- 本文章基于以下版本撰写
- VUE 版本: 3.0
- VUEX 版本:4.0.0
- Vuex仓库:https://github.com/vuejs/vuex/tree/v4.0.0
- Vux文档:https://vuex.vuejs.org/zh/
在 vue 中使用 vuex
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import { createStore } from 'vuex'
// 创建一个新的 store 实例
const store = createStore({
state () {
return {
count: 0
}
},
mutations: {
increment (state) {
state.count++
}
}
})
const app = createApp({ /* 根组件 */ })
// 将 store 实例作为插件安装
app.use(store)
从 createStore 引入讲起
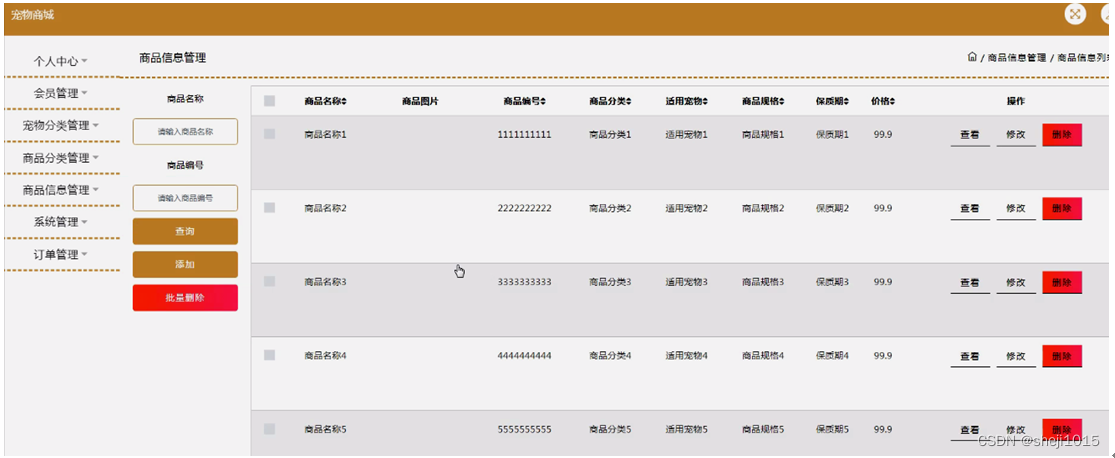
让我们先看一下 vuex/src 目录,引入 createStore 就是从 index.js 文件中引入
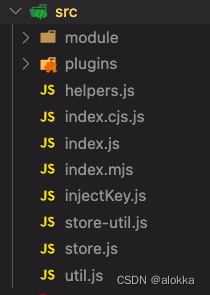
// src/index.js
⭐️import { Store, createStore } from './store'
import { storeKey, useStore } from './injectKey'
import { mapState, mapMutations, mapGetters, mapActions, createNamespacedHelpers } from './helpers'
import { createLogger } from './plugins/logger'
export default {
version: '__VERSION__',
Store,
storeKey,
⭐️createStore,
useStore,
mapState,
mapMutations,
mapGetters,
mapActions,
createNamespacedHelpers,
createLogger
}
export {
Store,
storeKey,
createStore,
useStore,
mapState,
mapMutations,
mapGetters,
mapActions,
createNamespacedHelpers,
createLogger
}
可以看到 createStore 是从 store 文件中引用,那么下面我们来看下 store 文件
// store.js
export function createStore(options) {
return new Store(options)
}
直接返回了一个 Store 的实例,所以我们知道 Store 肯定是一个 class,下面我们来看下 Store 类
// store.js
export class Store {
constructor(options = {}) {
if (__DEV__) {
assert(
typeof Promise !== 'undefined',
`vuex requires a Promise polyfill in this browser.`
)
assert(
this instanceof Store,
`store must be called with the new operator.`
)
}
const { plugins = [], strict = false, devtools } = options
// 存储内部状态
this._committing = false
this._actions = Object.create(null)
this._actionSubscribers = []
this._mutations = Object.create(null)
this._wrappedGetters = Object.create(null)
⭐️this._modules = new ModuleCollection(options)
this._modulesNamespaceMap = Object.create(null)
this._subscribers = []
this._makeLocalGettersCache = Object.create(null)
this._scope = null
this._devtools = devtools
const store = this
// 在实例自身身上挂两个方法分别是原型上的dispatch 、commit方法,并将函数内部的this指针强行指向当前创建的store对象。
const { dispatch, commit } = this
this.dispatch = function boundDispatch(type, payload) {
return dispatch.call(store, type, payload)
}
this.commit = function boundCommit(type, payload, options) {
return commit.call(store, type, payload, options)
}
// strict mode
this.strict = strict
const state = this._modules.root.state
// 初始化根Moudule
⭐️⭐️installModule(this, state, [], this._modules.root)
// 对State进行响应式处理
⭐️⭐️⭐️resetStoreState(this, state)
// 应用插件
plugins.forEach((plugin) => plugin(this))
}
⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️install (app, injectKey) {
app.provide(injectKey || storeKey, this)
app.config.globalProperties.$store = this
}
}
我们先看下 constructor 部分,我们知道通过 new 命令生成对象实例时,自动调用该方法。
1. 所以首先是存储内部状态
2. 在实例自身身上挂两个方法分别是原型上的dispatch 、commit方法,并将函数内部的this指针强行指向当前创建的store对象。
3. 初始化根Moudule
4. 对State进行响应式处理
5. 应用插件
6. 全局注册
⭐️ ModuleCollection 模块处理
我们从 this._modules = new ModuleCollection(options) 创建实例对象讲起,从字面意思可知是一个 module 收集的过程
// src/module/module-collection.js
export default class ModuleCollection {
constructor (rawRootModule) {
// register root module (Vuex.Store options)
this.register([], rawRootModule, false)
}
可以看到是调用 register 方法
// src/module/module-collection.js
register (path, rawModule, runtime = true) {
if (__DEV__) {
assertRawModule(path, rawModule)
}
const newModule = new Module(rawModule, runtime)
if (path.length === 0) {
this.root = newModule
} else {
const parent = this.get(path.slice(0, -1))
parent.addChild(path[path.length - 1], newModule)
}
// register nested modules
if (rawModule.modules) {
forEachValue(rawModule.modules, (rawChildModule, key) => {
this.register(path.concat(key), rawChildModule, runtime)
})
}
}
创建 Module 实例,先挂在到 root 属性上,然后看有没有 modules 属性,有的话就递归,给每个模块都创建一个 Module 实例对象,
// src/module/module.js
export default class Module {
constructor (rawModule, runtime) {
this.runtime = runtime
// Store some children item
this._children = Object.create(null)
// Store the origin module object which passed by programmer
this._rawModule = rawModule
const rawState = rawModule.state
// Store the origin module's state
this.state = (typeof rawState === 'function' ? rawState() : rawState) || {}
}
}
这样每个模块就有自己单独的 state,实现独立管理自己模块的状态
⭐️⭐️ 初始化根 Moudle installModule
// src/store-util.js
export function installModule (store, rootState, path, module, hot) {
const isRoot = !path.length
const namespace = store._modules.getNamespace(path)
// register in namespace map
⭐️if (module.namespaced) {
if (store._modulesNamespaceMap[namespace] && __DEV__) {
console.error(`[vuex] duplicate namespace ${namespace} for the namespaced module ${path.join('/')}`)
}
store._modulesNamespaceMap[namespace] = module
}
// set state
⭐️⭐️if (!isRoot && !hot) {
const parentState = getNestedState(rootState, path.slice(0, -1))
const moduleName = path[path.length - 1]
store._withCommit(() => {
if (__DEV__) {
if (moduleName in parentState) {
console.warn(
`[vuex] state field "${moduleName}" was overridden by a module with the same name at "${path.join('.')}"`
)
}
}
parentState[moduleName] = module.state
})
}
⭐️⭐️⭐️const local = module.context = makeLocalContext(store, namespace, path)
⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️module.forEachMutation((mutation, key) => {
const namespacedType = namespace + key
registerMutation(store, namespacedType, mutation, local)
})
⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️module.forEachAction((action, key) => {
const type = action.root ? key : namespace + key
const handler = action.handler || action
registerAction(store, type, handler, local)
})
⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️module.forEachGetter((getter, key) => {
const namespacedType = namespace + key
registerGetter(store, namespacedType, getter, local)
})
⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️module.forEachChild((child, key) => {
installModule(store, rootState, path.concat(key), child, hot)
})
}
⭐️:
若module.namespaced = true : 此Module将被加入store._modulesNamespaceMap内,其key为Module嵌套的路径。
⭐️⭐️:
非root Module时:子Module.state注入到父节点的state对象里。
⭐️⭐️⭐️:
对store进行局部化,这里主要对module.namespaced= true 的module进行另外处理,其内部的成员都需要进行namespace路径处理处理。
⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️:
对 mutation、action、getter 进行封装,放在 Store 对应的 _mutations、_actions、_wrappedGetters 里
⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️:
若当前module含有子module时,遍历当前model的_children属性,迭代执行installModule。
⭐️⭐️⭐️对State进行响应式处理 resetStoreState
// src/store-util.js
export function resetStoreState (store, state, hot) {
const oldState = store._state
const oldScope = store._scope
// bind store public getters
store.getters = {}
// reset local getters cache
store._makeLocalGettersCache = Object.create(null)
const wrappedGetters = store._wrappedGetters
const computedObj = {}
const computedCache = {}
// create a new effect scope and create computed object inside it to avoid
// getters (computed) getting destroyed on component unmount.
const scope = effectScope(true)
⭐️scope.run(() => {
forEachValue(wrappedGetters, (fn, key) => {
// use computed to leverage its lazy-caching mechanism
// direct inline function use will lead to closure preserving oldState.
// using partial to return function with only arguments preserved in closure environment.
computedObj[key] = partial(fn, store)
computedCache[key] = computed(() => computedObj[key]())
Object.defineProperty(store.getters, key, {
get: () => computedCache[key].value,
enumerable: true // for local getters
})
})
})
⭐️⭐️store._state = reactive({
data: state
})
// register the newly created effect scope to the store so that we can
// dispose the effects when this method runs again in the future.
store._scope = scope
// enable strict mode for new state
if (store.strict) {
enableStrictMode(store)
}
if (oldState) {
if (hot) {
// dispatch changes in all subscribed watchers
// to force getter re-evaluation for hot reloading.
store._withCommit(() => {
oldState.data = null
})
}
}
// dispose previously registered effect scope if there is one.
if (oldScope) {
oldScope.stop()
}
}
⭐️:
将 getter 注册为计算属性
⭐️⭐️:
让 state 变为响应式对象
⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️ Store 全局注册
我们知道当我们应用插件 app.use(store) 时候,会自动调用 install 方法
4.0版本 vuex 使用的是 provide / inject 来实现全局注册,因为 vue3 已经不支持 $ api
install (app, injectKey) {
app.provide(injectKey || storeKey, this)
app.config.globalProperties.$store = this
}
除了通过 app.config.globalProperties 设置全局属性$store,还provide了一个storeKey,这显然是为 useStore() 做准备。
// src/injectKey.js
import { inject } from 'vue'
export const storeKey = 'store'
export function useStore (key = null) {
return inject(key !== null ? key : storeKey)
}