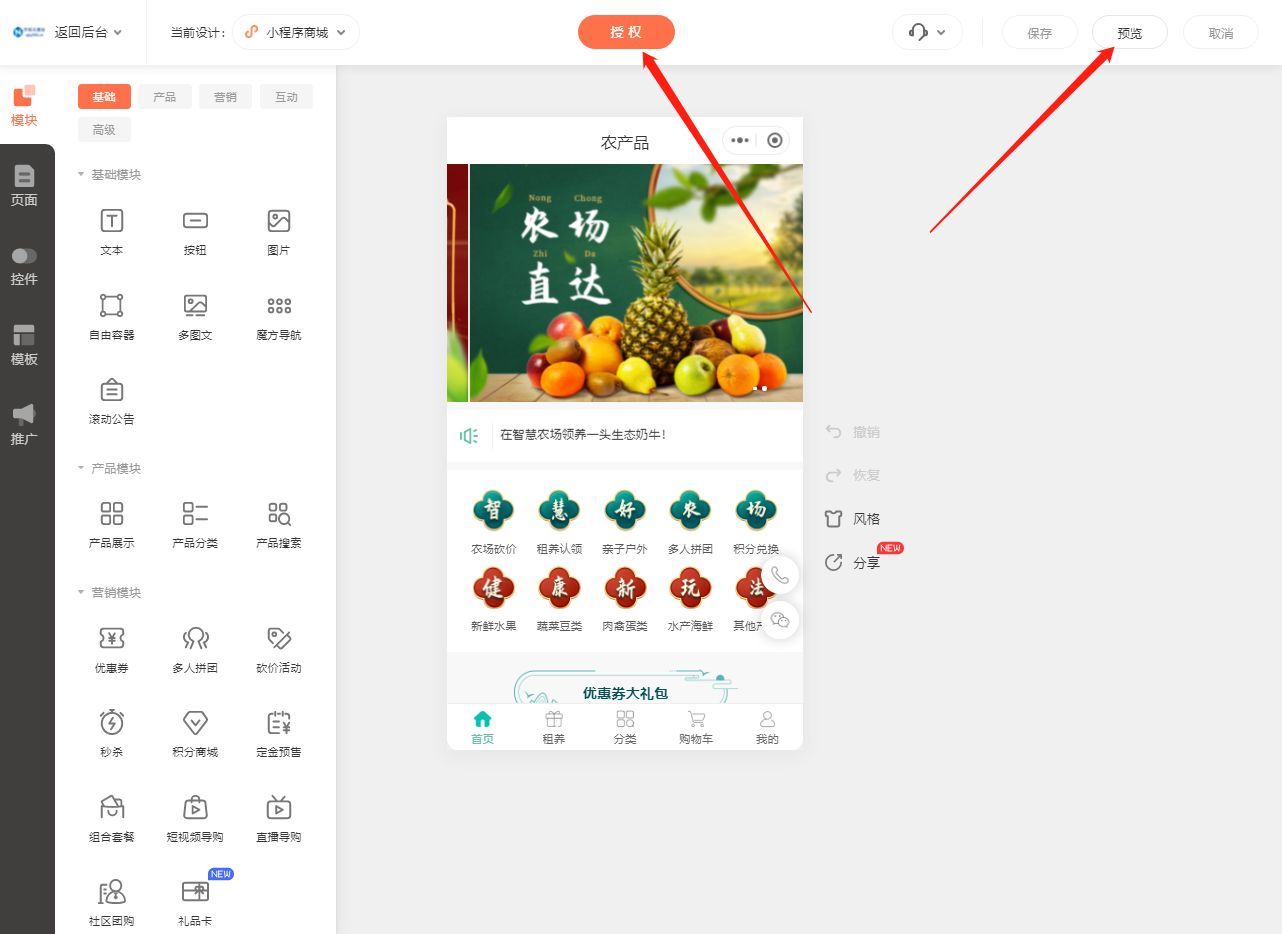
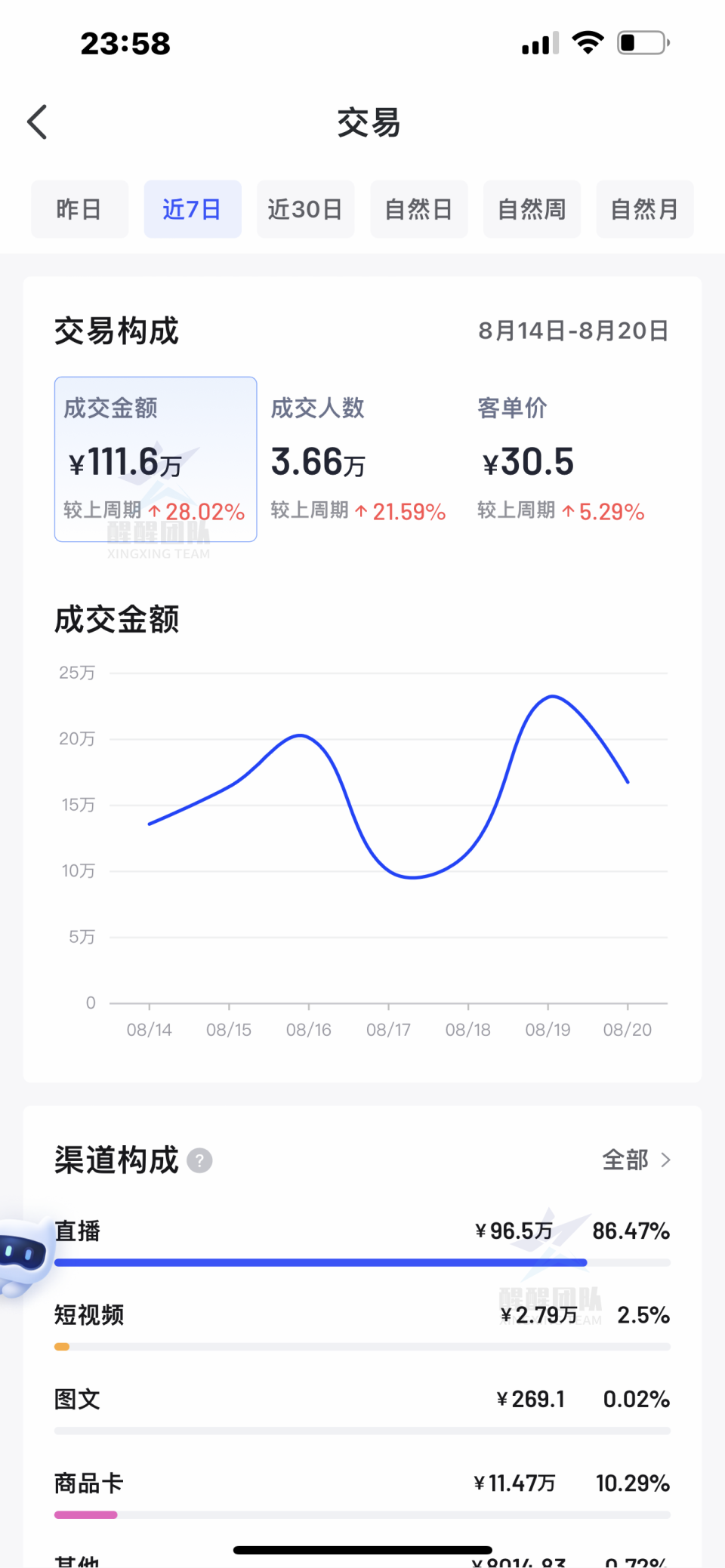
语义分割是对图像的每个像素分类
全卷积网络采用卷积神经网络实现从图像像素到像素类别的转换,全卷积网络将中间层特征的高和宽转换回输入图像的尺寸(引入转置卷积实现的)。
最终的类别预测与输入图像在像素上一一对应。
全卷积网络模型模型框架
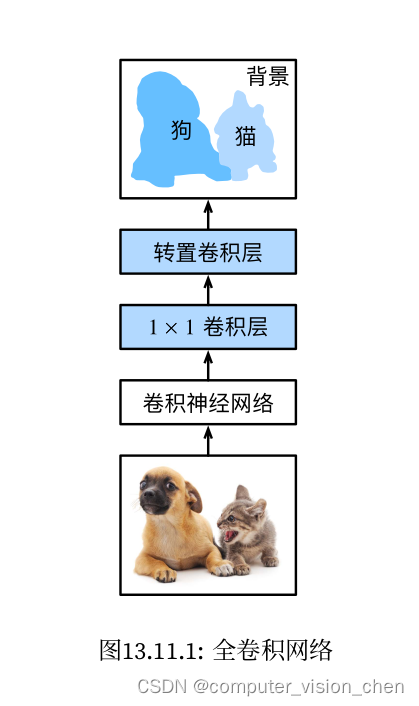
- 使用卷积神经网络提取图像特征。
- 1x1卷积层将通道数转换为类别数。
- 转置卷积层将特征图的高和宽转换为输入图像的大小。使最终模型的输入和输出高和宽相同。
- 最终输出通道包含了该空间位置像素的类别预测。
主代码
我的torch和torchvision版本
import torch
torch.__version__
‘1.7.1+cu110’
import torchvision
torchvision.__version__
‘0.8.2+cu110’
%matplotlib inline
import torch
import torchvision
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import functional as F
from d2l import torch as d2l
from tools import train_tool,data_tool
import time
'''
用ImageNet数据集上预训练的ResNet-18模型来提取图像特征,并将该网络记为pretrained_net。
ResNet-18模型的最后几层包括全局平均汇聚层和全连接层,全卷积网络中不需要它们。
'''
pretrained_net = torchvision.models.resnet18(pretrained=True)
# 输出最后3层
list(pretrained_net.children())[-3:]
输出:
[Sequential(
(0): BasicBlock(
(conv1): Conv2d(256, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(512, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(relu): ReLU(inplace=True)
(conv2): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm2d(512, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(downsample): Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(256, 512, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(2, 2), bias=False)
(1): BatchNorm2d(512, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
)
)
(1): BasicBlock(
(conv1): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(512, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(relu): ReLU(inplace=True)
(conv2): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm2d(512, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
)
),
AdaptiveAvgPool2d(output_size=(1, 1)),
Linear(in_features=512, out_features=1000, bias=True)]
# 创建全卷积网络Net,它复制ResNet18中的预训练层,去掉最后的两层:分别是全局平均汇聚层和全连接层
net = nn.Sequential(*list(pretrained_net.children())[:-2])
# 测试预训练模型的输出shape
X = torch.rand(size=(1,3,320,480))
net(X).shape # 变成了通道为512,shape为(10,18),h,w缩小到原来的1/32
'''为模型添加:1x1卷积层 和 全卷积层'''
num_classes=21
# 使用1x1卷积层,将输出通道转换为该数据集的类别数21
net.add_module('1x1_conv',nn.Conv2d(512,num_classes,kernel_size=1))
# 输入和输出通道不改变,但要把输出结果的h,w变回原始尺寸。
'''
输入:(batch_size,num_classes,10,18)
计算过程:
输出矩阵的高 = (输入的高-1) x 高方向的步长 - 2 x 高方向的填充 + 卷积核的高
=(10-1)x32 - 2x16 + 64
= 320
输出矩阵的高 = 480
成功将卷积提取的宽高减少到1/32的特征还原回了输入的尺寸
'''
net.add_module('transpose_conv',nn.ConvTranspose2d(num_classes,num_classes,kernel_size=64,padding=16,stride=32))
'''初始化转置卷积层,用双线性插值进行上采样放大图像'''
def bilinear_kernel(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size):
factor = (kernel_size + 1) // 2
if kernel_size % 2 == 1:
center = factor - 1
else:
center = factor - 0.5
og = (torch.arange(kernel_size).reshape(-1, 1),
torch.arange(kernel_size).reshape(1, -1))
filt = (1 - torch.abs(og[0] - center) / factor) * \
(1 - torch.abs(og[1] - center) / factor)
weight = torch.zeros((in_channels, out_channels,kernel_size, kernel_size))
weight[range(in_channels), range(out_channels), :, :] = filt
return weight
# 构建一个将输入的高和宽分别放大两倍的转置卷积层,并将该卷积核用bilinear_kernal函数初始化
conv_trans = nn.ConvTranspose2d(3, 3, kernel_size=4, padding=1, stride=2,bias=False)
'''
卷积层的参数是双线性插值的权重。
上面只是让转置卷积后的输出形状放大,不能保证图片内容不变。
转置矩阵的值使用双线性插值的权重,这样就可以用于将图片放大,不打乱图片的排布
'''
conv_trans.weight.data.copy_(bilinear_kernel(3, 3, 4)); # 分号是防止它输出
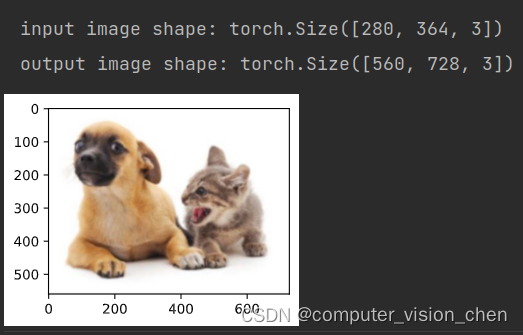
# 读取图像,展示上采样结果
img = torchvision.transforms.ToTensor()(d2l.Image.open('../data/images/cat_dog.jpg'))
X = img.unsqueeze(0)
Y = conv_trans(X)
out_img = Y[0].permute(1, 2, 0).detach()
d2l.set_figsize()
print('input image shape:', img.permute(1, 2, 0).shape)
d2l.plt.imshow(img.permute(1, 2, 0));
print('output image shape:', out_img.shape)
d2l.plt.imshow(out_img);
# 用双线性插值上采样的参数 初始化 模型转置卷积层的参数
W = bilinear_kernel(num_classes, num_classes, 64)
net.transpose_conv.weight.data.copy_(W);
batch_size, crop_size = 32, (320, 480)
train_iter, test_iter = data_tool.load_data_voc(batch_size, crop_size)
# 用通道的索引表示类别,该数据集共21个标签,那么就用21个通道
def loss(inputs, targets):
'''
交叉熵计算之后大概变成了(样本,h=21维的通道,h,w)
第一个mean(1):表示按照类别维度求和取平均值,求出这21个类别的平均损失
第二个mean(1):表示按照样本求平均值,在类别平均损失基础上,对每个样本求和取平均值
得到每个样本的每个类别的平均损失
'''
return F.cross_entropy(inputs, targets, reduction='none').mean(1).mean(1)
num_epochs, lr, wd, devices = 5, 0.001, 1e-3, d2l.try_all_gpus()
trainer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(),lr=lr,weight_decay=wd)
'''开始计时'''
start_time = time.time()
# 开始训练
train_tool.train_ch13(net, train_iter, test_iter, loss, trainer, num_epochs, devices)
# d2l.train_ch13(net, train_iter, test_iter, loss, trainer, num_epochs, devices)
'''计时结束'''
end_time = time.time()
run_time = end_time - start_time
# 将输出的秒数保留两位小数
if int(run_time)<60:
print(f'{round(run_time,2)}s')
else:
print(f'{round(run_time/60,2)}minutes')
工具代码
放在tools目录下:
data_tool.py
import torch
import torchvision
from d2l import torch as d2l
import os
VOC_COLORMAP = [[0, 0, 0], [128, 0, 0], [0, 128, 0], [128, 128, 0],[0, 0, 128], [128, 0, 128], [0, 128, 128], [128, 128, 128],
[64, 0, 0], [192, 0, 0], [64, 128, 0], [192, 128, 0],
[64, 0, 128], [192, 0, 128], [64, 128, 128], [192, 128, 128],
[0, 64, 0], [128, 64, 0], [0, 192, 0], [128, 192, 0],
[0, 64, 128]]
#@save
VOC_CLASSES = ['background', 'aeroplane', 'bicycle', 'bird', 'boat',
'bottle', 'bus', 'car', 'cat', 'chair', 'cow',
'diningtable', 'dog', 'horse', 'motorbike', 'person',
'potted plant', 'sheep', 'sofa', 'train', 'tv/monitor']
'''
筒装法得到一个列表
索引:3维RGB值转换的一维索引值 colormap[0] * 256 + colormap[1]) * 256 + colormap[2]
值:标签索引 0-20
'''
def voc_colormap2label():
"""
标签颜色 和 标签类别长度都是21
计算3维RGB值对应的一维索引。用的是筒装法(索引是3维RGB转成一维所计算的值,这21个像素对应的值是标签的索引 0-20),
"""
colormap2label = torch.zeros(256 ** 3, dtype=torch.long)
for i, colormap in enumerate(VOC_COLORMAP):
# RGB值与一维索引相对应
colormap2label[(colormap[0] * 256 + colormap[1]) * 256 + colormap[2]] = i
return colormap2label
def voc_label_indices(colormap, colormap2label):
"""将VOC标签中的RGB值映射到它们的类别索引"""
colormap = colormap.permute(1, 2, 0).numpy().astype('int32')
# 输入rgb值,计算3维RGB值对应的一维索引
idx = ((colormap[:, :, 0] * 256 + colormap[:, :, 1]) * 256 + colormap[:, :, 2])
# 访问列表得到像素标签对应的标签索引
return colormap2label[idx]
'''
预处理数据:之前是缩放图像使其符合模型的输入形状。然而在语义分割中,这样做还需要再映射回原始输入尺寸,这样做对语义分割来说不好。
具体的方法是使用图像增广中的随机裁减。要裁减输入图像和标签相同的区域。
'''
def voc_rand_crop(feature,label,height,width):
# 随机裁减特征图像和标签图像
rect = torchvision.transforms.RandomCrop.get_params(
feature,(height,width)
)
feature = torchvision.transforms.functional.crop(feature,*rect)
label = torchvision.transforms.functional.crop(label,*rect)
return feature,label
'''自定义语义分割数据集类'''
class VOCSegDataset(torch.utils.data.Dataset):
def __init__(self,is_train,crop_size,voc_dir):
self.transform = torchvision.transforms.Normalize(
mean=[0.485,0.456,0.406],std=[0.229,0.224,0.225])
self.crop_size = crop_size
# 得到列表形式的输入图片和标签图片
features,labels = read_voc_images(voc_dir,is_train=is_train)
# 过滤掉图像尺寸小于随机裁减所指定的输出尺寸,然后对输入图片进行归一化
self.features = [self.normalize_image(feature)
for feature in self.filter(features)]
self.labels = self.filter(labels)
# 用筒装法 计算3维RGB值对应的一维索引
self.colormap2label = voc_colormap2label()
print('read ' + str(len(self.features)) + ' examples')
# 把图像标准化的函数
def normalize_image(self,img):
return self.transform(img.float() / 255)
# 过滤函数:将图像尺寸小于随机裁减所指定的输出尺寸的图像过滤掉
def filter(self,imgs): # img.shape[0]应该是批次
return [img for img in imgs if (
img.shape[1]>=self.crop_size[0] and
img.shape[2]>=self.crop_size[1]
)]
'''
可以让对象通过索引来访问元素如:
vsd = VOCSegDataset()
vsd[0]
'''
def __getitem__(self, idx):
# 返回idx索引下的裁减后的feature,label
feature,label = voc_rand_crop(self.features[idx],self.labels[idx], *self.crop_size)
return (feature,voc_label_indices(label,self.colormap2label))
# 可以通过Len得到对象的长度
def __len__(self):
return len(self.features)
'''
ImageSets/Segmentation路径:用于训练和测试样本的文本文件
JPEGImages: 图像样本
SegmentationClass: 标签,标签也是图像格式,其尺寸和它所标注的输入图像的尺寸相同。颜色相同的像素属于同一个语义类别
'''
def read_voc_images(voc_dir,is_train=True):
'''读取 voc_dir/ImageSets/Segmentation/train.txt或val.txt'''
txt_fname = os.path.join(voc_dir,'ImageSets','Segmentation',
'train.txt' if is_train else 'val.txt')
# mode = torchvision.io.image.ImageReadMode.RGB
with open(txt_fname,'r') as f:
# split()方法是将内容按空格分割为一个列表 images
images = f.read().split()
features,labels = [],[]
for i,fname in enumerate(images):
# 把图像样本放到features中
features.append(torchvision.io.read_image(os.path.join(voc_dir,'JPEGImages',f'{fname}.jpg')))
# 读取标签,加载到labels中,mode是torchvision.io.image.ImageReadMode.RGB
labels.append(torchvision.transforms.ToTensor()(d2l.Image.open(
os.path.join(voc_dir,'SegmentationClass',f'{fname}.png')).convert('RGB')))
return features, labels
'''整合如上的所有函数,定义一个函数加载并读取语义分割数据集'''
def load_data_voc(batch_size,crop_size):
'''返回训练数据集dataloader 和 测试数据集dataloader'''
# 下载数据并返回文件目录
voc_dir = d2l.download_extract('voc2012',os.path.join('VOCdevkit', 'VOC2012'))
num_workers = d2l.get_dataloader_workers()
train_iter = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
VOCSegDataset(True,crop_size,voc_dir),batch_size,
shuffle=True,drop_last = True,num_workers=num_workers
)
test_iter = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
VOCSegDataset(False,crop_size,voc_dir),batch_size,
shuffle=True,drop_last = True,num_workers=num_workers
)
return train_iter,test_iter
train_tool.py
from torch import nn
from d2l import torch as d2l
import torch
def train_batch_ch13(net, X, y, loss, trainer, devices):
"""Train for a minibatch with mutiple GPUs (defined in Chapter 13).
Defined in :numref:`sec_image_augmentation`"""
if isinstance(X, list):
# Required for BERT fine-tuning (to be covered later)
X = [x.to(devices[0]) for x in X]
else:
X = X.to(devices[0])
y = y.to(devices[0])
net.train()
trainer.zero_grad()
pred = net(X)
l = loss(pred, y)
l.sum().backward()
trainer.step()
train_loss_sum = l.sum()
train_acc_sum = d2l.accuracy(pred, y)
return train_loss_sum, train_acc_sum
def train_ch13(net, train_iter, test_iter, loss, trainer, num_epochs,
devices=d2l.try_all_gpus()):
"""Train a model with mutiple GPUs (defined in Chapter 13).
Defined in :numref:`sec_image_augmentation`"""
timer, num_batches = d2l.Timer(), len(train_iter)
animator = d2l.Animator(xlabel='epoch', xlim=[1, num_epochs], ylim=[0, 1],
legend=['train loss', 'train acc', 'test acc'])
net = nn.DataParallel(net, device_ids=devices).to(devices[0])
'''改动'''
best_test_acc = 0
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
# Sum of training loss, sum of training accuracy, no. of examples,
# no. of predictions
metric = d2l.Accumulator(4)
for i, (features, labels) in enumerate(train_iter):
timer.start()
l, acc = train_batch_ch13(
net, features, labels, loss, trainer, devices)
metric.add(l, acc, labels.shape[0], labels.numel())
timer.stop()
if (i + 1) % (num_batches // 5) == 0 or i == num_batches - 1:
animator.add(epoch + (i + 1) / num_batches,
(metric[0] / metric[2], metric[1] / metric[3],
None))
test_acc = d2l.evaluate_accuracy_gpu(net, test_iter)
# 此处保存的是最高准确率的一轮
if test_acc > best_test_acc:
best_test_acc = test_acc
# 保存准确率最高的一轮训练参数
torch.save(net.state_dict(), 'best_segment_net_weights.pth')
animator.add(epoch + 1, (None, None, test_acc))
print(f'loss {metric[0] / metric[2]:.3f}, train acc '
f'{metric[1] / metric[3]:.3f}, test acc {test_acc:.3f}, best test acc {best_test_acc:.3f}')
print(f'{metric[2] * num_epochs / timer.sum():.1f} examples/sec on '
f'{str(devices)}')