K近邻法算法思想
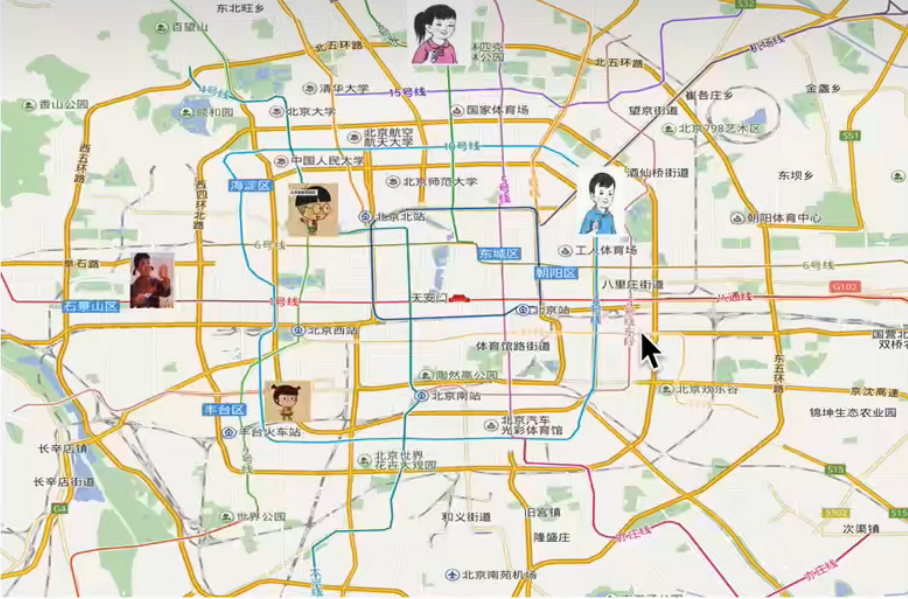
K近邻法(K-Nearest Neighbor,KNN)是一种基本的分类和回归方法,是监督学习方法里的一种常用方法。K近邻算法用一句通俗的古语来说就是:“物以类聚,人以群分”。有人说看一个人什么样,看他身边的朋友什么样就知道了。在机器学习中你要看一个实例的类别,你就可以看它附近都是什么类别。你要看你自己在北京哪个区,看理你最近的几个人(可以看K个人)是哪个区的,那么大概率你也是这个区的。
距离度量
欧式距离
小初高学的空间中两点距离公式欧式距离。
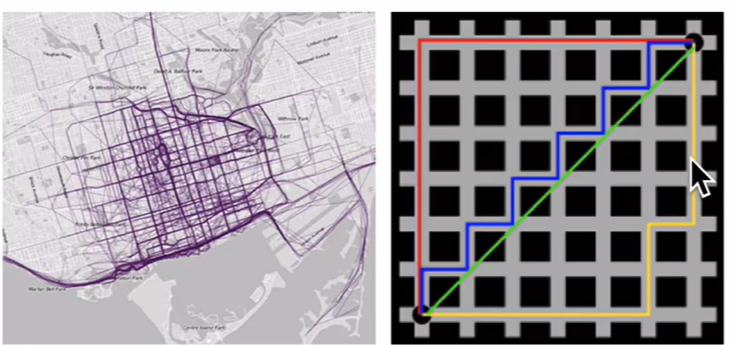
曼哈顿距离
在曼哈顿街区从一个十字路口开车到另一个十字路口,驾驶距离显然不是两点间直线距离。这个驾驶距离就是曼哈顿距离,曼哈顿距离也被称为城市街区距离。
切比雪夫距离
闵可夫斯基距离
标准化欧式距离
余弦距离
汉明距离
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
连续特征和离散特征的距离计算
导入数据
iris_data = load_iris()
iris_data.data[0:5, :]
array([[5.1, 3.5, 1.4, 0.2],
[4.9, 3. , 1.4, 0.2],
[4.7, 3.2, 1.3, 0.2],
[4.6, 3.1, 1.5, 0.2],
[5. , 3.6, 1.4, 0.2]])
# 特征值名称
iris_data.feature_names
['sepal length (cm)',
'sepal width (cm)',
'petal length (cm)',
'petal width (cm)']
# 分类标签
print(iris_data.target_names)
pd.DataFrame(iris_data.target).value_counts()
['setosa' 'versicolor' 'virginica']
0 50
1 50
2 50
dtype: int64
简单统计分析
X = pd.DataFrame(iris_data.data, columns=iris_data.feature_names)
y = iris_data.target
X.describe()
| sepal length (cm) | sepal width (cm) | petal length (cm) | petal width (cm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| count | 150.000000 | 150.000000 | 150.000000 | 150.000000 |
| mean | 5.843333 | 3.057333 | 3.758000 | 1.199333 |
| std | 0.828066 | 0.435866 | 1.765298 | 0.762238 |
| min | 4.300000 | 2.000000 | 1.000000 | 0.100000 |
| 25% | 5.100000 | 2.800000 | 1.600000 | 0.300000 |
| 50% | 5.800000 | 3.000000 | 4.350000 | 1.300000 |
| 75% | 6.400000 | 3.300000 | 5.100000 | 1.800000 |
| max | 7.900000 | 4.400000 | 6.900000 | 2.500000 |
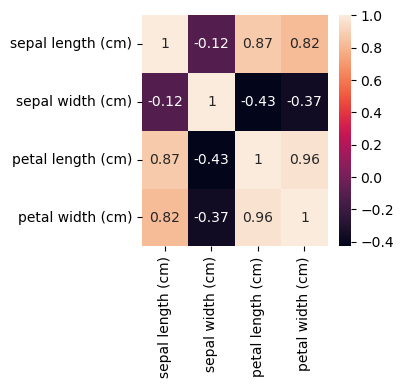
plt.figure(figsize=(3,3))
sns.heatmap(X.corr(), annot=True)
<Axes: >
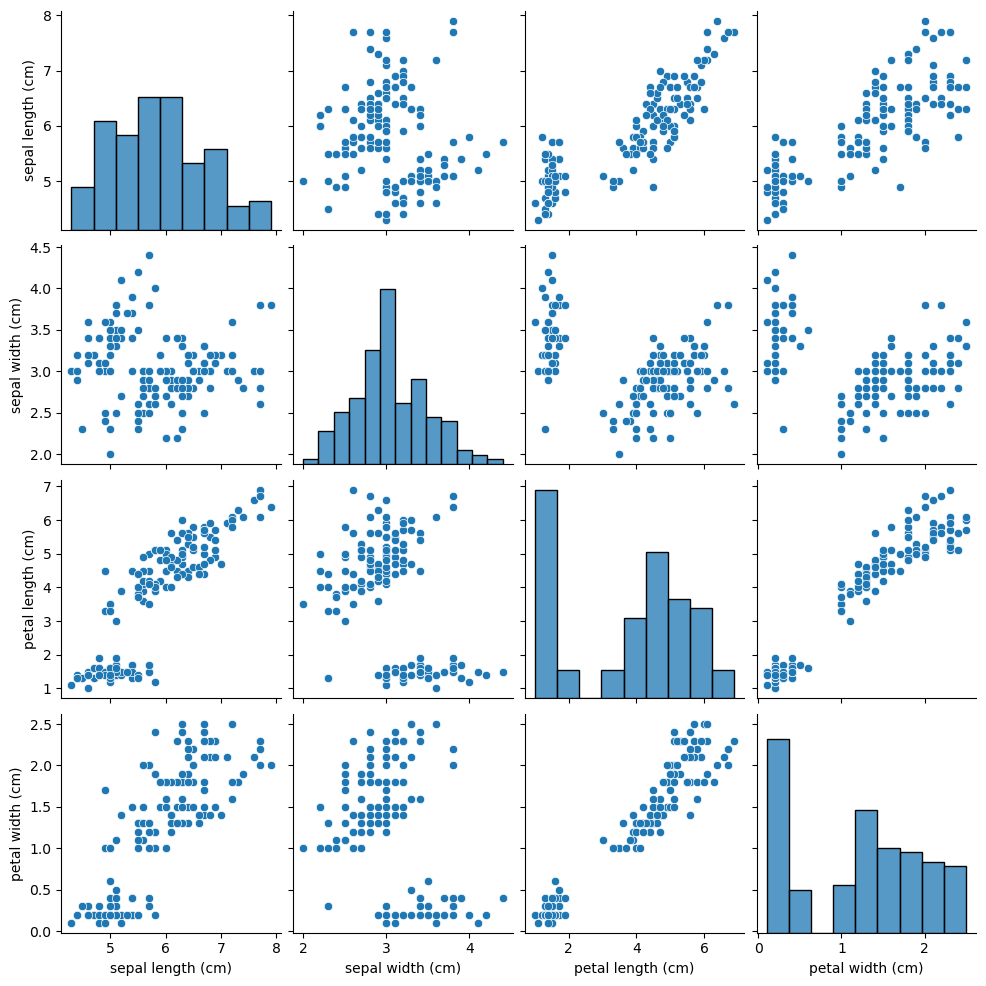
plt.figure(figsize=(4,4))
sns.pairplot(X)
<seaborn.axisgrid.PairGrid at 0x16b89fbf640>
<Figure size 400x400 with 0 Axes>
划分数据集
x_train, x_test , y_train,y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=.2 , random_state=47)
x_train.shape, y_train.shape, x_test.shape, y_test.shape
((120, 4), (120,), (30, 4), (30,))
特征工程
归一化/标准化
transfer = StandardScaler()
x_train = transfer.fit_transform(x_train)
x_test = transfer.transform(x_test)
x_train.shape, x_test.shape
((120, 4), (30, 4))
模型训练
knn_model = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=5)
knn_model.fit(x_train, y_train)
KNeighborsClassifier()In a Jupyter environment, please rerun this cell to show the HTML representation or trust the notebook.
On GitHub, the HTML representation is unable to render, please try loading this page with nbviewer.org.
KNeighborsClassifier()
模型评估
y_pred = knn_model.predict(x_test)
y_pred == y_test
array([ True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True,
True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True,
True, True, True, True, True, False, True, True, True,
True, True, True])
knn_model.score(x_train, y_train)
0.9666666666666667
knn_model.score(x_test, y_test)
0.9666666666666667







![java八股文面试[多线程]——AQS 详细介绍](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/b93de999f282b24932796045b9ef42fd.png)