目录
一、概念
二、优势
三、原理(代码逐步实现)
四、BlockingQueue的使用
一、概念
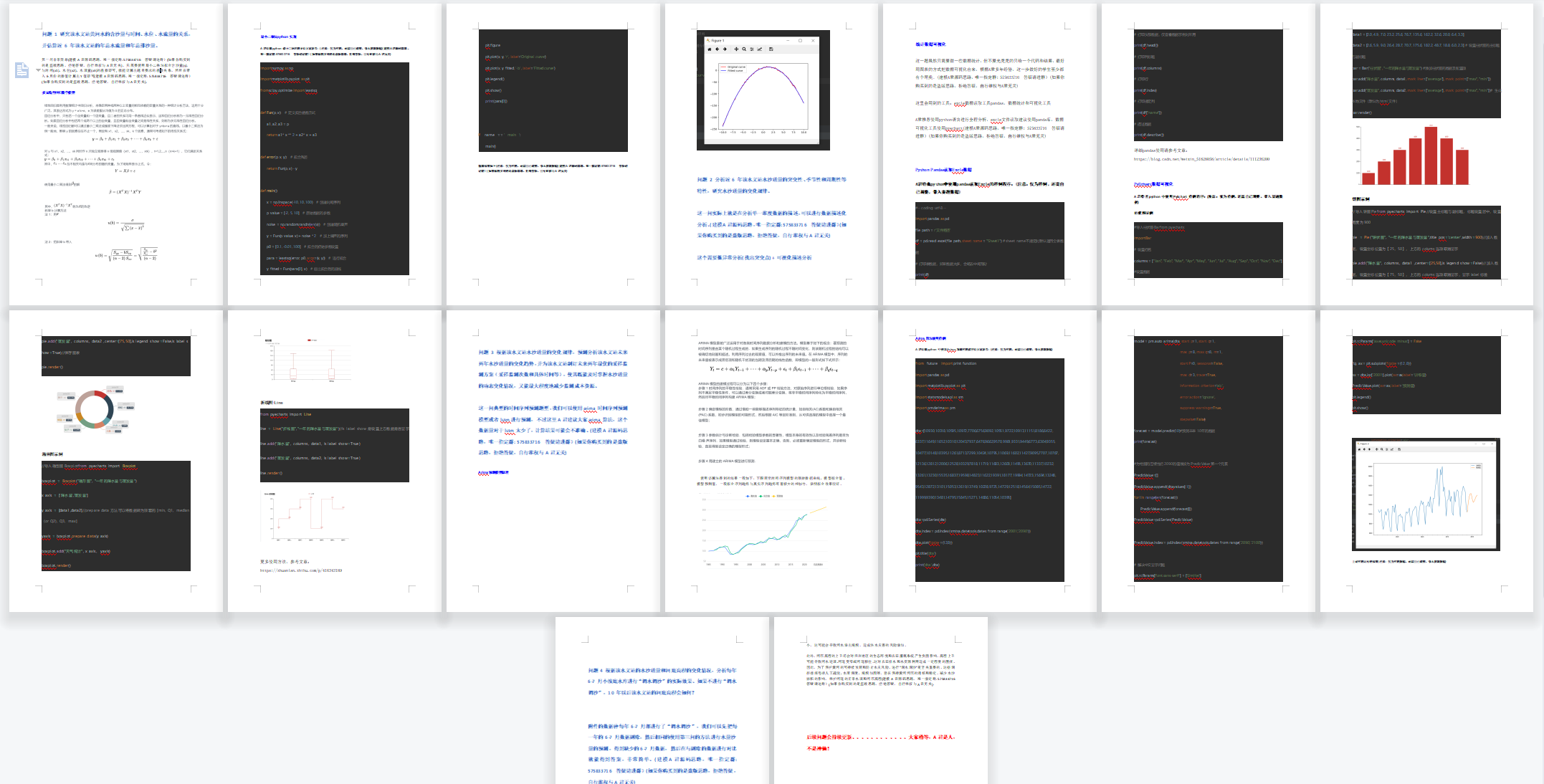
阻塞队列是一种的特殊的队列,他是带有阻塞的线程安全的队列。当队列已满时入队操作就会进入阻塞,当队列不空时才能执行入队操作;当队列为空时出队操作就会进入阻塞,当有元素插入阻塞就会被唤醒执行。它经常用于实现生产者消费者模型。
二、优势
1、阻塞队列的引入,有利于代码的解耦合
2、削峰填谷
3、异步提速
与消息队列类似,可参看【RabbitMQ】初识消息中间件MQ_西瓜霜润喉片的博客-CSDN博客![]() https://blog.csdn.net/qq_61903414/article/details/130138361?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_61903414/article/details/130138361?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
三、原理(代码逐步实现)
这里我们基于数组实现的循环队列来进行阻塞队列的实现,首先我们需要实现一个循环队列
【数据结构】队列与Queue接口_队列是接口吗_西瓜霜润喉片的博客-CSDN博客![]() https://blog.csdn.net/qq_61903414/article/details/128410608?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_61903414/article/details/128410608?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
lass MyBlockingQueue{
private int[] queue = new int[100]; // 用于实现队列的数组
private int front; // 队首下标
private int rear; // 队尾下标
private int size; // 元素个数
/**
* 入队
* @param data 待入队数据
*/
public void put(int data){
if((rear + 1) % this.queue.length == front){
// 队列满了,则不进行入队
return;
}
// 将数据入队后队尾下标自增
this.queue[rear] = data;
rear = (rear + 1) % this.queue.length;
}
/**
* 出队
* @return 队首元素
*/
public Integer take(){
if (rear == front){
// 队列为空
return null;
}
// 获取队首元素
int val = this.queue[front];
// 队首下标自增
front = (front + 1) % this.queue.length;
// 返回
return val;
}
}上述代码仅是简单的循环队列,在多线程的环境下是存在问题的,且还没有实现阻塞功能,上述入队出队方法都设计修改存在线程安全问题,此时我们可以通过加锁的方法来先保证线程安全
class MyBlockingQueue{
private int[] queue = new int[100]; // 用于实现队列的数组
private int front; // 队首下标
private int rear; // 队尾下标
private int size; // 元素个数
/**
* 入队
* @param data 待入队数据
*/
public void put(int data){
synchronized (this) {
if ((rear + 1) % this.queue.length == front) {
// 队列满了,则不进行入队
return;
}
// 将数据入队后队尾下标自增
this.queue[rear] = data;
rear = (rear + 1) % this.queue.length;
}
}
/**
* 出队
* @return 队首元素
*/
public Integer take(){
synchronized (this) {
if (rear == front) {
// 队列为空
return null;
}
// 获取队首元素
int val = this.queue[front];
// 队首下标自增
front = (front + 1) % this.queue.length;
// 返回
return val;
}
}
}在保证了线程安全后我们可以根据队满入队阻塞、队空出队阻塞来实现阻塞功能,在put方法中先进行if判断是否满了,如果满了我们进入if中使用wait方法进行阻塞,直到有线程调用take方法在take方法执行结束前调用notify唤醒阻塞;同理take方法进入时先if判断是否为空,如果为空则调用wait进入阻塞
class MyBlockingQueue{
private int[] queue = new int[100]; // 用于实现队列的数组
private int front; // 队首下标
private int rear; // 队尾下标
private int size; // 元素个数
/**
* 入队
* @param data 待入队数据
*/
public void put(int data) throws InterruptedException {
synchronized (this) {
if ((rear + 1) % this.queue.length == front) {
// 队列满了,则不进行入队
this.wait();
}
// 将数据入队后队尾下标自增
this.queue[rear] = data;
rear = (rear + 1) % this.queue.length;
// 唤醒阻塞的出队线程
this.notify();
}
}
/**
* 出队
* @return 队首元素
*/
public Integer take() throws InterruptedException {
synchronized (this) {
if (rear == front) {
// 队列为空
this.wait();
}
// 获取队首元素
int val = this.queue[front];
// 队首下标自增
front = (front + 1) % this.queue.length;
// 唤醒阻塞的入队线程
this.notify();
// 返回
return val;
}
}
}
此时阻塞功能也实现了,但是还存在一些问题,如果队列为空,有一个线程1执行take操作进入了阻塞,若干时间后该线程被唤醒,继续往后执行,但是此时该线程唤醒可能不是因为入队操作而唤醒的,也可能是因为其他原因(如interrupt) ,所以线程被唤醒后队列不一定非空,put方法也同理,所以我们需要在线程被唤醒后再次进行判断是否非空或者非满,此时我们可以将if改为while即可
class MyBlockingQueue{
private int[] queue = new int[100]; // 用于实现队列的数组
private int front; // 队首下标
private int rear; // 队尾下标
private int size; // 元素个数
/**
* 入队
* @param data 待入队数据
*/
public void put(int data) throws InterruptedException {
synchronized (this) {
if ((rear + 1) % this.queue.length == front) {
// 队列满了,则不进行入队
this.wait();
}
// 将数据入队后队尾下标自增
this.queue[rear] = data;
rear = (rear + 1) % this.queue.length;
// 唤醒阻塞的出队线程
this.notify();
}
}
/**
* 出队
* @return 队首元素
*/
public Integer take() throws InterruptedException {
synchronized (this) {
if (rear == front) {
// 队列为空
this.wait();
}
// 获取队首元素
int val = this.queue[front];
// 队首下标自增
front = (front + 1) % this.queue.length;
// 唤醒阻塞的入队线程
this.notify();
// 返回
return val;
}
}
}
四、BlockingQueue的使用
public static void main(String[] args){
BlockingQueue<Integer> queue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(100);
queue.put(100); // 带阻塞功能入队,下面是出队
queue.take();
}