Metrics Server简介
- Metrics Server 是 Kubernetes 集群核心监控数据的聚合器(定时从Kubelet的Summary API 采集指标信息),可以通过 Metrics API 的形式获取 Metrics 数据,不过仅仅是获取指标的最新值,数据不做存储,且不负责将指标转发到第三方目标。Metrics Server 还可以与 Kubectl 工具结合使用,提供 Kubectl Top 命令来展示集群中的指标数据
- 通俗地说,它存储了集群中各节点的监控数据,并且提供了API以供分析和使用。Metrics-Server作为一个 Deployment对象默认部署在Kubernetes集群中。不过准确地说,它是Deployment,Service,ClusterRole,ClusterRoleBinding,APIService,RoleBinding等资源对象的综合体
- 因为
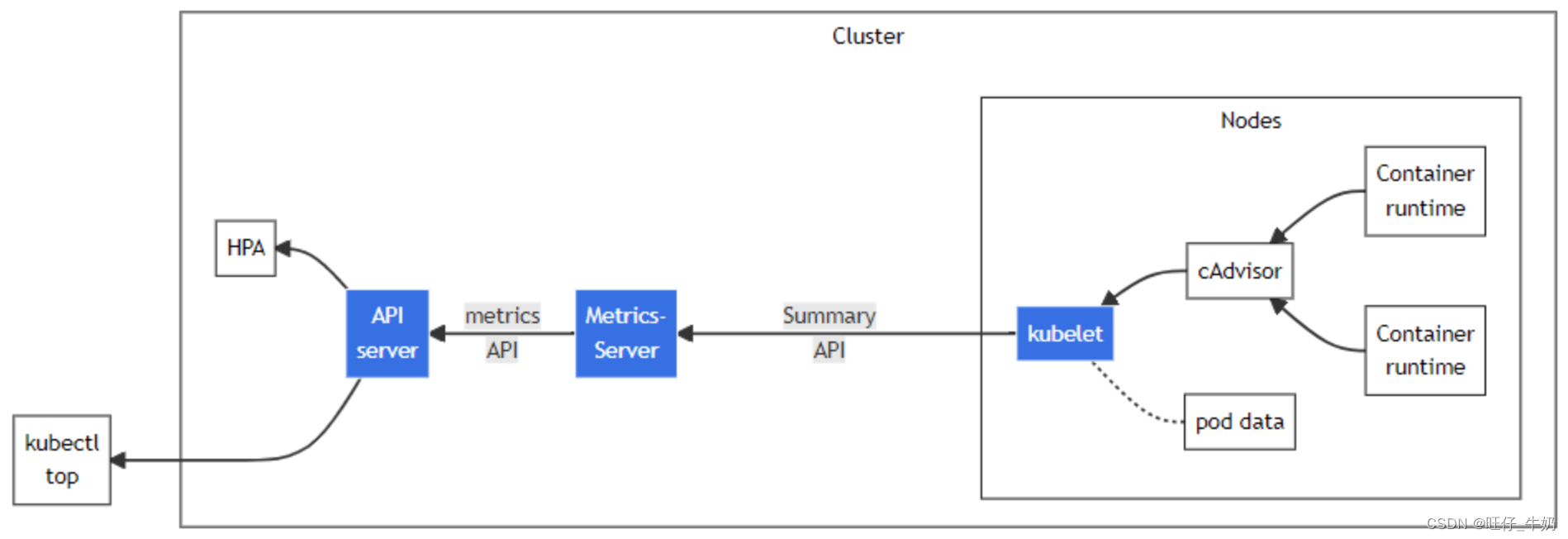
存放在内存中,因此监控数据是没有持久化的,可以通过第三方存储来拓展 - 看下Metrics-Server的架构:从 Kubelet、cAdvisor 等获取度量数据,再由metrics-server提供给 Dashboard、HPA 控制器等使用。本质上metrics-server相当于做了一次数据的转换,把cadvisor格式的数据转换成了kubernetes的api的json格式。由此我们不难猜测,metrics-server的代码中必然存在这种先从metric中获取接口中的所有信息,再解析出其中的数据的过程。我们给metric-server发送请求时,metrics-server中已经定期从中cadvisor获取好数据了,当请求发过来时直接返回缓存中的数据
Metrics Server部署要求
- 在安装 Metrics Server 之前需要先在 kube-apiserver 中
开启 API Aggregator。开启方式参考链接:https://kubernetes.io/zh-cn/docs/tasks/extend-kubernetes/configure-aggregation-layer/
# 通过以下 `kube-apiserver` 标志启用聚合层。 你的服务提供商可能已经为你完成了这些工作:
--requestheader-client-ca-file=<path to aggregator CA cert>
--requestheader-allowed-names=front-proxy-client
--requestheader-extra-headers-prefix=X-Remote-Extra-
--requestheader-group-headers=X-Remote-Group
--requestheader-username-headers=X-Remote-User
--proxy-client-cert-file=<path to aggregator proxy cert>
--proxy-client-key-file=<path to aggregator proxy key>
- 节点必须开启Webhook认证,参考链接:https://kubernetes.io/zh-cn/docs/reference/access-authn-authz/kubelet-authn-authz/
# kubelet webhook 部分配置
authentication:
anonymous:
enabled: false
webhook:
cacheTTL: 2m0s
enabled: true
x509:
clientCAFile: /etc/kubernetes/pki/kube-apiserver-ca.pem
authorization:
mode: Webhook
webhook:
cacheAuthorizedTTL: 5m0s
cacheUnauthorizedTTL: 30s
-
kubelet的证书必须要由签发K8S证书的CA机构签发(如果不是同一个CA机构,metrics-server需要配置:
--kubelet-insecure-tls) -
Container runtime必须实现了container metrics RPCs (or have cAdvisor support)
-
控制平面节点需要访问 Metrics Server 的 pod IP 和端口 10250(如果启用了 hostNetwork,则需要访问节点 IP 和自定义端口) -
所有节点上的 Metrics Server 到 Kubelet,Metrics 服务器需要到达节点地址和 Kubelet 端口。地址和端口在 Kubelet 中配置并作为 Node 对象的一部分发布。Addresses:
.status.addresses,port:``.status.daemonEndpoints.kubeletEndpoint.port (default 10250)。Metrics Server 将根据提供的列表选择第一个节点地址:kubelet-preferred-address-types,defaultInternalIP,ExternalIP,Hostname` in manifests
Metrics Server兼容性
| Metrics Server | Metrics API group/version | Supported Kubernetes version |
|---|---|---|
| 0.6.x | metrics.k8s.io/v1beta1 | 1.19+ |
| 0.5.x | metrics.k8s.io/v1beta1 | *1.8+ |
| 0.4.x | metrics.k8s.io/v1beta1 | *1.8+ |
| 0.3.x | metrics.k8s.io/v1beta1 | 1.8-1.21 |
Kubernetes versions lower than v1.16 require passing the --authorization-always-allow-paths=/livez,/readyz command line flag
Metrics Server部署
metrics-server配置修改,yaml下载链接:https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/metrics-server/releases/
# 编辑修改 metrics-server 的启动参数:
# --kubelet-insecure-tls 跳过 TLS 认证,否则会出现 x509 的认证问题,用于测试环境。
# --kubelet-preferred-address-types=InternalIP 使用 Node IP 进行通信。
# --kubelet-preferred-address-types=InternalIP metrics-server默认使用的是hostname,但是coredns中并没有三台物理机器的hostname和IP地址的关系,需要改为使用主机IP地址
# 优先使用 InternalIP 来访问 kubelet,这样可以避免节点名称没有 DNS 解析记录时,通过节点名称调用节点 kubelet API 失败的情况(未配置时默认的情况)
# type类型可以在节点状态可见
status:
addresses:
- address: 192.168.0.11
type: InternalIP
- address: k8s-master-1
type: Hostname
# metrics server修改参数
- args:
- --cert-dir=/tmp
- --secure-port=4443
- --kubelet-preferred-address-types=InternalIP # 修改这行,默认是InternalIP,ExternalIP,Hostname,kubelet的默认IP地址
- --kubelet-use-node-status-port # kubelet暴露的metrics port
- --metric-resolution=15s # metrics 默认抓取时间
- --kubelet-insecure-tls # 增加这行
# metrics server可提供参数如下:
[root@k8s-master-1 ~]# ctr -n k8s.io run -t --rm registry.k8s.io/metrics-server/metrics-server:v0.6.4 metrics-server
Error: error creating self-signed certificates: mkdir apiserver.local.config: permission denied
Usage:
[flags]
Metrics server flags:
--kubeconfig string
The path to the kubeconfig used to connect to the Kubernetes API server and the Kubelets (defaults to in-cluster config)
--metric-resolution duration
The resolution at which metrics-server will retain metrics, must set value at least 10s. (default 1m0s)
--version
Show version
Kubelet client flags:
--deprecated-kubelet-completely-insecure
DEPRECATED: Do not use any encryption, authorization, or authentication when communicating with the Kubelet. This is rarely the right option, since it leaves kubelet communication completely insecure. If you encounter auth errors, make sure you've enabled token webhook auth
on the Kubelet, and if you're in a test cluster with self-signed Kubelet certificates, consider using kubelet-insecure-tls instead.
--kubelet-certificate-authority string
Path to the CA to use to validate the Kubelet's serving certificates.
--kubelet-client-certificate string
Path to a client cert file for TLS.
--kubelet-client-key string
Path to a client key file for TLS.
--kubelet-insecure-tls
Do not verify CA of serving certificates presented by Kubelets. For testing purposes only.
--kubelet-port int
The port to use to connect to Kubelets. (default 10250)
--kubelet-preferred-address-types strings
The priority of node address types to use when determining which address to use to connect to a particular node (default [Hostname,InternalDNS,InternalIP,ExternalDNS,ExternalIP])
--kubelet-use-node-status-port
Use the port in the node status. Takes precedence over --kubelet-port flag.
Apiserver secure serving flags:
--bind-address ip
The IP address on which to listen for the --secure-port port. The associated interface(s) must be reachable by the rest of the cluster, and by CLI/web clients. If blank or an unspecified address (0.0.0.0 or ::), all interfaces will be used. (default 0.0.0.0)
--cert-dir string
The directory where the TLS certs are located. If --tls-cert-file and --tls-private-key-file are provided, this flag will be ignored. (default "apiserver.local.config/certificates")
--http2-max-streams-per-connection int
The limit that the server gives to clients for the maximum number of streams in an HTTP/2 connection. Zero means to use golang's default.
--permit-address-sharing
If true, SO_REUSEADDR will be used when binding the port. This allows binding to wildcard IPs like 0.0.0.0 and specific IPs in parallel, and it avoids waiting for the kernel to release sockets in TIME_WAIT state. [default=false]
--permit-port-sharing
If true, SO_REUSEPORT will be used when binding the port, which allows more than one instance to bind on the same address and port. [default=false]
--secure-port int
The port on which to serve HTTPS with authentication and authorization. If 0, don't serve HTTPS at all. (default 443)
--tls-cert-file string
File containing the default x509 Certificate for HTTPS. (CA cert, if any, concatenated after server cert). If HTTPS serving is enabled, and --tls-cert-file and --tls-private-key-file are not provided, a self-signed certificate and key are generated for the public address and
saved to the directory specified by --cert-dir.
--tls-cipher-suites strings
Comma-separated list of cipher suites for the server. If omitted, the default Go cipher suites will be used.
Preferred values: TLS_AES_128_GCM_SHA256, TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384, TLS_CHACHA20_POLY1305_SHA256, TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA, TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256, TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA, TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384,
TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_CHACHA20_POLY1305, TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_CHACHA20_POLY1305_SHA256, TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA, TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256, TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA, TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384, TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_CHACHA20_POLY1305,
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_CHACHA20_POLY1305_SHA256, TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA, TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256, TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA, TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384.
Insecure values: TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256, TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_RC4_128_SHA, TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_3DES_EDE_CBC_SHA, TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256, TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_RC4_128_SHA, TLS_RSA_WITH_3DES_EDE_CBC_SHA, TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256,
TLS_RSA_WITH_RC4_128_SHA.
--tls-min-version string
Minimum TLS version supported. Possible values: VersionTLS10, VersionTLS11, VersionTLS12, VersionTLS13
--tls-private-key-file string
File containing the default x509 private key matching --tls-cert-file.
--tls-sni-cert-key namedCertKey
A pair of x509 certificate and private key file paths, optionally suffixed with a list of domain patterns which are fully qualified domain names, possibly with prefixed wildcard segments. The domain patterns also allow IP addresses, but IPs should only be used if the
apiserver has visibility to the IP address requested by a client. If no domain patterns are provided, the names of the certificate are extracted. Non-wildcard matches trump over wildcard matches, explicit domain patterns trump over extracted names. For multiple
key/certificate pairs, use the --tls-sni-cert-key multiple times. Examples: "example.crt,example.key" or "foo.crt,foo.key:*.foo.com,foo.com". (default [])
Apiserver authentication flags:
--authentication-kubeconfig string
kubeconfig file pointing at the 'core' kubernetes server with enough rights to create tokenreviews.authentication.k8s.io.
--authentication-skip-lookup
If false, the authentication-kubeconfig will be used to lookup missing authentication configuration from the cluster.
--authentication-token-webhook-cache-ttl duration
The duration to cache responses from the webhook token authenticator. (default 10s)
--authentication-tolerate-lookup-failure
If true, failures to look up missing authentication configuration from the cluster are not considered fatal. Note that this can result in authentication that treats all requests as anonymous.
--client-ca-file string
If set, any request presenting a client certificate signed by one of the authorities in the client-ca-file is authenticated with an identity corresponding to the CommonName of the client certificate.
--requestheader-allowed-names strings
List of client certificate common names to allow to provide usernames in headers specified by --requestheader-username-headers. If empty, any client certificate validated by the authorities in --requestheader-client-ca-file is allowed.
--requestheader-client-ca-file string
Root certificate bundle to use to verify client certificates on incoming requests before trusting usernames in headers specified by --requestheader-username-headers. WARNING: generally do not depend on authorization being already done for incoming requests.
--requestheader-extra-headers-prefix strings
List of request header prefixes to inspect. X-Remote-Extra- is suggested. (default [x-remote-extra-])
--requestheader-group-headers strings
List of request headers to inspect for groups. X-Remote-Group is suggested. (default [x-remote-group])
--requestheader-username-headers strings
List of request headers to inspect for usernames. X-Remote-User is common. (default [x-remote-user])
Apiserver authorization flags:
--authorization-always-allow-paths strings
A list of HTTP paths to skip during authorization, i.e. these are authorized without contacting the 'core' kubernetes server. (default [/healthz,/readyz,/livez])
--authorization-kubeconfig string
kubeconfig file pointing at the 'core' kubernetes server with enough rights to create subjectaccessreviews.authorization.k8s.io.
--authorization-webhook-cache-authorized-ttl duration
The duration to cache 'authorized' responses from the webhook authorizer. (default 10s)
--authorization-webhook-cache-unauthorized-ttl duration
The duration to cache 'unauthorized' responses from the webhook authorizer. (default 10s)
Apiserver audit log flags:
--audit-log-batch-buffer-size int
The size of the buffer to store events before batching and writing. Only used in batch mode. (default 10000)
--audit-log-batch-max-size int
The maximum size of a batch. Only used in batch mode. (default 1)
--audit-log-batch-max-wait duration
The amount of time to wait before force writing the batch that hadn't reached the max size. Only used in batch mode.
--audit-log-batch-throttle-burst int
Maximum number of requests sent at the same moment if ThrottleQPS was not utilized before. Only used in batch mode.
--audit-log-batch-throttle-enable
Whether batching throttling is enabled. Only used in batch mode.
--audit-log-batch-throttle-qps float32
Maximum average number of batches per second. Only used in batch mode.
--audit-log-compress
If set, the rotated log files will be compressed using gzip.
--audit-log-format string
Format of saved audits. "legacy" indicates 1-line text format for each event. "json" indicates structured json format. Known formats are legacy,json. (default "json")
--audit-log-maxage int
The maximum number of days to retain old audit log files based on the timestamp encoded in their filename.
--audit-log-maxbackup int
The maximum number of old audit log files to retain. Setting a value of 0 will mean there's no restriction on the number of files.
--audit-log-maxsize int
The maximum size in megabytes of the audit log file before it gets rotated.
--audit-log-mode string
Strategy for sending audit events. Blocking indicates sending events should block server responses. Batch causes the backend to buffer and write events asynchronously. Known modes are batch,blocking,blocking-strict. (default "blocking")
--audit-log-path string
If set, all requests coming to the apiserver will be logged to this file. '-' means standard out.
--audit-log-truncate-enabled
Whether event and batch truncating is enabled.
--audit-log-truncate-max-batch-size int
Maximum size of the batch sent to the underlying backend. Actual serialized size can be several hundreds of bytes greater. If a batch exceeds this limit, it is split into several batches of smaller size. (default 10485760)
--audit-log-truncate-max-event-size int
Maximum size of the audit event sent to the underlying backend. If the size of an event is greater than this number, first request and response are removed, and if this doesn't reduce the size enough, event is discarded. (default 102400)
--audit-log-version string
API group and version used for serializing audit events written to log. (default "audit.k8s.io/v1")
--audit-policy-file string
Path to the file that defines the audit policy configuration.
--audit-webhook-batch-buffer-size int
The size of the buffer to store events before batching and writing. Only used in batch mode. (default 10000)
--audit-webhook-batch-max-size int
The maximum size of a batch. Only used in batch mode. (default 400)
--audit-webhook-batch-max-wait duration
The amount of time to wait before force writing the batch that hadn't reached the max size. Only used in batch mode. (default 30s)
--audit-webhook-batch-throttle-burst int
Maximum number of requests sent at the same moment if ThrottleQPS was not utilized before. Only used in batch mode. (default 15)
--audit-webhook-batch-throttle-enable
Whether batching throttling is enabled. Only used in batch mode. (default true)
--audit-webhook-batch-throttle-qps float32
Maximum average number of batches per second. Only used in batch mode. (default 10)
--audit-webhook-config-file string
Path to a kubeconfig formatted file that defines the audit webhook configuration.
--audit-webhook-initial-backoff duration
The amount of time to wait before retrying the first failed request. (default 10s)
--audit-webhook-mode string
Strategy for sending audit events. Blocking indicates sending events should block server responses. Batch causes the backend to buffer and write events asynchronously. Known modes are batch,blocking,blocking-strict. (default "batch")
--audit-webhook-truncate-enabled
Whether event and batch truncating is enabled.
--audit-webhook-truncate-max-batch-size int
Maximum size of the batch sent to the underlying backend. Actual serialized size can be several hundreds of bytes greater. If a batch exceeds this limit, it is split into several batches of smaller size. (default 10485760)
--audit-webhook-truncate-max-event-size int
Maximum size of the audit event sent to the underlying backend. If the size of an event is greater than this number, first request and response are removed, and if this doesn't reduce the size enough, event is discarded. (default 102400)
--audit-webhook-version string
API group and version used for serializing audit events written to webhook. (default "audit.k8s.io/v1")
Features flags:
--contention-profiling
Enable lock contention profiling, if profiling is enabled
--profiling
Enable profiling via web interface host:port/debug/pprof/ (default true)
Logging flags:
--add_dir_header
If true, adds the file directory to the header of the log messages (DEPRECATED: will be removed in a future release, see https://github.com/kubernetes/enhancements/tree/master/keps/sig-instrumentation/2845-deprecate-klog-specific-flags-in-k8s-components)
--alsologtostderr
log to standard error as well as files (DEPRECATED: will be removed in a future release, see https://github.com/kubernetes/enhancements/tree/master/keps/sig-instrumentation/2845-deprecate-klog-specific-flags-in-k8s-components)
--log-flush-frequency duration
Maximum number of seconds between log flushes (default 5s)
--log_backtrace_at traceLocation
when logging hits line file:N, emit a stack trace (DEPRECATED: will be removed in a future release, see https://github.com/kubernetes/enhancements/tree/master/keps/sig-instrumentation/2845-deprecate-klog-specific-flags-in-k8s-components) (default :0)
--log_dir string
If non-empty, write log files in this directory (DEPRECATED: will be removed in a future release, see https://github.com/kubernetes/enhancements/tree/master/keps/sig-instrumentation/2845-deprecate-klog-specific-flags-in-k8s-components)
--log_file string
If non-empty, use this log file (DEPRECATED: will be removed in a future release, see https://github.com/kubernetes/enhancements/tree/master/keps/sig-instrumentation/2845-deprecate-klog-specific-flags-in-k8s-components)
--log_file_max_size uint
Defines the maximum size a log file can grow to. Unit is megabytes. If the value is 0, the maximum file size is unlimited. (DEPRECATED: will be removed in a future release, see
https://github.com/kubernetes/enhancements/tree/master/keps/sig-instrumentation/2845-deprecate-klog-specific-flags-in-k8s-components) (default 1800)
--logtostderr
log to standard error instead of files (DEPRECATED: will be removed in a future release, see https://github.com/kubernetes/enhancements/tree/master/keps/sig-instrumentation/2845-deprecate-klog-specific-flags-in-k8s-components) (default true)
--one_output
If true, only write logs to their native severity level (vs also writing to each lower severity level) (DEPRECATED: will be removed in a future release, see
https://github.com/kubernetes/enhancements/tree/master/keps/sig-instrumentation/2845-deprecate-klog-specific-flags-in-k8s-components)
--skip_headers
If true, avoid header prefixes in the log messages (DEPRECATED: will be removed in a future release, see https://github.com/kubernetes/enhancements/tree/master/keps/sig-instrumentation/2845-deprecate-klog-specific-flags-in-k8s-components)
--skip_log_headers
If true, avoid headers when opening log files (DEPRECATED: will be removed in a future release, see https://github.com/kubernetes/enhancements/tree/master/keps/sig-instrumentation/2845-deprecate-klog-specific-flags-in-k8s-components)
--stderrthreshold severity
logs at or above this threshold go to stderr (DEPRECATED: will be removed in a future release, see https://github.com/kubernetes/enhancements/tree/master/keps/sig-instrumentation/2845-deprecate-klog-specific-flags-in-k8s-components) (default 2)
-v, --v Level
number for the log level verbosity
--vmodule moduleSpec
comma-separated list of pattern=N settings for file-filtered logging
panic: error creating self-signed certificates: mkdir apiserver.local.config: permission denied
Metrics Server验证
# kubectl top 命令从 metrics-server 获取集群节点基本的指标信息
╰─ kubectl top pods -n devops
NAME CPU(cores) MEMORY(bytes)
monitor-prometheus-node-exporter-d8gr6 1m 13Mi
monitor-prometheus-node-exporter-zln7r 1m 13Mi
nfs-provisioner-nfs-subdir-external-provisioner-8bfdc9f58-86rbc 3m 14Mi
# 查看节点信息
╰─ kubectl top nodes
NAME CPU(cores) CPU% MEMORY(bytes) MEMORY%
k8s-master-1 107m 5% 1867Mi 53%
k8s-node-1 45m 1% 1008Mi 5%
/apis/metrics.k8s.io/v1beta1/nodes 和 apis/metrics.k8s.io/v1beta1/pods 返回的 usage 包含 CPU 和 Memory
# 通过 kube-apiserver 或 kubectl proxy 访问:
https://192.168.0.11:6443/apis/metrics.k8s.io/v1beta1/nodes
https://192.168.0.11:6443/apis/metrics.k8s.io/v1beta1/nodes/<node-name>
https://192.168.0.11:6443/apis/metrics.k8s.io/v1beta1/pods
https://192.168.0.11:6443/apis/metrics.k8s.io/v1beta1/namespace/<namespace-name>/pods/<pod-name>
# 直接使用 kubectl 命令访问:
# 访问节点
╰─ kubectl get --raw /apis/metrics.k8s.io/v1beta1/nodes | jq .
{
"kind": "NodeMetricsList",
"apiVersion": "metrics.k8s.io/v1beta1",
"metadata": {},
"items": [
{
"metadata": {
"name": "k8s-master-1",
"creationTimestamp": "2023-08-30T08:07:21Z",
"labels": {
"beta.kubernetes.io/arch": "arm64",
"beta.kubernetes.io/os": "linux",
"kubernetes.io/arch": "arm64",
"kubernetes.io/hostname": "k8s-master-1",
"kubernetes.io/os": "linux"
}
},
"timestamp": "2023-08-30T08:07:15Z",
"window": "20.046s",
"usage": {
"cpu": "113738401n",
"memory": "1863688Ki"
}
},
{
"metadata": {
"name": "k8s-node-1",
"creationTimestamp": "2023-08-30T08:07:21Z",
"labels": {
"beta.kubernetes.io/arch": "arm64",
"beta.kubernetes.io/os": "linux",
"kubernetes.io/arch": "arm64",
"kubernetes.io/hostname": "k8s-node-1",
"kubernetes.io/os": "linux"
}
},
"timestamp": "2023-08-30T08:07:12Z",
"window": "20.027s",
"usage": {
"cpu": "38448095n",
"memory": "1040124Ki"
}
}
]
}
Metrics Server问题
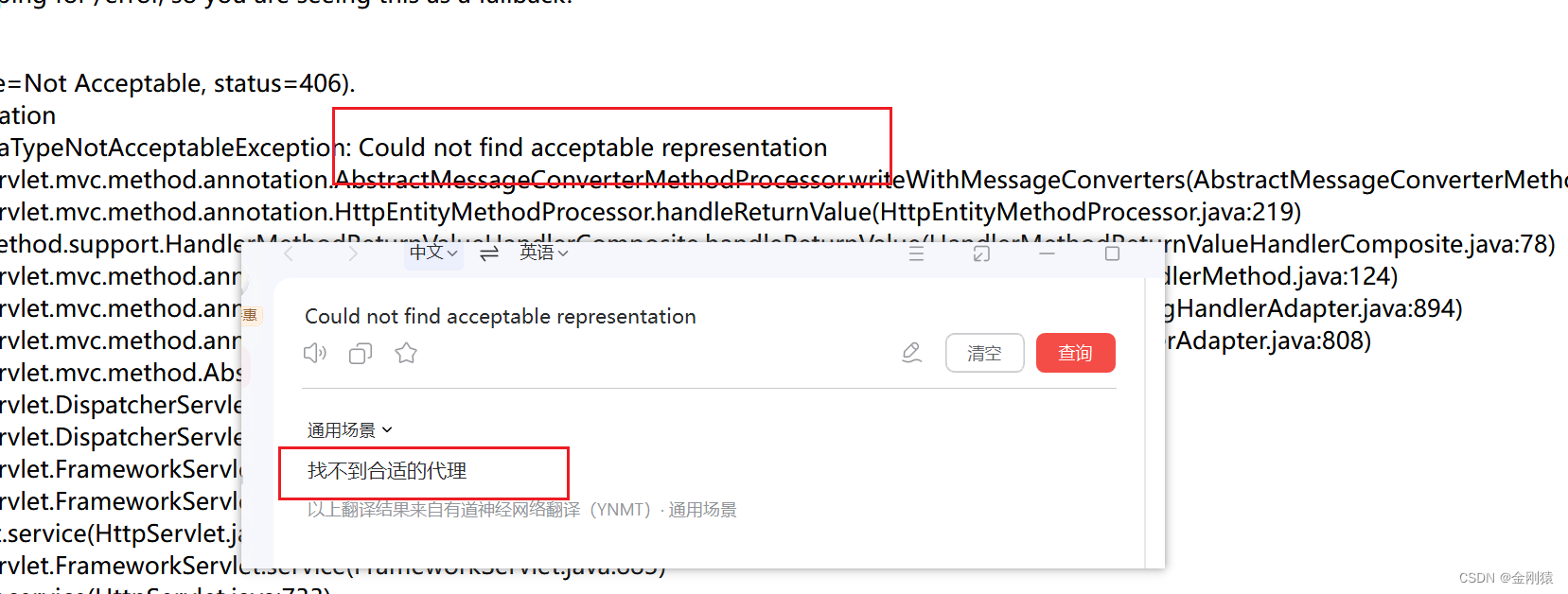
Metrics 证书问题
# 现象
"Failed to scrape node" err="Get \"https://192.168.0.11:10250/metrics/resource\": x509: cannot validate certificate for 192.168.0.11 because it doesn't contain any IP SANs" node="k8s-master-1"
# 解决办法,metrics server添加参数
- --kubelet-insecure-tls # 增加这行
Metrics网络问题
# 现象
Get https://172.24.1.239:10250/metrics/resource: context deadline exceeded node=172-24-1-239.node
# 解决办法
使用hostnetwork