一、排序概念
将一组杂乱无章的数据按一定规律顺次排列起来。
将无序序列排成一个有序序列(由小到大或由大到小)的运算。
二、排序方法分类
1、按数据存储介质
| 名称 | 描述 |
| 内部排序 | 数据量不大、数据在内存,无需内外交换存交换存储。 |
| 外部排序 | 数据量较大、数据在外存(文件排序)外部排序时,要将数据分批调入内存来排序,中间结果还是要及时放入外存,显然外部排序要复杂得多。 |
2、按比较器个数
| 名称 | 描述 |
| 串行排序 | 单处理机。(同一时刻比较一对元素) |
| 并行排序 | 多处理机。(同一时刻比较多对元素) |
3、按主要操作
| 名称 | 描述 |
| 比较排序 | 用比较的方法(插入排序、交换排序、选择排序、归并排序) |
| 基数排序 | 不比较元素的大小,仅仅根据元素本身的取值确定其有序位置。 |
4、按辅助空间
| 名称 | 描述 |
| 原地排序 | 辅助空间用量为O(1)的排序方法。(所占的辅助存储空间与参加排序的数据量大小无关) |
| 非原地排序 | 辅助空间用量超过O(1)的排序方法。 |
5、按稳定性
| 名称 | 描述 |
| 稳定排序 | 能够使任何数值相等的元素,排序以后相对次序不变。 |
| 非稳定排序 | 不是稳定排序的方法。 |
6、按自然性
| 名称 | 描述 |
| 自然排序 | 输入数据越有序,排序的速度越快的排序方法。 |
| 非自然排序 | 不是自然排序的方法。 |
三、排序稳定性的意义
排序的稳定性只对结构类型数据排序有意义。
例如说我们只对分数进行排序,相同分数排序后是否更换位置,对于结果是没有影响的。然而我们对于数学分数、语文分数和人名进行综合排序,虽然数学分数相同的两个同学,但语文成绩不同,名次先后也会有某种变化。
排序方法是否稳定,并不能衡量一个排序算法的优劣。
四、插入排序基本思想
每步将一个待排序的对象,按其关键码大小,插入到前面已经排好序的一组对象的适当位置上,直到对象全部插入为止。
即便插入边排序,保证子序列中随时都是排好序的。
五、直接插入排序(哨兵)
1、算法思路
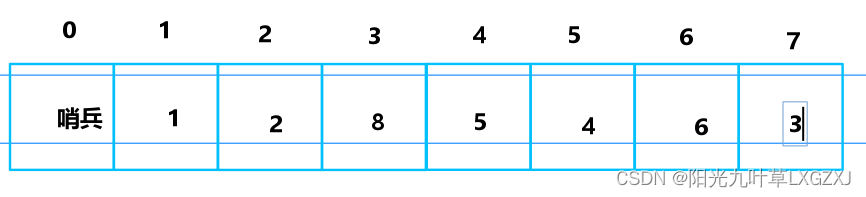
Data : [ 0 ,1 ,2 ,8 ,5 ,4 ,6 ,3 ]升序为例,1,2,8是排好序的,发现5比8小,将5放到哨兵位,8往后移动一位,哨兵再和2比,比2大,退出此次循环,原有8的位置换成哨兵5。
Data : [ 5 ,1 ,2 ,5 ,8 ,4 ,6 ,3 ]现在移动到下一位4,1,2,5,8是排好序的,发现4比8小,将4放到哨兵位,8往后移动一位,哨兵4再和5比发现小,5往后移动一位,哨兵再和2比,比2大,退出此次循环,原有5的位置换成哨兵4。
Data : [ 4 ,1 ,2 ,4 ,5 ,8 ,6 ,3 ]现在移动到下一位6,1,2,4,5,8是排好序的,发现6比8小,将6放到哨兵位,8往后移动一位,哨兵再和5比,比5大,退出此次循环,原有8的位置换成哨兵6。
Data : [ 6 ,1 ,2 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,8 ,3 ]现在移动到下一位6,1,2,4,5,6,8是排好序的,发现3比8小,将3放到哨兵位,且比4,5,6,8都小,4,5,6,8往后挪动一位,比2大,退出此次循环,原有4的位置换成哨兵3。
Data : [ 3 ,1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,8 ]2、源码
(1)DirectInsertSortSentrySqQueue
Status DirectInsertSortSentrySqQueue(SqQueue* Queue)
{
JudgeAllNullPointer(Queue);
if (Queue->Flag != INT_TYPE_FLAG)
{
return FailFlag;
}
int* Array = (int*)(Queue->Data);
QueueLenType i;
QueueLenType j;
for (i = 2; i < Queue->SqQueueLen; i++)
{
if (Array[i] < Array[i - 1])//升序或降序
{
Array[0] = Array[i];
for (j = i - 1; Array[0] < Array[j]; j--)
{
Array[j + 1] = Array[j];//移动元素
}
Array[j + 1] = Array[0];//插入到元素的后一位。
PrintfSqQueue(Queue);
}
}
LogFormat(Debug,"Direct Insert Sort Sentry SqQueue OK.\n");
return SuccessFlag;
}3、Linux环境编译测试
[gbase@czg2 Sort]$ make
gcc -Wall -Wextra -O3 InsertSort.c main.c -o TestSort -I /opt/Developer/ComputerLanguageStudy/C/DataStructureTestSrc/Log/ -I /opt/Developer/ComputerLanguageStudy/C/DataStructureTestSrc/PublicFunction/ -I /opt/Developer/ComputerLanguageStudy/C/DataStructureTestSrc/PublicFunction/HashTable/include/ -I /opt/Developer/ComputerLanguageStudy/C/DataStructureTestSrc/PublicFunction/SqQueue/ -I /opt/Developer/ComputerLanguageStudy/C/DataStructureTestSrc/PublicFunction/SqStack/ -L /opt/Developer/ComputerLanguageStudy/C/DataStructureTestSrc/PublicFunction/Make/Libs/ -lPublicFunction -lLog -lSqQueue
[gbase@czg2 Sort]$ time ./TestSort
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Init SqQueue OK
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Enter SqQueue OK
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Enter SqQueue OK
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Enter SqQueue OK
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Enter SqQueue OK
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Enter SqQueue OK
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Enter SqQueue OK
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Enter SqQueue OK
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Enter SqQueue OK
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--SqQueue Data :
Data : [ 0 ,1 ,2 ,8 ,5 ,4 ,6 ,3 ]
FrontIndex : 0
RearIndex : 0
SqQueueLen : 8
SqQueueMaxLen : 8
Flag : INT_TYPE_FLAG
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--SqQueue Data :
Data : [ 5 ,1 ,2 ,5 ,8 ,4 ,6 ,3 ]
FrontIndex : 0
RearIndex : 0
SqQueueLen : 8
SqQueueMaxLen : 8
Flag : INT_TYPE_FLAG
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--SqQueue Data :
Data : [ 4 ,1 ,2 ,4 ,5 ,8 ,6 ,3 ]
FrontIndex : 0
RearIndex : 0
SqQueueLen : 8
SqQueueMaxLen : 8
Flag : INT_TYPE_FLAG
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--SqQueue Data :
Data : [ 6 ,1 ,2 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,8 ,3 ]
FrontIndex : 0
RearIndex : 0
SqQueueLen : 8
SqQueueMaxLen : 8
Flag : INT_TYPE_FLAG
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--SqQueue Data :
Data : [ 3 ,1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,8 ]
FrontIndex : 0
RearIndex : 0
SqQueueLen : 8
SqQueueMaxLen : 8
Flag : INT_TYPE_FLAG
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Direct Insert Sort Sentry SqQueue OK.
2023-8-29--[ Info ]--Sort Function Elapsed Time : 0 s
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--SqQueue Data :
Data : [ 3 ,1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,8 ]
FrontIndex : 0
RearIndex : 0
SqQueueLen : 8
SqQueueMaxLen : 8
Flag : INT_TYPE_FLAG
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Destroy SqQueue OK
real 0m0.002s
user 0m0.001s
sys 0m0.001s六、二分插入排序(哨兵)
1、算法思路
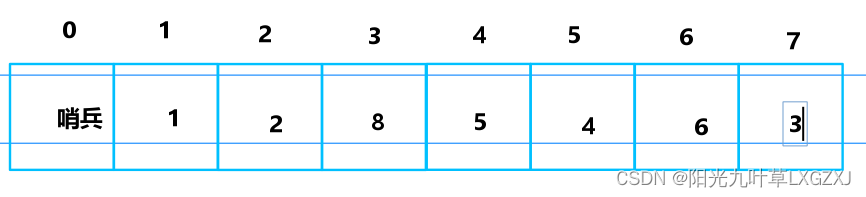
升序为例,1,2,8为有序序列,5小于8,5放到哨兵位, 开始进行二分查找,以Low <= High为进行条件。
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Low : 1, High : 3, Mid : 2.
Mid:2对应2,2小于5,Low = Mid + 1 = 3,Low <= High,继续循环。
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Low : 3, High : 3, Mid : 3.Mid:3对应8,5小于8,High = Mid - 1 = 2,不满足Low <= High,退出循环。
将8往后挪动一位。哨兵填写到原有8的位置,变化如下:
Data : [ 5 ,1 ,2 ,5 ,8 ,4 ,6 ,3 ]1,2,5,8为有序序列,4小于8,4放到哨兵位, 开始进行二分查找,以Low <= High为进行条件。
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Low : 1, High : 4, Mid : 2.Mid:2对应2,2小于4,Low = Mid + 1 = 3,Low <= High,继续循环。
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Low : 3, High : 4, Mid : 3.Mid:3对应5,4小于5,High = Mid - 1 = 2,不满足Low <= High,退出循环。
将5,8往后挪动一位。哨兵填写到原有5的位置,变化如下:
Data : [ 4 ,1 ,2 ,4 ,5 ,8 ,6 ,3 ]1,2,4,5,8为有序序列,6小于8,6放到哨兵位, 开始进行二分查找,以Low <= High为进行条件。
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Low : 1, High : 5, Mid : 3.Mid:3对应4,4小于6,Low = Mid + 1 = 4,Low <= High,继续循环。
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Low : 4, High : 5, Mid : 4.Mid:4对应5,5小于6,Low = Mid + 1 = 5,Low <= High,继续循环。
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Low : 5, High : 5, Mid : 5.Mid:5对应5,6小于8,High = Mid - 1 = 4,不满足Low <= High,退出循环。
将8往后挪动一位。哨兵填写到原有8的位置,变化如下:
Data : [ 6 ,1 ,2 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,8 ,3 ]1,2,4,5,6,8为有序序列,3小于8,3放到哨兵位, 开始进行二分查找,以Low <= High为进行条件。
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Low : 1, High : 6, Mid : 3.Mid:3对应4,3小于4,High = Mid - 1 = 2,Low <= High,继续循环。
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Low : 1, High : 2, Mid : 1.Mid:1对应1,1小于3,Low = Mid + 1 = 2,Low <= High,继续循环。
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Low : 2, High : 2, Mid : 2.Mid:2对应2,2小于3,Low = Mid + 1 = 3,不满足Low <= High,退出循环。
将4,5,6,8往后挪动一位。哨兵填写到原有4的位置,变化如下:
Data : [ 3 ,1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,8 ]2、源码
(1)BinaryInsertSortSentrySqQueue
Status BinaryInsertSortSentrySqQueue(SqQueue* Queue)
{
JudgeAllNullPointer(Queue);
if (Queue->Flag != INT_TYPE_FLAG)
{
return FailFlag;
}
int* Array = (int*)(Queue->Data);
QueueLenType i;
QueueLenType j;
QueueLenType Mid;
QueueLenType High;
QueueLenType Low;
for (i = 2; i < Queue->SqQueueLen; i++)
{
if (Array[i - 1] < Array[i])//如果已经是有序的就不用进行二分查找
{
continue;
}
Array[0] = Array[i];//存放哨兵
Low = 1;
High = i - 1;
while (Low <= High)//折半查找
{
Mid = (Low + High) / 2;
LogFormat(Debug,"Low : %lld, High : %lld, Mid : %lld.\n",Low,High,Mid);
if (Array[0] < Array[Mid])
{
High = Mid - 1;
}
else
{
Low = Mid + 1;
}
}
for (j = i - 1; j >= High + 1; j--)//为什么High + 1,下次看见需推导几次,方便加深记忆。
{
Array[j + 1] = Array[j];//移动元素
PrintfSqQueue(Queue,Debug);
}
Array[High + 1] = Array[0];//插入元素
}
LogFormat(Debug,"Binary Insert Sort Sentry SqQueue OK.\n");
return SuccessFlag;
}3、Linux环境编译测试
[gbase@czg2 Sort]$ time ./TestSort
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Init SqQueue OK
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Enter SqQueue OK
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Enter SqQueue OK
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Enter SqQueue OK
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Enter SqQueue OK
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Enter SqQueue OK
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Enter SqQueue OK
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Enter SqQueue OK
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Enter SqQueue OK
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--SqQueue Data :
Data : [ 0 ,1 ,2 ,8 ,5 ,4 ,6 ,3 ]
FrontIndex : 0
RearIndex : 0
SqQueueLen : 8
SqQueueMaxLen : 8
Flag : INT_TYPE_FLAG
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Low : 1, High : 3, Mid : 2.
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Low : 3, High : 3, Mid : 3.
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--SqQueue Data :
Data : [ 5 ,1 ,2 ,8 ,8 ,4 ,6 ,3 ]
FrontIndex : 0
RearIndex : 0
SqQueueLen : 8
SqQueueMaxLen : 8
Flag : INT_TYPE_FLAG
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Low : 1, High : 4, Mid : 2.
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Low : 3, High : 4, Mid : 3.
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--SqQueue Data :
Data : [ 4 ,1 ,2 ,5 ,8 ,8 ,6 ,3 ]
FrontIndex : 0
RearIndex : 0
SqQueueLen : 8
SqQueueMaxLen : 8
Flag : INT_TYPE_FLAG
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--SqQueue Data :
Data : [ 4 ,1 ,2 ,5 ,5 ,8 ,6 ,3 ]
FrontIndex : 0
RearIndex : 0
SqQueueLen : 8
SqQueueMaxLen : 8
Flag : INT_TYPE_FLAG
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Low : 1, High : 5, Mid : 3.
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Low : 4, High : 5, Mid : 4.
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Low : 5, High : 5, Mid : 5.
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--SqQueue Data :
Data : [ 6 ,1 ,2 ,4 ,5 ,8 ,8 ,3 ]
FrontIndex : 0
RearIndex : 0
SqQueueLen : 8
SqQueueMaxLen : 8
Flag : INT_TYPE_FLAG
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Low : 1, High : 6, Mid : 3.
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Low : 1, High : 2, Mid : 1.
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Low : 2, High : 2, Mid : 2.
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--SqQueue Data :
Data : [ 3 ,1 ,2 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,8 ,8 ]
FrontIndex : 0
RearIndex : 0
SqQueueLen : 8
SqQueueMaxLen : 8
Flag : INT_TYPE_FLAG
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--SqQueue Data :
Data : [ 3 ,1 ,2 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,6 ,8 ]
FrontIndex : 0
RearIndex : 0
SqQueueLen : 8
SqQueueMaxLen : 8
Flag : INT_TYPE_FLAG
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--SqQueue Data :
Data : [ 3 ,1 ,2 ,4 ,5 ,5 ,6 ,8 ]
FrontIndex : 0
RearIndex : 0
SqQueueLen : 8
SqQueueMaxLen : 8
Flag : INT_TYPE_FLAG
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--SqQueue Data :
Data : [ 3 ,1 ,2 ,4 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,8 ]
FrontIndex : 0
RearIndex : 0
SqQueueLen : 8
SqQueueMaxLen : 8
Flag : INT_TYPE_FLAG
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Binary Insert Sort Sentry SqQueue OK.
2023-8-29--[ Info ]--Sort Function Elapsed Time : 0 s
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--SqQueue Data :
Data : [ 3 ,1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,8 ]
FrontIndex : 0
RearIndex : 0
SqQueueLen : 8
SqQueueMaxLen : 8
Flag : INT_TYPE_FLAG
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Destroy SqQueue OK
real 0m0.003s
user 0m0.001s
sys 0m0.002s七、希尔排序(哨兵)
1、基本思想
先将整个待排记录序列分割成若干个子序列,分别进行直接插入排序,待整个序列中的记录“基本有序”时,再对全体记录进行一次直接插入排序。
2、特点
(1)一次移动,移动位置较大,跳跃式地接近排序后的最终位置。
(2)最后一次只需要少量移动。
(3)增量序列必须是递减的,最后一个必须是1。
(4)增量序列应该是互质的。
3、算法效率与增量序列
(1)Hibbard
Dk = 2^k - 1 (相邻元素互质)
| 猜想情况 | 算法时间复杂度 |
| 最坏 | O(n^(2 / 3)) |
| 平均 | O(n^(5 / 4)) |
(3)Sedgewick
Dk = 9 * 4^i - 9 * 2^i + 1 或者 4^i - 3 * 2^i + 1
| 猜想情况 | 算法时间复杂度 |
| 最坏 | O(n^(4 / 3)) |
| 平均 | O(n^(7 / 6)) |
4、算法思路

这个算法涉及步长,因为插入排序算法,需要两个大步,一个是查找插入位置,二是移动元素。希尔排序在直接插入排序的基础上优化第二大步移动元素,不像之前是一步步移动,而是几步、几十步、几百步的移动。
假设步长分别为3和1,实际算法中肯定不是这么设置的步长,只是举例,方便之后举一反三。
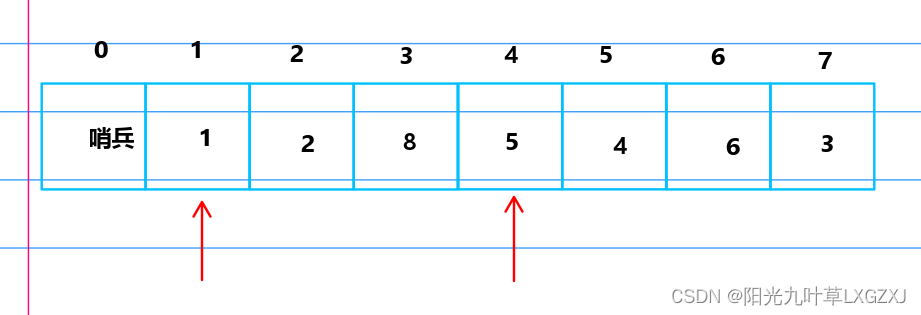
比较1和5,发现1小于5,不需要进行排序,1号位的1前推3格超过1号位,不需要回推,前进一格。

比较2和4,发现2小于4,不需要进行排序,2号位的2前推3格超过1号位,不需要回推,前进一格。

比较8和6,发现8大于6,进行排序,6放到哨兵位,将8挪动到6的位置,再将哨兵的6放到原来8的位置,3号位的6前推3格超过1号位,不需要回推,前进一格。
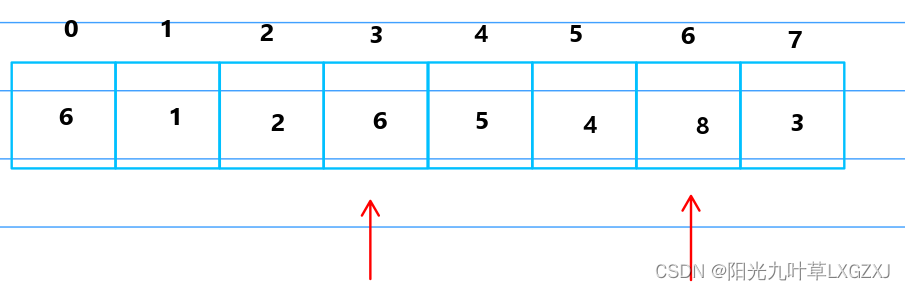 继续往后移动, 比较5和3,发现5大于3,进行排序。
继续往后移动, 比较5和3,发现5大于3,进行排序。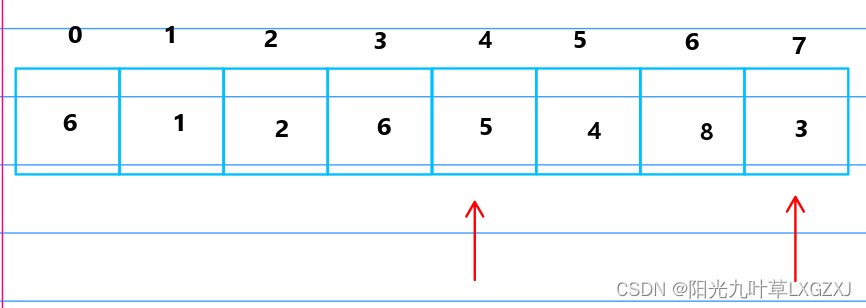
3放到哨兵位,将5挪动到3的位置,再将哨兵的3放到原来5的位置。
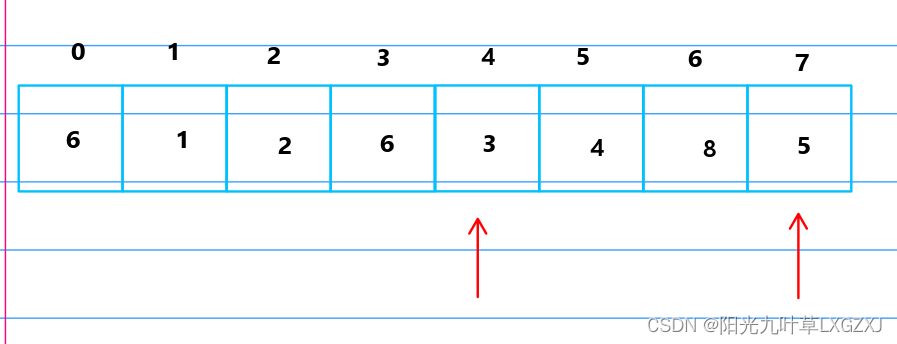 4号位的3比1号位的1大,不需要回推,3的步长排序结束了,现在开始步长为1的排序。
4号位的3比1号位的1大,不需要回推,3的步长排序结束了,现在开始步长为1的排序。
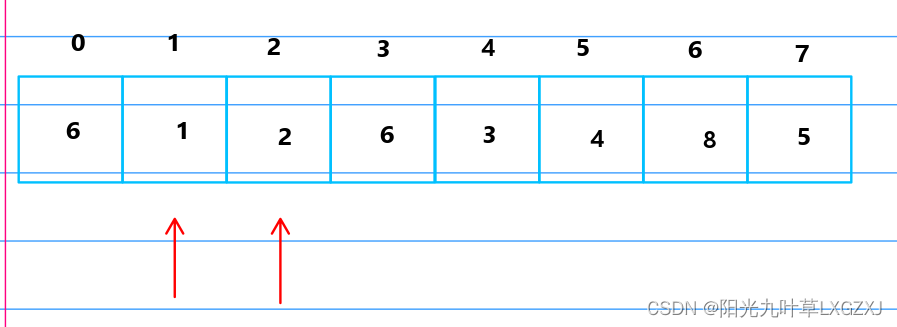
比较1和2,发现1小于2,不需要进行排序,1号位的1前推1格超过1号位,不需要回推,前进一格。
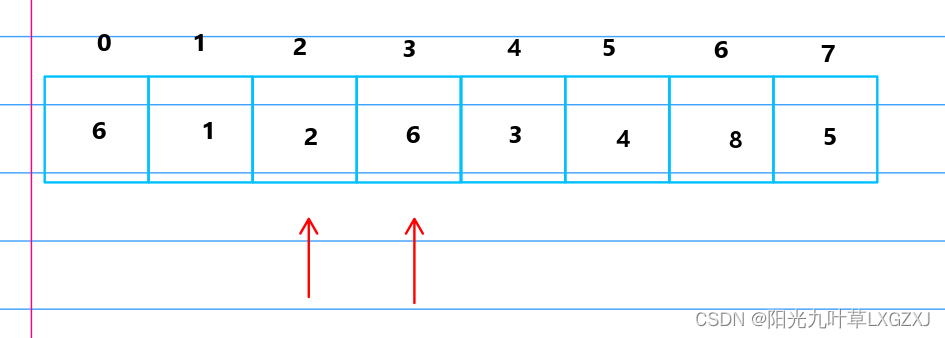
比较2和6,发现2小于6,不需要进行排序, 2号位的2比1号位的1大,不需要回推,往后挪动一位。

比较6和3,发现6大于3,进行排序,3放到哨兵位,将6挪动到3的位置,再将哨兵的3放到原来6的位置。
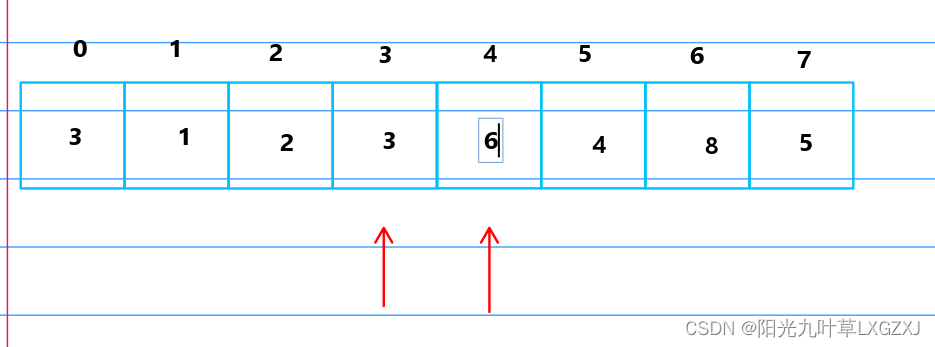
3号位的3比2号位的2大,不需要回推,往后挪动一位。

比较6和4,发现6大于4,进行排序,4放到哨兵位,将6挪动到4的位置,再将哨兵的4放到原来6的位置,4号位的4比3号位的3大,不需要回推,往后挪动一位。
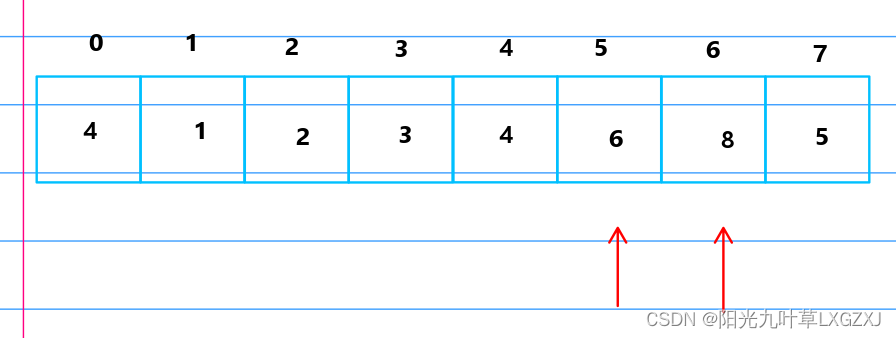
比较6和8,发现6小于8,不需要进行排序,往后挪动一位。
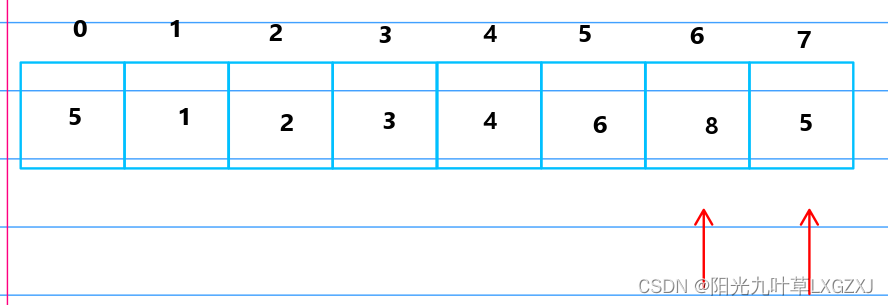
比较8和5,发现8大于5,进行排序,5放到哨兵位,将8挪动到5的位置,再将哨兵的5放到原来8的位置。
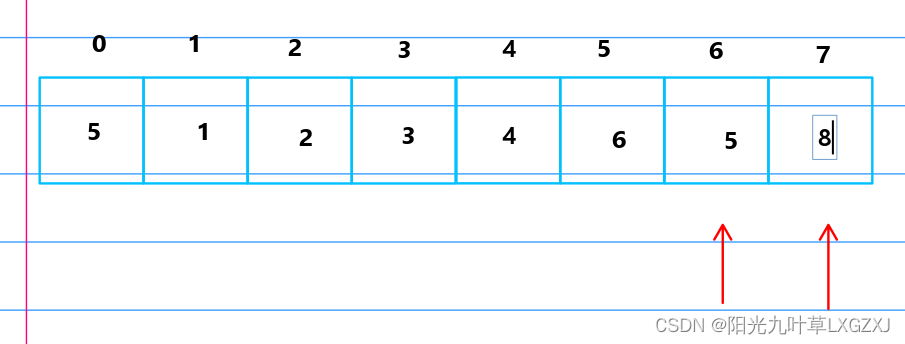
6号位的5比5号位的6小,需要回推。

5放到哨兵位,将6挪动到5的位置,再将哨兵的5放到原来6的位置。
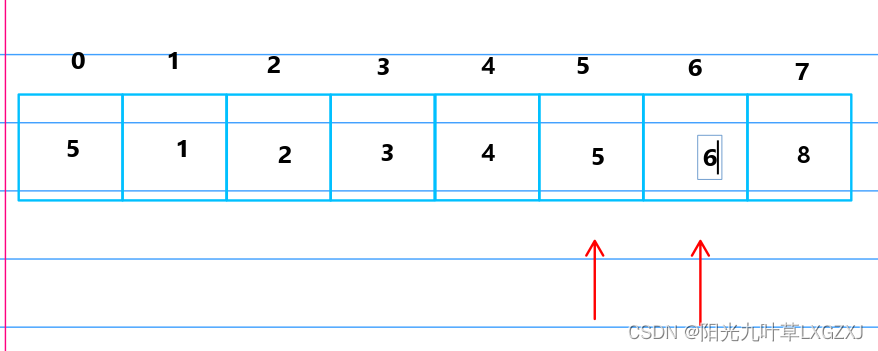
5号位的5比4号位的4大,不需要回推,结束排序。
5、源码
(1)ShellSortSentrySqQueue
Status ShellSortSentrySqQueue(SqQueue* SortQueue)
{
JudgeAllNullPointer(SortQueue);
if (SortQueue->Flag != INT_TYPE_FLAG)
{
return FailFlag;
}
SqQueue* InremrntSeqQueue = NULL;
StepLenType StepLen = 0;
QueueLenType i = 0;
QueueLenType j = 0;
QueueLenType x = 0;
int* Array = SortQueue->Data;
InitSqQueue(&InremrntSeqQueue, INCREMENT_SEQ_MAX_LEN, INT_TYPE_FLAG);//INCREMENT_SEQ_MAX_LEN队列长度需要待商量,这边我先给了一个大致初值。
CreateShellSortInremrntSeq(InremrntSeqQueue, SortQueue);
for (i = GetSqQueueLen(InremrntSeqQueue) - 1; i >= 0 ; i--)
{
ReadSqQueue(InremrntSeqQueue,i,&StepLen);//从增量序列中读出步长。
for (j = StepLen + 1; j < GetSqQueueLen(SortQueue); j++)
{
if (Array[j] < Array[j - StepLen])//当前值比减步长后的值小,说明需要交换位置。
{
Array[0] = Array[j];//将比较小的值,放入哨兵位。
for ( x = j - StepLen; x > 0 && (Array[0] < Array[x]); x = x - StepLen)//j为最大限制,按照步长向左推进。
{
Array[x + StepLen] = Array[x];
}
Array[x + StepLen] = Array[0];
PrintfSqQueue(SortQueue,Debug);
}
}
}
DestroySqQueue(&InremrntSeqQueue);
LogFormat(Debug,"Shell Sort Sentry SqQueue OK.\n");
return SuccessFlag;
}
(2)MyIntSquare
int MyIntSquare(int Base, int Index)
{
int i;
int Res = 1;
for ( i = 0; i < Index; i++)
{
Res *= Base;
}
return Res;
}返回Base的Index次方。
(3)CreateShellSortInremrntSeq
//希尔排序增量序列的最大值为排序队列长度的二分一。(小于)
Status CreateShellSortInremrntSeq(SqQueue* InremrntSeqQueue, SqQueue* SortQueue)
{
JudgeAllNullPointer(InremrntSeqQueue);
JudgeAllNullPointer(SortQueue);
StepLenType i = 0;
StepLenType Val = 0;
StepLenType Tmp = GetSqQueueLen(SortQueue) / INCREMENT_SEQ_SPLIT_VAL;
while (1)
{
Val = 9 * (MyIntSquare(4,i) - MyIntSquare(2,i)) + 1;
if (Val > Tmp)
{
break;
}
EnterSqQueue(InremrntSeqQueue,&Val);
i++;
}
PrintfSqQueue(InremrntSeqQueue,Debug);
LogFormat(Debug,"Create Shell Sort Inremrnt Sequence OK.\n");
return SuccessFlag;
}创建希尔排序使用的增量序列,增量序列的算法用的是Sedgewick。
6、Linux环境编译测试
[gbase@czg2 Sort]$ time ./TestSort
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Init SqQueue OK
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Enter SqQueue OK
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Enter SqQueue OK
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Enter SqQueue OK
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Enter SqQueue OK
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Enter SqQueue OK
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Enter SqQueue OK
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Enter SqQueue OK
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Enter SqQueue OK
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--SqQueue Data :
Data : [ 0 ,1 ,2 ,8 ,5 ,4 ,6 ,3 ]
FrontIndex : 0
RearIndex : 0
SqQueueLen : 8
SqQueueMaxLen : 8
Flag : INT_TYPE_FLAG
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Init SqQueue OK
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Enter SqQueue OK
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--SqQueue Data :
Data : [ 1 ]
FrontIndex : 0
RearIndex : 1
SqQueueLen : 1
SqQueueMaxLen : 20
Flag : INT_TYPE_FLAG
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Create Shell Sort Inremrnt Sequence OK.
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Read SqQueue OK
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--SqQueue Data :
Data : [ 5 ,1 ,2 ,5 ,8 ,4 ,6 ,3 ]
FrontIndex : 0
RearIndex : 0
SqQueueLen : 8
SqQueueMaxLen : 8
Flag : INT_TYPE_FLAG
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--SqQueue Data :
Data : [ 4 ,1 ,2 ,4 ,5 ,8 ,6 ,3 ]
FrontIndex : 0
RearIndex : 0
SqQueueLen : 8
SqQueueMaxLen : 8
Flag : INT_TYPE_FLAG
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--SqQueue Data :
Data : [ 6 ,1 ,2 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,8 ,3 ]
FrontIndex : 0
RearIndex : 0
SqQueueLen : 8
SqQueueMaxLen : 8
Flag : INT_TYPE_FLAG
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--SqQueue Data :
Data : [ 3 ,1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,8 ]
FrontIndex : 0
RearIndex : 0
SqQueueLen : 8
SqQueueMaxLen : 8
Flag : INT_TYPE_FLAG
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Destroy SqQueue OK
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Shell Sort Sentry SqQueue OK.
2023-8-29--[ Info ]--Sort Function Elapsed Time : 0 s
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--SqQueue Data :
Data : [ 3 ,1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,8 ]
FrontIndex : 0
RearIndex : 0
SqQueueLen : 8
SqQueueMaxLen : 8
Flag : INT_TYPE_FLAG
2023-8-29--[ Debug ]--Destroy SqQueue OK
real 0m0.002s
user 0m0.000s
sys 0m0.002s