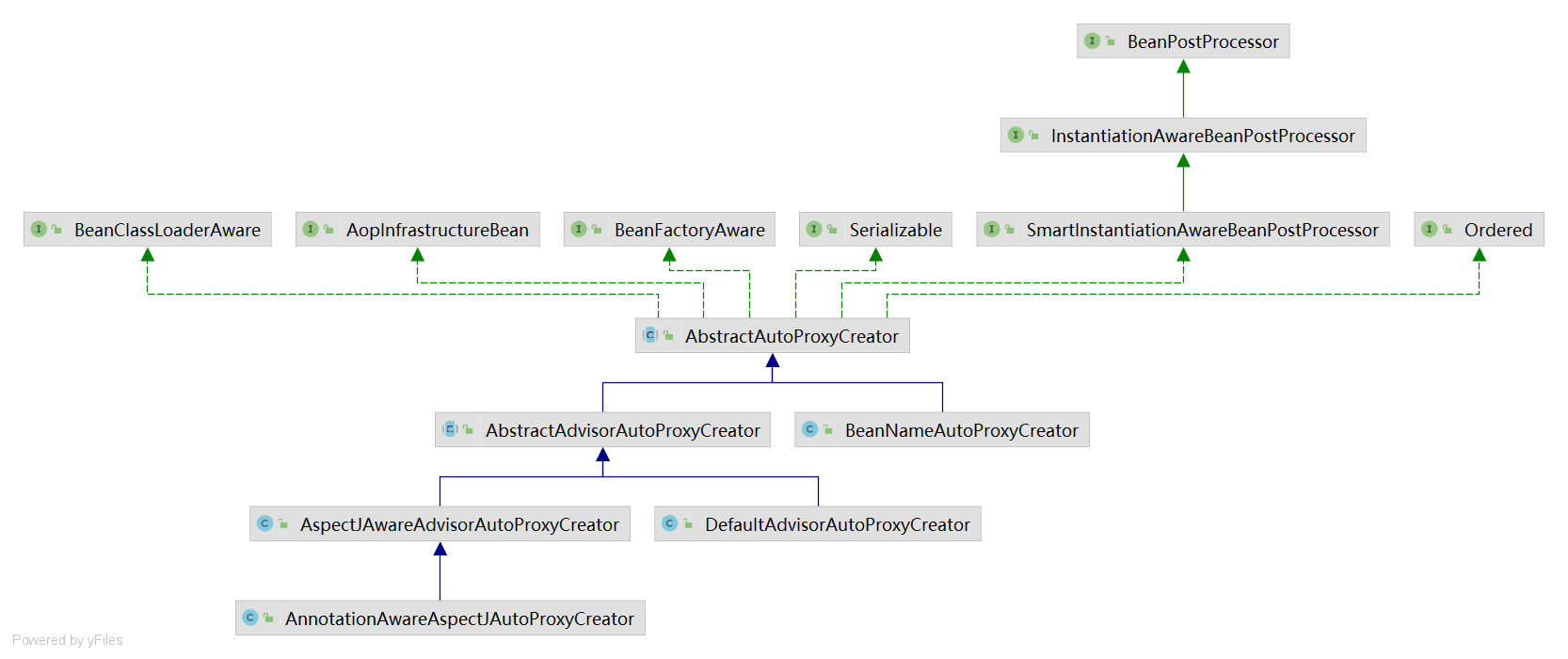
1. 示例代码:
1) status.h
/* DataStructure 预定义常量和类型头文件 */
#ifndef STATUS_H
#define STATUS_H
/* 函数结果状态码 */
#define TRUE 1 /* 返回值为真 */
#define FALSE 0 /* 返回值为假 */
#define RET_OK 0 /* 返回值正确 */
#define INFEASIABLE 2 /* 返回值未知 */
#define ERR_MEMORY 3 /* 访问内存错 */
#define ERR_NULL_PTR 4 /* 空指针错误 */
#define ERR_MEMORY_ALLOCATE 5 /* 内存分配错 */
#define ERR_NULL_STACK 6 /* 栈元素为空 */
#define ERR_PARA 7 /* 函数参数错 */
#define ERR_OPEN_FILE 8 /* 打开文件错 */
typedef int Status; /* Status 是函数的类型,其值是函数结果状态代码,如 OK 等 */
typedef int Bollean; /* Boolean 是布尔类型,其值是 TRUE 或 FALSE */
#endif // !STATUS_H2) sqStack.h
/* 栈的顺序存储表示头文件 */
#ifndef SQSTACK_H
#define SQSTACK_H
#define STACK_INIT_SIZE 10 /* 存储空间初始分配量 */
#define STACKINCREMENT 2 /* 存储空间分配增量 */
#include "status.h"
typedef int SElemType;
typedef struct SqStack
{
SElemType* base; /* 在栈构造之前和销毁之后,base的值为NULL */
SElemType* top; /* 栈顶指针 */
int stackSize; /* 当前已分配的存储空间,以元素为单位 */
} SqStack; /* 顺序栈 */
/* 构造一个空栈 S */
Status InitStack(SqStack* S);
/* 销毁栈 S */
void DestroyStack(SqStack* S);
/* 把 S 置为空栈 */
void ClearStack(SqStack* S);
/* 若栈 S 为空栈,则返回 TRUE,否则返回 FALSE */
Status StackEmpty(SqStack S);
/* 返回 S 的元素个数,即栈的长度 */
int StackLength(SqStack S);
/* 若栈不空,则用 e 返回 S 的栈顶元素,并返回 OK;否则返回 ERROR */
Status GetTop(SqStack S, SElemType* e);
/* 插入元素 e 为新的栈顶元素 */
Status Push(SqStack* S, SElemType e);
/* 若栈不空,则删除 S 的栈顶元素,用 e 返回其值,并返回 OK;否则返回 ERROR */
Status Pop(SqStack* S, SElemType* e);
/* 从栈底到栈顶依次对栈中每个元素调用函数 visit() */
void StackTraverse(SqStack S, void(*Visit)(SElemType));
#endif3) sqStack.c
/* 栈的顺序存储表示源文件 */
#include "sqStack.h"
#include "status.h"
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
/* 构造一个空栈 S */
Status InitStack(SqStack* S)
{
(*S).base = (SElemType*)malloc(STACK_INIT_SIZE * sizeof(SElemType));
if (!(*S).base) {
printf("FuncName: %-15s Line: %-5d ErrorCode: %-3d\n", __func__, __LINE__, ERR_MEMORY_ALLOCATE);
return ERR_MEMORY_ALLOCATE;
}
(*S).top = (*S).base;
(*S).stackSize = STACK_INIT_SIZE;
return RET_OK;
}
/* 销毁栈 S */
void DestroyStack(SqStack* S)
{
free((*S).base);
(*S).base = NULL;
(*S).top = NULL;
(*S).stackSize = 0;
}
/* 把 S 置为空栈 */
void ClearStack(SqStack* S)
{
(*S).top = (*S).base;
}
/* 若栈 S 为空栈,则返回 TRUE,否则返回 FALSE */
Status StackEmpty(SqStack S)
{
return (S.top == S.base) ? TRUE : FALSE;
}
/* 返回 S 的元素个数,即栈的长度 */
int StackLength(SqStack S)
{
return (int)(S.top - S.base);
}
/* 若栈不空,则用 e 返回 S 的栈顶元素,并返回 OK;否则返回 ERROR */
Status GetTop(SqStack S, SElemType* e)
{
if (S.top > S.base) {
*e = *(S.top - 1);
return RET_OK;
}
printf("FuncName: %-15s Line: %-5d ErrorCode: %-3d\n", __func__, __LINE__, ERR_NULL_STACK);
return ERR_NULL_STACK;
}
/* 插入元素 e 为新的栈顶元素 */
Status Push(SqStack* S, SElemType e)
{
if (((*S).top - (*S).base) == (*S).stackSize) {
(*S).base = (SElemType*)realloc((*S).base, (unsigned long long)(((*S).stackSize) + STACKINCREMENT) * sizeof(SElemType));
if (!(*S).base) {
printf("FuncName: %-15s Line: %-5d ErrorCode: %-3d\n", __func__, __LINE__, ERR_MEMORY_ALLOCATE);
return ERR_MEMORY_ALLOCATE;
}
(*S).top = (*S).base + (*S).stackSize;
(*S).stackSize += STACKINCREMENT;
}
*((*S).top)++ = e;
return RET_OK;
}
/* 若栈不空,则删除 S 的栈顶元素,用 e 返回其值,并返回 OK;否则返回 ERROR */
Status Pop(SqStack* S, SElemType* e)
{
if ((*S).top == (*S).base) {
printf("FuncName: %-15s Line: %-5d ErrorCode: %-3d\n", __func__, __LINE__, ERR_MEMORY_ALLOCATE);
return ERR_MEMORY_ALLOCATE;
}
*e = *(--(*S).top);
return RET_OK;
}
/* 从栈底到栈顶依次对栈中每个元素调用函数 visit() */
void StackTraverse(SqStack S, void(*Visit)(SElemType))
{
while (S.top > S.base) {
Visit(*S.base++);
}
}
4) auxiliary.h
/* 辅助函数头文件 */
#ifndef AUXILIARY_H
#define AUXILIARY_H
#include "sqStack.h"
/* 打印栈元素 */
void Print(SElemType e);
#endif // !AUXILIARY_H
5) auxiliary.c
/* 辅助函数实现源文件 */
#include "auxiliary.h"
#include <stdio.h>
/* 打印栈元素 */
void Print(SElemType e)
{
printf("%d ", e);
}
6) algorithm.h
/* 算法定义头文件 */
#ifndef ALGORITHM_H
#define ALGORITHM_H
#include "sqStack.h"
#include "status.h"
/* 算法 3.1, 对于输入的任意一个非负 10 进制整数,打印输出与其等值的 8 进制数 */
void Conversion(unsigned int num);
/* 算法 3.1<2>, 对于输入的任意一个非负 10 进制整数,打印输出与其等值的 16 进制数 */
void TransOctalToHexa(unsigned int num);
/* 对于输入的任意一个字符串,检验括号 ()、[] 是否配对 */
Status BracketMatchCheck(char str[], int strLength);
/* 算法 3.2, 利用字符栈 S,从终端接收一行并送至调用过程的数据区 */
Status LineEdit(void);
/* 算法 3.4, 算术表达式求值的算符优先算法。设 OPTR 和 OPND 分别为运算符栈和运算数栈 */
SElemType CaculateExpression(void);
/* 算法 3.4<2>, 算术表达式求值的算符优先算法。设 OPTR 和 OPND 分别为运算符栈和运算数栈
对算法 3.4 的优化,解除输入限制 */
SElemType CaculateExpression2(void);
#endif // !ALGORITHM_H
7) algorithm.c
/* 算法实现源文件 */
#include "algorithm.h"
#include "sqStack.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
/* 算法 3.1, 对于输入的任意一个非负十进制整数,打印输出与其等值的八进制数 */
void Conversion(unsigned int num)
{
SqStack S;
InitStack(&S);
/* step 1: 入栈 */
while (num) {
Push(&S, num % 8);
num /= 8;
}
/* step 2: 出栈 */
SElemType e;
while (!StackEmpty(S)) {
Pop(&S, &e);
printf("%d", e);
}
}
/* 算法 3.1<2>, 对于输入的任意一个非负 10 进制整数,打印输出与其等值的 16 进制数 */
void TransOctalToHexa(unsigned int num)
{
SqStack S;
InitStack(&S);
/* step 1: 入栈 */
while (num) {
Push(&S, num % 16);
num /= 16;
}
/* step 2: 出栈 */
SElemType e;
printf("0X");
while (!StackEmpty(S)) {
Pop(&S, &e);
if (e <= 9) {
printf("%d", e);
} else {
printf("%c", e + 55);
}
}
}
/* 对于输入的任意一个字符串,检验括号 ()、[] 是否配对 */
Status BracketMatchCheck(char str[], int strLength)
{
if (str == NULL) {
printf("FuncName: %-15s Line: %-5d ErrorCode: %-3d\n", __func__, __LINE__, ERR_NULL_PTR);
return FALSE;
}
if ((int)strlen(str) != strLength) {
printf("FuncName: %-15s Line: %-5d ErrorCode: %-3d\n", __func__, __LINE__, ERR_PARA);
return FALSE;
}
SqStack S = { 0 };
int ret = InitStack(&S);
if (ret != RET_OK) {
printf("FuncName: %-15s Line: %-5d ErrorCode: %-3d\n", __func__, __LINE__, ret);
return FALSE;
}
char* p = str;
SElemType e = 0;
while (*p) {
switch (*p) {
case '(':
case '[':
ret = Push(&S, *p++);
if (ret != RET_OK) {
printf("FuncName: %-15s Line: %-5d ErrorCode: %-3d\n", __func__, __LINE__, ret);
return FALSE;
}
break;
case ')':
case ']':
if (!StackEmpty(S)) {
ret = Pop(&S, &e);
if (ret != RET_OK) {
printf("FuncName: %-15s Line: %-5d ErrorCode: %-3d\n", __func__, __LINE__, ret);
return FALSE;
}
if (((*p == ')') && (e != '(')) || ((*p == ']') && (e != '['))) {
return FALSE;
} else {
++p;
break;
}
} else {
return FALSE;
}
default:
break;
}
}
if (StackEmpty(S)) {
return TRUE;
}
return FALSE;
}
/* 算法 3.2, 利用字符栈 S,从终端接收一行并送至调用过程的数据区 */
Status LineEdit(void)
{
SqStack S = { 0 };
int ret = InitStack(&S);
if (ret != RET_OK) {
printf("FuncName: %-15s Line: %-5d ErrorCode: %-3d\n", __func__, __LINE__, ret);
return FALSE;
}
FILE* fp = NULL;
errno_t err_ret = fopen_s(&fp, "ED.DAT", "w");
if (err_ret != 0) {
printf("FuncName: %-15s Line: %-5d ErrorCode: %-3d\n", __func__, __LINE__, ERR_OPEN_FILE);
return FALSE;
}
SElemType ch = getchar();
while (ch != '$') {
while ((ch != '$') && (ch != '\n')) {
switch (ch) {
case '#':
ret = Pop(&S, &ch);
if (ret != RET_OK) {
printf("FuncName: %-15s Line: %-5d ErrorCode: %-3d\n", __func__, __LINE__, ret);
return FALSE;
}
break;
case '@':
ClearStack(&S);
break;
default:
ret = Push(&S, ch);
if (ret != RET_OK) {
printf("FuncName: %-15s Line: %-5d ErrorCode: %-3d\n", __func__, __LINE__, ret);
return FALSE;
}
}
ch = getchar();
}
SElemType* sE = S.base;
while (S.top > sE) {
fputc(*sE++, fp);
}
ClearStack(&S);
if (ch != '$') {
fputc('\n', fp);
ch = getchar();
}
}
DestroyStack(&S);
fclose(fp);
return TRUE;
}
/* 获取 sE1 与 sE2 的优先级关系 */
SElemType OperPriority(SElemType sE1, SElemType sE2)
{
SElemType ret = '\0';
switch (sE2) {
case '+':
case '-':
if ((sE1 == '(') || (sE1 == '#')) {
ret = '<';
} else {
ret = '>';
}
break;
case '*':
case '/':
if ((sE1 == '*') || (sE1 == '/') || (sE1 == ')')) {
ret = '>';
} else {
ret = '<';
}
break;
case '(':
if (sE1 == ')') {
printf("FuncName: %-15s Line: %-5d ErrorCode: %-3d\n", __func__, __LINE__, ERR_PARA);
return ERR_PARA;
} else {
ret = '<';
}
break;
case ')':
switch (sE1) {
case '(':
ret = '=';
break;
case '#':
printf("FuncName: %-15s Line: %-5d ErrorCode: %-3d\n", __func__, __LINE__, ERR_PARA);
return ERR_PARA;
default:
ret = '>';
}
break;
case '#':
switch (sE1) {
case '#':
ret = '=';
case '(':
printf("FuncName: %-15s Line: %-5d ErrorCode: %-3d\n", __func__, __LINE__, ERR_PARA);
return ERR_PARA;
default:
ret = '>';
}
}
return ret;
}
/* 判断 ch 是否为运算符 */
Status IsOper(SElemType ch)
{
switch (ch) {
case '+':
case '-':
case '*':
case '/':
case '(':
case ')':
case '#':
return TRUE;
default:
return FALSE;
}
}
/* 通过操作符 oper 计算 元素 sE1 与 sE2 */
SElemType CaculateAction(SElemType sE1, SElemType sE2, SElemType oper)
{
SElemType ret = 0;
switch (oper) {
case '+':
ret = sE1 + sE2;
break;
case '-':
ret = sE1 - sE2;
break;
case '*':
ret = sE1 * sE2;
break;
case '/':
if (sE2 == 0) {
printf("FuncName: %-15s Line: %-5d ErrorCode: %-3d\n", __func__, __LINE__, ERR_PARA);
return ERR_PARA;
} else {
ret = sE1 / sE2;
}
}
return ret;
}
/* 算法 3.4, 算术表达式求值的算符优先算法。设 OPTR 和 OPND 分别为运算符栈和运算数栈
输入数值需要在 0 ~ 9 之间, 原因为运算数仅能保存于单个字符中 */
SElemType CaculateExpression(void)
{
SqStack OPTR = { 0 }, OPND = { 0 };
InitStack(&OPTR);
InitStack(&OPND);
Push(&OPTR, '#');
SElemType topSE = 0;
GetTop(OPTR, &topSE);
SElemType sE1 = 0, sE2 = 0, oper = 0;
SElemType ch = getchar();
while ((ch != '#') || (topSE != '#')) {
if (IsOper(ch)) {
switch (OperPriority(topSE, ch)) {
case '<':
Push(&OPTR, ch);
ch = getchar();
break;
case '=':
Pop(&OPTR, &topSE);
ch = getchar();
break;
case '>':
Pop(&OPTR, &oper);
Pop(&OPND, &sE2);
Pop(&OPND, &sE1);
Push(&OPND, CaculateAction(sE1, sE2, oper));
break;
}
} else if ((ch >= '0') && (ch <= '9')) {
/* 将 ASCII 码转换为数字, 数字 0 ~ 9 的 ASCII 码为 48 ~ 57 */
ch -= 48;
Push(&OPND, ch);
ch = getchar();
} else {
printf("FuncName: %-15s Line: %-5d ErrorCode: %-3d\n", __func__, __LINE__, ERR_PARA);
return ERR_PARA;
}
GetTop(OPTR, &topSE);
}
GetTop(OPND, &topSE);
return topSE;
}
/* 算法 3.4<2>, 算术表达式求值的算符优先算法。设 OPTR 和 OPND 分别为运算符栈和运算数栈
对算法 3.4 的优化,解除输入限制, 输入负数时使用 0 - n 的方式输入 */
SElemType CaculateExpression2(void)
{
SqStack OPTR = { 0 }, OPND = { 0 };
InitStack(&OPTR);
InitStack(&OPND);
Push(&OPTR, '#');
SElemType topSE = 0;
GetTop(OPTR, &topSE);
SElemType sE1 = 0, sE2 = 0, oper = 0;
char ch = getchar();
char numStr[6] = { 0 };
while ((ch != '#') || (topSE != '#')) {
if (IsOper(ch)) {
switch (OperPriority(topSE, ch)) {
case '<':
Push(&OPTR, ch);
ch = getchar();
break;
case '=':
Pop(&OPTR, &topSE);
ch = getchar();
break;
case '>':
Pop(&OPTR, &oper);
Pop(&OPND, &sE2);
Pop(&OPND, &sE1);
Push(&OPND, CaculateAction(sE1, sE2, oper));
break;
}
} else if ((ch >= '0') && (ch <= '9')) {
/* 将 ASCII 码转换为数字, 数字 0 ~ 9 的 ASCII 码为 48 ~ 57 */
int i;
for (i = 0; (ch >= '0') && (ch <= '9'); ++i) {
numStr[i] = ch;
ch = getchar();
}
numStr[i] = 0;
int num = atoi(numStr);
Push(&OPND, num);
} else {
printf("FuncName: %-15s Line: %-5d ErrorCode: %-3d\n", __func__, __LINE__, ERR_PARA);
return ERR_PARA;
}
GetTop(OPTR, &topSE);
}
GetTop(OPND, &topSE);
return topSE;
}8) main.c
/* 入口程序源文件 */
#include "status.h"
#include "sqStack.h"
#include "algorithm.h"
#include "auxiliary.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(void)
{
/* 测试基本功能 */
SqStack S;
int ret = InitStack(&S);
if (ret != RET_OK) {
printf("FuncName: %-15s Line: %-5d ErrorCode: %-3d\n", __func__, __LINE__, ret);
return ret;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 12; ++i) {
Push(&S, i + 1);
}
StackTraverse(S, Print);
printf("\n");
SElemType e;
ret = Pop(&S, &e);
if (ret != RET_OK) {
printf("FuncName: %-15s Line: %-5d ErrorCode: %-3d\n", __func__, __LINE__, ret);
return ret;
}
printf("The element of the top of the stack: %d\n", e);
printf("The stack is %s\n", (StackEmpty(S) == TRUE) ? "Empty" : "Not Empty");
ret = GetTop(S, &e);
if (ret != RET_OK) {
printf("FuncName: %-15s Line: %-5d ErrorCode: %-3d\n", __func__, __LINE__, ret);
}
printf("The element of the top of the stack: %d\n", e);
printf("The length of the stack is: %d\n", StackLength(S));
ClearStack(&S);
ret = GetTop(S, &e);
if (ret != RET_OK) {
printf("FuncName: %-15s Line: %-5d ErrorCode: %-3d\n", __func__, __LINE__, ret);
}
ret = Pop(&S, &e);
if (ret != RET_OK) {
printf("FuncName: %-15s Line: %-5d ErrorCode: %-3d\n", __func__, __LINE__, ret);
}
printf("The stack is %s\n", (StackEmpty(S) == TRUE) ? "Empty" : "Not Empty");
/* 算法 3.1 对于输入的任意一个非负十进制整数,打印输出与其等值的八进制数 */
printf("Please input a positive number: ");
unsigned int num;
scanf_s("%u", &num);
printf("The octal of the positive decimal number of %u is: ", num);
Conversion(num);
putchar('\n');
/* 算法 3.1<2>, 对于输入的任意一个非负 10 进制整数,打印输出与其等值的 16 进制数 */
printf("The hexadecimal of the positive decimal number of %u is: ", num); \
TransOctalToHexa(num);
putchar('\n');
getchar();
/* 对于输入的任意一个字符串,检验括号 ()、[] 是否配对 */
char str[80] = { 0 };
printf("Please input a string to check if the string is match: ");
if (gets_s(str, sizeof(str)) == NULL) {
printf("FuncName: %-15s Line: %-5d ErrorCode: %-3d\n", __func__, __LINE__, ERR_MEMORY);
return ERR_MEMORY;
}
ret = BracketMatchCheck(str, (int)strlen(str));
if (ret == TRUE) {
printf("The string is match\n");
}
else {
printf("The string is not match\n");
}
/* 算法 3.2, 利用字符栈 S,从终端接收一行并送至调用过程的数据区 */
printf("Please input a string:\n");
ret = LineEdit();
if (ret != TRUE) {
printf("FuncName: %-15s Line: %-5d ErrorCode: %-3d\n", __func__, __LINE__, ret);
}
putchar('\n');
getchar();
/* 算法 3.4<2>, 算术表达式求值的算符优先算法。设 OPTR 和 OPND 分别为运算符栈和运算数栈
对算法 3.4 的优化,解除输入限制 */
printf("Please input the arithmetic expression: ");
ret = CaculateExpression2();
printf("ret = %d\n", ret);
DestroyStack(&S);
return 0;
}
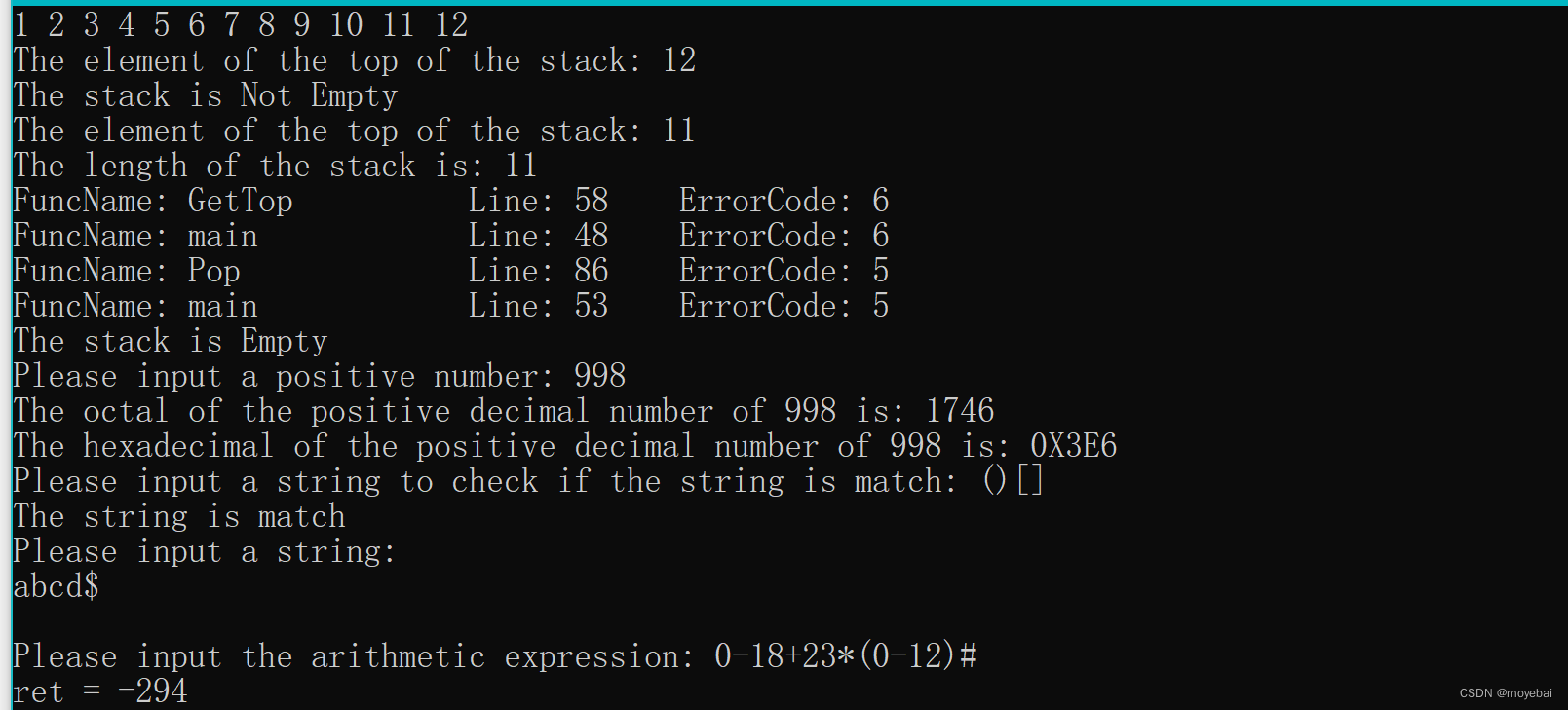
2. 输出示例: