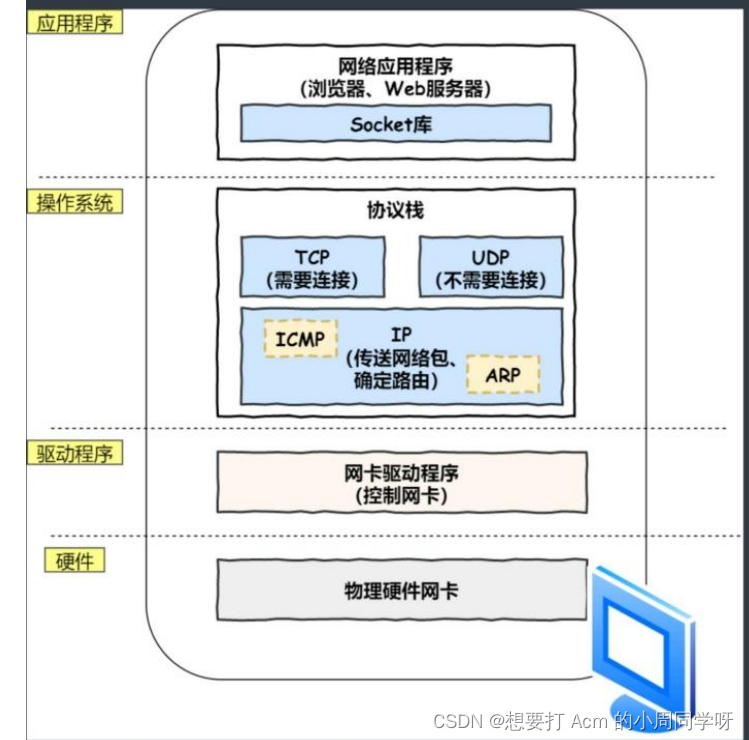
背景
Jetpack Compose 提供了强大的 Material Design 组件,其中 TabRow 组件可以用于实现 Material Design 规范的选项卡界面。但是默认的 TabRow 样式可能无法满足所有场景,所以我们有时需要自定义 TabRow 的样式。
Jetpack Compose 中使用 TabRow
简单使用 TabRow 一般可以分为以下几步:
-
定义 Tab 数据模型
每个 Tab 对应一个数据类,包含标题、图标等信息:
data class TabItem( val title: String, val icon: ImageVector? ) -
在 TabRow 中添加 Tab 项
使用 Tab 组件添加选项卡,传入标题、图标等:
TabRow { tabItems.forEach { item -> Tab( text = { Text(item.title) }, icon = { item.icon?.let { Icon(it) } } ) } } -
处理 Tab 选择事件
通过
selectedTabIndex跟踪选中的 tab,在onTabSelected回调中处理点击事件:var selectedTabIndex by remember { mutableStateOf(0) } TabRow( selectedTabIndex = selectedTabIndex, onTabSelected = { selectedTabIndex = it } ){ // ... }
具体详细可以看我之前的文章 Jetpack Compose TabRow与HorizontalPager 联动
笔记共享App
我新开发的笔记共享App 也用上了TabRow与HorizontalPager联动效果
效果图

自定义 TabRow 的样式
效果图

演示图的姓名都是随机生成的,如有雷同纯属巧合
证据如下
val lastNames = arrayOf(
"赵", "钱", "孙", "李", "周", "吴", "郑", "王", "刘", "张", "杨", "陈", "郭", "林", "徐", "罗", "陆", "海"
)
val firstNames = arrayOf(
"伟", "芳", "娜", "敏", "静", "立", "丽", "强", "华", "明", "杰", "涛", "俊", "瑶", "琨", "璐"
)
val secondNames =
arrayOf("燕", "芹", "玲", "玉", "菊", "萍", "倩", "梅", "芳", "秀", "苗", "英")
// 随机选择一个姓氏
val lastName = lastNames.random()
// 随机选择一个名字
val firstName = firstNames.random()
val secondName = secondNames.random()
代码解释
重写TabRow
通过查看TabRow 组件的源代码 ,单单自定义indicator 指示器是行不通的
layout(tabRowWidth, tabRowHeight) {
//绘制 tab文本
tabPlaceables.forEachIndexed { index, placeable ->
placeable.placeRelative(index * tabWidth, 0)
}
//绘制 divider 分割线
subcompose(TabSlots.Divider, divider).forEach {
val placeable = it.measure(constraints.copy(minHeight = 0))
placeable.placeRelative(0, tabRowHeight - placeable.height)
}
//最后绘制 Indicator 指示器
subcompose(TabSlots.Indicator) {
indicator(tabPositions)
}.forEach {
it.measure(Constraints.fixed(tabRowWidth, tabRowHeight)).placeRelative(0, 0)
}
}
根据源代码可以看出TabRow 先绘制文本 再绘制 指示器,这的显示效果,当Indicator高度充满TabRow的时候Tab文本是显示不出来的,因为Indicator挡住了,
所以解决办法就是先绘制Indicator再绘制tab文本
layout(tabRowWidth, tabRowHeight) {
//先绘制 Indicator 指示器
subcompose(TabSlots.Indicator) {
indicator(tabPositions)
}.forEach {
it.measure(Constraints.fixed(tabRowWidth, tabRowHeight)).placeRelative(0, 0)
}
//因为divider用不上,我便注释了
//subcompose(TabSlots.Divider, divider).forEach {
// val placeable = it.measure(constraints.copy(minHeight = 0))
// placeable.placeRelative(0, tabRowHeight - placeable.height)
//}
//再绘制 tab文本
tabPlaceables.forEachIndexed { index, placeable ->
placeable.placeRelative(index * tabWidth, 0)
}
}
把TabRow宽度改成由内容匹配
未修改时的TabRow宽度由父布局决定,效果图如下

TabRow的宽度从源码上看是,直接获取SubcomposeLayout的最大宽度(constraints.maxWidth)
接着利用宽度和tabCount计算平均值,就是每个tab文本的宽度
SubcomposeLayout(Modifier.fillMaxWidth()) { constraints ->
//最大宽度
val tabRowWidth = constraints.maxWidth
val tabMeasurables = subcompose(TabSlots.Tabs, tabs)
val tabCount = tabMeasurables.size
var tabWidth = 0
if (tabCount > 0) {
tabWidth = (tabRowWidth / tabCount)
}
...
}
我们需要TabRow宽度由内容匹配,而不是父布局的最大宽度,这样就要修改测量流程\
不再直接使用constraints.maxWidth作为tabRowWidth,而是记为最大宽度maxWidth
接着封装一个函数,使用标签内容宽度的求和作为 TabRow 的宽度,不再和 maxWidth 做比较
fun measureTabRow(
measurables: List<Measurable>,
minWidth: Int
): Int {
// 依次测量标签页宽度并求和
val widths = measurables.map {
it.minIntrinsicWidth(Int.MAX_VALUE)
}
var width = widths.max() * measurables.size
measurables.forEach {
width += it.minIntrinsicWidth(Int.MAX_VALUE)
}
//maxWidth的作用
// 如果标签较多,可以取一个较小值作为最大标签宽度,防止过宽
return minOf(width, minWidth)
}

这样就舒服多了
自定义的 Indicator
主要逻辑是在 Canvas 上绘制指示器
- indicator 的宽度根据当前 tab 的宽度及百分比计算
- indicator 的起始 x 轴坐标根据切换进度在当前 tab 和前/后 tab 之间插值
- indicator 的高度是整个 Canvas 的高度,即占据了 TabRow 的全高
fraction 和前后 tab 的 lerping 实现了滑动切换时指示器平滑过渡的效果
具体可以看代码的注释
使用方法
//默认显示第一页
val pagerState = rememberPagerState(initialPage = 1, pageCount = { 3 } )
WordsFairyTabRow(
modifier = Modifier
.align(Alignment.BottomCenter)
.padding(bottom = 86.dp, start = 24.dp, end = 24.dp),
selectedTabIndex = pagerState.currentPage,
indicator = { tabPositions ->
if (tabPositions.isNotEmpty()) {
PagerTabIndicator(tabPositions = tabPositions, pagerState = pagerState)
}
},
) {
// 添加选项卡
tabs.forEachIndexed { index, title ->
val selected = (pagerState.currentPage == index)
Tab(
selected = selected,
selectedContentColor = WordsFairyTheme.colors.textWhite,
unselectedContentColor = WordsFairyTheme.colors.textSecondary,
onClick = {
scope.launch {
feedback.vibration()
pagerState.animateScrollToPage(index)
}
},
modifier = Modifier.wrapContentWidth() // 设置Tab的宽度为wrapContent
) {
Text(
text = title,
fontWeight = FontWeight.Bold,
modifier = Modifier.padding(9.dp)
)
}
}
}
完整代码
PagerTabIndicator.kt
@OptIn(ExperimentalFoundationApi::class)
@Composable
fun PagerTabIndicator(
tabPositions: List<TabPosition>, // TabPosition列表
pagerState: PagerState, // PageState用于获取当前页和切换进度
color: Color = WordsFairyTheme.colors.themeUi, // 指示器颜色
@FloatRange(from = 0.0, to = 1.0) percent: Float = 1f // 指示器宽度占Tab宽度的比例
) {
// 获取当前选中的页和切换进度
val currentPage by rememberUpdatedState(newValue = pagerState.currentPage)
val fraction by rememberUpdatedState(newValue = pagerState.currentPageOffsetFraction)
// 获取当前tab、前一个tab、后一个tab的TabPosition
val currentTab = tabPositions[currentPage]
val previousTab = tabPositions.getOrNull(currentPage - 1)
val nextTab = tabPositions.getOrNull(currentPage + 1)
Canvas(
modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize(), // 充满TabRow的大小
onDraw = {
// 计算指示器宽度
val indicatorWidth = currentTab.width.toPx() * percent
// 计算指示器x轴起始位置
val indicatorOffset = if (fraction > 0 && nextTab != null) {
// 正在向右滑动到下一页,在当前tab和下一tab之间插值
lerp(currentTab.left, nextTab.left, fraction).toPx()
} else if (fraction < 0 && previousTab != null) {
// 正在向左滑动到上一页,在当前tab和上一tab之间插值
lerp(currentTab.left, previousTab.left, -fraction).toPx()
} else {
// 未在滑动,使用当前tab的left
currentTab.left.toPx()
}
// 绘制指示器
val canvasHeight = size.height // 高度为整个Canvas高度
drawRoundRect(
color = color,
topLeft = Offset( // 设置圆角矩形的起始点
indicatorOffset + (currentTab.width.toPx() * (1 - percent) / 2),
0F
),
size = Size( // 设置宽高
indicatorWidth + indicatorWidth * abs(fraction),
canvasHeight
),
cornerRadius = CornerRadius(26.dp.toPx()) // 圆角半径
)
}
)
}
WordsFairyTabRow.kt
@Composable
fun WordsFairyTabRow(
selectedTabIndex: Int,
modifier: Modifier = Modifier,
indicator: @Composable (tabPositions: List<TabPosition>) -> Unit = @Composable { tabPositions ->
if (selectedTabIndex < tabPositions.size) {
TabRowDefaults.Indicator(
Modifier.tabIndicatorOffset(tabPositions[selectedTabIndex])
)
}
},
tabs: @Composable () -> Unit
) {
ImmerseCard(
modifier = modifier.selectableGroup(),
shape = RoundedCornerShape(26.dp),
backgroundColor = WordsFairyTheme.colors.whiteBackground.copy(alpha = 0.7f)
) {
SubcomposeLayout(Modifier.wrapContentWidth()) { constraints ->
val tabMeasurables = subcompose(TabSlots.Tabs, tabs)
val tabRowWidth = measureTabRow(tabMeasurables, constraints.maxWidth)
val tabCount = tabMeasurables.size
var tabWidth = 0
if (tabCount > 0) {
tabWidth = (tabRowWidth / tabCount)
}
val tabRowHeight = tabMeasurables.fold(initial = 0) { max, curr ->
maxOf(curr.maxIntrinsicHeight(tabWidth), max)
}
val tabPlaceables = tabMeasurables.map {
it.measure(
constraints.copy(
minWidth = tabWidth,
maxWidth = tabWidth,
minHeight = tabRowHeight,
maxHeight = tabRowHeight,
)
)
}
val tabPositions = List(tabCount) { index ->
TabPosition(tabWidth.toDp() * index, tabWidth.toDp())
}
layout(tabRowWidth, tabRowHeight) {
subcompose(TabSlots.Indicator) {
indicator(tabPositions)
}.forEach {
it.measure(Constraints.fixed(tabRowWidth, tabRowHeight)).placeRelative(0, 0)
}
tabPlaceables.forEachIndexed { index, placeable ->
placeable.placeRelative(index * tabWidth, 0)
}
}
}
}
}
fun measureTabRow(
measurables: List<Measurable>,
minWidth: Int
): Int {
// 依次测量标签页宽度并求和
val widths = measurables.map {
it.minIntrinsicWidth(Int.MAX_VALUE)
}
var width = widths.max() * measurables.size
measurables.forEach {
width += it.minIntrinsicWidth(Int.MAX_VALUE)
}
// 如果标签较多,可以取一个较小值作为最大标签宽度,防止过宽
return minOf(width, minWidth)
}
@Immutable
class TabPosition internal constructor(val left: Dp, val width: Dp) {
val right: Dp get() = left + width
override fun equals(other: Any?): Boolean {
if (this === other) return true
if (other !is TabPosition) return false
if (left != other.left) return false
if (width != other.width) return false
return true
}
override fun hashCode(): Int {
var result = left.hashCode()
result = 31 * result + width.hashCode()
return result
}
override fun toString(): String {
return "TabPosition(left=$left, right=$right, width=$width)"
}
}
/**
* Contains default implementations and values used for TabRow.
*/
object TabRowDefaults {
/** Default container color of a tab row. */
val containerColor: Color
@Composable get() =
WordsFairyTheme.colors.whiteBackground
/** Default content color of a tab row. */
val contentColor: Color
@Composable get() =
WordsFairyTheme.colors.whiteBackground
@Composable
fun Indicator(
modifier: Modifier = Modifier,
height: Dp = 3.0.dp,
color: Color =
WordsFairyTheme.colors.navigationBarColor
) {
Box(
modifier
.fillMaxWidth()
.height(height)
.background(color = color)
)
}
fun Modifier.tabIndicatorOffset(
currentTabPosition: TabPosition
): Modifier = composed(
inspectorInfo = debugInspectorInfo {
name = "tabIndicatorOffset"
value = currentTabPosition
}
) {
val currentTabWidth by animateDpAsState(
targetValue = currentTabPosition.width,
animationSpec = tween(durationMillis = 250, easing = FastOutSlowInEasing)
)
val indicatorOffset by animateDpAsState(
targetValue = currentTabPosition.left,
animationSpec = tween(durationMillis = 250, easing = FastOutSlowInEasing)
)
fillMaxWidth()
.wrapContentSize(Alignment.BottomStart)
.offset(x = indicatorOffset)
.width(currentTabWidth)
}
}
private enum class TabSlots {
Tabs,
Divider,
Indicator
}
/**
* Class holding onto state needed for [ScrollableTabRow]
*/
private class ScrollableTabData(
private val scrollState: ScrollState,
private val coroutineScope: CoroutineScope
) {
private var selectedTab: Int? = null
fun onLaidOut(
density: Density,
edgeOffset: Int,
tabPositions: List<TabPosition>,
selectedTab: Int
) {
// Animate if the new tab is different from the old tab, or this is called for the first
// time (i.e selectedTab is `null`).
if (this.selectedTab != selectedTab) {
this.selectedTab = selectedTab
tabPositions.getOrNull(selectedTab)?.let {
// Scrolls to the tab with [tabPosition], trying to place it in the center of the
// screen or as close to the center as possible.
val calculatedOffset = it.calculateTabOffset(density, edgeOffset, tabPositions)
if (scrollState.value != calculatedOffset) {
coroutineScope.launch {
scrollState.animateScrollTo(
calculatedOffset,
animationSpec = ScrollableTabRowScrollSpec
)
}
}
}
}
}
private fun TabPosition.calculateTabOffset(
density: Density,
edgeOffset: Int,
tabPositions: List<TabPosition>
): Int = with(density) {
val totalTabRowWidth = tabPositions.last().right.roundToPx() + edgeOffset
val visibleWidth = totalTabRowWidth - scrollState.maxValue
val tabOffset = left.roundToPx()
val scrollerCenter = visibleWidth / 2
val tabWidth = width.roundToPx()
val centeredTabOffset = tabOffset - (scrollerCenter - tabWidth / 2)
// How much space we have to scroll. If the visible width is <= to the total width, then
// we have no space to scroll as everything is always visible.
val availableSpace = (totalTabRowWidth - visibleWidth).coerceAtLeast(0)
return centeredTabOffset.coerceIn(0, availableSpace)
}
}
private val ScrollableTabRowMinimumTabWidth = 90.dp
/**
* The default padding from the starting edge before a tab in a [ScrollableTabRow].
*/
private val ScrollableTabRowPadding = 52.dp
/**
* [AnimationSpec] used when scrolling to a tab that is not fully visible.
*/
private val ScrollableTabRowScrollSpec: AnimationSpec<Float> = tween(
durationMillis = 250,
easing = FastOutSlowInEasing
)