进程概述
程序是包含一系列信息的文件,描述了如何在运行时创建一个进程;
进程是正在运行的程序的实例,可以用一个程序来创建多个进程;
用户内存空间包含程序代码以及代码所使用的变量,内核数据结构用于维护进程状态信息;
进程控制块(PCB):维护进程相关的信息,task_struct结构体
PCB内部成员:进程id、进程的状态、进程切换时需要保存和恢复的一些CPU寄存器、虚拟地址空间信息、控制终端信息等
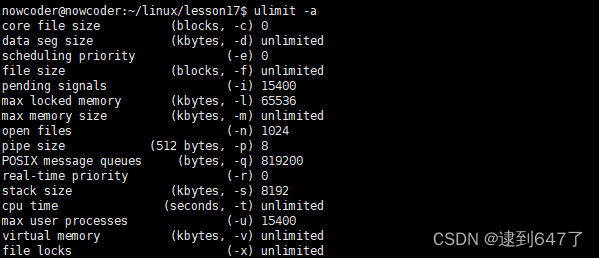
进程可以使用的资源上线可以调用: ulimit -a 进行查询
进程状态转换
三态模型:就绪、运行、阻塞
五态模型:新建、就绪、运行、阻塞、终止
阻塞态不能直接变为运行态,需要先变为就绪态;
新建态:进程刚被创建,还没有分配资源,尚未进入就绪队列;
终止态:进程完成任务到达正常结束点,或出现错误而异常终止,或被新操作系统以及有终止权的进程所终止;
查看进程:ps aux/ajx(不能动态显示)
a - 显示终端所有进程;
u - 显示进程详细信息
x - 显示没有控制终端的进程;
j - 列出与作业控制相关的信息
实时显示进程动态:top (-d 指定时间间隔)
按键排序:
M - 内存降序
P - CPU占有率降序
U - 根据用户名筛选
K - 杀死进程
T - 根据运行时长排序
杀死进程:kill PID
kill -9 PID(强制杀死进程)
killall name 根据进程名杀死进程;
进程号相关函数
进程号的范围 0~32767;
getpid(void)、getppid(void)、getpgid(pid_t pid)
进程创建
/*
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
pid_t fork(void);
返回值:
返回两次;一次在父进程中,一次在子进程中
父进程中返回子进程的ID
子进程中返回0
如何区分父进程和子进程 - 通过fork返回值;
父进程中返回-1表示创建子进程失败,并设置errno
失败的原因:
1. 进程数上限
2. 系统内存不足
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
// 创建子进程
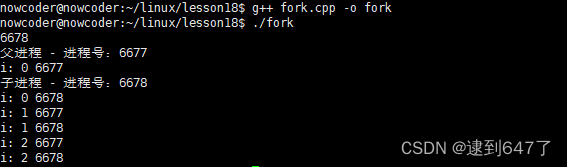
pid_t pid = fork();
// 判断父子进程
if(pid>0){
cout<<pid<<endl;
cout<<"父进程 - 进程号:"<<getpid()<<endl;
}
else if(pid == 0){
cout<<"子进程 - 进程号:"<<getpid()<<endl;
}
for(int i = 0 ; i<3 ; i++){
cout<<"i: "<<i<<" "<<getpid()<<endl;
sleep(1);
}
return 0;
}
父子进程虚拟地址空间的情况
子进程用户区数据和父进程一样,内核区也会拷贝,但pid不同;
fork()是通过写时拷贝实现的,资源的复制在需要写入时才进行,在此之前以只读方式进行共享;
父子进程的关系及GDB多线程调试
父子进程间的关系
区别:
1. fork()返回值不同
2. pcb中的一些数据 eg. 当前进程pid ppid、信号集
共同点:
子进程刚被创建,没执行任何写操作
- 用户区数据
- 文件描述符表
父子进程对变量是不是共享的?
- 读时共享,写时拷贝;
GDB多进程调试
GDB默认只能跟踪一个进程 默认跟踪父进程;
- 显示跟踪进程:show follow-fork-mode
- 设置调试父进程和子进程:set follow-fork-mode [parent(默认)|child]
- 显示调试模式:show detach-on-fork
- 设置调试模式:set detach-on-fork [on|off]
默认为on,表示调式当前进程时,其他进程继续运行;off表示调式当前进程,其它进程被GDB挂起,停在fork处;
- 查看调试的进程:info inferiors
- 切换调试进程:inferior 进程编号 后 c即可
- 使进程脱离GDB调试:detach inferior id
exec函数族(一系列函数)
作用:根据指定文件名找到可执行文件;用其取代调用进程的内容(在调用进程内部执行一个可执行文件);但它不会生成新的进程
exec函数族的函数执行成功不返回,调用失败会返回-1 , 从调用点接着往下执行;


execl函数
/*
#include <unistd.h>
int execl(const char *path, const char *arg, ...);
参数:
path - 需要指定的可执行文件路径/名称
a.out /home/nowcoder/a.out(推荐)
arg - 可执行文件所需的参数列表
1st - 一般没有作用,一般写执行程序名称
参数列表必须以NULL结束(哨兵)
返回值:出错返回-1 并设置errno
*/
#include <unistd.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
// 创建一个子进程 在子进程执行exec函数族中的函数
pid_t pid = fork();
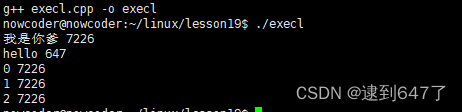
if(pid>0){
cout<<"我是你爹"<<" "<<getpid()<<endl;
sleep(1);
}
else if(pid == 0){
execl("hello" , "hello" , NULL);
cout<<"我是你儿子"<<" "<<getpid()<<endl;
}
for(int i = 0 ; i<3 ; i++){
cout<<i<<" "<<getpid()<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
execlp 从环境变量查可执行文件
/*
#include <unistd.h>
int execlp(const char *file, const char *arg,);
-- 会到环境变量中查可执行文件 找不到执行失败
参数:
file - 需要指定的可执行文件的文件名
a.out /home/nowcoder/a.out(推荐)
arg - 可执行文件所需的参数列表
1st - 一般没有作用,一般写执行程序名称
参数列表必须以NULL结束(哨兵)
返回值:出错返回-1 并设置errno
*/
#include <unistd.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
// 创建一个子进程 在子进程执行exec函数族中的函数
pid_t pid = fork();
if(pid>0){
cout<<"我是你爹"<<" "<<getpid()<<endl;
sleep(1);
}
else if(pid == 0){
execlp("ps" , "ps" , "aux" , NULL);
cout<<"我是你儿子"<<" "<<getpid()<<endl;
}
for(int i = 0 ; i<3 ; i++){
cout<<i<<" "<<getpid()<<endl;
}
return 0;
}进程退出、孤儿进程、僵尸进程
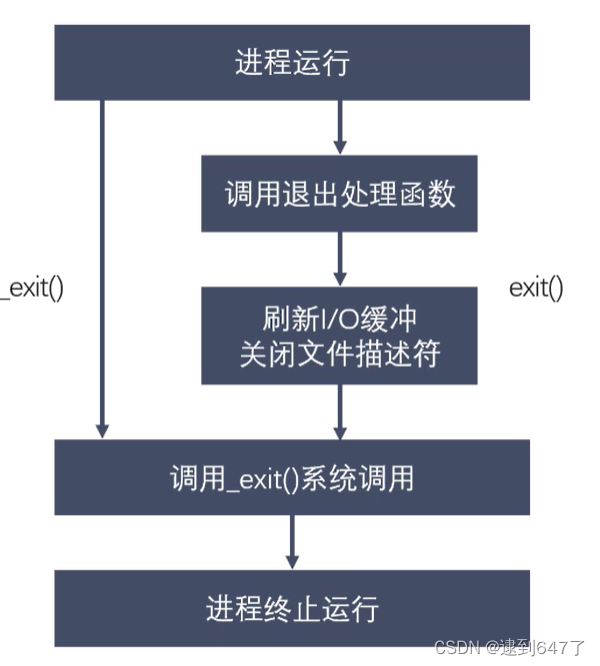
进程退出:exit(标准C库)、_exit(linux系统函数)
/*
#include <stdlib.h>
void exit(int status);
#include <unistd.h>
void _exit(int status);
status - 进程退出时的状态信息 父进程回收子进程资源时可以获取
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
cout<<"hello"<<endl;
cout<<"world";
// exit(0); // hello world
_exit(0); // hello
return 0;
}孤儿进程:父进程运行结束,子进程还在运行 -> 孤儿进程;
- 内核会把孤儿进程的父进程设置为init , init进程会循环wait()退出的子进程;
#include <iostream>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
// 创建子进程
pid_t pid = fork();
// 判断父子进程
if(pid>0){
cout<<pid<<endl;
cout<<"父进程 - 进程号:"<<getpid()<<endl;
}
else if(pid == 0){
sleep(1);
cout<<"子进程 - 进程号:"<<getpid()<<endl;
cout<<"子进程 - 父进程:"<<getppid()<<endl;
}
for(int i = 0 ; i<3 ; i++){
cout<<"i: "<<i<<" "<<getpid()<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
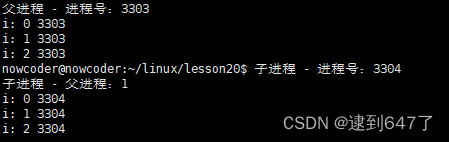
父进程死亡后切换到前台(出现上述现象);
僵尸进程:进程终止,可以释放用户区的数据,内核区的PCB没办法自己释放,需要父进程进行释放。如果父进程尚未回收,子进程残留资源存放于内核;变成僵尸进程;
不能被kill -9 杀死;
#include <iostream>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
// 创建子进程
pid_t pid = fork();
// 判断父子进程
if(pid>0){
cout<<pid<<endl;
while(1){
cout<<"父进程 - 进程号:"<<getpid()<<endl;
sleep(1);
}
}
else if(pid == 0){
cout<<"子进程 - 进程号:"<<getpid()<<endl;
cout<<"子进程 - 父进程:"<<getppid()<<endl;
}
for(int i = 0 ; i<3 ; i++){
cout<<"i: "<<i<<" "<<getpid()<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
![]()
处理方法:
1. 父进程调wait()/waitpid()
2. 杀死父进程,让Init接管子进程进行释放处理;
wait/waitpid 函数
wait()函数会阻塞,waitpid()可以设置不阻塞,并且waitpid()可以指定等待哪个子进程结束;
一次wait/waitpid只能清理一个子进程,清理多个子进程应该使用循环;
wait()
调用wait的进程会被挂起,直到其一个子进程退出或遇到不可忽略的信号;
如果其没有子进程或者子进程都结束了会立刻返回-1;

/*
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
pid_t wait(int *wstatus);
等待任一子进程结束 然后回收子进程资源;
参数:
wstatus - 进程退出时的状态信息(传出参数)
返回值:
成功 - 被回收的子进程id
失败 - -1
1. 所有的子进程都结束
2. 调用函数失败
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
// 创建5个子进程
pid_t pid;
for(int i = 0 ; i<5 ; i++){
pid = fork();
if(pid == 0){
break;
}
}
if(pid>0){
while(1){
cout<<"我是你爹: "<<getpid()<<endl;
int ret = wait(NULL);// NULL 不获取状态
if(ret == -1){
break;
}
cout<<"捕获到了子进程:"<<ret<<endl;
sleep(2);
}
}
else if(pid == 0){
while(1){
cout<<"我是你儿子: "<<getpid()<<endl;
sleep(2);
}
}
return 0;
}waitpid()
/*
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
pid_t waitpid(pid_t pid, int *wstatus, int options);
功能:回收指定进程号子进程 设置阻塞/非阻塞
参数:
pid
<-1 - 回收某个进程组的子进程 组id == abs(pid)
-1 - 回收所有子进程 相当于wait()
0 - 回收当前进程组的所有子进程
>0 - 回收指定子进程ID进程
watatus - 同wait
options
0 - 阻塞
WNOHANG - 非阻塞
返回值:
>0 - 子进程ID
=0 - options=WNOHANG 表示还有子进程
-1 - 错误/没有子进程
waitpid(-1 , __ , 0) = wait(__);
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
// 创建5个子进程
pid_t pid;
for(int i = 0 ; i<5 ; i++){
pid = fork();
if(pid == 0){
break;
}
}
if(pid>0){
while(1){
cout<<"我是你爹: "<<getpid()<<endl;
sleep(2);
int st;
// int ret = waitpid(-1 , &st , 0);
int ret = waitpid(-1 , &st , WNOHANG);
if(ret == -1){
break;
}
if(ret == 0){
cout<<"他妈的怎么还有子进程"<<endl;
continue;
}
else{
if(WIFEXITED(st)){
cout<<"退出的状态码:"<<WEXITSTATUS(st)<<endl;
}
if(WIFSIGNALED(st)){
cout<<"被哪个信号干掉:"<<WTERMSIG(st)<<endl;
}
cout<<"捕获到了子进程:"<<ret<<endl;
}
}
}
else if(pid == 0){
while(1){
cout<<"我是你儿子: "<<getpid()<<endl;
sleep(2);
}
}
return 0;
}