保姆级 Keras 实现 Faster R-CNN 十一
- 一 RoI 区域
- 二. 定义 RoiPoolingLyaer
- 1. call 函数
- 2. compute_output_shape 函数
- 三. 将 RoiPoolingLayer 加入模型
上一篇 文章中我们实现了 ProposalLyaer 层, 它将的功能是输出建议区域矩形. 本文要实现另一个自定义层 RoiPoolingLayer. 在 Faster R-CNN 中, RoiPooling 层的目的是将不同大小的感兴趣区域(Region of Interest,ROI) 转换为固定大小的特征图作为后续步骤的输入
一 RoI 区域
还是先把论文中的图贴出来
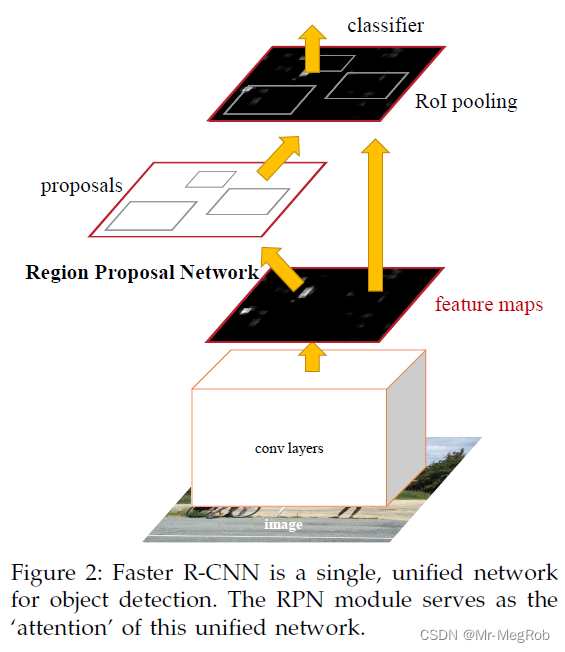
上图中已经标明了 RoI pooling 的位置, 个人觉得这张图是有问题的. 依据如下
- 图中 feature maps 的尺寸应该远比输入的图像的尺寸要小才对. 当然这个也不是问题, 可能是为了方便作图故意把输入图像画得比较小
- proposals 中的框和 RoI pooling 位置特征图中的框一样大. 这个是有问题的, 因为 RPN 输出的是建议框, 是 anchor_box 经过修正再做 NMS 后的矩形. 也是替代 Selective Search 区域的矩形. 建议框的坐标系是原图, 也就是说 proposals 位置的红框的尺寸要和原图一样大才对. 而 RoI pooling 需要将建议框缩放到 feature maps 尺度以 feature maps 为坐标系. 所以图中两处框的大小应该是不一样的
有了上面的解释后, 相信理解 RoiPooling 会相对容易一点
二. 定义 RoiPoolingLyaer
Keras 自定义层的套路在 保姆级 Keras 实现 Faster R-CNN 十 中已经讲过了, 这里就不那么细致的解释了. 不完全定义如下, 后面慢慢补全
class RoiPoolingLayer(Layer):
def __init__(self, pool_size = (7, 7), **kwargs):
self.pool_size = pool_size
super(RoiPoolingLayer, self).__init__(**kwargs)
def build(self, input_shape):
super(RoiPoolingLayer, self).build(input_shape)
def call(self, inputs):
pass
def compute_output_shape(self, input_shape):
pass
在上面的定义中, 需要一个初始化参数 pool_size, 指明我们需要将输出变形到什么样的尺寸. 默认是 (7, 7), 你要喜欢其他数字也可以
1. call 函数
我们要在 call 函数中实现 RoI pooling 的功能. 一开始, 我被这个名称误导了, 看到 Pooling 自然的想到了 MaxPooling 这样的, 其实和 MaxPooling 这样的函数没有半毛钱关系, 只是一个 裁切 + 变形
先秀代码, 下面再解释
def call(self, inputs):
images, features, rois = inputs
image_shape = tf.shape(images)[1: 3]
feature_shape = tf.shape(features)
roi_shape = tf.shape(rois)
batch_size = feature_shape[0]
num_rois = roi_shape[1]
feature_channels = feature_shape[3]
y_scale = 1.0 / tf.cast(image_shape[0] - 1, dtype = tf.float32)
x_scale = 1.0 / tf.cast(image_shape[1] - 1, dtype = tf.float32)
y1 = rois[..., 0] * y_scale
x1 = rois[..., 1] * x_scale
y2 = rois[..., 2] * y_scale
x2 = rois[..., 3] * x_scale
rois = tf.stack([y1, x1, y2, x2], axis = -1)
# 为每个 roi 分配对应 feature 的索引序号
indices = tf.range(batch_size, dtype = tf.int32)
indices = tf.repeat(indices, num_rois, axis = -1)
rois = tf.reshape(rois, (-1, roi_shape[-1]))
crops = tf.image.crop_and_resize(image = features,
boxes = rois,
box_indices = indices,
crop_size = self.pool_size,
method = "bilinear")
crops = tf.reshape(crops,
(batch_size, num_rois,
self.pool_size[0], self.pool_size[1], feature_channels))
return crops
对于变量的定义, 从名字就可以理解其意思. inputs 是一个列表, 有三个元素, 一个是原图, 二是特征图, 三是建议框. 这样的话, 就可以拆分成 image, feature_map, rois
那为什么需要 image 这个参数呢, 有了这个参数就可以动态的获取输入图像的尺寸. 从而适应输入图像大小变化的情况. 还有一个主要的原因是要将建议框缩小到特征图的尺度, 需要计算一个缩小的倍数, 在代码中有两个倍数, 分别是 y_scale 与 x_scale
两个计算式都有在图像尺寸上减 1, 这是为什么?
因为我们要将建议框坐标归一化到 [0, 1] 的范围, 从而在特征图上的坐标也是 [0, 1] 的范围. 这样并不能解释为什么要减 1. 举个具体数字的例子, 假设输入图你的尺寸是 (350, 400), 有一个建议框的坐标是 (200, 349, 300, 399), 坐标顺序是 (y1, x1, y2, x2), 因为坐标是从 0 开始的, 所以最大坐标到不了 350 和 400. 那归一化后最大坐标就不能取到 1. 将图像尺寸减 1 后, 最大坐标就是 349 与 399, 这样就可以取到 [0, 1] 范围
代码中将建议框各坐标乘以相应的缩小的倍数怎么可以将建议框坐标缩小到特征图的尺度并且还是 [0, 1] 的范围呢呢, 也是一样用刚才的例子
缩小倍数:
y_scale = 1 / 349 = 0.0028653
x_scale = 1 / 399 = 0.0025062
在原图上的归一化坐标:
y 1 = 200 ∗ 0.0028653 = 0.57306590 y 2 = 349 ∗ 0.0028653 = 0.99999999 x 1 = 300 ∗ 0.0025062 = 0.75187969 x 2 = 399 ∗ 0.0025062 = 0.99999999 \begin{aligned} y_1 = 200 * 0.0028653= 0.57306590 \\ y_2 = 349 * 0.0028653= 0.99999999 \\ \\ x_1 = 300 * 0.0025062= 0.75187969 \\ x_2 = 399 * 0.0025062= 0.99999999 \\ \end{aligned} y1=200∗0.0028653=0.57306590y2=349∗0.0028653=0.99999999x1=300∗0.0025062=0.75187969x2=399∗0.0025062=0.99999999
特征图相对于原图缩小了 16 倍, 所以要计算建议框在特征图上映射的坐标(此时还没有归一化), 可以按下面的计算式
y 1 = 200 / / 16 = 12 y 2 = 349 / / 16 = 21 x 1 = 300 / / 16 = 18 x 2 = 399 / / 16 = 24 \begin{aligned} y_1 = 200 // 16 = 12 \\ y_2 = 349 // 16 = 21 \\ \\ x_1 = 300 // 16 = 18 \\ x_2 = 399 // 16 = 24 \\ \end{aligned} y1=200//16=12y2=349//16=21x1=300//16=18x2=399//16=24
现在将其归一化, 在此之前先要计算特征图的尺寸, 这个也简单
h = 350 / / 16 = 21 w = 400 / / 16 = 25 \begin{aligned} h = 350 // 16 = 21 \\ w = 400 // 16 = 25 \\ \end{aligned} h=350//16=21w=400//16=25
归一化的坐标如下
y 1 = 12 / 21 = 0.57142857 y 2 = 21 / 21 = 1.00000000 x 1 = 18 / 25 = 0.72000000 x 2 = 24 / 25 = 0.96000000 \begin{aligned} y_1 = 12 / 21 = 0.57142857 \\ y_2 = 21 / 21 = 1.00000000 \\ \\ x_1 = 18 / 25 = 0.72000000 \\ x_2 = 24 / 25 = 0.96000000 \\ \end{aligned} y1=12/21=0.57142857y2=21/21=1.00000000x1=18/25=0.72000000x2=24/25=0.96000000
和在原图归一化后的坐标相比, 是很接近了, 误差源于原图不是 16 的整数倍, 会有舍入误差
为什么要将坐标归一化, 原来的坐标不好吗?
原来的坐标也不是不好, 只是不方便函数并行统一的操作. 还有一个根本的原因是我们要使用 TensorFlow 提供的函数 tf.image.crop_and_resize, 这个函数的参数就是这样规定的, 你不按规定来就得不到正确的结果
既然提到了 tf.image.crop_and_resize, 就有必要解释一下函数的各个参数. 函数原型如下
tf.image.crop_and_resize(
image,
boxes,
box_indices,
crop_size,
method = "bilinear",
extrapolation_value = 0.0,
name = None
)
- image: 输入图像, 这里是特征图, 形状为 [batch_size, height, width, channels]
- boxes: 一个浮点型的 Tensor, 形状为 [num_boxes, 4], 表示每个 RoI 区域的边界框坐标. 每个边界框的坐标是一个四元组 (y1, x1, y2, x2), 其中 (y1, x1) 是左上角的坐标, (y2, x2) 是右下角的坐标. 坐标值应在 0 到 1 之间
- box_indices: 一个整型的 Tensor, 形状为 [num_boxes], 表示每个 RoI 区域所属的样本索引, 也就是当前的 RoI 区域对应一个 batch 中的哪一张图像(在这里是特征图). 一个 RoI 区域就要对应一个索引
- crop_size: 一个整型的元组, 表示裁剪后的大小, 形状为 [crop_height, crop_width]
- method: 缩放时的插值方式
- extrapolation_value: 一个浮点数, 表示当裁剪的位置超出输入图像范围(也就是坐标值大于了图像尺寸)时, 使用的填充值. 默认值为 0. 比如特征图的尺寸是 (18, 25), 你要裁切的矩形是 (14, 19, 15, 26), 那超过特征图的那些位置就要填充
- name: 操作的名称
理解了各参数的意义之后, 上面的代码就容易理解了, 可能有一点蒙的是下面这一段代码
# 为每个 roi 分配对应 feature 的索引序号
indices = tf.range(batch_size, dtype = tf.int32)
indices = tf.repeat(indices, num_rois, axis = -1)
rois = tf.reshape(rois, (-1, roi_shape[-1]))
这一段的功能是为每个 roi 分配对应 feature 的索引序号, ProposalLyaer 输出的建议框的坐标, 形状是 [batch_size, num_rois, 4], 这些建议框个数在一个 batch 内的图像之间是平均分配的. 0 ~ num_rois - 1 的序号对就第一张图, num_rois ~ 2 * num_rois - 1 对应第二张图, 这样类推下去
- indices = tf.range(batch_size, dtype = tf.int32): 产生 0 ~ batch_size - 1 的序列, 比如 batch 为 4, 那序列就是 [0, 1, 2, 3]. 表示建议框分别对应的图像索引有 0, 1, 2, 3 四张
- indices = tf.repeat(indices, num_rois, -1): 将 0, 1, 2, 3 这些数字重复, 一个序号重复 num_rois 次, 这样就为每一个建议框分配了一个对应于 batch 内特征图的索引序号, 重复后的形式了 [0, 0, 0, …, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, …, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, …, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, …, 3, 3, 3]
- rois = tf.reshape(rois, (-1, roi_shape[-1])): 将 rois 的形状从 [batch_size, num_rois, 4] 变成 tf.image.crop_and_resize 需要的 [num_boxes, 4]
经过上面的一顿操作, tf.image.crop_and_resize 就能正常使用了, 实现了从特征图中将建议框对应的地方抠出来, 变形到 (7, 7) 的形状, 最后一句
crops = tf.reshape(crops,
(batch_size, num_rois,
self.pool_size[0], self.pool_size[1], feature_channels))
将输出变到能做到 batch 操作的形状
2. compute_output_shape 函数
这个就比较容易了, 指定输出的形状
def compute_output_shape(self, input_shape):
image_shape, feature_shape, roi_shape = input_shape
batch_size = image_shape[0]
num_rois = roi_shape[1]
feature_channels = feature_shape[3]
return (batch_size, num_rois, self.pool_size[0], self.pool_size[1], feature_channels)
这样 RoiPoolingLayer 就完成了, 完整的定义如下
# 定义 Proposal Layer
class ProposalLayer(Layer):
# base_anchors: 9 个大小长宽不一的 anchor_box 列表
# stride: 特征图相对于原始输入图像的缩小的倍数
# num_rois: 输出的建议区域的个数
# iou_thres: 做 nms 时 IoU 阈值
def __init__(self,
base_anchors, stride = FEATURE_STRIDE,
num_rois = TRAIN_NUM, iou_thres = 0.7, **kwargs):
self.base_anchors = tf.constant(base_anchors, dtype = tf.float32)
self.stride = stride
self.num_rois = num_rois
self.iou_thres = iou_thres
self.ANCHOR_DIMS = 4 # 一个 anchor_box 需要 4 个值, 这个不需要传入, 只是做成一个各成员函数可以访问的量
self.K = len(base_anchors) # 一个 anchor 对应的 anchor_box 数量
super(ProposalLayer, self).__init__(**kwargs)
def build(self, input_shape):
super(ProposalLayer, self).build(input_shape)
def call(self, inputs): # inputs 是一个列表, 可以拆分为下面的参数
# image: 输入的原始图像
# targets: rpn 输出的分类部分
# adjust: rpn 输出的回归部分
image, targets, deltas = inputs
batch_size = tf.shape(image)[0]
image_shape = tf.shape(image)[1: 3]
feature_shape = tf.shape(targets)[1: 3]
# 依据当前图像大小生成 anchor_boxe
anchor_boxes = self.create_tensor_anchors(batch_size, feature_shape)
# 提取分数最大的 anchor_box 和对应的修正量
scores, anchor_boxes, deltas = self.get_boxes_deltas(batch_size, feature_shape,
targets, anchor_boxes, deltas)
# 回归修正, 修正后的 anchor_boxes 的 shape == (feature_shape[0] × feature_shape[1] , 4)
anchor_boxes = self.apply_box_deltas(image_shape, anchor_boxes, deltas)
# 拆分与组合操作
selected_boxes = tf.map_fn(
lambda i: self.batch_process(image_shape,
tf.reshape(anchor_boxes, (batch_size, -1, self.ANCHOR_DIMS)),
tf.reshape(scores, (batch_size, -1)),
i),
tf.range(batch_size, dtype = tf.int32),
dtype = tf.float32,
back_prop = False)
anchor_boxes = tf.reshape(selected_boxes, (batch_size, -1, self.ANCHOR_DIMS))
return anchor_boxes
def compute_output_shape(self, input_shape):
return (input_shape[0][0], self.num_rois, self.ANCHOR_DIMS)
# 将 base_anchors 加到各 anchor(点) 映射回原图的坐标点上, 每个坐标点形成 k 个 anchor box
def create_tensor_anchors(self, batch_size, feature_shape):
feature_rows = feature_shape[0]
feature_cols = feature_shape[1]
ax = (tf.cast(tf.range(feature_cols), tf.float32)) * self.stride + 0.5 * self.stride
ay = (tf.cast(tf.range(feature_rows), tf.float32)) * self.stride + 0.5 * self.stride
ax, ay = tf.meshgrid(ax, ay)
# 变换形状方便下面的 tf.stack
ax = tf.reshape(ax, (-1, 1))
ay = tf.reshape(ay, (-1, 1))
# 这里 anchor 只是像素点坐标(anchor box 中心坐标),
# stack([ax, ay, ax, ay]) 成这样的格式, 是为了分别加上 base_anchor 的左上角坐标和右下角坐标
anchors = tf.stack([ax, ay, ax, ay], axis = -1)
# anchro box (x1, y1, x2, y2) = 中心坐标 + base_anchors
# 此时 shape == (feature_shape[0] × feature_shape[1], 9, 4)
anchor_boxes = anchors + self.base_anchors
# 同一 batch 内, 图像大小一样,
# 所以 anchor_box 在没有调整前是一样的, 就可以复制成 batch_size 数量
# 完成后 shape = (batch_size, feature_shape[0], feature_shape[1], 9, 4)
anchor_boxes = tf.reshape(anchor_boxes, (feature_shape[0], feature_shape[1], self.K, self.ANCHOR_DIMS))
anchor_boxes = tf.expand_dims(anchor_boxes, axis = 0)
anchor_boxes = tf.tile(anchor_boxes, [batch_size, 1, 1, 1, 1])
return anchor_boxes
# 找出 anchor 处最大分数, 最大分数对应的 anchor_box 和修正参数
# targets: 各 anchor 处 9 个分数
# boxes: create_tensor_anchors 生成的 anchor_boxe
# deltas: 回归修正参数
def get_boxes_deltas(self, batch_size, feature_shape, targets, boxes, deltas):
# k 个 anchor 中最大分数
scores = tf.reduce_max(targets, axis = -1)
# 获取最大值和对应的索引, k = 1, 表示我们只关心最大的一个
values, indices = tf.math.top_k(targets, k = 1)
# 创建掩码,只有最大值位置为 1, 其他为 0
mask = tf.one_hot(indices, depth = targets.shape[-1])
# 如果有多个最大值,只保留一个
valid_mask = tf.reduce_sum(mask, axis = -2)
# 提取分数最大的 anchor_box
# 得到的 shape == (batch_size × feature_shape[0] × feature_shape[1], 4)
boxes = tf.boolean_mask(boxes, valid_mask, axis = 0)
# deltas 未变形前的 shape == (batch_size, feature_shape[0], feature_shape[1], 36)
# 做 boolean_mask 时不兼容, 所以需要变形为 (batch_size, feature_shape[0], feature_shape[1], 9, 4)
deltas = tf.reshape(deltas, (batch_size, feature_shape[0], feature_shape[1], self.K, self.ANCHOR_DIMS))
# 提取分数最大的 anchor_box 对应的修参数
# 得到的 shape == (batch_size × feature_shape[0] × feature_shape[1], 4)
deltas = tf.boolean_mask(deltas, valid_mask, axis = 0)
return scores, boxes, deltas
# 修正 anchor_box
def apply_box_deltas(self, image_shape, anchor_boxes, deltas):
# 宽度和高度
w = anchor_boxes[..., 2] - anchor_boxes[..., 0]
h = anchor_boxes[..., 3] - anchor_boxes[..., 1]
# 中心坐标
x = anchor_boxes[..., 0] + w * 0.5
y = anchor_boxes[..., 1] + h * 0.5
# 修正 anchor_box
x += deltas[..., 0] * w
y += deltas[..., 1] * h
w *= tf.exp(deltas[..., 2])
h *= tf.exp(deltas[..., 3])
# 转换成 y1, x1, y2, x2 格式
x1 = x - w * 0.5
y1 = y - h * 0.5
x2 = x + w * 0.5
y2 = y + h * 0.5
# 不管是训练还是预测, 超出范围的框分数也可能比较大, 所以都截断保留
x1 = tf.maximum(x1, 0)
y1 = tf.maximum(y1, 0)
x2 = tf.minimum(x2, tf.cast(image_shape[1], dtype = tf.float32))
y2 = tf.minimum(y2, tf.cast(image_shape[0], dtype = tf.float32))
# 如果用 tf.image.non_max_suppression 的话, 要按 y1, x1, y2, x2 的格式
anchor_boxes = tf.stack([y1, x1, y2, x2], axis = -1)
return anchor_boxes
# 填充随机矩形
# boxes: 需要填充的建议框矩形
# pad_num: 填充数量
def box_pad(self, image_shape, boxes, pad_num):
image_rows = tf.cast(image_shape[0], dtype = tf.float32)
image_cols = tf.cast(image_shape[1], dtype = tf.float32)
# 保证 x2 > x1, y2 > y1, 也就是最小宽度与高度, 也是一个随机值
space = tf.cast(tf.random.uniform(shape = (),
minval = 16, maxval = 64), dtype = tf.float32)
x1 = tf.random.uniform(shape = (pad_num, 1), minval = 0, maxval = image_cols - space)
y1 = tf.random.uniform(shape = (pad_num, 1), minval = 0, maxval = image_rows - space)
x2 = tf.random.uniform(shape = (pad_num, 1), minval = x1 + space, maxval = image_cols)
y2 = tf.random.uniform(shape = (pad_num, 1), minval = y1 + space, maxval = image_rows)
random_boxes = tf.concat((y1, x1, y2, x2), axis = -1)
random_boxes = tf.reshape(random_boxes, (-1, self.ANCHOR_DIMS))
boxes = tf.concat((boxes, random_boxes), axis = 0)
return boxes
# 处理 batch 内一个数据
# boxes: 修正后的建议区域矩形
# scores: 建议框矩形对应的分数
# i: batch 内第几个数据
def batch_process(self, image_shape, boxes, scores, i):
selected_indices = tf.image.non_max_suppression(boxes[i], scores[i], self.num_rois, self.iou_thres)
selected_boxes = tf.gather(boxes[i], selected_indices)
num_selected_boxes = tf.shape(selected_boxes)[0]
pad_num = self.num_rois - num_selected_boxes
selected_boxes = tf.cond(num_selected_boxes < self.num_rois,
lambda: self.box_pad(image_shape, selected_boxes, pad_num),
lambda: selected_boxes)
return selected_boxes
三. 将 RoiPoolingLayer 加入模型
现在把 RoiPoolingLayer 加入到模型如下
# RoiPooling 模型
x = keras.layers.Input(shape = (None, None, 3), name = "input")
feature = vgg16_conv(x)
rpn_cls, rpn_reg = rpn(feature)
proposal = ProposalLayer(base_anchors, num_rois = TRAIN_NUM, iou_thres = 0.7,
name = "proposal")([x, rpn_cls, rpn_reg])
roi_pooling = RoiPoolingLayer(name = "roi_pooling")([x, feature, proposal])
roi_pooling_model = keras.Model(x, roi_pooling, name = "roi_pooling_model")
roi_pooling_model.summary()
有了模型, 就可以测试一下效果了, 不过在之前, 要加载 保姆级 Keras 实现 Faster R-CNN 八 训练好的参数
# 加载训练好的参数
roi_pooling_model.load_weights(osp.join(log_path, "faster_rcnn_weights.h5"), True)
再定义一个预测函数
# roi_pooling 模型预测
# 一次预测一张图像
# x: 输入图像或图像路径
# 返回值: 返回原图像和预测结果
def roi_pooling_predict(x):
# 如果是图像路径, 那要将图像预处理成网络输入格式
# 如果不是则是 input_reader 返回的图像, 已经满足输入格式
if isinstance(x, str):
img_src = cv.imread(x)
img_new, scale = new_size_image(img_src, SHORT_SIZE)
x = [img_new]
x = np.array(x).astype(np.float32) / 255.0
y = roi_pooling_model.predict(x)
return y
# 利用训练时划分的测试集
test_reader = input_reader(test_set, CATEGORIES, batch_size = 4, train_mode = False)
接下来就是见证奇迹的时刻了
# roi_pooling 测试
x, y = next(test_reader)
outputs = roi_pooling_predict(x)
print(x.shape, outputs.shape)
print(outputs)
输出如下
(4, 325, 400, 3) (4, 256, 7, 7, 512)
[[[[[0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 ... 0.00000000e+00
8.52627680e-03 0.00000000e+00]
[0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 ... 0.00000000e+00
3.18351114e-04 0.00000000e+00]
[0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 ... 0.00000000e+00
9.16954782e-03 0.00000000e+00]
...
[0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 ... 0.00000000e+00
2.82486826e-02 0.00000000e+00]
[0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 ... 0.00000000e+00
3.77882309e-02 0.00000000e+00]
[0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 ... 0.00000000e+00
3.84687856e-02 0.00000000e+00]]
可以看到输出的形状对了, 数值对不对以后验证
上一篇: 保姆级 Keras 实现 Faster R-CNN 十
下一篇: 保姆级 Keras 实现 Faster R-CNN 十二