文章目录
- 前言
- A - Dijkstra Algorithm
- 0x00 算法题目
- 0x01 算法思路
- 0x02 代码实现
- B - 最长路
- 0x00 算法题目
- 0x01 算法思路
- 0x02 代码实现
- C - 二分图最大匹配
- 0x00 算法题目
- 0x01 算法思路
- 0x02 代码实现
- D - 搭配飞行员
- 0x00 算法题目
- 0x01 算法思路
- 0x02 代码实现
- E - The Perfect Stall
- 0x00 算法题目
- 0x01 算法思路
- 0x02 代码实现
- F - Asteroids
- 0x00 算法题目
- 0x01 算法思路
- 0x02 代码实现
- G - Til the Cows Come Home
- 0x00 算法题目
- 0x01 算法思路
- 0x02 代码实现
- H - 拓扑排序
- 0x00 算法题目
- 0x01 算法思路
- 0x02 代码实现
- 总结
前言
最短路Dijkstra,spfa,图论二分图算法AYIT—ACM训练(模板版)
A — Dijkstra
B — spfa/Dijkstra
C — 二分图
D — 二分图
E — 二分图
F — 二分图
G — Dijkstra
H — Topsort
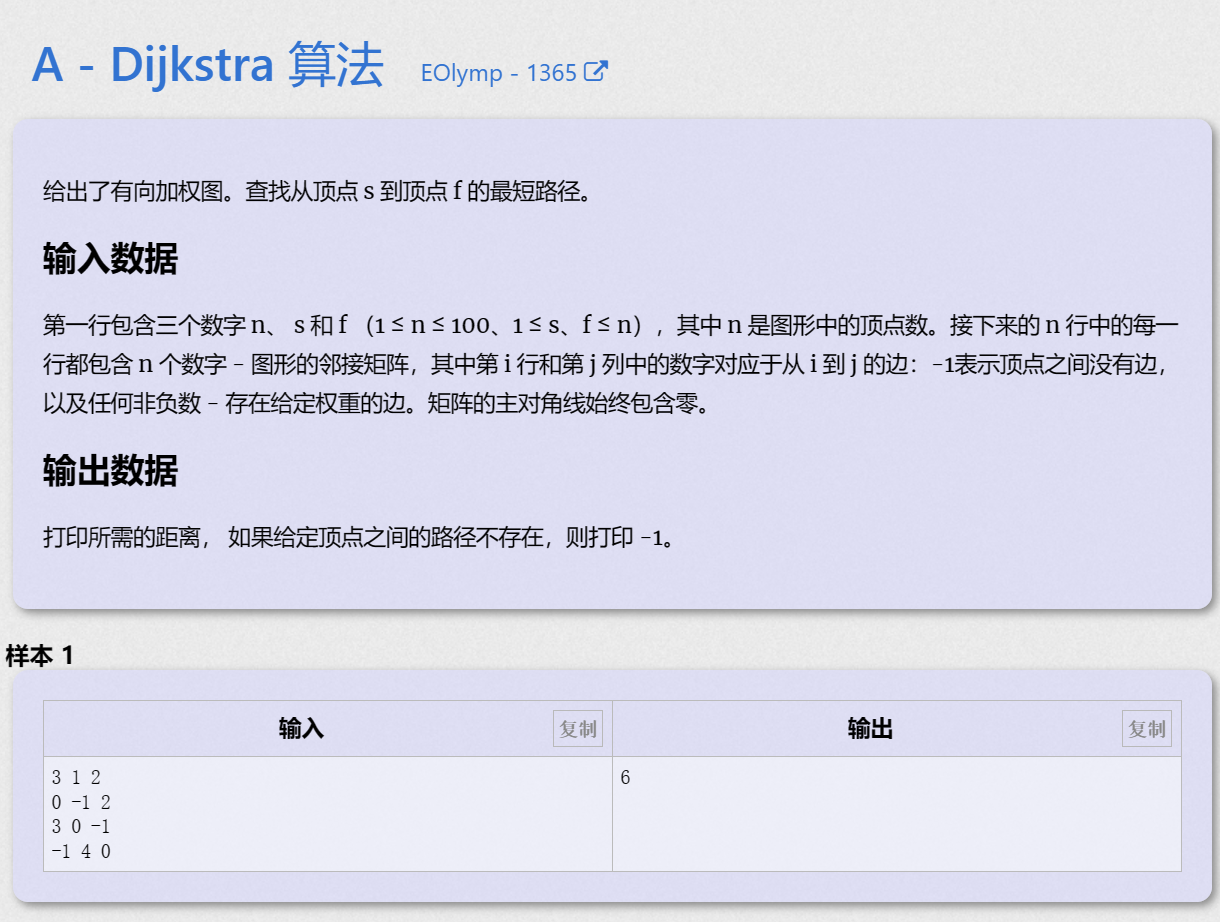
A - Dijkstra Algorithm
0x00 算法题目
0x01 算法思路
Dijkstra算法基础模板题
💬 模板演示:
int dijkstra()
{
memset(dist,0x3f,sizeof dist);
dist[1]=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
int t=-1;
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)
{
if(!st[j] && (t==-1 || dist[t] > dist[j]))
t=j;
}
st[t]=true;
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)
dist[j]=min(dist[j],dist[t]+g[t][j]);
}
if(dist[n]==0x3f3f3f3f) return -1;
return dist[n];
}
0x02 代码实现
朴素版本Dijkstra:
💬 代码演示:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 510;
int g[N][N];
bool st[N];
int dist[N];
int n,s,f;
int dijkstra()
{
memset(dist,0x3f,sizeof dist);
dist[s]=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
int t=-1;
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)
if(!st[j] && (t==-1 || dist[t] > dist[j]))
t=j;
st[t]=true;
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)
dist[j]=min(dist[j],dist[t]+g[t][j]);
}
if(dist[f]==0x3f3f3f3f) return -1;
return dist[f];
}
int main()
{
cin>>n>>s>>f;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)
{
int x;
cin>>x;
if(x==-1) g[i][j]=0x3f3f3f3f;
else g[i][j]=x;
}
}
int t =dijkstra();
cout<<t<<endl;
return 0;
}
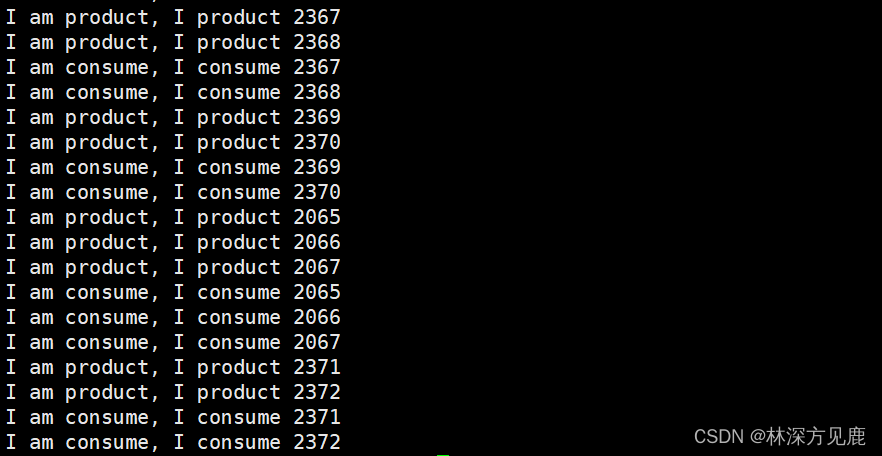
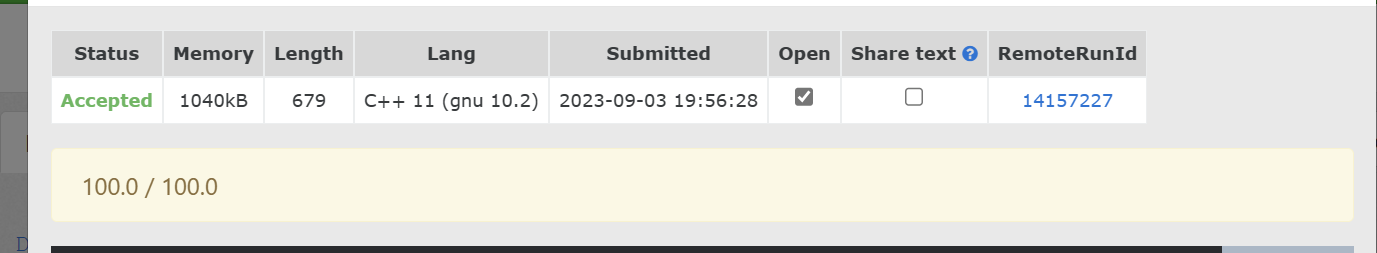
🚩 运行结果:
spfa算法:
💬 代码演示:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
const int N=110,M=110*110;
int n,s,f;
bool st[N];
int h[N],w[M],ne[M],e[M],idx;
int dist[N];
void add(int a,int b,int c)
{
e[idx]=b,w[idx]=c,ne[idx]=h[a],h[a]=idx++;
}
int spfa()
{
memset(dist,0x3f,sizeof dist);
dist[s]=0;
queue<int> q;
q.push(s);
while(q.size())
{
int t = q.front();
q.pop();
st[t]=false;
for(int i=h[t];i!=-1;i=ne[i])
{
int j=e[i];
if(dist[j] > dist[t] + w[i])
{
dist[j]=dist[t]+w[i];
if(!st[j])
{
q.push(j);
st[j]=true;
}
}
}
}
if(dist[f]==0x3f3f3f3f) return -1;
else return dist[f];
}
int main()
{
cin>>n>>s>>f;
memset(h,-1,sizeof h);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)
{
int x;
cin>>x;
//if(x==-1) continue;
if(x>0) add(i,j,x);
}
}
cout<<spfa()<<endl;
return 0;
}
🚩 运行结果:

B - 最长路
0x00 算法题目
0x01 算法思路
spfa算法基础模板题
💬 模板演示:
int spfa()
{
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof dist);
dist[1] = 0;
queue<int> q;
q.push(1);
while(q.size())
{
auto t = q.front();
q.pop();
st[t]=false;
for(int i=h[t];i!=-1;i=ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
if(dist[j] > dist[t]+w[i])
{
dist[j]=dist[t]+w[i];
if(!st[j])
{
q.push(j);
st[j]=true;
}
}
}
}
return dist[n];
}
0x02 代码实现
spfa算法:
💬 代码演示:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
using namespace std;
const int N = 1510,INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int n,m;
int dist[N];
int g[N][N];
queue<int> q;
void spfa()
{
memset(dist,-1,sizeof dist);
dist[1]=0;
q.push(1);
while(!q.empty())
{
int t = q.front();
q.pop();
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)
{
if(g[t][j] && dist[j] < dist[t] + g[t][j])
{
dist[j] = dist[t] + g[t][j];
q.push(j);
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
int a,b,c;
cin>>a>>b>>c;
g[a][b]=max(g[a][b],c);
}
spfa();
cout<<dist[n]<<endl;
return 0;
}
🚩 运行结果:

C - 二分图最大匹配
0x00 算法题目
0x01 算法思路
二分图模板题
💬 模板演示:
//邻接表
bool find(int x)
{
for (int i = h[x]; i != -1; i = ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
if (!st[j])
{
st[j] = true;
if (match[j] == 0 || find(match[j]))
{
match[j] = x;
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
//邻接矩阵
bool find(int x)
{
for(int i=0;i<g[x].size();++i)
{
int j = g[x][i];
if(!st[j])
{
st[j]=true;
if(match[j]==0 || find(match[j]))
{
match[j]=x;
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
0x02 代码实现
💬 代码演示:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 510,M=5e4+10;
int n,m,q;
int h[N],e[M],ne[M],idx;
int match[N];
bool st[N];
void add(int a,int b)
{
e[idx]=b,ne[idx]=h[a],h[a]=idx++;
}
bool find(int x)
{
for(int i=h[x];i!=-1;i=ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
if(!st[j])
{
st[j]=true;
if(match[j]==0 || find(match[j]))
{
match[j]=x;
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
cin>>n>>m>>q;
memset(h,-1,sizeof h);
while(q--)
{
int u,v;
cin>>u>>v;
add(u,v);
}
int res=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
memset(st,false,sizeof st);
if(find(i)) res++;
}
cout<<res<<endl;
return 0;
}
🚩 运行结果:

D - 搭配飞行员
0x00 算法题目

0x01 算法思路
二分图模板题
💬 模板演示:
//邻接表
bool find(int x)
{
for (int i = h[x]; i != -1; i = ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
if (!st[j])
{
st[j] = true;
if (match[j] == 0 || find(match[j]))
{
match[j] = x;
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
//邻接矩阵
bool find(int x)
{
for(int i=0;i<g[x].size();++i)
{
int j = g[x][i];
if(!st[j])
{
st[j]=true;
if(match[j]==0 || find(match[j]))
{
match[j]=x;
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
0x02 代码实现
💬 代码演示:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 110;
int n,m;
int map[N][N];
int match[N];
bool st[N];
vector<int> g[N];
bool find(int x)
{
for(int i=0;i<g[x].size();++i)
{
int j = g[x][i];
if(!st[j])
{
st[j]=true;
if(match[j]==0 || find(match[j]))
{
match[j]=x;
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d %d",&n,&m);
int a,b;
while(cin>>a>>b)
{
g[a].push_back(b);
}
int res = 0;
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
memset(st,false,sizeof st);
if(find(i))
{
res++;
}
}
cout<<res;
return 0;
}
🚩 运行结果:

E - The Perfect Stall
0x00 算法题目

0x01 算法思路
二分图模板题
💬 模板演示:
//邻接表
bool find(int x)
{
for (int i = h[x]; i != -1; i = ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
if (!st[j])
{
st[j] = true;
if (match[j] == 0 || find(match[j]))
{
match[j] = x;
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
//邻接矩阵
bool find(int x)
{
for(int i=0;i<g[x].size();++i)
{
int j = g[x][i];
if(!st[j])
{
st[j]=true;
if(match[j]==0 || find(match[j]))
{
match[j]=x;
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
0x02 代码实现
💬 代码演示:
#include<algorithm>
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 510,M=5e4+10;
int n,m;
int match[N];
bool st[N];
vector<int> g[N];
bool find(int x)
{
for(int i=0;i<g[x].size();++i)
{
int j = g[x][i];
if(!st[j])
{
st[j]=true;
if(match[j]==0 || find(match[j]))
{
match[j]=x;
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
while(~scanf("%d%d",&n,&m))
{
memset(st,false,sizeof st);
memset(match,0,sizeof match);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
g[i].clear();
int s;
cin>>s;
while(s--)
{
int q;
cin>>q;
g[i].push_back(q);
}
}
int res=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
memset(st,false,sizeof st);
if(find(i)) res++;
}
cout<<res<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
🚩 运行结果:

F - Asteroids
0x00 算法题目

0x01 算法思路
二分图模板题
💬 模板演示:
//邻接表
bool find(int x)
{
for (int i = h[x]; i != -1; i = ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
if (!st[j])
{
st[j] = true;
if (match[j] == 0 || find(match[j]))
{
match[j] = x;
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
//邻接矩阵
bool find(int x)
{
for(int i=0;i<g[x].size();++i)
{
int j = g[x][i];
if(!st[j])
{
st[j]=true;
if(match[j]==0 || find(match[j]))
{
match[j]=x;
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
0x02 代码实现
💬 代码演示:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 510,M=5e4+10;
int n,m,q;
int h[N],e[M],ne[M],idx;
int match[N];
bool st[N];
void add(int a,int b)
{
e[idx]=b,ne[idx]=h[a],h[a]=idx++;
}
bool find(int x)
{
for(int i=h[x];i!=-1;i=ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
if(!st[j])
{
st[j]=true;
if(match[j]==0 || find(match[j]))
{
match[j]=x;
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
cin>>n>>m;
memset(h,-1,sizeof h);
while(m--)
{
int u,v;
cin>>u>>v;
add(u,v);
}
int res=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
memset(st,false,sizeof st);
if(find(i)) res++;
}
cout<<res<<endl;
return 0;
}
🚩 运行结果:

G - Til the Cows Come Home
0x00 算法题目

0x01 算法思路
Dijkstra算法基础模板题
💬 模板演示:
int dijkstra()
{
memset(dist,0x3f,sizeof dist);
dist[1]=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
int t=-1;
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)
{
if(!st[j] && (t==-1 || dist[t] > dist[j]))
t=j;
}
st[t]=true;
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)
dist[j]=min(dist[j],dist[t]+g[t][j]);
}
if(dist[n]==0x3f3f3f3f) return -1;
return dist[n];
}
0x02 代码实现
💬 代码演示:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<stdbool.h>
using namespace std;
const int N=1010,inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int n,m;
bool st[N];
int dist[N];
int g[N][N];
int dijkstra()
{
memset(dist,inf,sizeof(dist));
dist[1]= 0;
for(int i=1;i <= n;i++)
{
int t=-1;
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)
if(!st[j] && (t==-1 || dist[t] > dist[j]))
t=j;
st[t]=true;
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)
dist[j]=min(dist[j],dist[t]+g[t][j]);
}
return dist[n];
}
int main()
{
cin>>m>>n;
memset(g,inf,sizeof g);
for(int i=0;i<m;++i)
{
int a,b,c;
cin>>a>>b>>c;
g[a][b]=g[b][a]=min(g[a][b],c);
}
cout<< dijkstra() <<endl;
return 0;
}
🚩 运行结果:

H - 拓扑排序
0x00 算法题目
0x01 算法思路
拓扑排序算法基础模板题
💬 模板演示:
bool topsort()
{
int hh=0,tt=-1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
if (!d[i])
q[ ++ tt] = i;
while(hh<=tt)
{
int t = q[hh ++ ];
for (int i = h[t]; i != -1; i = ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
if (-- d[j] == 0)
q[ ++ tt] = j;
}
}
return tt==n-1;
}
0x02 代码实现
💬 代码演示:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
const int N=100010;
int n,m;
vector<int> v[N];
int size,d[N];
int ans[N];
void topsort()
{
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int> > q;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
if(!d[i]) q.push(i);
while(!q.empty())
{
int t = q.top();
q.pop();
ans[size++] = t;
for(auto it : v[t])
{
d[it]--;
if(!d[it]) q.push(it);
}
}
}
int main()
{
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
{
int a,b;
cin>>a>>b;
v[a].push_back(b);
d[b]++;
}
topsort();
for(int i=0 ; i<size ;i++)
cout<< 'v' << ans[i] <<' ';
return 0;
}
🚩 运行结果:

总结
这次训练很明显涉及到了最短路Dijkstra,spfa,图论二分图算法,以及topsort算法,这次考的比较基础,但是让我意识到了,算法必须熟练记忆模板是很重要的。