1. 数字操作

常见的模板
// 使用一个数组判断元素是否入过队
int inqueue[N] = {0};// 层数或者可以称为深度
int step = 0;
// 判断是否可以入队的条件
int isvalid(){
}BFS(int x){
// 将初始的元素压入队列
// 注意每次压队的时候都要将inque[x] = 1,表明入队过
queue<int> q;
q.push(x);
inqueue[x] = 1;//大循环 队列q不为空
while (!q.empty()){
// 获得这一层的所有元素 ,因为咱们是广度优先
int cnt = q.size();
//小循环
while (cnt--){
int temp = q.front();
q.pop();
// BFS寻找的目的,这里就是temp 是否 == n
if (temp == n){
return ;//视情况而定
}
// 以此节点开始寻找下一层的有效节点
if (isvalid(temp+1)){
q.push(temp+1);
// 注意压队就要伴随着inqueue[]的变化
inqueue[temp+1] = 1;
}
// ....同理
}
// 在小循环结束后,意味着整层的元素都被遍历过了,若没有,则下一层
step++;
}
}
#include <cstdio>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5+10;
int n;
int inqueue[N] = {0};
int isvalid(int x){
if (x<=n && inqueue[x] == 0)return 1;
else return 0;
}
int step = 0;
void BFS(){
queue<int> q;
q.push(1);
inqueue[1] = 1;
while (!q.empty()){
int cnt = q.size();
while (cnt--){
int temp = q.front();
q.pop();
if (temp == n){
return;
}
if (isvalid(temp+1)){
q.push(temp+1);
inqueue[temp+1] = 1;
}
if (isvalid(temp*2)){
q.push(temp*2);
inqueue[temp*2] = 1;
}
}
step++;
}
}
int main(){
scanf("%d",&n);
BFS();
printf("%d",step);
return 0;
}2. 矩阵的块


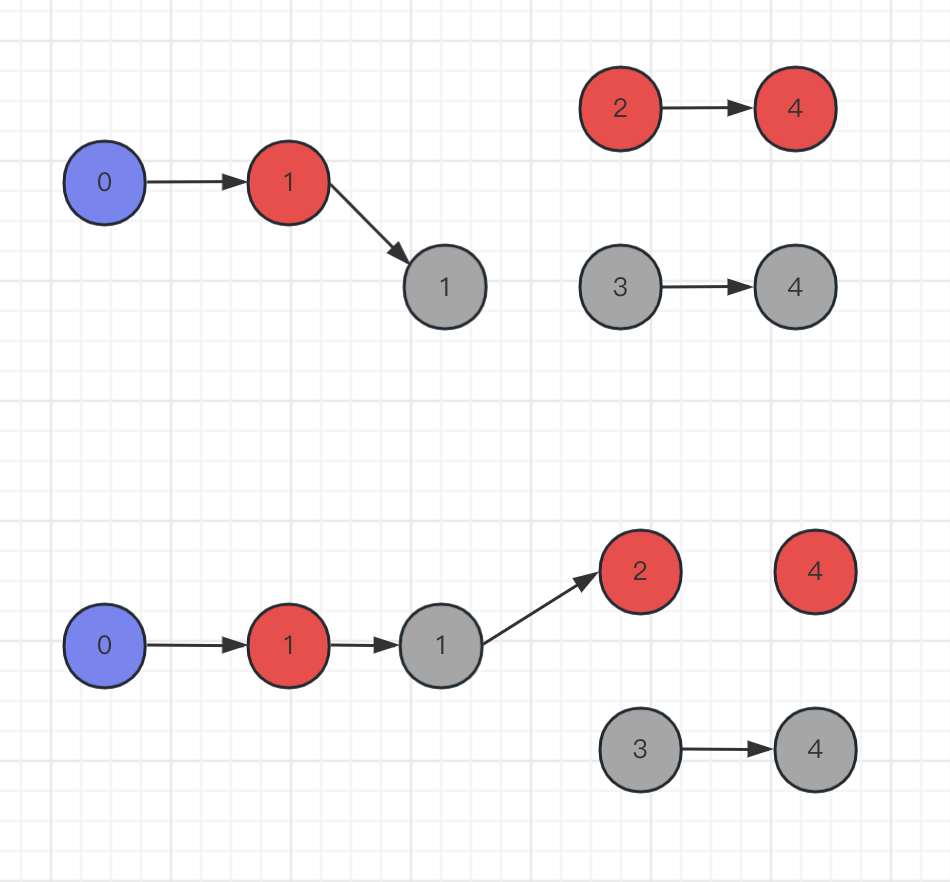
题目的思路很简单,首先就是从头到尾遍历数组,当遇到1并且未如过队(证明其是一个全新的块)时进行BFS,直到周围都是0无法进展为止,在BFS过程中,遍历过的1都被压入队中,因此inqueue为1,那么经过几次BFS,证明就有几个块。
#include <cstdio>
#include <queue>
#include <utility>
using namespace std;
// 由于需要压队,那么队内的元素为PII
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
const int N = 110;
int n,m;
// 是否入队,位置用二维数组即可
int inqueue[N][N] = {0};
// 存储整个矩阵
int A[N][N];
// 块的数量
int count = 0;
// 为了便于上下左右的移动,可以设置两个数组,表示上下左右的变量
int dx[4] = {-1,1,0,0};
int dy[4] = {0,0,-1,1};
int isvalid(int x,int y){
// 有效的压队条件,x,y未逾越矩阵的范围,未入过队,并且值为1
if (x>=1 && x<=n && y>=1 && y<=m && inqueue[x][y] == 0 && A[x][y] == 1)return 1;
else return 0;
}
void BFS(int i,int j){
queue<PII> q;
q.push(make_pair(i,j));
inqueue[i][j] = 1;
while (!q.empty()){
int cnt = q.size();
while (cnt--){
PII temp = q.front();
q.pop();
// 我们无需返回什么,因此这里不需要写return 的语句
// 开始寻找下一个有效的节点
for (int i=0;i<4;i++){
int nextx = temp.first+dx[i];
int nexty = temp.second+dy[i];
if (isvalid(nextx,nexty)){
q.push(make_pair(nextx,nexty));
inqueue[nextx][nexty] = 1;
}
}
}
}
}
int main(){
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)
for (int j=1;j<=m;j++)
scanf("%d",&A[i][j]);
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)
for (int j=1;j<=m;j++)
if (A[i][j] == 1 && inqueue[i][j] == 0){
BFS(i,j);
count++;
}
printf("%d",count);
return 0;
}