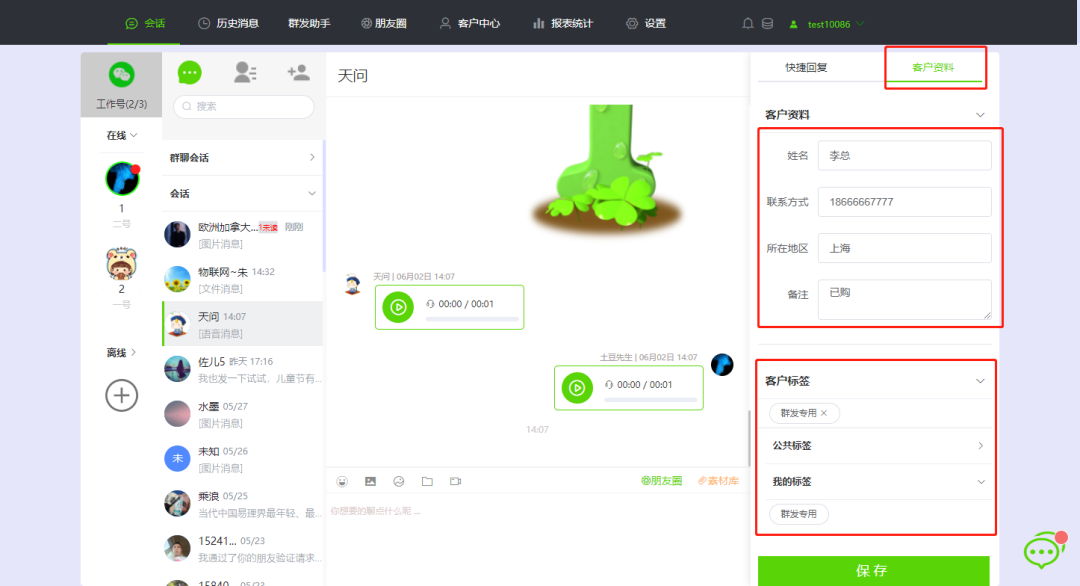
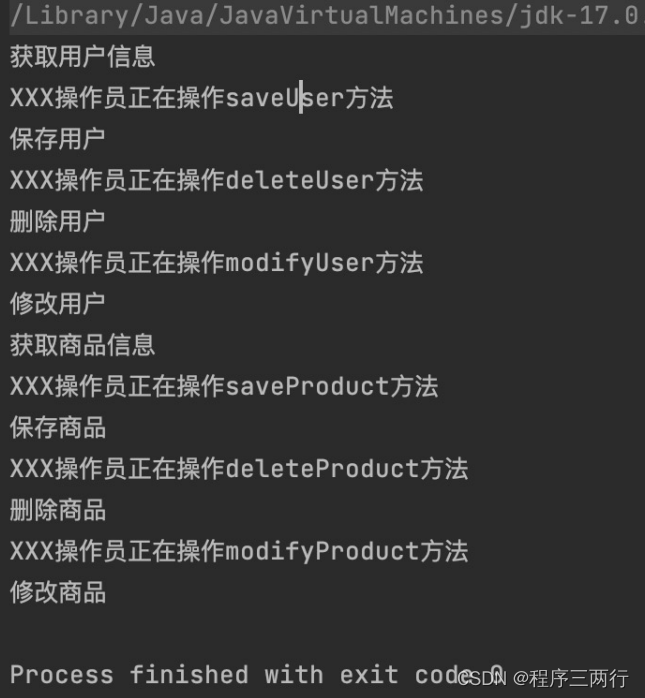
一)floodfill算法简介:
二)图像渲染
733. 图像渲染 - 力扣(LeetCode)
class Solution { int[] dx = {1, 0, 0, -1}; int[] dy = {0, 1, -1, 0}; //上下搜索的时候要使用向量数组 int row=0; int col=0; int target=0; public void dfs(int[][] image,int i,int j,int color){ if(image[i][j]==target){ image[i][j]=color; } for(int k=0;k<4;k++){ int x=i+dx[k]; int y=j+dy[k]; if(x>=0&&x<row&&y>=0&&y<col&&image[x][y]==target){ //四个方向进行深度优先遍历 dfs(image,x,y,color); } } } public int[][] floodFill(int[][] image, int i, int j, int color) { if(color==image[i][j]) return image;//防止走到重复元素的情况 this.target=image[i][j]; this.row=image.length; this.col=image[0].length; dfs(image,i,j,color); return image; } }
三)岛屿数量
200. 岛屿数量 - 力扣(LeetCode)
class Solution { public boolean[][] check; int[] dx = {1, 0, 0, -1}; int[] dy = {0, 1, -1, 0}; int row=0; int col=0; public void dfs(char[][] array,int i,int j){ check[i][j]=true; for(int k=0;k<4;k++){ int x=i+dx[k]; int y=j+dy[k]; if(x>=0&&x<row&&y>=0&&y<col&&array[x][y]=='1'&&check[x][y]==false){ check[x][y]=true; dfs(array,x,y); } } } public int numIslands(char[][] array) { this.row=array.length; this.col=array[0].length; this.check=new boolean[row][col]; int ret=0; for(int i=0;i<row;i++){ for(int j=0;j<col;j++){ if(array[i][j]=='1'&&check[i][j]==false){ check[i][j]=true; ret++; dfs(array,i,j); } } } return ret; } }
四)岛屿的最大面积:
695. 岛屿的最大面积 - 力扣(LeetCode)
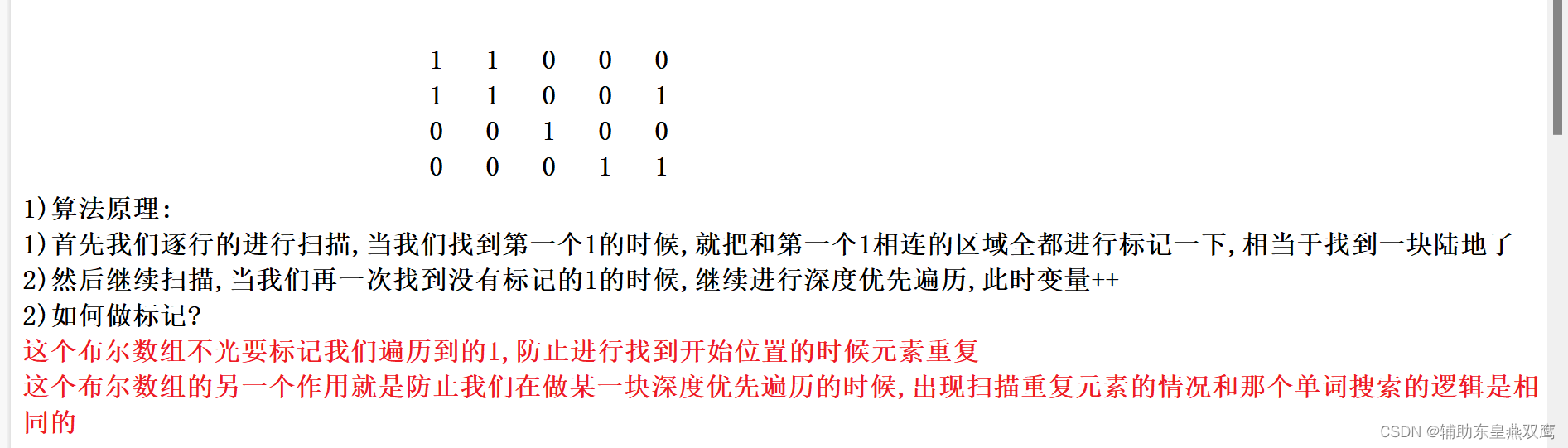
算法原理:
1)想要解决本题核心的思路还是做一次深度优先遍历,我们一开始来遍历这个岛屿,当扫描到一个陆地之后(这个数组的值等于1),就从这个陆地也就是1开始来做一次深度优先遍历,上下左右都来进行扫描
2)此时定义一个全局的变量count,在深度优先遍历,只要进入一次dfs,就让这个count++,因为在每一次进入到dfs函数的时候,都是相当于是进入到了一块陆地,档次是针对这个起始陆地深度优先遍历完成之后,此时的这个count值就是统计这块岛屿的面积,然后再使用ret统计最终的结果;
3)下面的写法是dfs带有返回值和dfs不带有返回值的写法:
class Solution { public boolean[][] check; int[] dx = {1, 0, 0, -1}; int[] dy = {0, 1, -1, 0}; int row=0; int col=0; int ret=0; int count=0; public void dfs(int[][] array,int i,int j){ count++; for(int k=0;k<4;k++){ int x=i+dx[k]; int y=j+dy[k]; if(x>=0&&x<row&&y>=0&&y<col&&array[x][y]==1&&check[x][y]==false){ check[x][y]=true; dfs(array,x,y); } } } public int maxAreaOfIsland(int[][] array) { this.row=array.length; this.col=array[0].length; this.check=new boolean[row][col]; for(int i=0;i<row;i++){ for(int j=0;j<col;j++){ if(array[i][j]==1&&check[i][j]==false){ check[i][j]=true; count=0; dfs(array,i,j); ret=Math.max(count,ret); } } } return ret; } }class Solution { public boolean[][] check; int[] dx = {1, 0, 0, -1}; int[] dy = {0, 1, -1, 0}; int row=0; int col=0; int ret=0; public int dfs(int[][] array,int i,int j){ int count=1; for(int k=0;k<4;k++){ int x=i+dx[k]; int y=j+dy[k]; if(x>=0&&x<row&&y>=0&&y<col&&array[x][y]==1&&check[x][y]==false){ check[x][y]=true; count+=dfs(array,x,y); } } return count; } public int maxAreaOfIsland(int[][] array) { this.row=array.length; this.col=array[0].length; this.check=new boolean[row][col]; for(int i=0;i<row;i++){ for(int j=0;j<col;j++){ if(array[i][j]==1&&check[i][j]==false){ check[i][j]=true; ret=Math.max(dfs(array,i,j),ret); } } } return ret; } }
五)被围绕的区域
130. 被围绕的区域 - 力扣(LeetCode)
算法原理:
1)首先遍历整个二维矩阵的边界,先找到边界区域的圆圈,先进行标记一下,那么剩下的圆圈自然就是在内部的圆圈,标记的时候可以搞一个check数组,也可以把边界的情况处理成一个额外字符
2)然后直接修改内部的圆圈;
class Solution { public boolean[][] check; public int row=0; public int col=0; int[] dx = {1, 0, 0, -1}; int[] dy = {0, 1, -1, 0}; public void dfs(char[][] board,int i,int j,char ch){ check[i][j]=true; board[i][j]=ch; for(int k=0;k<4;k++){ int x=i+dx[k]; int y=j+dy[k]; if(x>=0&&x<row&&y>=0&&y<col&&board[x][y]=='O'&&check[x][y]==false){ dfs(board,x,y,ch); } } } public void solve(char[][] board) { //1.先进行初始化操作 this.row=board.length; this.col=board[0].length; this.check=new boolean[row][col]; //2.进行处理边界情况下的O字符 for(int i=0;i<col;i++){ if(board[0][i]=='O'&&check[0][i]==false){ dfs(board,0,i,'O'); } if(board[row-1][i]=='O'&&check[row-1][i]==false){ dfs(board,row-1,i,'O'); } } for(int j=0;j<row;j++){ if(board[j][0]=='O'&&check[j][0]==false){ dfs(board,j,0,'O'); } if(board[j][col-1]=='O'&&check[j][col-1]==false){ dfs(board,j,col-1,'O'); } } System.out.println(Arrays.deepToString(check)); //3.开始处理非边界上的O for(int i=0;i<row;i++){ for(int j=0;j<col;j++){ if(board[i][j]=='O'&&check[i][j]==false){ dfs(board,i,j,'X'); } } } } }
六)太平洋大西洋水流问题
417. 太平洋大西洋水流问题 - 力扣(LeetCode)
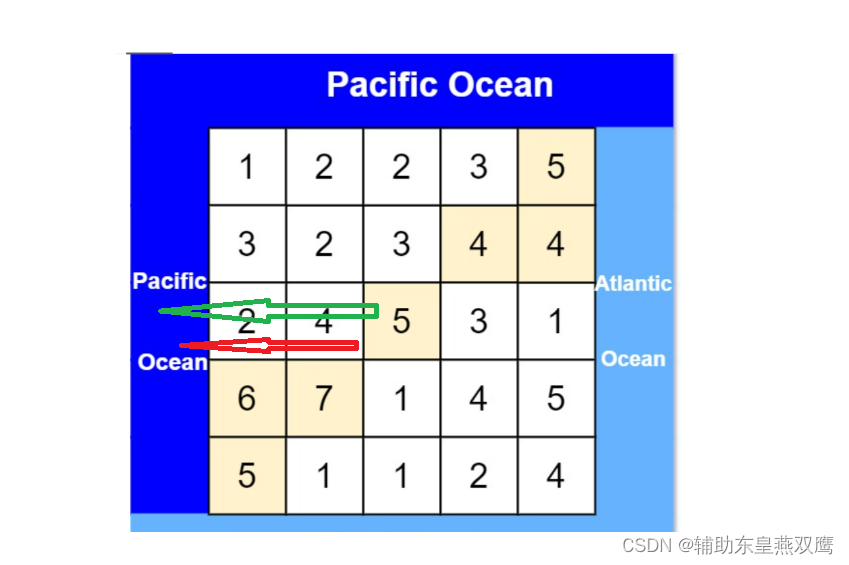
解法1:直接来解决这个问题,直接进行遍历二维数组中的每一个点,直接判断某一个点是否能够到达太平洋也可以到达大西洋,但是可能会出现重复路径的情况,所以说时间有可能会超时
解法2:正难则反:反着看,假设太平洋或者是大西洋的水能够逆着来,能够走到哪些位置,直接看大于等于当前位置的位置,此时我们枚举完成第一行和最后一行的所有元素,并且针对与这些所有元素全部做一次深度优先遍历,将所有能够流向大西洋的点进行标记
class Solution { List<List<Integer>> ret=new ArrayList<>(); int row=0; int col=0; int[] dx = {1, 0, 0, -1}; int[] dy = {0, 1, -1, 0}; public void dfs(int[][] array,int i,int j,boolean[][] check){ check[i][j]=true; for(int k=0;k<4;k++){ int x=i+dx[k]; int y=j+dy[k]; if(x>=0&&x<row&&y>=0&&y<col&&check[x][y]==false&&array[i][j]<=array[x][y]){ dfs(array,x,y,check); } } } public List<List<Integer>> pacificAtlantic(int[][] array) { this.row=array.length; this.col=array[0].length; boolean[][] pac=new boolean[row][col]; boolean[][] atc=new boolean[row][col]; //1.先处理太平洋 for(int i=0;i<col;i++){ dfs(array,0,i,pac);//处理上边界,上边界是找所有可能从大西洋从(i,j)方向逆流到哪一个位置 } for(int j=0;j<row;j++){ dfs(array,j,0,pac);//处理左边界 } //2.再来处理大西洋 for(int i=0;i<col;i++){ dfs(array,row-1,i,atc);//处理下边界 } for(int j=0;j<row;j++){ dfs(array,j,col-1,atc);//处理右边界,右边界是找所有可能从大西洋从(i,j)方向逆流到哪一个位置 } //3.最后进行提取结果 for(int i=0;i<row;i++){ for(int j=0;j<col;j++){ if(pac[i][j]==true&&atc[i][j]==true){ List<Integer> temp=new ArrayList<>(); temp.add(i); temp.add(j); ret.add(temp); } } } //4.返回最终结果 return ret; } }