Excerpt
- C#是微软公司发布的一种面向对象的、运行于 .NET Framework和 .NET Core(完全开源,跨平台)之上的高级程序设计语言。- C#是一种安全的、稳定的、简单的、优雅的,由C和C++衍生出来的面向对象的编程语言。它在继承C和C++强大功能的同时去掉了一些他们的复杂特性。- C#是面向对象的编程语言。
C#基础
一、C#语言及其特点
- C#是微软公司发布的一种面向对象的、运行于 .NET Framework和 .NET Core(完全开源,跨平台)之上的高级程序设计语言。
- C#是一种安全的、稳定的、简单的、优雅的,由C和C++衍生出来的面向对象的编程语言。它在继承C和C++强大功能的同时去掉了一些他们的复杂特性。
- C#是面向对象的编程语言。
二、认识 .NET Framework/.NET Core
.NET 是一个开发平台,而 C# 是一种在 .NET 开发平台上使用的编程语言,目前能在 .NET 平台上使用的开发语言很多,例如 Visual Basic .NET、Python、J#、Visual C++.NET 等。但在 .NET 平台上使用最多的是 C# 语言。
.NET 框架的目的是便于开发人员容易地建立 Web 应用程序和 Web 服务,使得 Internet 上的各应用程序之间可以使用 Web 服务进行沟通。
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-WFXjHQap-1663903134182)(https://kevin-1311972042.cos.ap-chengdu.myqcloud.com/img/241f95cad1c8a786c91727da2e5dde3d70cf3ac7fa91)]
.NET框架由三部分组成。执行环境称为CLR(Common Language Runtime,公共语言运行库)。CLR在运行时管理程序的执行,包括:内存管理和垃圾收集;代码安全验证;代码执行、线程管理和异常处理。BCL(Base Class Library,基类库)是.NET框架使用的一个大的类库,而且也可以在你的程序中使用。
三、C#语法基础
3.1 cs文件结构
结构展示:

3.2 C#基本语法
注意:
- C#是大小写敏感的
- 所有的语句和表达式必须以分号结尾
- 与Java不同的是,文件名可以不同于类的名称
C#是一种面向对象的编程语言。在面向对象的程序设计方法中,程序由各种对象组成,相同种类的对象通常具有相同的类型
案例:
以人类为例,从人类中诞生出的具体对象”C罗“和”梅西“,同属于人类。故两人的类型相同
关键字
关键字,是对编译器有特殊意义的预定义保留标识符,它们不能再程序中用作标识符
-
using关键字
在任何C#程序中的第一条语句都是:
using System;using 关键字用于在程序中包含命名空间,一个程序可以包含多个using语句
-
class关键字
class关键字用于声明一个类
-
C#的注释方式
/* 多行注释 */ //单行注释 ///文档注释 一般用于方法或者类名上
变量
- 变量是一个供程序存储数据的盒子。在C#中,每个变量都有一个特定的类型,不同类型的变量其内存大小也不尽相同。
C#中提供的基本类型大致可以分为一下几类:
| 类型 | 举例 |
|---|---|
| 整数类型 | byte、short、int、long |
| 浮点型 | float、double |
| 十进制类型 | decimal |
| 布尔类型 | bool |
| 字符类型 | string、char |
| 空类型 | null |
3.3 C#语法进阶
表达式
-
表达式由操作数和操作符构成。运算符包括+、-、*、/和new等。操作数包括文本、字段、局部变量和表达式。
-
当表达式包含多个运算符时,运算符的优先级控制各运算符的计算顺序。例如,表达式 x+y_z 按 x+(y_z)计算,因为*运算符的优先级高于+运算符。
-
(了解)大多数运算符都可以重载。运算符重载允许指定用户定义的运算符来执行运算,这些运算的操作数中至少有一个,甚至所有操作数都属于用户定义的类类型或者结构类型。
-
下表总结了C#简单常用的运算符,并按优先级从高到低的顺序列出各运算符类别。同一类别中的运算符优先级相同。
类别 表达式 说明 基本 x.m 成员访问 x(…) 方法和委托调用 x[…] 数组和索引器访问 new T(…) 对象和委托创建 new T(…){…} 使用初始值设定项创建对象 new {…} 匿名对象初始值设定项 new T{…} 数组创建
分支语句
if语句
if(条件){
语句
}
if-else语句
if(条件){
语句
}else{
...
}
if(条件){
语句
}else if(条件){
语句
}else{
...
}
switch语句
switch( i ){
case 1:
...
break;
case 2:
...
break;
...
default:
...
break;
}
案例
- 班级中有张三、李四、王五、赵六、田七、周八六位同学
- 请找出赵六同学送他回家
- 分别是用for循环和while循环实现
-
思考?
-
以上案例需要设置几个变量?
string[] classStudent = new string[]{"张三","李四","王五","赵六","田七","周八"}; -
需要声明何种类型的变量?
-
for循环和while循环实现上有何差异?
-
用do-while循环如何实现?
-
-
string[] classStudent = new string[6] { "张三", "李四", "王五", "赵六", "田七", "周八" }; for (int i=0; i<classStudent.Length; i++) { //MessageBox.Show(classStudent[i]); if (classStudent[i]=="赵六") { MessageBox.Show("找到了"+ classStudent[i]+",并送他回家了"); break; } }
函数初识
函数即方法!
-
函数的命名规范
- 函数命名使用大驼峰命名,即开头首字母大写(注:java使用的是驼峰命名!)
- 多个单词拼接时,所有单词首字母大写
AddCount(); -
函数的参数设置和传参行为
- 参数可认为是外部需要的函数帮忙处理的数据
- 外部通过传递参数的形式,将需要处理的数据交给函数处理
-
函数返回值的设置
- 函数返回值可以认为是外部调用某种行为后得到的一种反馈
-
实操
//C#程序的主方法 private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e) { SendMessage("你好,xiaoshu"); } public void SendMessage(string message) { MessageBox.Show(message); }
参数修饰符
- 无修饰符:如果一个参数没有用参数修饰符标记,则认为它将按值进行传递,这将意味着被调用的方法收到原始数据的一份副本。
- out:输出参数由被调用的方法赋值,因此按引用传递。如果被调用的方法没有输出参数赋值,就会出现编译错误。out最大的用途就是调用者只使用一次方法的调用就能获得多个返回值。(在C#7.0中要实现一次方法的调用就能获得多个返回值,建议使用元组。)
- ref:调用者赋初值,并且可以由被调用的方法可选的重新赋值(数据是按引用传递的)。如果被调用的方法未能给ref参数赋值,也不会有编译器错误。
四、面向对象
相比较函数,面向对象是更大的封装,根据职责,在一个对象中封装多个方法
- 在完成某一个需求全部,首先确定职责,要做的事情(方法)
- 根据职责确定不同的对象,在对象内部封装不同的方法(多个)
- 最后完成代码,就是顺序的让不同的对象调用不同的方法
特点:
- 注重对象和职责,不同的对象承担不同的职责
- 更加适合应对复杂的需求变化,是专门应对复杂项目的开发,提供固定套路
- 需要在面向过程的基础上,再学习一些面向对象的语法
4.1 类的设计
在使用面向对象开发前,应该首先分析需求,确定一下程序中需要包含哪些类
在程序开发中要设计一个类,通常需要满足以下三个要素:
- 类名:这类事务的名称,满足大驼峰命名
- 属性:这类事务具有什么样的特征
- 方法:这类事物具有什么样的行为
4.2 类和对象的使用
声明属性
-
属性依旧遵循大驼峰命名法
-
属性最常用的书写方法
public int Age{get;set} //公有的 private int Age{get;set} //私有的 internal int Age{get;set} //内部的
访问修饰符
- public:公有的 所有的类都可以访问
- private: 私有的 当前类内部可以访问
- protected: 受保护的 只限于本项目内可以访问,其他的不能访问
- internal:内部的 只限于本项目内访问,其他的不能访问
- protected internal:内部保护访问 只能是本项目内部或者子类访问 其他类不能访问
静态方法、属性
- 静态方法和属性通过static 关键字修饰
- 静态和属性可以通过类型直接获取,非静态则必须通过实现化的对象获取
4.3 委托
委托(delegate)是一种存储函数引用的类型
委托的定义指定了一个返回类型和一个参数列表
定义了委托之后,就可以声明该委托的变量,接着就可以把一个返回类型跟参数列表跟委托一样的函数赋值给和这个变量
委托的使用分两步
- 定义
- 声明
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Delegate
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//声明委托
MyDelegate delegate1;
delegate1 = Multiply;
Console.WriteLine(delegate1(5,6));
Console.ReadKey();
MyDelegate delegate2;
delegate2 = Divide;
Console.WriteLine(delegate2(5,6));
Console.ReadKey();
}
static double Multiply(double param1,double param2)
{
return param1 * param2;
}
static double Divide(double param1,double param2)
{
return (param1 / param2);
}
//定义一个委托
delegate double MyDelegate(double param1, double param2);
}
}
4.4 委托事件
什么叫事件?事件就是委托的安全版本
- 在定义事件类的外部,是不能使用 = 号来操作,只能用+=
- 在定义事件的外部不能调用事件
- 事件就是在委托的前面加上一个event关键字
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace DelegateEvent
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
EventFunc eventFunc = new EventFunc();
InvokeDefine invokeDefine = new InvokeDefine();
//在定义事件类的外部,是不能使用 = 号来操作,只能用+=
invokeDefine.StudentEvent += eventFunc.Student1;
invokeDefine.Invoke();
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
//定义一个委托
delegate void StudentDelegate();
/// <summary>
/// 定义事件和调用事件 一定要放在一个类中
/// </summary>
class InvokeDefine
{
//定义一个委托事件,必须放在类中
public event StudentDelegate StudentEvent;
public void Invoke()
{
StudentEvent?.Invoke(); //?.(null检查运算符):判断后面跟的东西是否为空,不为空才调用
//相当于下面的语句:
//if (StudentEvent != null)
//{
// StudentEvent.Invoke();
//}
}
}
class EventFunc
{
public void Student1()
{
Console.WriteLine("我是学生1——小舒");
}
public void Student2()
{
Console.WriteLine("我是学生2——小明");
}
}
}
4.5 正则表达式
注意:^:取反 取得除了什么之外的字符
- [^,] 除了逗号之外的任何字符
- [^,]* 0或者多个非逗号字符
等价:
等价是等同于的意思,表示同样的功能,用不同符号来书写。
?,*,+,\d,\w 都是等价字符
?等价于匹配长度{0,1}
*等价于匹配长度{0,}
+等价于匹配长度{1,}
\d等价于[0-9]
\D等价于[^0-9]
\w等价于[A-Za-z_0-9]
\W等价于[^A-Za-z_0-9]
常用运算符与表达式:
^ 开始
()域段
[] 包含,默认是一个字符长度
[^] 不包含,默认是一个字符长度
{n,m} 匹配长度
. 任何单个字符(\. 字符点)
| 或 将两个匹配条件进行逻辑或(or)运算
\ 转义
$ 结尾
[A-Z] 26个大写字母
[a-z] 26个小写字母
[0-9] 0至9数字
[A-Za-z0-9] 26个大写字母、26个小写字母和0至9数字
, 分割
重复描述字符
{n} 匹配前面的字符n次
{n,} 匹配前面的字符n次或多于n次
{n,m} 匹配前面的字符n到m次
? 重复零次或一次
+ 重复一次或更多次
* 重复一次或更多次
string str1 = "12355m";
string str2 = "554866";
string str3 = " I am blue cat";
//Console.WriteLine(Regex.IsMatch(str1, ""));
//@:让标记的字符串中的一些特殊字符失效,这样不让编译器去解析其中的转义字符,比如 \;因为 \ 也是正则表达式的语法规则,所以使用时需要在前面加上@"正则表达式"
//Console.WriteLine(@"1\n1\t2\\");
// ^:匹配开始 $:匹配结尾 ^\d*$:匹配以数字开头和以数字结尾的字符串
//Console.WriteLine(Regex.IsMatch(str1, @"\d")); //IsMatch:只要有一个符合条件就会返回true
Console.WriteLine(Regex.Replace(str3,"^", "准备开始:")); //IsMatch:只要有一个符合条件就会返回true
Console.WriteLine(Regex.Replace(str3,"$", "结束了")); //IsMatch:只要有一个符合条件就会返回true
4.6 匿名方法和Lambda表达式
匿名方法:简单方法(一两行代码的方法)适合用匿名方法,需要声明为delegate
Lambda表达式的基本形式:
(input params)=> expression
其中,input params表示输入参数,expression表示表达式
//匿名方法:简单方法(一两行代码的方法)适合用匿名方法,需要声明为delegate
//Func<int, int, int> plus = delegate (int a, int b) { return a + b; };
//int res = plus(1, 2);
//Console.WriteLine(res);
//Console.ReadLine();
//lambda:匿名方法的简写
//Func<int, int, int>:泛型中前两个参数类型是匿名方法的参数类型,第三个参数类型是返回值类型
//Func<int, int, int> plus = ( a, b) => { return a + b; }; 方法只有一条返回语句可以将括号和return给去掉,多条语句需要加上
//Func<int, int, int> plus = ( a, b) => a + b ;
//int res = plus(1, 2);
//Console.WriteLine(res);
//Console.ReadLine();
Func<double,double> square = (x) => x * x ; 方法只有一个参数可以将括号去掉
//Func<double,double> square = x => x * x ;
//lambda表达式可以访问外部变量
int a = 5;
Func<double,double> fun = x => x + a ;
Console.WriteLine(fun(5));
Console.ReadKey();
4.7 委托和Lambda表达式的练习
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Lambda
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
/*string[] strs = new string[] { "C#编程", "C#学习", "小舒" };
//使用lambda表达式查询出包含"C#"的字符串
string[] str = Array.FindAll(strs, s => (s.IndexOf("C#") >= 0));
foreach (string s in str)
{
Console.WriteLine(s);
}
Console.ReadLine();*/
string[] strs = new string[] { "C#编程", "C#学习", "小舒" };
//使用lambda表达式查询出包含"C#"的字符串
string[] str = Array.FindAll(strs, Func);
foreach (string s in str)
{
Console.WriteLine(s);
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
static bool Func(string s){
if(s.IndexOf("C#") >= 0)
{
return true;
}else
{
return false;
}
}
}
}
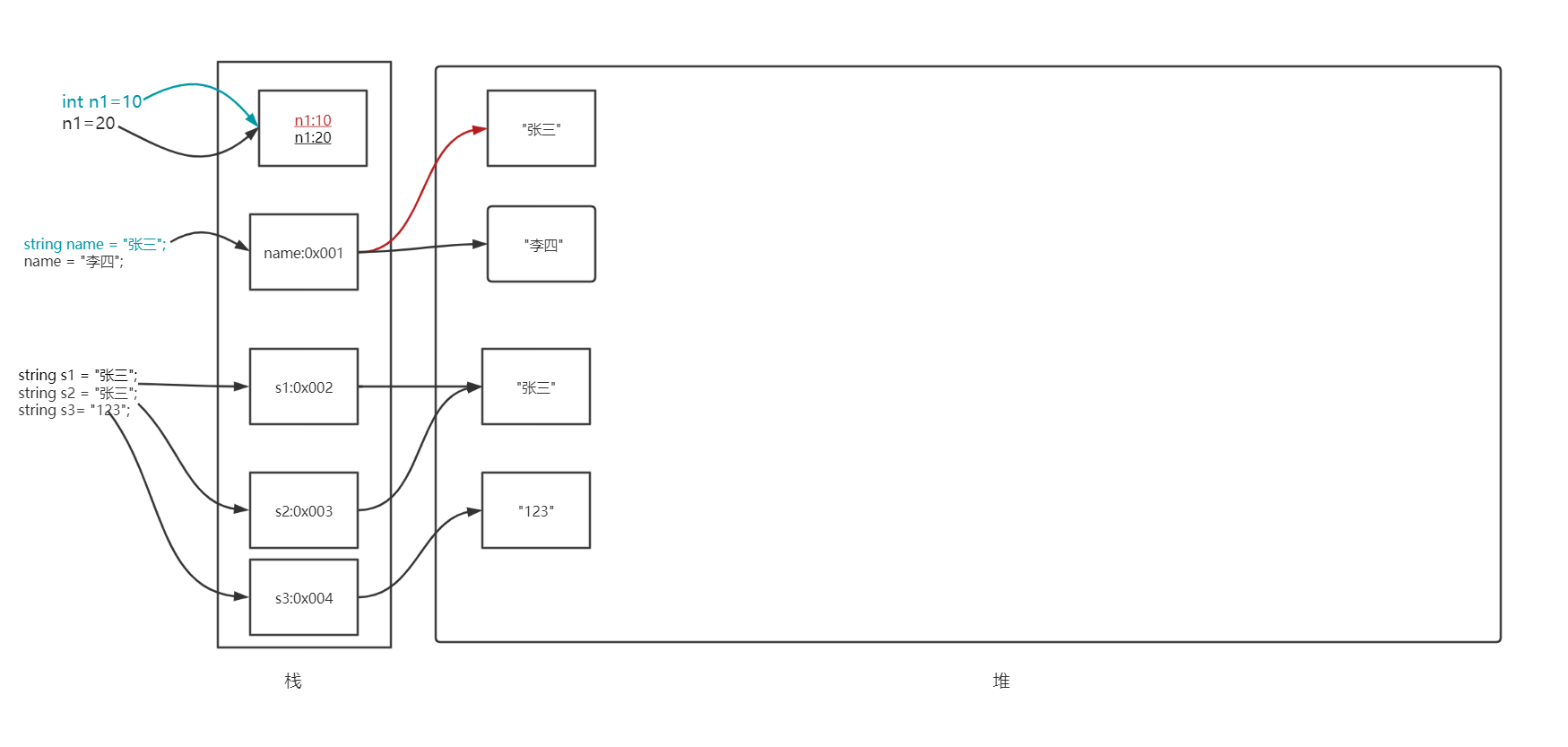
4.8 值类型和引用类型
类型被分为两种:
- 值类型:整数,bool,struct,char,小数,枚举类型(每一个枚举类型对应的是一个数字,所以是值类型)
- 引用类型:string,数组,自定义的类,内置的类
内存分析:
- 值类型只需要一段单独的内存,用于存储实际的数据(单独定义的时候放在栈中)
- 引用类型需要两段内存:
- 第一段存储实际的数据,它总是位于堆中
- 第二段是一个引用,指向数据在堆中的存放位置
五、集合和字典的初识
集合与数组比较类似,都用于存放一组值
在集合类中,List是最基础的一种集合:它是一种有序列表
注意:数组需要用for或者foreach遍历
5.1 List与泛型的使用
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace list_study
{
public class Person
{
public int Age { get; set; }
public int Height { get; set; }
public string name { get; set; }
}
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
List<Person> people = new List<Person>();
Person person1 = new Person
{
Age = 18,
Height = 177,
name = "xiaoshu"
};
people.Add(person1);
foreach (Person p in people)
{
Console.WriteLine("{0} {1} {2}",p.Age,p.Height,p.name);
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
5.2 ArrayList、Dictionary的使用
ArrayList的使用:
- ArrayList是 .NET Framework提供的用于数据存储和检索的专用类
- 它是命名空间System.Collections下的部分
- 长度问题:每次集合中实际包含的元素个数(count)超过了可以包含的元素的个数(capacity)
Dictionary(Map)
与JavaMap类似
-
在声明Dictionary字典时,需要同时为其声明Dictionary字典内键与值的类型
-
示例
Dictionary<int,string> dictionary = new Dictionary<int,string>()键与值可以是任何类型,但是键必须在设置是是唯一的,而值可以不唯一,就好比每个学生的学号是唯一的,而所有的成绩可以不唯一
5.3 foreach的使用
int[] ints = new int[] { 1, 2, 3 };
foreach (int i in ints)
{
MessageBox.Show(i.ToString());
}
Dictionary<int, string> dictionary = new Dictionary<int, string>();
dictionary.Add(0, "xiaoshu");
dictionary.Add(1, "小舒");
foreach (var s in dictionary)
{
Console.WriteLine(s.Key+" "+s.Value);
}
Console.ReadKey();
5.4 Dictionary<T1,T2>和Hashtable的异同
首先很多人都认同一个观点,说Dictionary<T1,T2>是HashTable的泛型版本,这一点在大致上是正确的,可是当我们运行这样一段代码时,便可看出他们的不同:
using System.Collections;
Console.WriteLine("Dictionary:");
Dictionary<int, int> dic = new Dictionary<int, int>();
dic.Add(1, 5);
dic.Add(10, 3);
dic.Add(2, 5);
foreach (int key in dic.Keys)
{
Console.Write(key+" ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("Hashtable:");
Hashtable hashtable = new Hashtable();
hashtable.Add(1, 5);
hashtable.Add(10, 3);
hashtable.Add(2, 5);
foreach (object key in hashtable.Keys)
{
Console.Write(key.ToString()+" ");
}
输出:
Dictionary:
1 10 2
Hashtable:
10 2 1
Dictionary<T1,T2>是根据插入的顺序来遍历,但是Hashtable在插入时会打乱其位置。
并且我们在用Reflector看源码的时候也会发现Hashtable是线程安全的,而Dictionary明显不具备如此特性。
六、常量、枚举
常量
声明常量的语法:
const 变量类型 变量名 = 值;
注意:常量不能被重新赋值
枚举
语法:
[public] enum 枚举名{
值1,
值2,
值3,
...
}
enum:关键字,声明枚举的关键字
枚举就是一个变量,int double string decimal
只是枚举声明、赋值、使用的方式跟那些普通的变量类型不一样。本质还是存数据
七、字符串
7.1 字符串的不可变性
当你给一个字符串重新赋值之后,原来的值并不会销毁,而是重新开辟一块空间存储一个新值
当程序结束后,GC扫描整个内存,如果发现有的空间没有被指向,则立即把它销毁

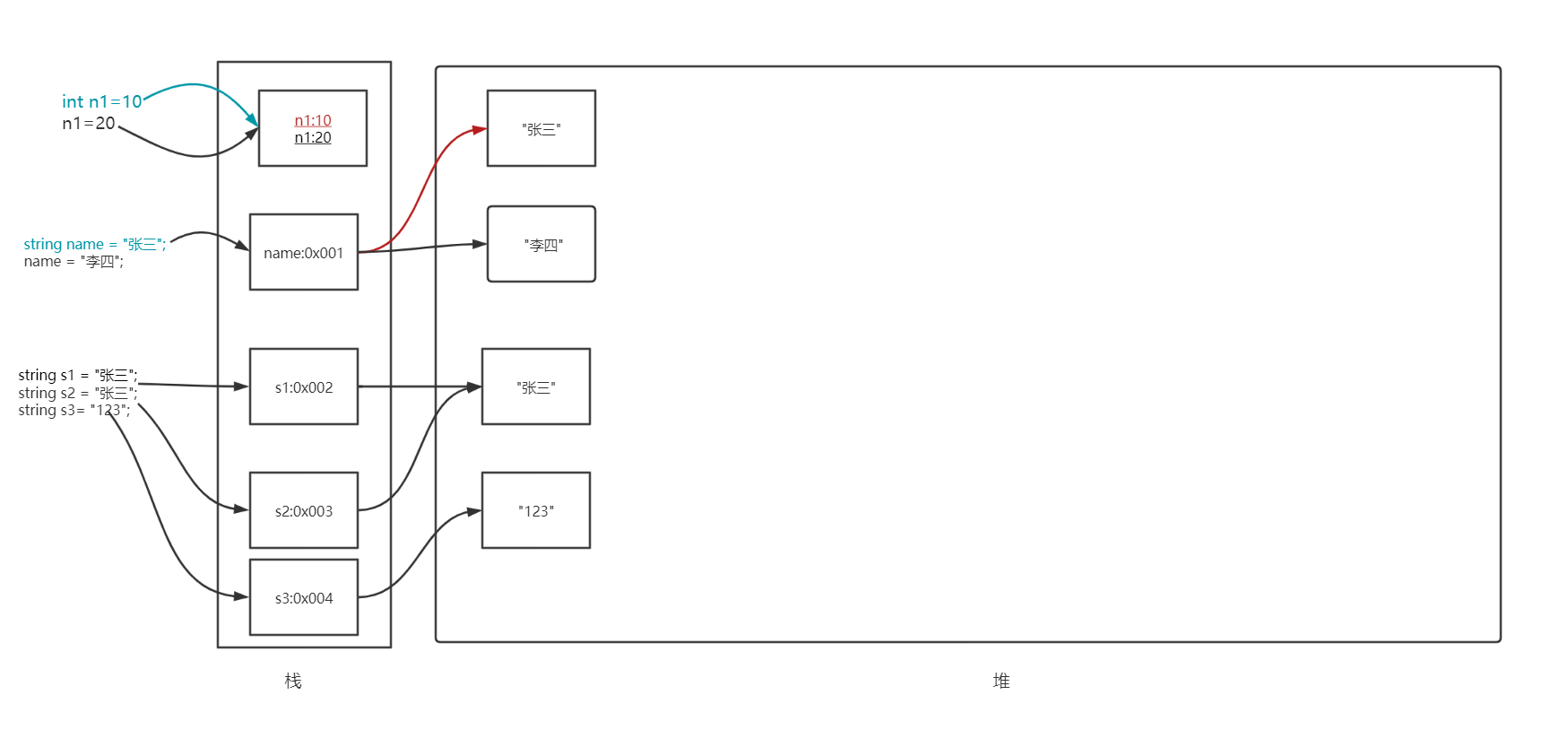
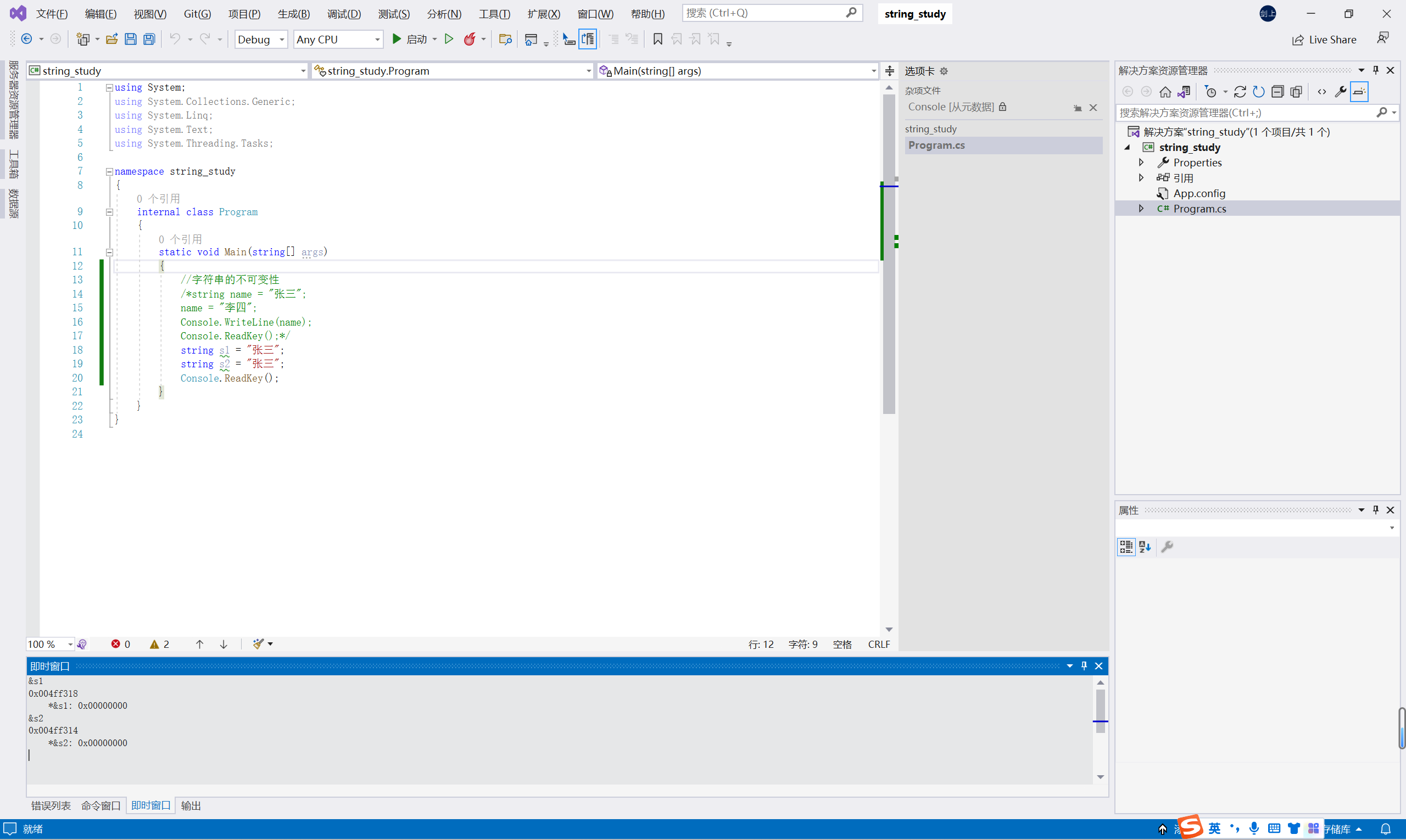
7.2 可以将字符串看做是一个char类型的只读数组
//可以将字符串看做是一个char类型的只读数组,所以可以通过下标去访问字符串中的某一个元素
string s = "abcdefg";
Console.WriteLine(s[2]);
//ReadKey()是在按下任意一个键时就会关闭命令窗口,而ReadLine()是在当用户按下回车键是才会关闭命令窗口,也可以输入!
/*Console.ReadKey();*/
Console.ReadLine();
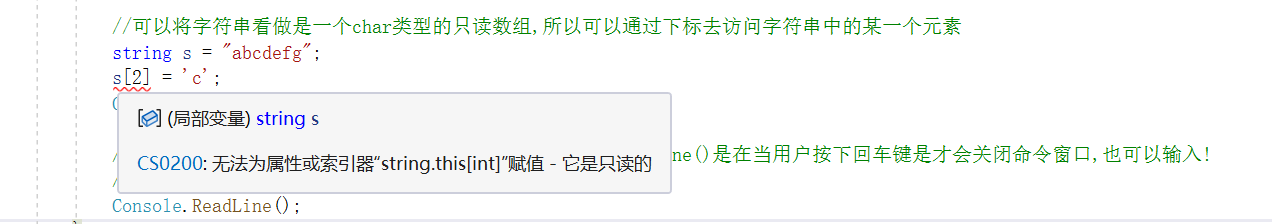
//需求:将第一个a换成b
//1、将字符串转换为char类型的数组
char[] chs = s.ToCharArray();
//2、给数组赋值(数组可读可写)
chs[0] = 'b';
Console.WriteLine(chs);
Console.ReadKey();
//3、将字符数组转换为字符串
Console.WriteLine("*****************************");
s = new string(chs);
Console.WriteLine(s);
Console.ReadLine();
7.3 StringBuilder
//00:00:00.0060079
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
//00:00:07.1849033
string str = null;
//创建了一个计时器,用来记录程序运行的时间
Stopwatch stopwatch = new Stopwatch();
stopwatch.Start(); //开始计时
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++)
{
/*str += i;*/
sb.Append(i);
}
stopwatch.Stop(); // 结束计时
Console.WriteLine(stopwatch.Elapsed);
Console.ReadLine();
7.4 字符串方法练习
- Length():获得当前字符串中字符的个数
- ToUpper():将字符串转换为大写形式
- ToLower():将字符串转换成小写形式
练习一:随机输入一个名字,然后输出它的字符串长度
/*Trans.ShowColorConsole(ConsoleColor.Yellow, () => Console.WriteLine("请随机输入一个名字: "));
*//*Console.WriteLine("请随机输入一个名字:");*//*
string name = Console.ReadLine();
Console.WriteLine("它的字符串长度是{0}",name.Length);
Console.ReadKey();
//练习二:输入各自喜欢的课程,如果一样,则输出你们喜欢相同的课程,否则输出你们喜欢不同的课程
Console.WriteLine("假如你叫小红,请输入你喜欢的课程名称:");
string xiaohong = Console.ReadLine();
//字符串的大小写转换
string xiaoHong = xiaohong.ToUpper();
string XiaoHong = xiaohong.ToLower();
Console.WriteLine("假如你叫小明,请输入你喜欢的课程名称:");
string xiaoming = Console.ReadLine();
string xiaoMing = xiaoming.ToUpper();
string XiaoMing = xiaoming.ToLower();
if(xiaoHong == xiaoMing)
{
Console.WriteLine("你们喜欢相同的课程");
}
else {
Console.WriteLine("你们喜欢不同的课程");
}
Console.ReadKey();
-
参数1(string类型).Equals(参数2(string类型),StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase)
- StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase:忽略大小写
string xiaoHong = xiaohong.ToUpper(); string XiaoHong = xiaohong.ToLower();*//* Console.WriteLine("假如你叫小明,请输入你喜欢的课程名称:"); string xiaoming = Console.ReadLine(); *//*string xiaoMing = xiaoming.ToUpper(); string XiaoMing = xiaoming.ToLower();*//* if(xiaohong.Equals(xiaoming,StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase)) { Console.WriteLine("你们喜欢相同的课程"); } else { Console.WriteLine("你们喜欢不同的课程"); } Console.ReadKey(); -
Split(Char[], StringSplitOptions)
- 根据指定的分隔字符和选项将字符串拆分为子字符串。
//练习三:将2022-09-07转换成2022年9月7日 //1、引入 //Split:分割字符串 string s = "a + b ,,,, c"; char[] chs = { ' ', '+', ',' }; string[] str = s.Split(chs, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries); var s1 = string.Join(" ", str); foreach (var s2 in s1) { Console.Write(s2); } //2、将2022-09-07转换成2022年9月7日 string s2 = "2022-09-07"; char[] chs2 = { '-' }; string[] date = s2.Split(chs2, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries); foreach(string d in date) { Console.Write(d); } Console.WriteLine(); Console.WriteLine("{0}年{1}月{2}日",date[0],date[1],date[2]); -
Replace(string oldValue, string? newValue)
string s2 = "自在飞hua轻似梦"; if (s2.Contains("hua")) { s2 = s2.Replace("hua", "花"); } Console.WriteLine(s2); -
Substring(int startIndex, int length)
//Substring():截取字符串 string s = "自在飞花轻似梦"; s = s.Substring(2,4); Console.WriteLine(s); -
判断一个字符串是否以某一个字符串结尾
string s = "自在飞花轻似梦";
/*if (s.StartsWith("自在")) {*/
if (s.EndsWith("自在")) {
Console.WriteLine("是");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("不是");
}
-
判断字符出现的位置
//判断字符第一次出现的位置 string s = "自在飞花轻似梦,自在飞花轻似梦"; int index = s.IndexOf('自'); Console.WriteLine(index); //判断字符最后一次出现的位置 string s2 = "自在飞花轻似梦,自在飞花轻似梦"; int index2 = s2.LastIndexOf('自'); Console.WriteLine(index2); -
Trim()
//trim():去除字符串前面和后面的空格 string s = " *小舒 xiaoshu* "; //s = s.Trim(); s = s.TrimStart(); //去除字符串前面的空格 //s = s.TrimEnd(); //去除字符串后面的空格 Console.Write(s); Console.ReadLine(); -
string.Join():将数组按照指定的字符串连接,返回一个字符串
//在字符串中加入字符 string[] names = { "张三", "李四", "王五" }; //张三|李四|王五 string str = string.Join("|", names); Console.WriteLine(str); Console.ReadLine(); -
文本文件中存储了多个文章标题、作者,标题和作者之间用若干空格(数量不定)隔开,每行一个,标题有的长有的短,输出到控制台的时候最多标题长度10,如果超过10,则截取长度为8的子串并且最后添加“…”,加一个竖线后输出作者的名字。
//练习四: //文本文件中存储了多个诗词标题、作者, //标题和作者之间用若干空格(数量不定)隔开,每行一个, //标题有的长有的短,输出到控制台的时候最多标题长度10, //如果超过10,则截取长度为8的子串并且最后添加“...”,加一个竖线后输出作者的名字。 string path = @"E:\诗词清单.txt"; string[] contents = File.ReadAllLines(path); for (int i = 0; i < contents.Length; i++) { string[] strNew = contents[i].Split(new char[] {' '}, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries); Console.WriteLine((strNew[0].Length>10 ? strNew[0].Substring(0,8) + "......" : strNew[0])+"|"+strNew[1]); } Console.ReadLine();
7.5 字符串格式化方法
预定义的数字格式
下表标识了预定义的数字格式名称。
int nums = 1234567;
Console.WriteLine(String.Format("{0:G}", nums));
Console.ReadKey();
| 格式名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
General Number、G 或 g | 显示没有千位分隔符的数字。 例如,String.Format("{0:G}", nums) 返回 1234567。 |
Currency、C 或 c | 显示具有千位分隔符的数字(如果适用);显示小数分隔符右侧的两位数字。 输出基于系统区域设置。 例如,String.Format("{0:C}", nums) 返回 $1,234,567.00。 |
Fixed、F 或 f | 小数点分隔符左侧至少显示一个数字,右侧至少显示两个数字。 例如,String.Format("{0:f}", nums) 返回 1234567.00。 |
Standard、N 或 n | 显示具有千位分隔符的数字,左侧至少有一位数字,小数点分隔符右侧至少有一位数字。 例如,String.Format("{0:f}", nums) 返回 1,234,567.00。 |
P、或 p | 将带有千位分隔符的数字乘以 100 后显示,并在右侧追加百分号 (%) 并用单个空格分隔;小数点分隔符右侧总是显示两位。 例如,String.Format("{0:P}", nums)) 返回 123,456,700.00%。 |
E、或 e | 使用标准的科学记数法,并且提供六个有效位数。 例如,String.Format("{0:E}", nums)) 返回 1.234567e+006。 |
D、或 d | 将数字显示为字符串,该字符串包含采用十进制(以 10 为底)格式的数字值。 仅支持整数类型 (Byte``Short、 Long) Integer此选项。 例如,String.Format("{0:D}", nums)) 返回 1234567。 |
X、或 x | 将数字显示为字符串,该字符串包含采用十六进制(以 16 为底)格式的数字值。 仅支持整数类型 (Byte``Short、 Long) Integer此选项。 例如,String.Format("{0:X}", nums)) 返回 12D687。 |
八、File类
8.1 Path类
专门用来操作路径的
//获得指定路径下的文件名字
String path = @"E:\海天瑞声\9.6\podcast\0 - j1vtfQrCU__0001.wav";
//获得文件名
string str = Path.GetFileName(path);
/*
使用截取的方法获取文件名:
int index = path.LastIndexOf("\\");
path = path.Substring(index + 1);
Console.WriteLine(path);
*/
Console.WriteLine(str);
//获取不带扩展名的文件名
Console.WriteLine(Path.GetFileNameWithoutExtension(path));
//获取文件的扩展名
Console.WriteLine(Path.GetExtension(path));
//获取文件所在的文件夹的名称
Console.WriteLine(Path.GetDirectoryName(path));
//获取文件绝对路径
Console.WriteLine(Path.GetFullPath(path));
//将两个字符串组合成一个路径
Console.WriteLine(Path.Combine(@"C:\a\","b.txt"));
Console.ReadLine();
8.2 File类
//创建文件,若重复运行则操作的是第一次创建的文件,后面的创建并不是覆盖创建,而是修改文件
/*File.Create(@"C:\Users\kevin\Desktop\file.txt");
Console.WriteLine("创建成功");
Console.ReadLine();*/
//删除一个文件,连回收站也没有
/*File.Delete(@"C:\Users\kevin\Desktop\file.txt");
Console.WriteLine("删除成功");
Console.ReadLine();*/
File.Copy(@"C:\Users\kevin\Desktop\file.txt", @"C:\Users\kevin\Desktop\newfile.txt");
Console.WriteLine("复制成功");
Console.ReadLine();
8.3 综合练习
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace file_study02
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
/*
里氏替换:
1、子类可以赋值给父类(如果一个方法需要一个父类作为参数,我们可以传递一个子类对象)
2、如果父类中装的是子类对象,则可以将这个父类强转为子类对象
*/
/*Person person = new Person();
person.PersonSay();*/
/*Person person = new Student();
person.PersonSay();*/
/*Person person = new Student();*/
//is:类型转换
/*if (person is Student) {
//((Student)person):将person强转为Student类型
((Student)person).StudentSay();
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("转换失败");
}*/
//as:类型转换
/*Student student = person as Student;
student.StudentSay();
student.PersonSay();*/
/*Hashtable hashtable = new Hashtable();
hashtable.Add(1, "张三");
hashtable.Add(true, "男");
hashtable.Add(3.14, 5000m);
//在键值对集合中,键必须是唯一的
*//*hashtable[1] = "王五";*//*
//item:表示集合中的每一项
//hashtable.Keys:表示需要遍历的东西,此处表示遍历hashtable的键,因为可以根据键表示出来值
foreach (var item in hashtable.Keys)
{
*//*string.Format("{1}{0}", item, hashtable[item]);*//*
Console.WriteLine("{0}----------{1}", item, hashtable[item]);
}
Console.ReadLine();*/
/*Dictionary<int, string> dictionary = new Dictionary<int, string>();
dictionary.Add(0, "xiaoshu");
dictionary.Add(1, "小舒");
foreach (var s in dictionary)
{
Console.WriteLine(s.Key + " " + s.Value);
}
Console.ReadKey();*/
}
}
public class Person
{
public void PersonSay()
{
Console.WriteLine("我是人类");
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
public class Student : Person
{
public void StudentSay()
{
Console.WriteLine("我是学生");
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
8.4 File 类的读写文件
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace file_study03
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//File相关方法
//1、读数据(可读取非文本文件,因为所有的东西都是以字节的形式存储的)
/*string path = @"E:\诗词清单.txt";
byte[] b = File.ReadAllBytes(path);
//将字节数组中的每一个元素都要按照指定的编码格式解码成字符串
//Default:ANSI
//string str = Encoding.Default.GetString(b); 出现乱码则说明不是使用ANSI编码,需要查看文件的编码格式
string str = Encoding.GetEncoding("UTF-8").GetString(b);
Console.WriteLine(str);
Console.ReadLine();*/
//2、写数据
//没有这个文件的话会给你创建一个,有的话则会覆盖掉
/*string str = "自在飞花轻似梦 秦观";
//需要字符串转换为字节数组
byte[] b = Encoding.Default.GetBytes(str);
string path = @"E:\诗词清单.txt";
File.WriteAllBytes(path, b);
Console.WriteLine("写入成功");
Console.ReadKey();*/
//以行的形式进行读取(读取文本文件)
/*string[] str = File.ReadAllLines(@"E:\诗词清单.txt",Encoding.Default);
foreach (string s in str)
{
Console.WriteLine(s);
}
Console.ReadLine();*/
//读取文本文件
/*string str = File.ReadAllText(@"E:\诗词清单.txt",Encoding.Default);
Console.WriteLine(str);
Console.ReadLine();*/
//以行的形式写入
/*File.WriteAllLines(@"E:\诗词清单.txt", new string[] { "无边丝雨细如愁", "秦观" });
Console.WriteLine("写入成功");
Console.ReadLine();*/
//以文本形式写入
/*File.WriteAllText(@"E:\诗词清单.txt", "自在飞花轻似梦");
Console.WriteLine("写入成功");
Console.ReadLine();*/
File.AppendAllText(@"E:\诗词清单.txt", "无边丝雨细如愁");
Console.WriteLine("追加成功");
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
8.5 补充
绝对路径和相对路径
- 绝对路径:通过给定的这个路径直接能在我的电脑中找到这个文件
- 相对路径:文件相对于应用程序的路径 ,将文件放入下图中的路径下即可直接使用文件名去进行文件的各种操作
结论:我们在开发中应该尽量去使用相对路径
8.6 问题总结
-
Dictionary和Hashtable的区别?
-
hashtable不支持泛型,而dictionary支持泛型。
-
hashtable的元素属于object类型,所以在存储和检索值类型时通常发生装箱和拆箱的操作,所以你可能需要进行一些类型转换的操作,而对于int、float这些值类型还需要进行装箱等操作,非常耗时。
-
单线程程序中推荐使用dictionary,有泛型有事,且读取速度较快,容量利用更充分。多线程程序中推荐使用hashtable,默认的hashtable允许单线程写入,多线程读取,对hashtable进一步调用synchronize方法可以获得安全线程安全的类型,而dictionary非线程安全,必须人为使用lock语句进行保护,效率大减。
-
在通过代码测试的时候发现key是整数型dictionary的效率比hashtable快,如果key是字符串型,dictionary的效率比hashtable快。
-
-
==和Equals的区别?
一、对象类型不同
1、equals():是超类Object中的方法。
2、==:是操作符。
二、比较的对象不同
1、equals():equals是Object中的方法,在Object中equals方法实际"ruturn (thisobj)“,用到的还是”“,说明如果对象不重写equals方法,实际该对象的equals和”“作用是一样的,都是比较的地址值(因为”"比较的就是地址值),但是大部分类都会重写父类的equals方法,用来检测两个对象是否相等,即两个对象的内容是否相等,例如String就重写了equals方法,用来比较两个字符串内容是否相同。

2、:用于比较引用和比较基本数据类型时具有不同的功能,比较引用数据类型时,如果该对象没有重写equals方法,则比较的是地址值,如果重写了,就按重写的规则来比较两个对象;基本数据类型只能用""比较两个值是否相同,不能用equals(因为基本数据类型不是类,不存在方法)。
三、运行速度不同
1、equals():没有==运行速度快。
2、:运行速度比equals()快,因为只是比较引用。
-
Replace(string oldValue, string? newValue)中的问号是什么意思?
答:? 表示参数可以为空
string s = "abcdefg"; string s1 = s.Replace("a",""); Console.WriteLine(s1); Console.ReadLine();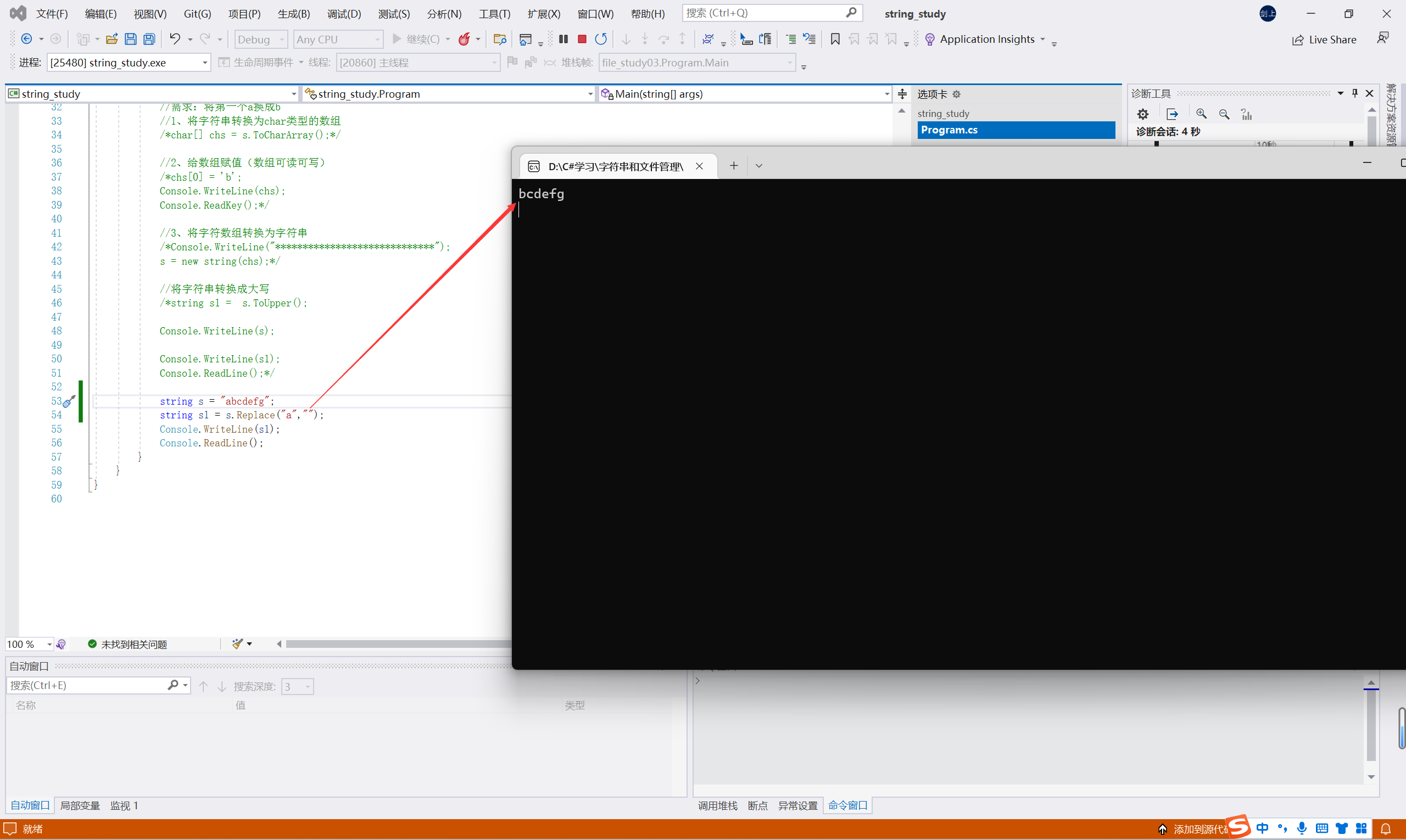
-
string s2 = "自在飞hua轻似梦"; if (s2.Contains("hua")) { s2 = s2.Replace("hua", "花"); //将其替换为"",或者将" "替换为""会怎么样?答:其作用相当于删除,如下图 } Console.WriteLine(s2);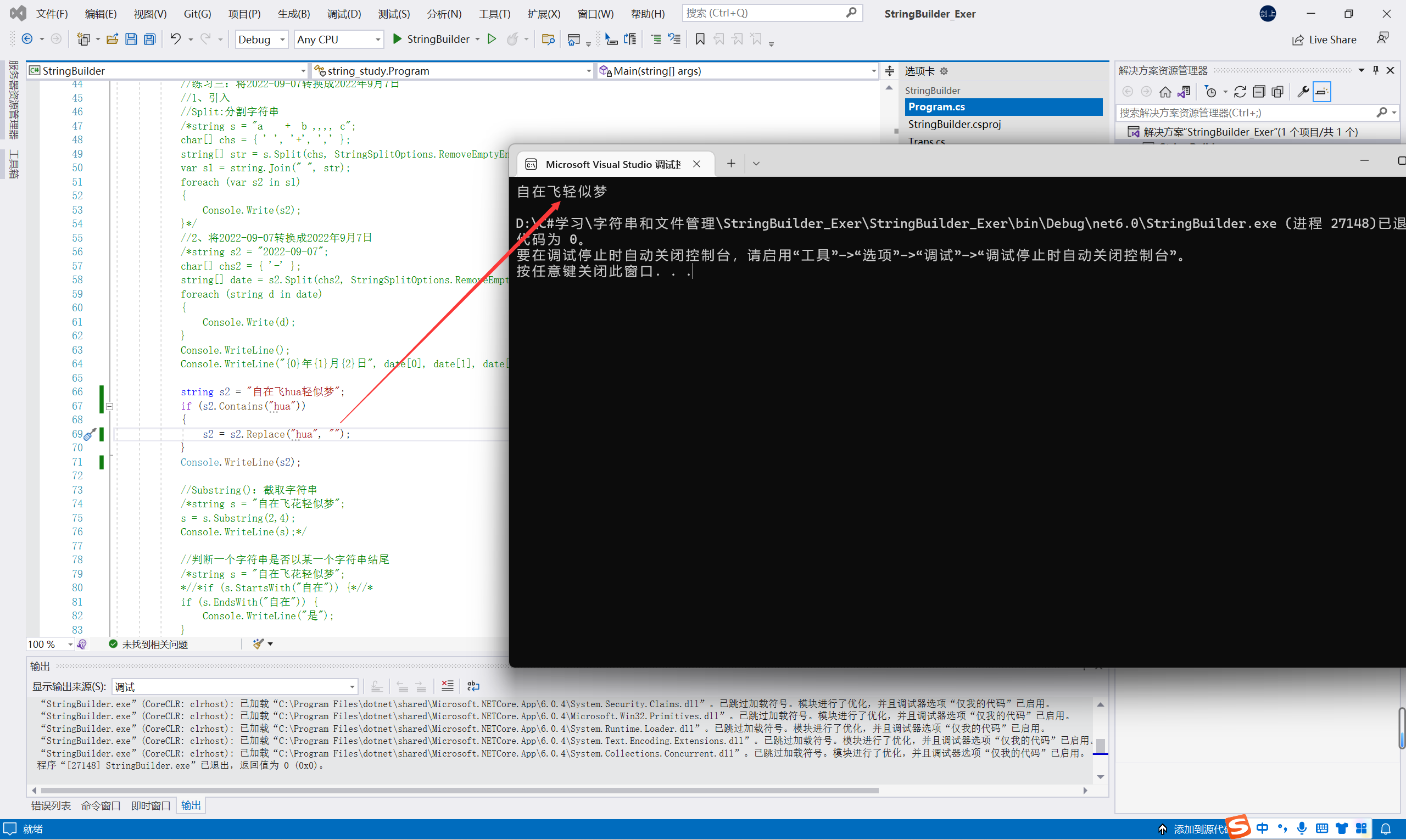
-
下面语句中s = s.Substring(2,8); 会出现什么情况?
//Substring():截取字符串 string s = "自在飞花轻似梦"; s = s.Substring(2,4); //s = s.Substring(2,8); 会出现什么情况? Console.WriteLine(s);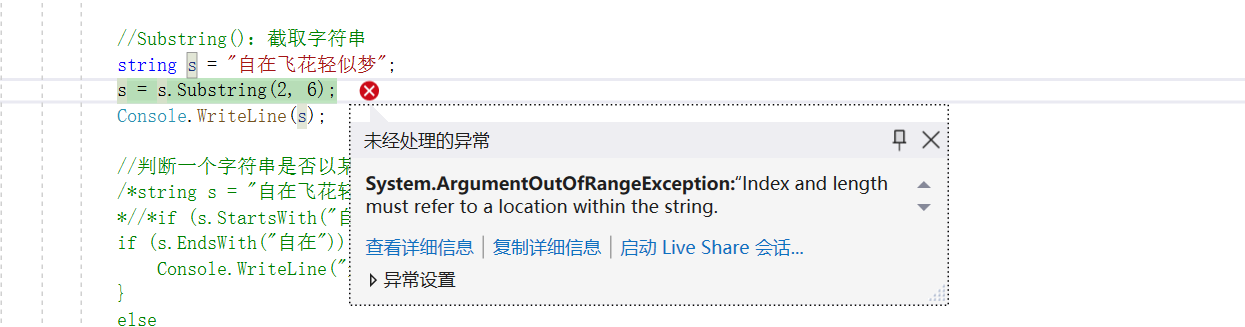
会报如下异常(类似于数组下标越界异常):
System.ArgumentOutOfRangeException:“Index and length must refer to a location within the string.must refer to a location within the string. Arg_ParamName_Name” System.ArgumentOutOfRangeException:“索引和长度必须引用字符串内的位置。必须引用字符串中的位置。Arg_ParamName_Name” -
trim()函数不止是去除空格?还可以去除什么?可以去除\n吗?
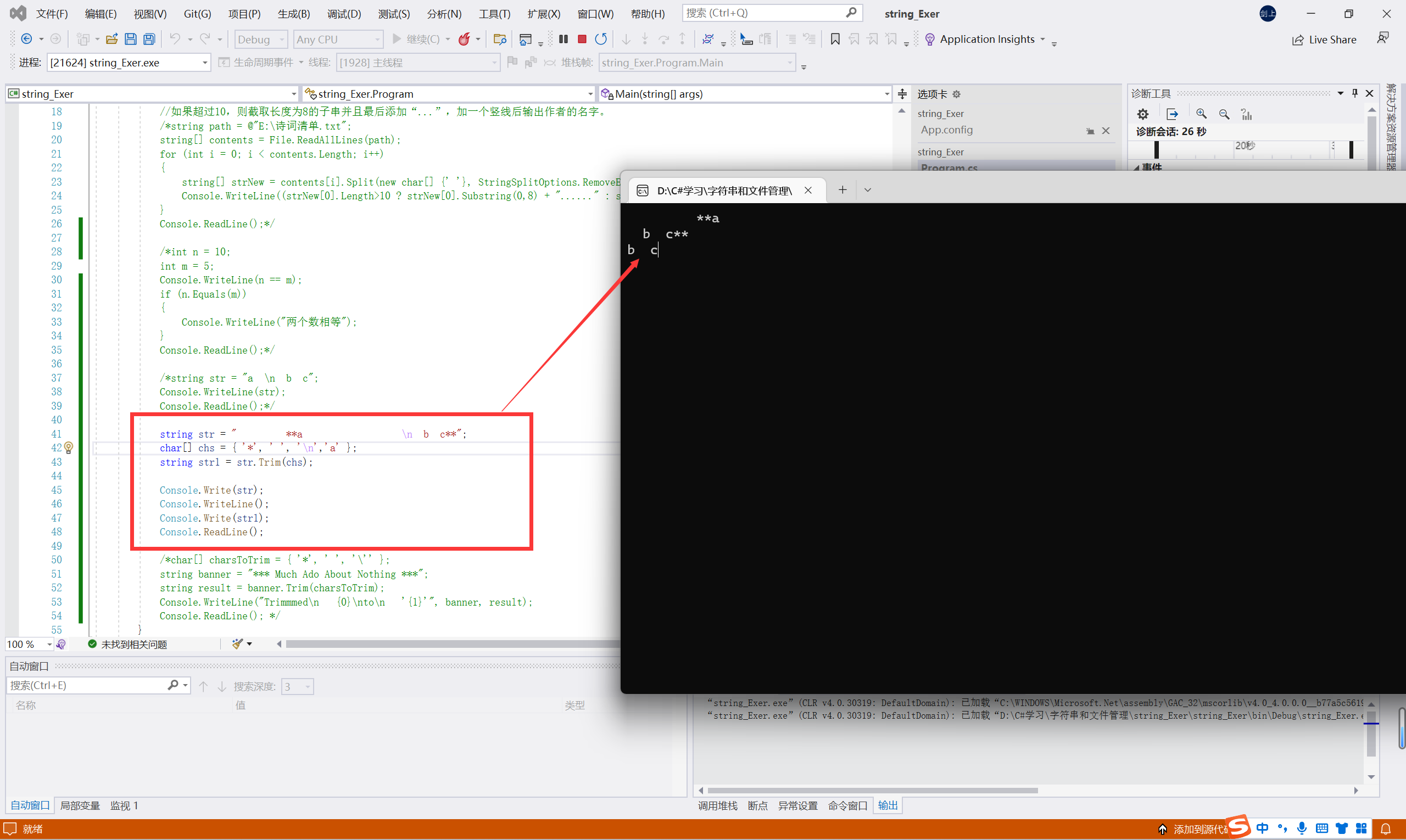
答:还可以去除指定的字符(通过char[] 声明需要去除的字符),\n不能被去除,如上图所示。
-
如何读取指定文件内容?
//读取文件的行以查找包含指定字符串的行
var lines = File.ReadLines(@"E:\诗词清单.txt",Encoding.Default);
foreach (var line in lines)
{
if (line.Contains("杜甫"))
{
Console.WriteLine(line);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}

8.7 多文本内容的合并
/// <summary>
/// 合并文件
/// </summary>
/// <param name="isOverreadPath">是否重载目录</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static async Task MergeTxt(bool isOverreadPath = false)
{
if (!isOverreadPath)
{
Trans.ShowColorConsole(ConsoleColor.Yellow, () => Console.WriteLine("输入查询目录:"));
ImportDir = Console.ReadLine().TrimPath().ShouldDirectoryExist();
Trans.ShowColorConsole(ConsoleColor.Yellow, () => Console.WriteLine("输入导出目录:"));
ExportDir = Console.ReadLine().TrimPath().ShouldDirectoryExist();
}
//获取所有文本文件
var files = Directory.GetFiles(ImportDir, "*.txt", searchOption: SearchOption.AllDirectories).Where(x => !x.Contains("日志") && !x.Contains("统计"));
var dictionary = new Dictionary<string, List<string>>();
foreach (var file in files)
{
//拿到文件的内容
var contents = File.ReadAllLines(file);
//将文件内容添加到字典中
dictionary.Add(file, contents.ToList());
}
//组合文件路径
var savePath = Path.Combine(ExportDir,"合并文件");
var saveFile = Path.Combine(savePath, "生成的含有全部内容的新文件.txt");
if (!Directory.Exists(savePath))
{
//在文件用户提供的导出目录下新建一个合并文件
Directory.CreateDirectory(savePath);
}
else
{
//存在,先删除再创建
Directory.Delete(savePath, true);
Directory.CreateDirectory(savePath);
}
//判断文件是否存在
if (File.Exists(saveFile))
{
File.Delete(saveFile);
}
//将文件全部内容追加进新文件下
foreach (var item in dictionary.Values)
{
File.AppendAllLines(saveFile, item);
}
}
九、out、ref、params
9.1 out参数
如果你在一个方法中,返回多个相同类型的值的时候,可以考虑返回一个数组
但是,如果返回多个不同类型的值的时候,返回数组就不行了,那么这个时候我们可以考虑使用out参数;out参数就侧重于在一个方法中可以返回多个不同类型的值。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace CSharp_out
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//写一个方法 求一个数组中的最大值、最小值、总和、平均值
//方法一:
int[] numbers = { 1, 10, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 };
//将要返回的4个值,放到一个数组中返回
/*int[] ints = GetMaxMinSumAvg(numbers);
*//*foreach (int i in ints)
{
Console.WriteLine(i);
}
Console.ReadLine();*//*
Console.WriteLine("最大值是{0},最小值是{1},总和是{2},平均值是{3}", ints[0], ints[1], ints[2], ints[3]);
Console.ReadLine();*/
//方法二:
/*int max1 = 0;
int min1 = 0;
int sum1 = 0;
int avg1 = 0;
Test(numbers, out max1, out min1, out sum1, out avg1);*/
Test(numbers, out int max1, out int min1, out int sum1, out int avg1,out bool b,out string s,out double d);
Console.WriteLine(max1);
Console.WriteLine(min1);
Console.WriteLine(sum1);
Console.WriteLine(avg1);
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine(b);
Console.WriteLine(s);
Console.WriteLine(d);
Console.ReadLine();
}
public static int[] GetMaxMinSumAvg(int[] nums)
{
int[] res = new int[4];
//假设res[0] 最大值 res[1] 最小值 res[3] 总和 res[3] 平均值
res[0] = nums[0]; //Max
res[1] = nums[0]; //Min
res[2] = 0; //Sum
for (int i = 0; i < nums.Length; i++)
{
//如果当前循环到的元素比我假定的最大值还大
if(nums[i] >res[0])
{
//将当前循环到的元素赋值给我的最大值
res[0]=nums[i];
}
//如果当前循环到的元素比我假定的最小值还小
if (nums[i] < res[1])
{
//将当前循环到的元素赋值给我的最小值
res[1] = nums[i];
}
res[2]+=nums[i]; //总和
}
res[3] = res[2] / nums.Length; //平均值
return res;
}
//out 参数类型 参数:表示需要多余需要返回的参数
/// <summary>
/// 计算一个整数数组的最大值、最小值、总和、平均值
/// </summary>
/// <param name="nums">要求值的数组</param>
/// <param name="max">多余返回的最大值</param>
/// <param name="min">多余返回的最小值</param>
/// <param name="sum">多余返回的总和</param>
/// <param name="avg">多余返回的平均值</param>
public static void Test(int[] nums,out int max,out int min,out int sum,out int avg, out bool b, out string s, out double d)
{
//out参数要求在方法的内部必须为其赋值
max = nums[0];
min = nums[0];
sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.Length; i++)
{
//如果当前循环到的元素比我假定的最大值还大
if (nums[i] > max)
{
//将当前循环到的元素赋值给我的最大值
max = nums[i];
}
//如果当前循环到的元素比我假定的最小值还小
if (nums[i] < min)
{
//将当前循环到的元素赋值给我的最小值
min = nums[i];
}
sum += nums[i]; //总和
}
avg = sum / nums.Length; //平均值
b = true;
s = "123";
d = 3.14;
}
}
}
9.2 ref参数
能够将一个变量带入一个方法中进行改变,改变完成后,再将改变后的值带出方法。
ref参数要求在方法外必须为其赋值,而方法内可以不赋值
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace CSharp_ref
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
double salary = 5000;
Bonus(ref salary);
/*Deduct(ref salary);*/
Console.WriteLine(salary);
Console.ReadLine();
}
public static void Bonus(ref double s)
{
s += 500;
}
public static void Deduct(ref double s)
{
s -= 500;
}
}
}
练习:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace CSharp_refexer
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//使用方法来交换两个int类型的变量
int n1 = 10;
int n2 = 20;
Swap(ref n1, ref n2);
Console.WriteLine(n1);
Console.WriteLine(n2);
Console.ReadLine();
/*int temp = n1;
n1 = n2;
n2 = temp;*/
/*n1=n1 - n2; //-10 20
n2 = n1 + n2; //-10 10
n1 = n2 - n1; //20 10*/
}
/// <summary>
/// 交换两个数
/// </summary>
/// <param name="n"></param>
/// <param name="m"></param>
public static void Swap(ref int n,ref int m)
{
int temp = n;
n = m;
m = temp;
}
}
}
9.3 params可变参数
将实参列表中跟可变参数数组类型一致的元素都当做数组的元素去处理
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace CSharp_params
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//int[] ints = { 1, 2, 3 };
Test("张三", 1, 2, 3 , 88 , 100,110);
Console.ReadLine();
}
public static void Test(string name, int id,params int[] score )
{
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < score.Length; i++)
{
sum += score[i];
}
Console.WriteLine("{0}这次考试的总成绩是{1},学号是{2}",name,sum,id);
}
}
}
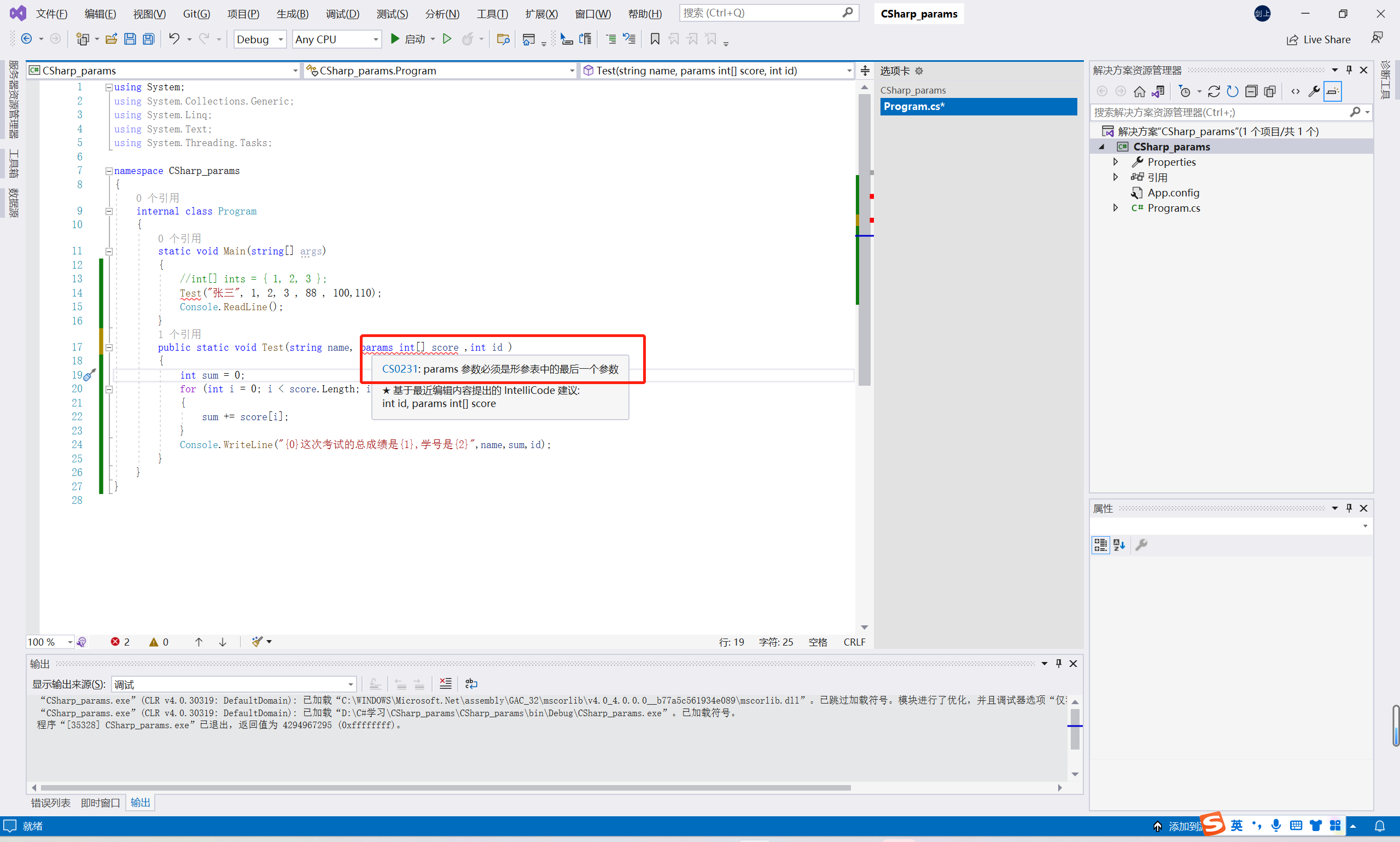
注意:params参数必须是形参列表中的最后一个参数,并且一个参数列表中只能存在一个可变参数
十、文件操作的综合练习
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Text.RegularExpressions;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Text
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string path = @"E:\test.txt";
//ReadAllTextGrid(path);
/*string s = ReadTextGridLine(path);
Console.WriteLine(s);
Console.ReadLine();*/
//ReplaceTextGridContents(path);
ReplaceFileContent(path, "I am totally thrilled to", "自在飞花轻似梦,无边丝雨细如愁");
Console.WriteLine("替换成功");
Console.ReadLine();
//以文本形式写入内容到指定文件(此方法会覆盖写入文件)
/*File.WriteAllText(path,"自在飞花轻似梦");
Console.WriteLine("写入成功");
Console.ReadLine();*/
//追加内容,不会改变原文件内容
/*File.AppendAllText(path,"无边丝雨细如愁");
Console.WriteLine("追加成功");
Console.ReadLine();*/
}
/// <summary>
/// 读取所有的TextGrid文件内容
/// </summary>
/// <param name="path">传入需要读取文件的路径</param>
public static void ReadAllTextGrid(string path)
{
//判断是否存在需要读取的文件,如果不存在则创建一个并写入内容
try
{
if (!File.Exists(path))
{
// 创建一个文件并写入内容
using (StreamWriter sw = File.CreateText(path))
{
sw.WriteLine("自在飞花轻似梦,无边丝雨细如愁");
}
}
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine("创建失败 {0}", e.ToString());
}
/*byte[] contents = File.ReadAllBytes(path);
//将字节数组中的每一个元素都要按照指定的编码格式解码成字符串
//Default:ANSI
//string str = Encoding.Default.GetString(b); 出现乱码则说明不是使用ANSI编码,需要查看文件的编码格式
string str = Encoding.GetEncoding("UTF-8").GetString(contents);
Console.WriteLine(str);
Console.ReadLine();*/
// 读取所有文件内容
using (StreamReader sr = File.OpenText(path))
{
string s;
while ((s = sr.ReadToEnd()) != null)
{
Console.WriteLine(s);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 读取包含指定内容的行
/// </summary>
/// <param name="path">传入需要读取文件的路径</param>
/// <returns>返回包含指定内容的行</returns>
public static string ReadTextGridLine(string path)
{
string str = "";
var lines = File.ReadLines(path);
while ((lines != null))
{
foreach (var line in lines)
{
//if (line.Contains("I am totally thrilled to"))
if (line.Contains("I am totally thrilled to"))
{
str = line.Trim();
}
}
break;
}
return str;
}
/*public static void ReadTextGridLine(string path)
{
var lines = File.ReadLines(path, Encoding.Default);
foreach (var line in lines)
{
//if (line.Contains("intervals [1]:"))
if (line.Contains("I am totally thrilled to"))
{
Console.WriteLine(line);
}
}
Console.ReadLine();
}*/
/// <summary>
/// 替换指定内容行的内容
/// </summary>
/// <param name="path">传入需要读取文件的路径</param>
public static void ReplaceTextGridContents(string path)
{
string s = ReadTextGridLine(path);
string lineNew = "";
if (s.Contains("I am totally thrilled to"))
{
lineNew = s.Replace("I am totally thrilled to", "自在飞花轻似梦,无边丝雨细如愁");
Console.WriteLine("指定的内容已替换为:{0}",lineNew);
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("文件中没有您需要替换的内容");
Console.ReadKey();
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
/// <summary>
/// Regex.Replace(String, String, String)
/// 查找替换文件内容
/// </summary>
/// <param name="filePath">文件路径</param>
/// <param name="searchText">查找内容</param>
/// <param name="replaceText">替换为什么</param>
public static void ReplaceFileContent(string filePath, string searchText, string replaceText)
{
StreamReader reader = new StreamReader(filePath);
string content = reader.ReadToEnd();
reader.Close();
content = Regex.Replace(content, searchText, replaceText);
StreamWriter writer = new StreamWriter(filePath);
writer.Write(content);
writer.Close();
}
}
}