题 4-5 存疑,仅供参考,欢迎交流
文章目录
- 题4-9:
- 题4-5求解代码: Python
- 题6-7求解代码: Python
- 求解 θ4-θ6 时, 记得 将 R 改成相应的!!!!
- 题8-9求解代码: Python
- 题10-15 方法一 Cartesian space
- 求解代码【10-15】_Python
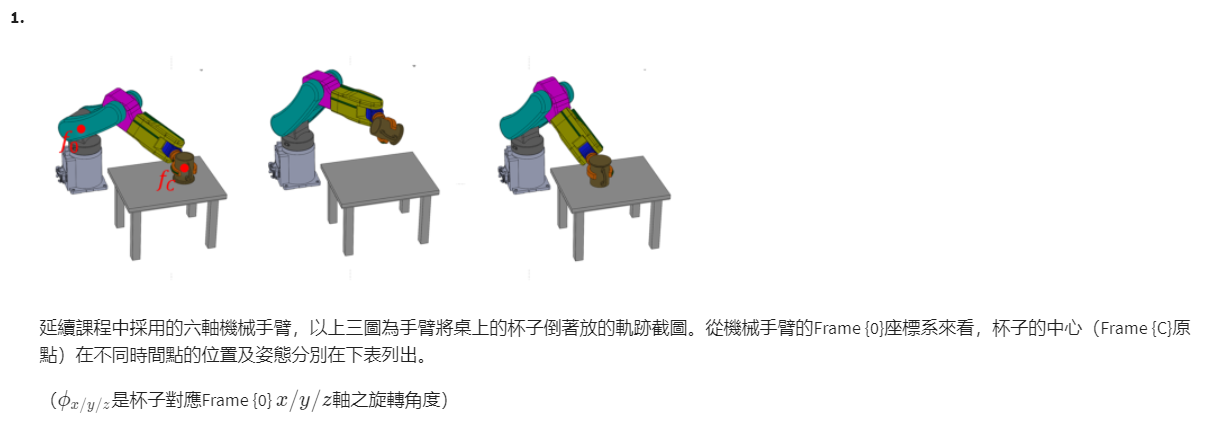
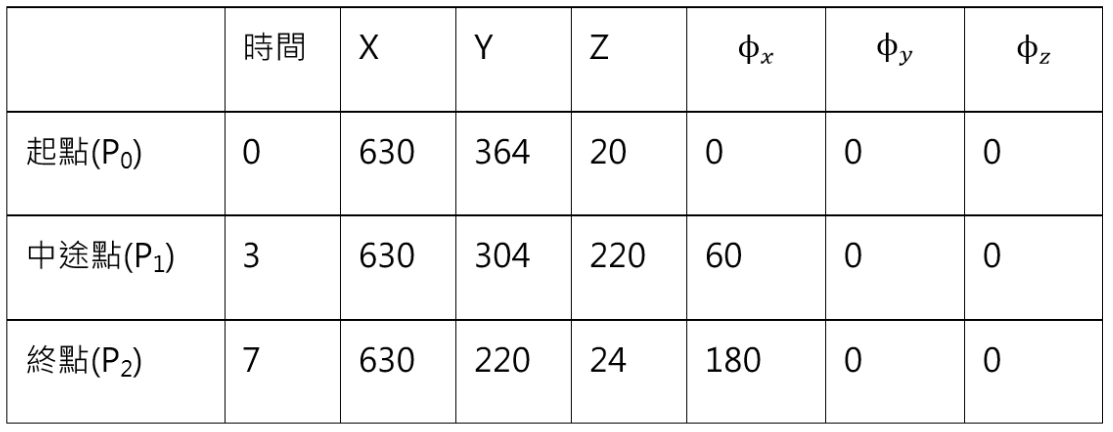
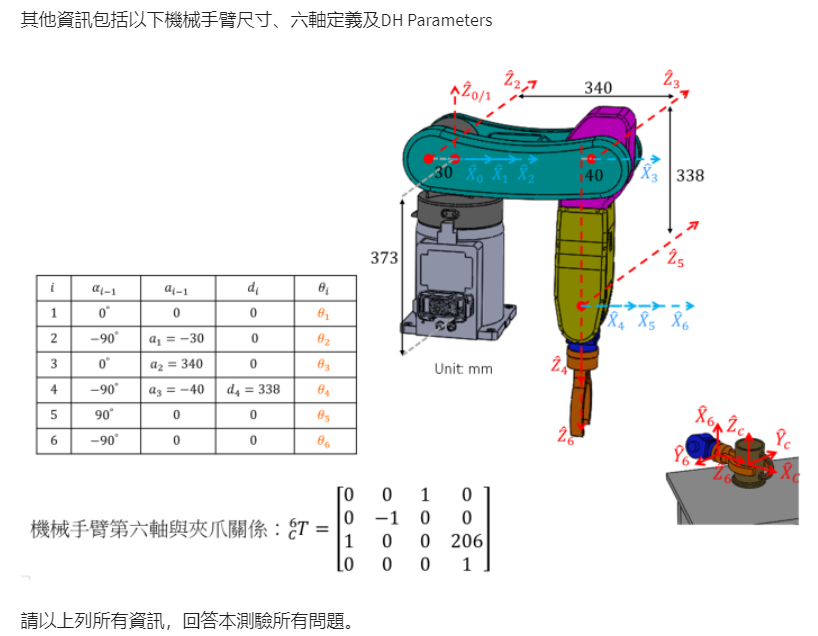


由
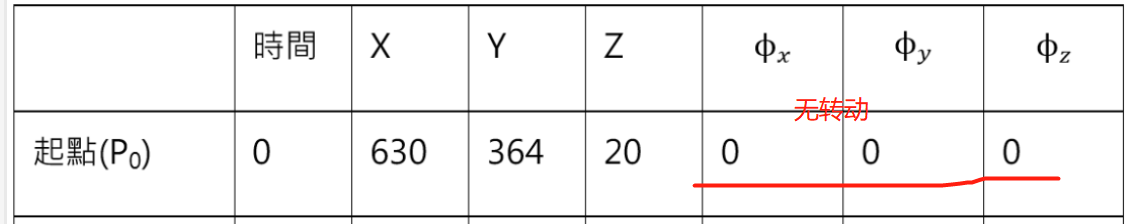
import numpy as np
## 杯子 中心 C 在 点 P0 处
T_0C = [[1, 0, 0, 630],
[0, 1, 0, 364],
[0, 0, 1, 20],
[0, 0, 0, 1]]
## 已知 T_6C
T_6C = [[0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, -1, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 0, 206],
[0, 0, 0, 1]]
# T_0C = T_06 * T_6C
T_06 = np.dot(T_0C, np.linalg.inv(T_6C))
print(T_06)

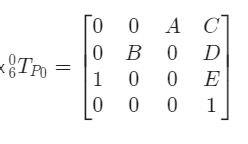
A = 1, B = -1, C = 424, D= 364, E = 20
第1题答案: 1//-1//424//364//20

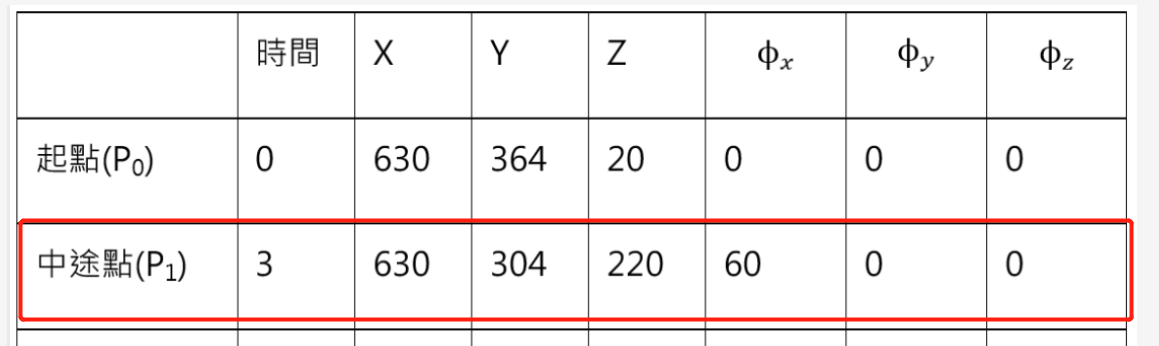
只沿 X 轴 旋转 60°
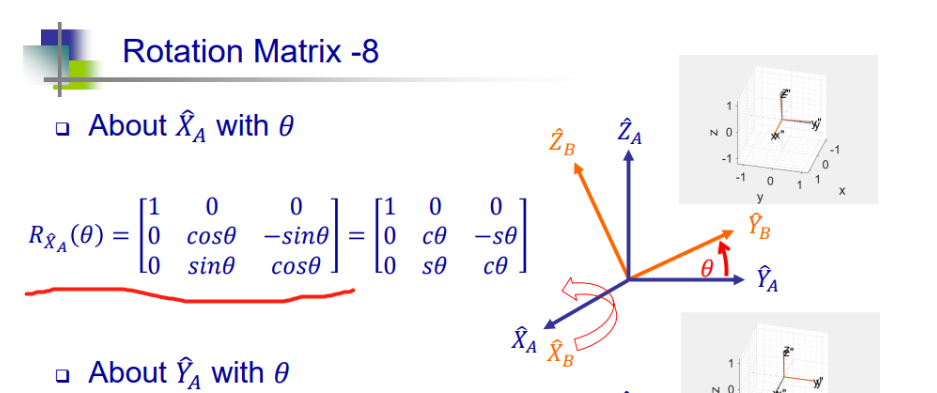
import numpy as np
## 杯子 中心 C 在 点 P1 处
## 只沿着 X 轴 转 60°
θ = np.pi * 60 / 180
R = [[1,0, 0],
[0, np.cos(θ), -np.sin(θ)],
[0, np.sin(θ), np.cos(θ)]]
a = np.row_stack((R,[[0, 0, 0]])) ## 扩展 行 这样 不用 将 R 打印出来
P = np.array([[630, 304, 220, 1]]) ## 扩展 列
T_0C = np.column_stack((a, P.T))
## 已知 T_6C
T_6C = [[0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, -1, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 0, 206],
[0, 0, 0, 1]]
# T_0C = T_06 * T_6C
T_06 = np.dot(T_0C, np.linalg.inv(T_6C))
T_06 = [[float(format(x, '.3g')) for x in T_06[i]] for i in range(len(T_06))]
print(np.array(T_06))
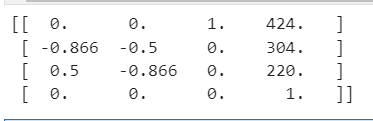

A = -0.866 B = 0.5 C = 424 D = 304
第2题答案: -0.866//0.5//424//304

import numpy as np
np.set_printoptions(suppress = True)
## 杯子 中心 C 在 点 P2 处
## 只沿着 X 轴 转 180°
θ = np.pi * 180 / 180
R = [[1, 0, 0],
[0, np.cos(θ), -np.sin(θ)],
[0, np.sin(θ), np.cos(θ)]]
a = np.row_stack((R,[[0, 0, 0]])) ## 扩展 行 这样 不用 将 R 打印出来
P = np.array([[630, 220, 24, 1]]) ## 扩展 列
T_0C = np.column_stack((a, P.T))
## 已知 T_6C
T_6C = [[0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, -1, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 0, 206],
[0, 0, 0, 1]]
# T_0C = T_06 * T_6C
T_06 = np.dot(T_0C, np.linalg.inv(T_6C))
T_06 = [[float(format(x, '.3g')) for x in T_06[i]] for i in range(len(T_06))]
print(np.array(T_06))

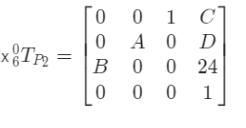
第3题答案: 1//-1//424//220
题4-9:


题4-5求解代码: Python
import numpy as np
## 杯子 中心 C 在 点 P0 处
T_0C = [[1, 0, 0, 630],
[0, 1, 0, 364],
[0, 0, 1, 20],
[0, 0, 0, 1]]
## 已知 T_6C
T_6C = [[0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, -1, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 0, 206],
[0, 0, 0, 1]]
# T_0C = T_06 * T_6C
T_06 = np.dot(T_0C, np.linalg.inv(T_6C))
print(T_06)
### 当 杯子中心 C 在 点 P0
# T_06 = [[ 0. 0. 1. 424.]
# [ 0. -1. 0. 364.]
# [ 1. 0. 0. 20.]
# [ 0. 0. 0. 0.]]
######## 求解 θ3 [-90, 0]
### 注意这里 的 x, y, z 是 T_06 的
x, y, z = 424, 364, 20
##################
import numpy as np
α2, a2, d3 = 0, 340, 0 ## θ3
α3, a3, d4 = np.pi*(-90)/180, -40, 338 ## θ4
'''
## 仅与 θ3 有关
f1 = a3 * np.cos(θ3) + d4 * np.sin(α3)*np.sin(θ3) + a2
#f2 = a3 * np.cos(α2)*np.sin(θ3) - d4 * np.sin(α3)*np.cos(α2)*np.cos(θ3) -\
# d4 * np.sin(α2)*np.cos(α3) - d3 * np.sin(α2)
f2 = a3 * np.sin(θ3) - d4 * np.sin(α3) * np.cos(θ3)
#f3 = a3 * np.sin(α2)* np.sin(θ3)- d4 * np.sin(α3)* np.sin(α2) * np.cos(θ3) + \
# d4 * np.cos(α2) * np.cos(α3) + d3 * np.cos(α2)
f3 = d4 * np.cos(α3)
# print(f3)
'''
# 对 i= 1 i= 2
α0, a0, d1 = 0, 0, 0 ## θ1
α1, a1, d2 = np.pi*(-90)/180, -30, 0 ## θ2
'''
## 和 θ2,θ3有关
g1 = np.cos(θ2)* f1 - np.sin(θ2) * f2 + a1
# g2 = np.sin(θ2)* np.cos(α1) * f1 + np.cos(θ2) * np.cos(α1)* f2 -\
# np.sin(α1) * f3 - d2 * np.sin(α1)
## 化简
g2 = np.sin(θ2)* np.cos(α1) * f1 + np.cos(θ2) * np.cos(α1)* f2 -\
np.sin(α1) * f3
# g3 = np.sin(θ2)* np.sin(α1) * f1 + np.cos(θ2) * np.sin(α1)* f2 +\
# np.cos(α1) * f3 + d2 * np.cos(α1)
## 化简
g3 = np.sin(θ2)* np.sin(α1) * f1 + np.cos(θ2) * np.sin(α1)* f2 +\
np.cos(α1) * f3
'''
'''
## a1 不等于 0
k1 = f1
k2 = -f2
#k3 = f1**2 + f2**2 + f3**2 + a1**2 + d2**2 + 2*d2*f3
k3 = f1**2 + f2**2 + f3**2 + a1**2
#k4 = f3 * np.cos(α1) + d2 * np.cos(α1)
k4 = 0
'''
##
r = x**2 + y**2 + z**2 ## 可解
'''
f1 = a3 * np.cos(θ3) + d4 * np.sin(α3)*np.sin(θ3) + a2
f2 = a3 * np.sin(θ3) - d4 * np.sin(α3) * np.cos(θ3)
f3 = d4 * np.cos(α3)
k1 = f1
k2 = -f2
k3 = f1**2 + f2**2 + f3**2 + a1**2
k4 = 0
'''
### 解 超越方程
from sympy import *
θ3 = symbols('θ3')
f = (r-a1**2- (a3 * cos(θ3) + d4 * sin(α3)*sin(θ3) + a2 )**2 \
- (a3 * sin(θ3) - d4 * sin(α3) * cos(θ3))**2 \
- (d4 * cos(α3))**2 )**2/(4 * a1**2) \
+ z**2/(sin(α1))**2 \
- (a3 * cos(θ3) + d4 * sin(α3)*sin(θ3) + a2)**2 \
- (a3 * sin(θ3) - d4 * sin(α3) * cos(θ3))**2
# f = ((r - k3)**2)/(4*a1**2) + ((z-k4)**2)/(np.sin(α1))**2 - k1**2 - k2**2
root3 = solve([f],[θ3])
print('θ3(弧度值): ', root3)
θ3_du = [180 * root3[i][0] / np.pi for i in range(len(root3))] ## θ3 弧度换角度
print('θ3(以度为单位): ', θ3_du )

## 求解 θ2 [-90, 0]
# θ3结果汇总
# θ3(弧度值): [(-3.04783066903255,), (-2.73611423041923,), (-0.641069066911731,), (-0.329352628298420,)]
# θ3(以度为单位): [-174.627834006099, -156.767797668707, -36.7305519104320, -18.8705155730404]
# θ3 = -0.641069066911731 【角度】 -37
# [-0.558019327136135, -0.490112155159801]
# θ2(以度为单位): [-31.9721523316306, -28.0813579787176]
# θ3 = -0.329352628298420
# θ2 无 符合 条件的
# θ3的有效解 -0.641069066911731 , -0.329352628298420
θ3 = -0.641069066911731
f1 = a3 * np.cos(θ3) + d4 * np.sin(α3)*np.sin(θ3) + a2
f2 = a3 * np.cos(α2)*np.sin(θ3) - d4 * np.sin(α3)*np.cos(α2)*np.cos(θ3) - d4 * np.sin(α2)*np.cos(α3) - d3 * np.sin(α2)
f3 = a3 * np.sin(α2)* np.sin(θ3)- d4 * np.sin(α3)* np.sin(α2) * np.cos(θ3) + d4 * np.cos(α2) * np.cos(α3) + d3 * np.cos(α2)
k1 = f1
k2 = -f2
k3 = f1**2 + f2**2 + f3**2 + a1**2 + d2**2 + 2*d2*f3
θ2 = symbols('θ2')
f = (k1 * cos(θ2) + k2 * sin(θ2)) * 2 * a1 + k3 - r
root2 = solve([f],[θ2])
θ2 = [root2[i][0] for i in range(len(root2))]
print(θ2)
θ2_du = [180 * root2[i][0] / np.pi for i in range(len(root2))] ## θ3 弧度换角度
print('θ2(以度为单位): ', θ2_du )
小结:
θ3 = -0.641069066911731 【角度】 -37
θ2(弧度): [-0.558019327136135, -0.490112155159801]
θ2(角度): [-31.9721523316306, -28.0813579787176]
## 求解 θ1 [-90, 90]
## 结果汇总
# θ2 = -0.558019327136135
# θ1: [-0.709402669487201, 0.709402669487201]
# θ1(以度为单位): [-40.6457789369307, 40.6457789369307]
###
# θ2 = -0.490112155159801
# θ1(弧度):[-0.709402669487201, 0.709402669487201]
# θ1(以度为单位): [-40.6457789369307, 40.6457789369307]
θ2 = -0.490112155159801
g1 = np.cos(θ2)* f1 - np.sin(θ2) * f2 + a1
g2 = np.sin(θ2)* np.cos(α1) * f1 + np.cos(θ2) * np.cos(α1)* f2 -\
np.sin(α1) * f3 - d2 * np.sin(α1)
g3 = np.sin(θ2)* np.sin(α1) * f1 + np.cos(θ2) * np.sin(α1)* f2 +\
np.cos(α1) * f3 + d2 * np.cos(α1)
θ1 = symbols('θ1')
f = g1 * cos(θ1) - g2 * sin(θ1) - x
root1 = solve([f],[θ1])
θ1 = [root1[i][0] for i in range(len(root1))]
print(θ1)
θ1_du = [180 * root1[i][0] / np.pi for i in range(len(root1))] ## θ3 弧度换角度
print('θ1(以度为单位): ', θ1_du )
结果小结:
θ2 = -0.558019327136135
θ1: [-0.709402669487201, 0.709402669487201]
θ1(以度为单位): [-40.6457789369307, 40.6457789369307]
θ2 = -0.490112155159801
θ1(弧度):[-0.709402669487201, 0.709402669487201]
θ1(以度为单位): [-40.6457789369307, 40.6457789369307]
import numpy as np
# 求解 θ4 [-180, 180], θ5 [0, 90] θ6 [-180, 180]
## θ1
θ = -0.709402669487201 ## 可选 [-1.12251898466604, 1.12251898466604]
α = 0
R_01 = [[np.cos(θ), -np.sin(θ), 0],
[np.sin(θ)*np.cos(α), np.cos(θ)*np.cos(α), -np.sin(α)],
[np.sin(θ)*np.sin(α), np.cos(θ)*np.sin(α), np.cos(α)]]
## θ2
θ = -0.490112155159801 ##
α = np.pi * (-90)/180
R_12 = [[np.cos(θ), -np.sin(θ), 0],
[np.sin(θ)*np.cos(α), np.cos(θ)*np.cos(α), -np.sin(α)],
[np.sin(θ)*np.sin(α), np.cos(θ)*np.sin(α), np.cos(α)]]
# θ3 仅一个 解
θ = -0.641069066911731
α = 0
R_23 = [[np.cos(θ), -np.sin(θ), 0],
[np.sin(θ)*np.cos(α), np.cos(θ)*np.cos(α), -np.sin(α)],
[np.sin(θ)*np.sin(α), np.cos(θ)*np.sin(α), np.cos(α)]]
R = np.dot(R_01, R_12)
R_03 = np.dot(R, R_23)
# print(R_03)
## 由之前 计算的 T_06 ############## 记得 修改 R !!!!!!!
R_06 = [[0, 0, 1],
[0, -1, 0],
[1, 0, 0]]
### 注意这一步处理,这里 和 PPT 里不一样
θ = np.pi * (-90)/180
R_34X = [[1, 0, 0],
[0, np.cos(θ), -np.sin(θ)],
[0, np.sin(θ), np.cos(θ)]]
R_36 = np.dot(np.linalg.inv(np.dot(R_03, R_34X)), R_06) ## 需要 先将 Z3 转到 Z4 , 才能 继续 使用 ZYZ 欧拉角 计算
# print(R_36)
r31 = R_36[2][0]
r32 = R_36[2][1]
r33 = R_36[2][2]
r23 = R_36[1][2]
r13 = R_36[0][2]
import math
β = math.atan2(math.sqrt(r31**2 + r32**2), r33) ## 此外, 当 β 选负时,还有 一种 姿态选项, 而后续的θ4和 θ6 仅与 β的选值有关
print("解1:")
# print(β) ## 1.1033617668479667 63
## 由PPT P25 DH定义 与 ZYZ 欧拉角度 转换关系
print('θ5:',180*β/np.pi)
# β = 1.1033617668479667
α = math.atan2(r23/np.sin(β), r13/np.sin(β))
print('θ4:',180*α/np.pi + 180)
γ = math.atan2(r32/np.sin(β), -r31/np.sin(β))
print('θ6:', 180*γ/np.pi + 180)
###
print("解2:")
β = -β ## 另一组姿态
print('θ5:',180*β/np.pi)
α = math.atan2(r23/np.sin(β), r13/np.sin(β))
print('θ4:',180*α/np.pi + 180)
γ = math.atan2(r32/np.sin(β), -r31/np.sin(β))
print('θ6:', 180*γ/np.pi + 180)

全部结果汇总:
θ3 = -0.641069066911731 【角度】 -36.7305519104320
θ3 = -0.641069066911731 【角度】 -37
[-0.558019327136135, -0.490112155159801]
θ2(以度为单位): [-31.9721523316306, -28.0813579787176]
θ2 = -0.558019327136135 【角度】-32
θ1: [-0.709402669487201, 0.709402669487201]
θ1(以度为单位): [-40.6457789369307, 40.6457789369307]
θ2 = -0.490112155159801 【角度】-28
[-0.709402669487201, 0.709402669487201]
θ1(以度为单位): [-40.6457789369307, 40.6457789369307]
| θ2 | θ1 | θ5[0-90] | θ4 | θ6 | 与T_06一致 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -31.9721523316306 | -40.6457789369307 | 45.01393753545229 | 112.93208396493651 | 239.10090329561015-360 | ❌ P有负的 |
| -31.9721523316306 | 40.6457789369307 | 45.01393753545229 | 247.0679160350635-360 | 120.89909670438985 | |
| -28.0813579787176 | -40.6457789369307 | 46.63798552151713 | 116.36961993396041 | 234.16993087828823-360 | ❌ P有负的 |
| -28.0813579787176 | 40.6457789369307 | 46.63798552151713 | 243.63038006603958-360 | 125.83006912171177 |

这两组看起来半斤八两。🤣
## 通过 T_06 再次验证
import numpy as np
np.set_printoptions(suppress = True)
def getT(α, a, d, θ):
α = np.pi * α / 180
θ = np.pi * θ / 180 ## 2和 3 不好区分, 增加精度
T = [[np.cos(θ), -np.sin(θ), 0, a],
[np.sin(θ)*np.cos(α), np.cos(θ)*np.cos(θ), -np.sin(α), -np.sin(α) * d],
[np.sin(θ)*np.sin(α), np.cos(θ)*np.sin(α), np.cos(α), np.cos(α) * d],
[0, 0, 0, 1]]
return T
T_01 = getT(0, 0, 0, 40.6457789369307) ## θ1
T_12 = getT(-90, -30, 0, -28.0813579787176) ## θ2
T = np.dot(T_01, T_12)
T_23 = getT(0, 340, 0, -36.7305519104320) ## θ3 不改
T = np.dot(T, T_23)
T_34 = getT(-90, -40,338, 243.63038006603958-360) ## θ4
T = np.dot(T, T_34)
T_45 = getT(90, 0, 0, 46.63798552151713) ## θ5
T = np.dot(T, T_45)
T_56 = getT(-90, 0, 0, 125.83006912171177) ## θ6
T_06 = np.dot(T, T_56)
print(T_06)
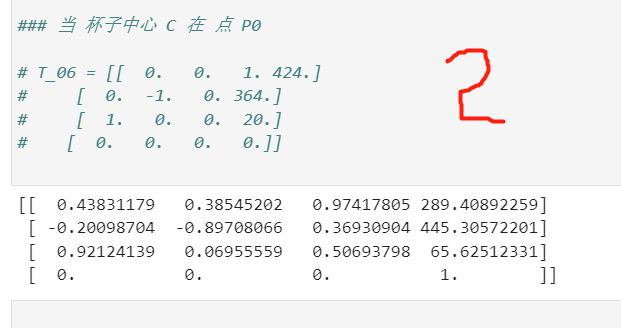
### 当 杯子中心 C 在 点 P0
# T_06 = [[ 0. 0. 1. 424.]
# [ 0. -1. 0. 364.]
# [ 1. 0. 0. 20.]
# [ 0. 0. 0. 0.]]
【这两题都是在答案系统里试的。。🤣】
第4题答案: 41//-32//-37 【2选1】
第5题答案: -113//45//121 【题4定则题5定】


题6-7求解代码: Python
import numpy as np
## 杯子 中心 C 在 点 P1 处
## 只沿着 X 轴 转 60°
θ = np.pi * 60 / 180
R = [[1,0, 0],
[0, np.cos(θ), -np.sin(θ)],
[0, np.sin(θ), np.cos(θ)]]
a = np.row_stack((R,[[0, 0, 0]])) ## 扩展 行 这样 不用 将 R 打印出来
P = np.array([[630, 304, 220, 1]]) ## 扩展 列
T_0C = np.column_stack((a, P.T))
## 已知 T_6C
T_6C = [[0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, -1, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 0, 206],
[0, 0, 0, 1]]
# T_0C = T_06 * T_6C
T_06 = np.dot(T_0C, np.linalg.inv(T_6C))
T_06 = [[float(format(x, '.3g')) for x in T_06[i]] for i in range(len(T_06))]
print(np.array(T_06))
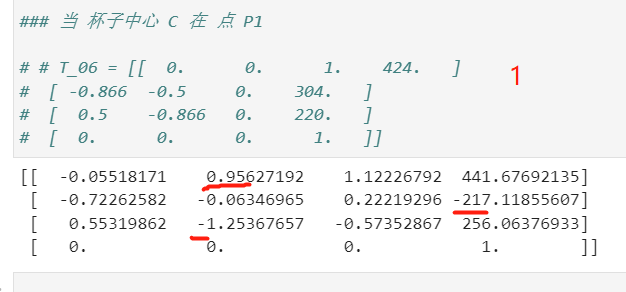
### 当 杯子中心 C 在 点 P1
# # T_06 = [[ 0. 0. 1. 424. ]
# [ -0.866 -0.5 0. 304. ]
# [ 0.5 -0.866 0. 220. ]
# [ 0. 0. 0. 1. ]]
######## 求解 θ3 [-90, 0]
### 注意这里 的 x, y, z 是 T_06 的
x, y, z = 424, 304, 220
##################
import numpy as np
α2, a2, d3 = 0, 340, 0 ## θ3
α3, a3, d4 = np.pi*(-90)/180, -40, 338 ## θ4
'''
## 仅与 θ3 有关
f1 = a3 * np.cos(θ3) + d4 * np.sin(α3)*np.sin(θ3) + a2
#f2 = a3 * np.cos(α2)*np.sin(θ3) - d4 * np.sin(α3)*np.cos(α2)*np.cos(θ3) -\
# d4 * np.sin(α2)*np.cos(α3) - d3 * np.sin(α2)
f2 = a3 * np.sin(θ3) - d4 * np.sin(α3) * np.cos(θ3)
#f3 = a3 * np.sin(α2)* np.sin(θ3)- d4 * np.sin(α3)* np.sin(α2) * np.cos(θ3) + \
# d4 * np.cos(α2) * np.cos(α3) + d3 * np.cos(α2)
f3 = d4 * np.cos(α3)
# print(f3)
'''
# 对 i= 1 i= 2
α0, a0, d1 = 0, 0, 0 ## θ1
α1, a1, d2 = np.pi*(-90)/180, -30, 0 ## θ2
'''
## 和 θ2,θ3有关
g1 = np.cos(θ2)* f1 - np.sin(θ2) * f2 + a1
# g2 = np.sin(θ2)* np.cos(α1) * f1 + np.cos(θ2) * np.cos(α1)* f2 -\
# np.sin(α1) * f3 - d2 * np.sin(α1)
## 化简
g2 = np.sin(θ2)* np.cos(α1) * f1 + np.cos(θ2) * np.cos(α1)* f2 -\
np.sin(α1) * f3
# g3 = np.sin(θ2)* np.sin(α1) * f1 + np.cos(θ2) * np.sin(α1)* f2 +\
# np.cos(α1) * f3 + d2 * np.cos(α1)
## 化简
g3 = np.sin(θ2)* np.sin(α1) * f1 + np.cos(θ2) * np.sin(α1)* f2 +\
np.cos(α1) * f3
'''
'''
## a1 不等于 0
k1 = f1
k2 = -f2
#k3 = f1**2 + f2**2 + f3**2 + a1**2 + d2**2 + 2*d2*f3
k3 = f1**2 + f2**2 + f3**2 + a1**2
#k4 = f3 * np.cos(α1) + d2 * np.cos(α1)
k4 = 0
'''
##
r = x**2 + y**2 + z**2 ## 可解
'''
f1 = a3 * np.cos(θ3) + d4 * np.sin(α3)*np.sin(θ3) + a2
f2 = a3 * np.sin(θ3) - d4 * np.sin(α3) * np.cos(θ3)
f3 = d4 * np.cos(α3)
k1 = f1
k2 = -f2
k3 = f1**2 + f2**2 + f3**2 + a1**2
k4 = 0
'''
### 解 超越方程
from sympy import *
θ3 = symbols('θ3')
f = (r-a1**2- (a3 * cos(θ3) + d4 * sin(α3)*sin(θ3) + a2 )**2 \
- (a3 * sin(θ3) - d4 * sin(α3) * cos(θ3))**2 \
- (d4 * cos(α3))**2 )**2/(4 * a1**2) \
+ z**2/(sin(α1))**2 \
- (a3 * cos(θ3) + d4 * sin(α3)*sin(θ3) + a2)**2 \
- (a3 * sin(θ3) - d4 * sin(α3) * cos(θ3))**2
# f = ((r - k3)**2)/(4*a1**2) + ((z-k4)**2)/(np.sin(α1))**2 - k1**2 - k2**2
root3 = solve([f],[θ3])
print('θ3(弧度值): ', root3)
θ3_du = [180 * root3[i][0] / np.pi for i in range(len(root3))] ## θ3 弧度换角度
print('θ3(以度为单位): ', θ3_du )
θ3(弧度值): [(-3.00276174766702,), (-2.70746877163218,), (-0.669714525698784,), (-0.374421549663944,)]
θ3(以度为单位): [-172.045575024647, -155.126533777993, -38.3718158011460, -21.4527745544920]
## 求解 θ2 [-90, 0]
# θ3结果汇总
# θ3(弧度值): [(-3.00276174766702,), (-2.70746877163218,), (-0.669714525698784,), (-0.374421549663944,)]
# θ3(以度为单位): [-172.045575024647, -155.126533777993, -38.3718158011460, -21.4527745544920]
# θ3 = -0.669714525698784 【角度】 -38
# [-0.889163787914293, -0.130302262671859]
# θ2(以度为单位): [-50.9453323433544, -7.46576971210258]
# θ3 = -0.374421549663944 角度 -21
# θ2 无符合 条件的
# θ3的有效解
θ3 = -0.374421549663944
f1 = a3 * np.cos(θ3) + d4 * np.sin(α3)*np.sin(θ3) + a2
f2 = a3 * np.cos(α2)*np.sin(θ3) - d4 * np.sin(α3)*np.cos(α2)*np.cos(θ3) - d4 * np.sin(α2)*np.cos(α3) - d3 * np.sin(α2)
f3 = a3 * np.sin(α2)* np.sin(θ3)- d4 * np.sin(α3)* np.sin(α2) * np.cos(θ3) + d4 * np.cos(α2) * np.cos(α3) + d3 * np.cos(α2)
k1 = f1
k2 = -f2
k3 = f1**2 + f2**2 + f3**2 + a1**2 + d2**2 + 2*d2*f3
θ2 = symbols('θ2')
f = (k1 * cos(θ2) + k2 * sin(θ2)) * 2 * a1 + k3 - r
root2 = solve([f],[θ2])
θ2 = [root2[i][0] for i in range(len(root2))]
print(θ2)
θ2_du = [180 * root2[i][0] / np.pi for i in range(len(root2))] ## θ3 弧度换角度
print('θ2(以度为单位): ', θ2_du ) # [-174.801389740395, -158.156748814047, -35.3416007650924, -18.6969598387445]
#θ3 = -0.669714525698784 【角度】 -38
#[-0.889163787914293, -0.130302262671859]
#θ2(以度为单位): [-50.9453323433544, -7.46576971210258]
## 求解 θ1 [-90, 90]
## 结果汇总
# θ2 = -0.889163787914293
# [-0.539863702101135, 0.539863702101135]
# θ1(以度为单位): [-30.9319116427030, 30.9319116427030]
###
# θ2 = -0.130302262671859
# [-0.230814088745282, 0.230814088745282]
# θ1(以度为单位): [-13.2246731372627, 13.2246731372627]
θ2 = -0.130302262671859
g1 = np.cos(θ2)* f1 - np.sin(θ2) * f2 + a1
g2 = np.sin(θ2)* np.cos(α1) * f1 + np.cos(θ2) * np.cos(α1)* f2 -\
np.sin(α1) * f3 - d2 * np.sin(α1)
g3 = np.sin(θ2)* np.sin(α1) * f1 + np.cos(θ2) * np.sin(α1)* f2 +\
np.cos(α1) * f3 + d2 * np.cos(α1)
θ1 = symbols('θ1')
f = g1 * cos(θ1) - g2 * sin(θ1) - x
root1 = solve([f],[θ1])
θ1 = [root1[i][0] for i in range(len(root1))]
print(θ1)
θ1_du = [180 * root1[i][0] / np.pi for i in range(len(root1))] ## θ3 弧度换角度
print('θ1(以度为单位): ', θ1_du )
θ2 = -0.889163787914293 -51
[-0.539863702101135, 0.539863702101135]
θ1(以度为单位): [-30.9319116427030, 30.9319116427030]
θ2 = -0.130302262671859 -7
[-0.230814088745282, 0.230814088745282]
θ1(以度为单位): [-13.2246731372627, 13.2246731372627]
求解 θ4-θ6 时, 记得 将 R 改成相应的!!!!
import numpy as np
# 求解 θ4 [-180, 180], θ5 [0, 90] θ6 [-180, 180]
## θ1
θ = 0.622032015289154
α = 0
R_01 = [[np.cos(θ), -np.sin(θ), 0],
[np.sin(θ)*np.cos(α), np.cos(θ)*np.cos(α), -np.sin(α)],
[np.sin(θ)*np.sin(α), np.cos(θ)*np.sin(α), np.cos(α)]]
## θ2
θ = -0.130302262671859 ##
α = np.pi * (-90)/180
R_12 = [[np.cos(θ), -np.sin(θ), 0],
[np.sin(θ)*np.cos(α), np.cos(θ)*np.cos(α), -np.sin(α)],
[np.sin(θ)*np.sin(α), np.cos(θ)*np.sin(α), np.cos(α)]]
# θ3 仅一个 解
θ = -0.669714525698784 #【角度】
α = 0
R_23 = [[np.cos(θ), -np.sin(θ), 0],
[np.sin(θ)*np.cos(α), np.cos(θ)*np.cos(α), -np.sin(α)],
[np.sin(θ)*np.sin(α), np.cos(θ)*np.sin(α), np.cos(α)]]
R = np.dot(R_01, R_12)
R_03 = np.dot(R, R_23)
# print(R_03)
########################################### 记得 修改 R !!!!
## 由之前 计算的 T_06
R_06 = [[0, 0, 1],
[-0.866, -0.5, 0],
[0.5, -0.866, 0]]
### 注意这一步处理,这里 和 PPT 里不一样
θ = np.pi * (-90)/180
R_34X = [[1, 0, 0],
[0, np.cos(θ), -np.sin(θ)],
[0, np.sin(θ), np.cos(θ)]]
R_36 = np.dot(np.linalg.inv(np.dot(R_03, R_34X)), R_06) ## 需要 先将 Z3 转到 Z4 , 才能 继续 使用 ZYZ 欧拉角 计算
# print(R_36)
r31 = R_36[2][0]
r32 = R_36[2][1]
r33 = R_36[2][2]
r23 = R_36[1][2]
r13 = R_36[0][2]
import math
β = math.atan2(math.sqrt(r31**2 + r32**2), r33) ## 此外, 当 β 选负时,还有 一种 姿态选项, 而后续的θ4和 θ6 仅与 β的选值有关
print("解1:")
# print(β) ## 1.1033617668479667 63
## 由PPT P25 DH定义 与 ZYZ 欧拉角度 转换关系
print('θ5:',180*β/np.pi)
# β = 1.1033617668479667
α = math.atan2(r23/np.sin(β), r13/np.sin(β))
print('θ4:',180*α/np.pi + 180)
γ = math.atan2(r32/np.sin(β), -r31/np.sin(β))
print('θ6:', 180*γ/np.pi + 180)
###
print("解2:")
β = -β ## 另一组姿态
print('θ5:',180*β/np.pi)
α = math.atan2(r23/np.sin(β), r13/np.sin(β))
print('θ4:',180*α/np.pi + 180)
γ = math.atan2(r32/np.sin(β), -r31/np.sin(β))
print('θ6:', 180*γ/np.pi + 180)
答案汇总
θ3 = -0.669714525698784 【角度】 -38.3718158011460
θ2:
[-0.889163787914293, -0.130302262671859]
θ2(以度为单位): [-50.9453323433544, -7.46576971210258]
θ1:
[-0.622032015289154, 0.622032015289154]
θ1(以度为单位): [-35.6398091980856, 35.6398091980856]
[-0.622032015289152, 0.622032015289151]
θ1(以度为单位): [-35.6398091980855, 35.6398091980855]
| θ2 | θ1 | θ5[0-90] | θ4[-180-180] | θ6[-180-180] | 与T_06一致 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -50.9453323433544 | -35.6398091980856 | 35.64488712689306 | 90.95228839698065 | 328.8274800404136-360 | ❌ P有负的 |
| -50.9453323433544 | 35.6398091980856 | 35.64488712689307 | 269.04771160301937-360 | 151.17106439793167 | |
| -7.46576971210258 | -35.6398091980856 | 54.33743693103992 | 134.1778531447378 | 270.96209986285226-360 | ❌ P有负的 |
| -7.46576971210258 | 35.6398091980856 | 54.337436931039925 | 225.8221468552622-360 | 209.03644457549302-360 | ❌ P有负的 |

第6题答案:: 36//-51//-38
第7题答案::-91//36//151
## 通过 T_06 再次验证
import numpy as np
np.set_printoptions(suppress = True)
def getT(α, a, d, θ):
α = np.pi * α / 180
θ = np.pi * θ / 180 ## 2和 3 不好区分, 增加精度
T = [[np.cos(θ), -np.sin(θ), 0, a],
[np.sin(θ)*np.cos(α), np.cos(θ)*np.cos(θ), -np.sin(α), -np.sin(α) * d],
[np.sin(θ)*np.sin(α), np.cos(θ)*np.sin(α), np.cos(α), np.cos(α) * d],
[0, 0, 0, 1]]
return T
T_01 = getT(0, 0, 0, 35.6398091980856) ## θ1
T_12 = getT(-90, -30, 0, -7.46576971210258) ## θ2
T = np.dot(T_01, T_12)
T_23 = getT(0, 340, 0, -38.3718158011460) ## θ3 不改
T = np.dot(T, T_23)
T_34 = getT(-90, -40,338, 225.8221468552622-360) ## θ4
T = np.dot(T, T_34)
T_45 = getT(90, 0, 0, 54.33743693103992) ## θ5
T = np.dot(T, T_45)
T_56 = getT(-90, 0, 0, 209.03644457549302-360) ## θ6
T_06 = np.dot(T, T_56)
print(T_06)
### 当 杯子中心 C 在 点 P1
# # T_06 = [[ 0. 0. 1. 424. ]
# [ -0.866 -0.5 0. 304. ]
# [ 0.5 -0.866 0. 220. ]
# [ 0. 0. 0. 1. ]]


题8-9求解代码: Python
import numpy as np
np.set_printoptions(suppress = True)
## 杯子 中心 C 在 点 P2 处
## 只沿着 X 轴 转 180°
θ = np.pi * 180 / 180
R = [[1, 0, 0],
[0, np.cos(θ), -np.sin(θ)],
[0, np.sin(θ), np.cos(θ)]]
a = np.row_stack((R,[[0, 0, 0]])) ## 扩展 行 这样 不用 将 R 打印出来
P = np.array([[630, 220, 24, 1]]) ## 扩展 列
T_0C = np.column_stack((a, P.T))
## 已知 T_6C
T_6C = [[0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, -1, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 0, 206],
[0, 0, 0, 1]]
# T_0C = T_06 * T_6C
T_06 = np.dot(T_0C, np.linalg.inv(T_6C))
T_06 = [[float(format(x, '.3g')) for x in T_06[i]] for i in range(len(T_06))]
print(np.array(T_06))
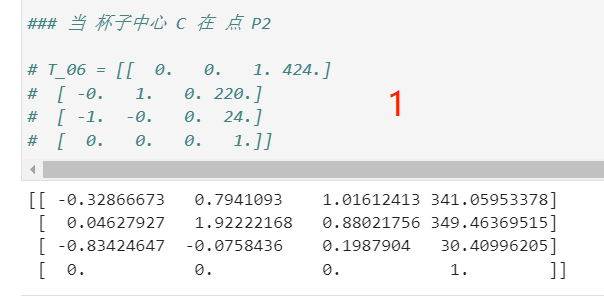
### 当 杯子中心 C 在 点 P2
# T_06 = [[ 0. 0. 1. 424.]
# [ -0. 1. 0. 220.]
# [ -1. -0. 0. 24.]
# [ 0. 0. 0. 1.]]
######## 求解 θ3 [-90, 0]
### 注意这里 的 x, y, z 是 T_06 的
x, y, z = 424, 220, 24
##################
import numpy as np
α2, a2, d3 = 0, 340, 0 ## θ3
α3, a3, d4 = np.pi*(-90)/180, -40, 338 ## θ4
'''
## 仅与 θ3 有关
f1 = a3 * np.cos(θ3) + d4 * np.sin(α3)*np.sin(θ3) + a2
#f2 = a3 * np.cos(α2)*np.sin(θ3) - d4 * np.sin(α3)*np.cos(α2)*np.cos(θ3) -\
# d4 * np.sin(α2)*np.cos(α3) - d3 * np.sin(α2)
f2 = a3 * np.sin(θ3) - d4 * np.sin(α3) * np.cos(θ3)
#f3 = a3 * np.sin(α2)* np.sin(θ3)- d4 * np.sin(α3)* np.sin(α2) * np.cos(θ3) + \
# d4 * np.cos(α2) * np.cos(α3) + d3 * np.cos(α2)
f3 = d4 * np.cos(α3)
# print(f3)
'''
# 对 i= 1 i= 2
α0, a0, d1 = 0, 0, 0 ## θ1
α1, a1, d2 = np.pi*(-90)/180, -30, 0 ## θ2
'''
## 和 θ2,θ3有关
g1 = np.cos(θ2)* f1 - np.sin(θ2) * f2 + a1
# g2 = np.sin(θ2)* np.cos(α1) * f1 + np.cos(θ2) * np.cos(α1)* f2 -\
# np.sin(α1) * f3 - d2 * np.sin(α1)
## 化简
g2 = np.sin(θ2)* np.cos(α1) * f1 + np.cos(θ2) * np.cos(α1)* f2 -\
np.sin(α1) * f3
# g3 = np.sin(θ2)* np.sin(α1) * f1 + np.cos(θ2) * np.sin(α1)* f2 +\
# np.cos(α1) * f3 + d2 * np.cos(α1)
## 化简
g3 = np.sin(θ2)* np.sin(α1) * f1 + np.cos(θ2) * np.sin(α1)* f2 +\
np.cos(α1) * f3
'''
'''
## a1 不等于 0
k1 = f1
k2 = -f2
#k3 = f1**2 + f2**2 + f3**2 + a1**2 + d2**2 + 2*d2*f3
k3 = f1**2 + f2**2 + f3**2 + a1**2
#k4 = f3 * np.cos(α1) + d2 * np.cos(α1)
k4 = 0
'''
##
r = x**2 + y**2 + z**2 ## 可解
'''
f1 = a3 * np.cos(θ3) + d4 * np.sin(α3)*np.sin(θ3) + a2
f2 = a3 * np.sin(θ3) - d4 * np.sin(α3) * np.cos(θ3)
f3 = d4 * np.cos(α3)
k1 = f1
k2 = -f2
k3 = f1**2 + f2**2 + f3**2 + a1**2
k4 = 0
'''
### 解 超越方程
from sympy import *
θ3 = symbols('θ3')
f = (r-a1**2- (a3 * cos(θ3) + d4 * sin(α3)*sin(θ3) + a2 )**2 \
- (a3 * sin(θ3) - d4 * sin(α3) * cos(θ3))**2 \
- (d4 * cos(α3))**2 )**2/(4 * a1**2) \
+ z**2/(sin(α1))**2 \
- (a3 * cos(θ3) + d4 * sin(α3)*sin(θ3) + a2)**2 \
- (a3 * sin(θ3) - d4 * sin(α3) * cos(θ3))**2
# f = ((r - k3)**2)/(4*a1**2) + ((z-k4)**2)/(np.sin(α1))**2 - k1**2 - k2**2
root3 = solve([f],[θ3])
print('θ3(弧度值): ', root3)
θ3_du = [180 * root3[i][0] / np.pi for i in range(len(root3))] ## θ3 弧度换角度
print('θ3(以度为单位): ', θ3_du )
θ3(弧度值): -0.234149167415370
θ3(以度为单位): -13.4157590694029
## 求解 θ2 [-90, 0]
# θ3的有效解
θ3 = -0.234149167415370
f1 = a3 * np.cos(θ3) + d4 * np.sin(α3)*np.sin(θ3) + a2
f2 = a3 * np.cos(α2)*np.sin(θ3) - d4 * np.sin(α3)*np.cos(α2)*np.cos(θ3) - d4 * np.sin(α2)*np.cos(α3) - d3 * np.sin(α2)
f3 = a3 * np.sin(α2)* np.sin(θ3)- d4 * np.sin(α3)* np.sin(α2) * np.cos(θ3) + d4 * np.cos(α2) * np.cos(α3) + d3 * np.cos(α2)
k1 = f1
k2 = -f2
k3 = f1**2 + f2**2 + f3**2 + a1**2 + d2**2 + 2*d2*f3
θ2 = symbols('θ2')
f = (k1 * cos(θ2) + k2 * sin(θ2)) * 2 * a1 + k3 - r
root2 = solve([f],[θ2])
θ2 = [root2[i][0] for i in range(len(root2))]
print(θ2)
θ2_du = [180 * root2[i][0] / np.pi for i in range(len(root2))] ## θ3 弧度换角度
print('θ2(以度为单位): ', θ2_du )
[-0.774929259641440, -0.680451426622777]
θ2(以度为单位): [-44.4001759986521, -38.9869949091409]
## 求解 θ1 [-90, 90]
## 结果汇总
# θ2 = -0.774929259641440
# [-0.478627761768163, 0.478627761768163]
# θ1(以度为单位): [-27.4233507071088, 27.4233507071088]
###
# θ2 = -0.680451426622777
# [-0.478627761768163, 0.478627761768163]
# θ1(以度为单位): [-27.4233507071088, 27.4233507071088]
θ2 = -0.680451426622777
g1 = np.cos(θ2)* f1 - np.sin(θ2) * f2 + a1
g2 = np.sin(θ2)* np.cos(α1) * f1 + np.cos(θ2) * np.cos(α1)* f2 -\
np.sin(α1) * f3 - d2 * np.sin(α1)
g3 = np.sin(θ2)* np.sin(α1) * f1 + np.cos(θ2) * np.sin(α1)* f2 +\
np.cos(α1) * f3 + d2 * np.cos(α1)
θ1 = symbols('θ1')
f = g1 * cos(θ1) - g2 * sin(θ1) - x
root1 = solve([f],[θ1])
θ1 = [root1[i][0] for i in range(len(root1))]
print(θ1)
θ1_du = [180 * root1[i][0] / np.pi for i in range(len(root1))] ## θ3 弧度换角度
print('θ1(以度为单位): ', θ1_du )
import numpy as np
# 求解 θ4 [-180, 180], θ5 [0, 90] θ6 [-180, 180]
## θ1
θ = 0.478627761768163
α = 0
R_01 = [[np.cos(θ), -np.sin(θ), 0],
[np.sin(θ)*np.cos(α), np.cos(θ)*np.cos(α), -np.sin(α)],
[np.sin(θ)*np.sin(α), np.cos(θ)*np.sin(α), np.cos(α)]]
## θ2
θ = -0.680451426622777##
α = np.pi * (-90)/180
R_12 = [[np.cos(θ), -np.sin(θ), 0],
[np.sin(θ)*np.cos(α), np.cos(θ)*np.cos(α), -np.sin(α)],
[np.sin(θ)*np.sin(α), np.cos(θ)*np.sin(α), np.cos(α)]]
# θ3 仅一个 解
θ = -0.234149167415370 #【角度】
α = 0
R_23 = [[np.cos(θ), -np.sin(θ), 0],
[np.sin(θ)*np.cos(α), np.cos(θ)*np.cos(α), -np.sin(α)],
[np.sin(θ)*np.sin(α), np.cos(θ)*np.sin(α), np.cos(α)]]
R = np.dot(R_01, R_12)
R_03 = np.dot(R, R_23)
# print(R_03)
## 由之前 计算的 T_06 !!!!记得修改 R !!!检查
R_06 = [[0, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 0],
[-1, 0, 0]]
### 注意这一步处理,这里 和 PPT 里不一样
θ = np.pi * (-90)/180
R_34X = [[1, 0, 0],
[0, np.cos(θ), -np.sin(θ)],
[0, np.sin(θ), np.cos(θ)]]
R_36 = np.dot(np.linalg.inv(np.dot(R_03, R_34X)), R_06) ## 需要 先将 Z3 转到 Z4 , 才能 继续 使用 ZYZ 欧拉角 计算
# print(R_36)
r31 = R_36[2][0]
r32 = R_36[2][1]
r33 = R_36[2][2]
r23 = R_36[1][2]
r13 = R_36[0][2]
import math
β = math.atan2(math.sqrt(r31**2 + r32**2), r33) ## 此外, 当 β 选负时,还有 一种 姿态选项, 而后续的θ4和 θ6 仅与 β的选值有关
print("解1:")
# print(β) ## 1.1033617668479667 63
## 由PPT P25 DH定义 与 ZYZ 欧拉角度 转换关系
print('θ5:',180*β/np.pi)
# β = 1.1033617668479667
α = math.atan2(r23/np.sin(β), r13/np.sin(β))
print('θ4:',180*α/np.pi + 180)
γ = math.atan2(r32/np.sin(β), -r31/np.sin(β))
print('θ6:', 180*γ/np.pi + 180)
###
print("解2:")
β = -β ## 另一组姿态
print('θ5:',180*β/np.pi)
α = math.atan2(r23/np.sin(β), r13/np.sin(β))
print('θ4:',180*α/np.pi + 180)
γ = math.atan2(r32/np.sin(β), -r31/np.sin(β))
print('θ6:', 180*γ/np.pi + 180)
答案汇总
θ3 = -0.234149167415370 【角度】 -13.4157590694029
[-0.774929259641440, -0.680451426622777]
θ2(以度为单位): [-44.4001759986521, -38.9869949091409]
#θ2 = -0.774929259641440
#[-0.478627761768163, 0.478627761768163]
#θ1(以度为单位): [-27.4233507071088, 27.4233507071088]
#θ2 = -0.680451426622777
#[-0.478627761768163, 0.478627761768163]
#θ1(以度为单位): [-27.4233507071088, 27.4233507071088]
| θ2 | θ1 | θ5[0-90] | θ4[-180-180] | θ6[-180-180] | 与T_06一致 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -44.4001759986521 | 27.4233507071088 | 41.30243673701658 | 224.249565060963-360 | 323.8029365281974-360 | |
| -44.4001759986521 | -27.4233507071088 | 41.30243673701657 | 135.750434939037 | 36.197063471802636 | ❌ P 有负的 |
| -38.9869949091409 | -27.4233507071088 | 45.30889772059033 | 139.62036985874533 | 30.884102139831043 | ❌ P 有负的 |
| -38.9869949091409 | 27.4233507071088 | 45.30889772059034 | 220.37963014125467-360 | 329.11589786016896-360 | ❌ P 有负的 |
第8题答案: 27//-44//-13
第9题答案: -136//41//-36
## 通过 T_06 再次验证
import numpy as np
np.set_printoptions(suppress = True)
def getT(α, a, d, θ):
α = np.pi * α / 180
θ = np.pi * θ / 180 ## 2和 3 不好区分, 增加精度
T = [[np.cos(θ), -np.sin(θ), 0, a],
[np.sin(θ)*np.cos(α), np.cos(θ)*np.cos(θ), -np.sin(α), -np.sin(α) * d],
[np.sin(θ)*np.sin(α), np.cos(θ)*np.sin(α), np.cos(α), np.cos(α) * d],
[0, 0, 0, 1]]
return T
T_01 = getT(0, 0, 0, 27.4233507071088) ## θ1
T_12 = getT(-90, -30, 0, -44.4001759986521) ## θ2
T = np.dot(T_01, T_12)
T_23 = getT(0, 340, 0, -13.4157590694029) ## θ3 不改
T = np.dot(T, T_23)
T_34 = getT(-90, -40,338, 224.249565060963-360) ## θ4
T = np.dot(T, T_34)
T_45 = getT(90, 0, 0, 41.30243673701658 ) ## θ5
T = np.dot(T, T_45)
T_56 = getT(-90, 0, 0, 143.80293652819736) ## θ6
T_06 = np.dot(T, T_56)
print(T_06)
### 当 杯子中心 C 在 点 P2
# T_06 = [[ 0. 0. 1. 424.]
# [ -0. 1. 0. 220.]
# [ -1. -0. 0. 24.]
# [ 0. 0. 0. 1.]]
题10-15 方法一 Cartesian space

- 第10题答案: 0//-21.82//72.73

- 第11题答案: 0//-22.4//-52.27
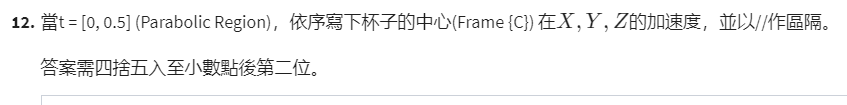
- 第12题答案: 0//-43.64//145.45

- 第13题答案: 0//-1.16//-249.99

- 第14题答案: 0//44.8//104.53

- 第15题答案: 630//336.73//110.91
求解代码【10-15】_Python
## import numpy as np
np.set_printoptions(precision=2,suppress = True)
t0, t1, tf = 0, 3, 7
x0, x1, xf = 630, 630, 630
y0, y1, yf = 364, 304, 220
z0, z1, zf = 20, 220, 24
tk = 0.5
### 1、求 各 DOF(X, Y, θ) 在每段的速度 及 加速度
## 中间 线段 计算
def getV_in(x1, x2, t1, t2):
return (x2 - x1)/(t2 - t1)
## 头尾 线段 计算
def getV_0f(x1, x2, t1, t2):
return (x2 - x1)/(t2 - t1 - tk/2)
### 2、 建立 各 DOF(X, Y, θ) 在每段的方程
"""
平滑 t ∈ [0, 0.5]
直线 t ∈ [0.5, 2.75]
平滑 t ∈ [2.75, 3.25]
直线 t ∈ [3.25, 6.5]
平滑 t ∈ [6.5, 7]
"""
## 求解 X(t)
## 平滑化 段
def getX_parabolic(x, V, a, ti0, ti1, t):
return x + V * (t - ti0) + 0.5 * a * (t - ti1)**2
## 直线段
def getX_linear(x, V, ti, t):
return x + V * (t - ti)
############# 求解 X 部分
print('X:')
V0 = 0
V1 = getV_0f(x0, x1, t0, t1)
V2 = getV_0f(x1, xf, t1, tf) ## 这里 也属于 端点了
Vf = 0
print('V1[0.5 ~ 2.75]:', np.round(V1, 2))
print('V2[3.25 ~ 6.5]:', np.round(V2, 2))
def geta(V1, V2):
return (V2 - V1)/tk
a0 = geta(V0, V1)
a1 = geta(V1, V2)
af = geta(V2, Vf)
print('a0:', np.round(a0, 2))
print('a1:', np.round(a1, 2))
print('af:', np.round(af, 2))
## 属于 直线部分
print('t ∈ [0.5, 2.75] t = 1.5 , X2 = :', np.round(getX_linear(x0, V1, 0.25, 1.5), 2))
print('t ∈ [3.25, 6.5] t = 5 , X4 = :', np.round(getX_linear(x1, V2, 3, 5), 2))
## 平滑部分
print('t ∈ [2.75, 3.25] t = 3 , X3 = :', np.round(getX_parabolic(x0, V1, a1, 0.25, 2.75,3), 2))
############# 求解 Y 部分
print('Y:')
V0 = 0
V1 = getV_0f(y0, y1, t0, t1)
V2 = getV_0f(y1, yf, t1, tf)
Vf = 0
print('V1[0.5 ~ 2.75]:', np.round(V1, 2))
print('V2[3.25 ~ 6.5]:', np.round(V2, 2))
def geta(V1, V2):
return (V2 - V1)/tk
a0 = geta(V0, V1)
a1 = geta(V1, V2)
af = geta(V2, Vf)
print('a0:', np.round(a0, 2))
print('a1:', np.round(a1, 2))
print('af:', np.round(af, 2))
###
print('t ∈ [0.5, 2.75] t = 1.5 , Y2 = :', np.round(getX_linear(y0, V1, 0.25, 1.5), 2))
print('t ∈ [3.25, 6.5] t = 5 , Y4 = :', np.round(getX_linear(y1, V2, 3, 5), 2))
## 平滑部分
print('t ∈ [2.75, 3.25] t = 3 , Y3 = :', np.round(getX_parabolic(y0, V1, a1, 0.25, 2.75,3), 2))
############# 求解 θ 部分
print('Z:')
V0 = 0
V1 = getV_0f(z0, z1, t0, t1)
V2 = getV_0f(z1, zf, t1, tf)
Vf = 0
print('V1[0.5 ~ 2.75]:', np.round(V1, 2))
print('V2[3.25 ~ 6.5]:', np.round(V2, 2))
def geta(V1, V2):
return (V2 - V1)/tk
a0 = geta(V0, V1)
a1 = geta(V1, V2)
af = geta(V2, Vf)
print('a0:', np.round(a0, 2))
print('a1:', np.round(a1, 2))
print('af:', np.round(af, 2))
print('t ∈ [0.5, 2.75] t = 1.5 , Z2 = :', np.round(getX_linear(z0, V1, 0.25, 1.5), 2))
print('t ∈ [3.25, 6.5] t = 5 , Z4 = :', np.round(getX_linear(z1, V2, 3, 5), 2))
## 平滑部分
print('t ∈ [2.75, 3.25] t = 3 , Z3 = :', np.round(getX_parabolic(z0, V1, a1, 0.25, 2.75,3), 2))

其它题:
630//259.2//115.47

630//303.96//212.19