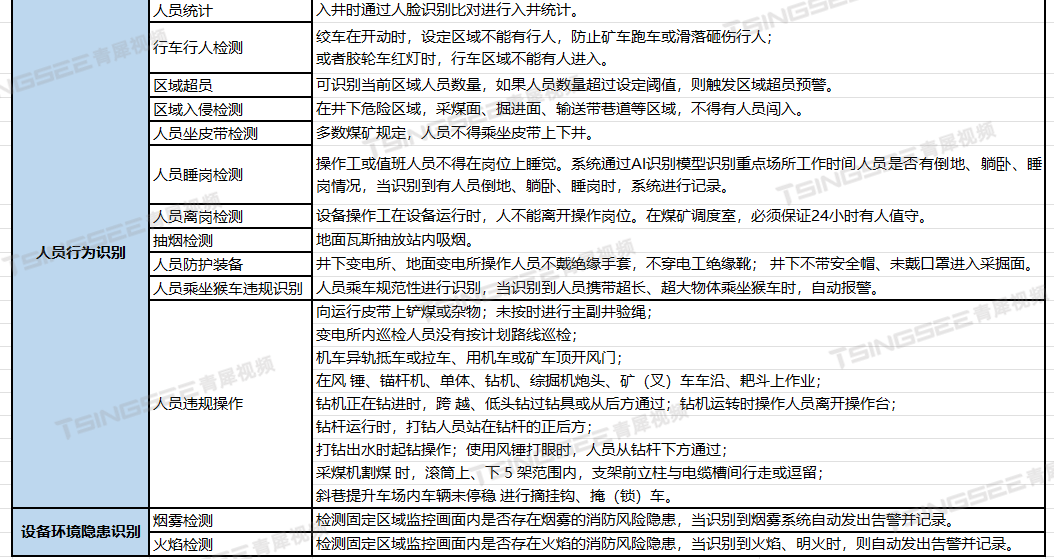
- Android中的
SharedPreference是轻量级的数据存储方式,能够保存简单的数据类型。比如String、int、boolean值等。 - 其内部是以
XML结构保存在/data/data/包名/shared_prefs文件夹下,数据以键值对的形式保存。 - 是线程安全的,但不是进程安全的。
1. 基本使用
- 获取到SharedPreference对象
- put数据
SharedPreferences.Editor editor = getSharedPreferences("data" , MODE_PRIVATE).edit();
editor.putString("name" , "Tom");
editor.putInt("age" , 28);
editor.putBoolean("married" , false);
editor.apply();
- 读数据时,也是获取到SharedPreference对象,通过get方法获取
SharedPreferences pref = getSharedPreferences("data" , MODE_PRIVATE);
String name = pref.getInt("age" , 0);

1.1 读操作
- 使用内存缓存机制
- 当通过Context.getSharedPreferences()初始化SharedPreference对象。
- 对xml文件进行一次读取,并将所有文件内所有内容(即所有的键值对)缓存到内存的一个Map中
- 这样接下来的操作只要从这个Map中读取就好了。
2. getSharedPreference
- getSharedPreference对象时,系统做了什么?
- 会调用
Context.getSharedPreferences(),里面使用了synchronized关键字来构建SharedPreferences(线程安全的)- 会先去内存缓存(ArrayMap<File,SharedpreferencesImpl> cahce)中找,不存在找的SharedPreference对象,则重新构造一个SharedPreferencesImpl对象,放入cache中。
- 如果找到的话,直接返回。
- 构造
SharedPreferencesImpl的话,会开启一个子线程从磁盘中加载数据。- 加载过程是异步的,通过new Thread来执行,所以不会在构造SharedPreferences的时候堵塞线程,但是会阻塞getXxx/putXxx/remove/clear等调用
- 在SharedPreferenceImpl类中,在写磁盘前还会创建一个
.bak的备份文件的内存对象。之后get异步加载数据时,判断磁盘中有没有这个备份文件。- 有的话,说明之前写入出错了,将备份文件改名为原文件,然后进行读这个改名后的备份文件。(回滚)
- 没有的话,说明之前写入一切正常,就用原文件进行读操作即可。
- 保存读取到的相关数据(mMap、文件修改时间戳、文件大小)
- 异步加载数据完成后,将mLoaded设置为true,调用
notifyAll()方法通知唤醒其他等待线程,数据加载完毕。
3. getXxx
- getXxx是线程安全的。(使用了synchronized)
- getXxx会判断数据是否加载完毕并存到了mMap中,没加载完毕的话,就会wait()阻塞
- 结束了,就从内存中的mMap中根据传入的key读取value。
4. putXxx
- 抽象出了一个Editor类,所有对SharedPreferences的写操作都是基于sharedPreferences.edit()返回的这个
SharedPreferences.Editor类。在 Android 系统中,Editor是一个接口,它的具体实现类是EditorImpl。
- putXxx是线程安全的。(使用了Synchronized)
- 对 键值对数据 的增删记录保存在了
Map<string , Object> mModified中,而不是直接对SharedPreferences中的mMap进行操作。 - mModified会在
commit/apply方法中起到同步内存(SharedPreferences.mMap)以及同步磁盘数据的作用。
5. commit()
- 首先通过
commitToMemory()方法,将mModified同步到内存的SharedPreferences.mMap中。 - 调用
enqueueDiskWrite方法将数据写入到磁盘中。(内部会通过wirteToFile进行写入操作) - 同步等待写磁盘操作完成。(这是commit()方法会同步阻塞等待的原因)
- 通知监听者(可以通过registerOnSharedPreferenceChangeListener方法注册监听)
- 返回执行结果(布尔类型)
关于commitToMemory()和enqueueDiskWirte内部的操作可以看下面的源码解析
6. apply()
- 首先通过
commitToMemory()方法,将mModified同步到内存的SharedPreferences.mMap中。 - 调用
enqueueDiskWrite方法调用writeToFile方法将所有数据用 异步单线程线程池写入到磁盘中。
- 在Service.onStartCommand、Service.onDestroy、Activity.onPause、Activity.onStop等生命周期回调时,主线程会调用QueuedWork.waitToFinish()去等待所有写入任务的执行完成。
- 如果异步提交的任务过多,会阻塞主线程造成ANR。

7. 源码解析
7.1 获取SharedPreference对象
- 首先查看
ContextImpl.getSharedPreferences的源码: - 创建了一个文件夹,内部用XML结构来保存
- 调用
getSharedPreference(File file , int mode) - 里面使用
synchronized关键字,确保SharedPreference对象的创建是线程安全的。 - 在SharedPreference对象缓存中查找有没有缓存的对象(通过file作为key来查找),没有的话就需要重新构造一个
SharedPreferenceImpl对象,并放入到缓存当中。

@Override
public SharedPreferences getSharedPreferences(String name, int mode) {
// At least one application in the world actually passes in a null
// name. This happened to work because when we generated the file name
// we would stringify it to "null.xml". Nice.
if (mPackageInfo.getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion <
Build.VERSION_CODES.KITKAT) {
if (name == null) {
name = "null";
}
}
File file;
synchronized (ContextImpl.class) {
if (mSharedPrefsPaths == null) {
mSharedPrefsPaths = new ArrayMap<>();
}
file = mSharedPrefsPaths.get(name);
if (file == null) {
// 2.创建一个对应路径 /data/data/packageName/name 的 File 对象
file = getSharedPreferencesPath(name);
mSharedPrefsPaths.put(name, file);
}
}
// 3.这里调用了 getSharedPreferences(File file, int mode) 方法
return getSharedPreferences(file, mode);
}
@Override
public SharedPreferences getSharedPreferences(File file, int mode) {
SharedPreferencesImpl sp;
// 4.这里使用了 synchronized 关键字,确保了 SharedPreferences 对象的构造是线程安全的
synchronized (ContextImpl.class) {
// 5.获取SharedPreferences 对象的缓存
final ArrayMap<File, SharedPreferencesImpl> cache = getSharedPreferencesCacheLocked();
// 5.以参数 file 作为 key,获取缓存对象
sp = cache.get(file);
if (sp == null) { // 5.如果缓存中不存在 SharedPreferences 对象
checkMode(mode);
if (getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion >= android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.O) {
if (isCredentialProtectedStorage()
&& !getSystemService(UserManager.class)
.isUserUnlockingOrUnlocked(UserHandle.myUserId())) {
throw new IllegalStateException("SharedPreferences in credential encrypted "
+ "storage are not available until after user is unlocked");
}
}
// 5.构造一个 SharedPreferencesImpl 对象
sp = new SharedPreferencesImpl(file, mode);
// 5.放入缓存 cache 中,方便下次直接从缓存中获取
cache.put(file, sp);
// 5.返回新构造的 SharedPreferencesImpl 对象
return sp;
}
}
// 这里涉及到多进程的逻辑
if ((mode & Context.MODE_MULTI_PROCESS) != 0 ||
getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion < android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.HONEYCOMB) {
// If somebody else (some other process) changed the prefs
// file behind our back, we reload it. This has been the
// historical (if undocumented) behavior.
// 如果由其他进程修改了这个 SharedPreferences 文件,我们将会重新加载它
sp.startReloadIfChangedUnexpectedly();
}
// 程序走到这里,说明命中了缓存,SharedPreferences 已经创建,直接返回
return sp;
}
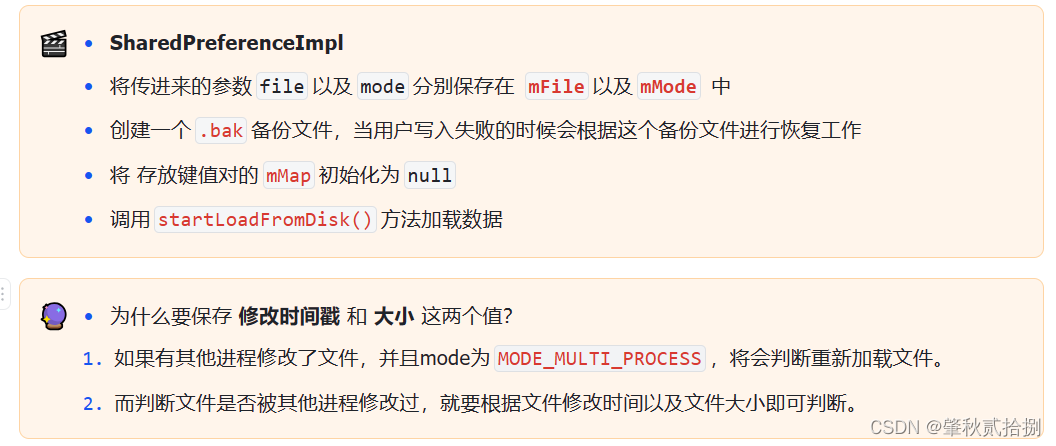
7.2 构造SharedPreferenceImpl
- 构造
SharedPreferenceImpl类 - 调用
startLoadFromDisk()来加载数据 - SharedPreference开启一个异步线程来异步加载数据,调用了
loadFromDisk()方法。 - 如果有备份文件,直接使用备份文件进行回滚。
- 如果是第一次调用getSharedPreferences方法的话(构造的情况下),会从磁盘中加载数据( Os.stat() )
- 将解析到的 键值对数据 保存在map中。
- 将文件的修改时间戳以及大小分别保存在mStatTimestamp以及mStatSize中。
- 数据加载完后,调用
notifyAll()方法唤醒其他等待线程。
// SharedPreferencesImpl.java
// 构造方法
SharedPreferencesImpl(File file, int mode) {
mFile = file;
// 创建灾备文件,命名为prefsFile.getPath() + ".bak"
mBackupFile = makeBackupFile(file);
mMode = mode;
// mLoaded代表是否已经加载完数据
mLoaded = false;
// 解析 xml 文件得到的键值对就存放在mMap中
mMap = null;
// 7.顾名思义,这个方法用于加载 mFile 这个磁盘上的 xml 文件
startLoadFromDisk();
}
// 创建灾备文件,用于当用户写入失败的时候恢复数据
private static File makeBackupFile(File prefsFile) {
return new File(prefsFile.getPath() + ".bak");
}
// SharedPreferencesImpl.java
private void startLoadFromDisk() {
synchronized (this) {
mLoaded = false;
}
//注意:这里我们可以看出,SharedPreferences 是通过开启一个线程来异步加载数据的
new Thread("SharedPreferencesImpl-load") {
public void run() {
// 8.这个方法才是真正负责从磁盘上读取 xml 文件数据
loadFromDisk();
}
}.start();
}
private void loadFromDisk() {
synchronized (SharedPreferencesImpl.this) {
// 如果正在加载数据,直接返回
if (mLoaded) {
return;
}
// 9.如果备份文件存在,删除原文件,把备份文件重命名为原文件的名字
// 我们称这种行为叫做回滚
if (mBackupFile.exists()) {
mFile.delete();
mBackupFile.renameTo(mFile);
}
}
// Debugging
if (mFile.exists() && !mFile.canRead()) {
Log.w(TAG, "Attempt to read preferences file " + mFile + " without permission");
}
Map map = null;
StructStat stat = null;
try {
// 获取文件信息,包括文件修改时间,文件大小等
stat = Os.stat(mFile.getPath());//10.磁盘加载数据
if (mFile.canRead()) {
BufferedInputStream str = null;
try {
// 读取数据并且将数据解析为jia
str = new BufferedInputStream(
new FileInputStream(mFile), *);
map = XmlUtils.readMapXml(str);
} catch (XmlPullParserException | IOException e) {
Log.w(TAG, "getSharedPreferences", e);
} finally {
IoUtils.closeQuietly(str);
}
}
} catch (ErrnoException e) {
/* ignore */
}
synchronized (SharedPreferencesImpl.this) {
// 加载数据成功,设置 mLoaded 为 true
mLoaded = true;
if (map != null) {
// 11.将解析得到的键值对数据赋值给 mMap
mMap = map;
// 12.将文件的修改时间戳保存到 mStatTimestamp 中
mStatTimestamp = stat.st_mtime;
// 12.将文件的大小保存到 mStatSize 中
mStatSize = stat.st_size;
} else {
mMap = new HashMap<>();
}
// 13.通知唤醒所有等待的线程
notifyAll();
}
}
7.3 getXxx的源码
- 这里通过getString来分析这个问题
- 通过
synchronized关键字保证getString方法是线程安全的。 - 调用
awaitLoadedLocked来判断数据是否读取完毕了。(里面判断mLoaded是否为true,为true,表示SharedPreferenceImpl中已经加载完数据了) - 从内存中的mMap中根据传入的key读取Value。

@Nullable
public String getString(String key, @Nullable String defValue) {
// 1.synchronize 关键字用于保证 getString 方法是线程安全的
synchronized (this) {
// 2.方法 awaitLoadedLocked() 用于确保加载完数据并保存到 mMap 中才进行数据读取
awaitLoadedLocked();
// 根据 key 从 mMap中获取 value
String v = (String)mMap.get(key);
// 如果 value 不为 null,返回 value,如果为 null,返回默认值
return v != null ? v : defValue;
}
}
private void awaitLoadedLocked() {
if (!mLoaded) {
// Raise an explicit StrictMode onReadFromDisk for this
// thread, since the real read will be in a different
// thread and otherwise ignored by StrictMode.
BlockGuard.getThreadPolicy().onReadFromDisk();
}
// 前面我们说过,mLoaded 代表数据是否已经加载完毕
while (!mLoaded) {
try {
// 等待数据加载完成之后才返回继续执行代码
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException unused) {
}
}
}
7.4 putXxx的源码
- 说到写操作方法,首先想到的是通过
sharedPreferences.edit()方法返回的SharedPreferences.Editor - 所有对SharedPreferences的写操作都是基于这个Editor类的。(在Android系统中,Editor是一个接口类,它的具体实现类是EditorImpl)
- 写操作都是线程安全的(使用了synchronized关键字)
- 对 键值对数据 的增删操作 都会先保存在
mModified中。(而不是直接对SharedPreferences.mMap进行操作) - mModified会在
commit/apply方法中起到同步内存SharedPreferences.mMap以及磁盘数据的作用。
public final class EditorImpl implements Editor {
// putXxx/remove/clear等写操作方法都不是直接操作 mMap 的,而是将所有
// 的写操作先记录在 mModified 中,等到 commit/apply 方法被调用,才会将
// 所有写操作同步到 内存中的 mMap 以及磁盘中
private final Map<String, Object> mModified = Maps.newHashMap();
//
private boolean mClear = false;
public Editor putString(String key, @Nullable String value) {
synchronized (this) {
mModified.put(key, value);
return this;
}
}
public Editor putStringSet(String key, @Nullable Set<String> values) {
synchronized (this) {
mModified.put(key, (values == null) ? null : new HashSet<String>(values));
return this;
}
}
public Editor putInt(String key, int value) {
synchronized (this) {
mModified.put(key, value);
return this;
}
}
public Editor putLong(String key, long value) {
synchronized (this) {
mModified.put(key, value);
return this;
}
}
public Editor putFloat(String key, float value) {
synchronized (this) {
mModified.put(key, value);
return this;
}
}
public Editor putBoolean(String key, boolean value) {
synchronized (this) {
mModified.put(key, value);
return this;
}
}
public Editor remove(String key) {
synchronized (this) {
mModified.put(key, this);
return this;
}
}
......
其他方法
......
}
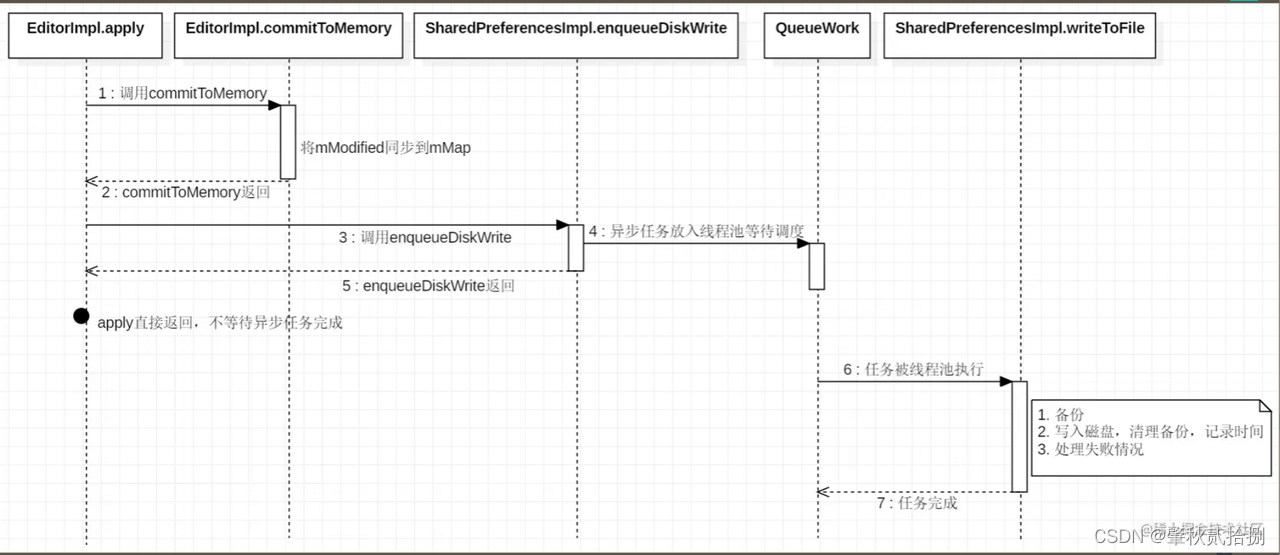
7.5 commit()同步写磁盘源码
- 首先通过
commitToMemory()方法,将mModified同步写入到内存的SharedPreferences.mMap中。 - 调用enqueueDiskWrite方法将数据写入到磁盘中。
- 同步等待写磁盘操作完成。(这是commit()方法会同步阻塞等待的原因)
- 通知监听者(可以通过registerOnSharedPreferenceChangeListener方法注册监听)
- 返回执行结果(布尔类型)
public boolean commit() {
// 前面我们分析 putXxx 的时候说过,写操作的记录是存放在 mModified 中的
// 1.在这里,commitToMemory() 方法就负责 将 mModified 保存的 写记录同步到内存中的 mMap 中
// 并且返回一个 MemoryCommitResult 对象
MemoryCommitResult mcr = commitToMemory();
// 2.enqueueDiskWrite 方法负责将 数据落地到磁盘 上
SharedPreferencesImpl.this.enqueueDiskWrite( mcr, null /* sync write on this thread okay */);
try {
// 3.同步等待数据落地磁盘工作完成 才返回
mcr.writtenToDiskLatch.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
return false;
}
// 通知观察者
notifyListeners(mcr);
return mcr.writeToDiskResult;
}
7.5.1 CommitToMemory
-
首先通过
commitToMemory()方法,将mModified同步到内存的SharedPreferences.mMap中。 -
具体做了什么
- mDiskWritesInFlight自增加1。
- 将mMap赋值给mcr.mapToWriteToDisk 。(那么它代表的就是最终要写入磁盘的数据,指向了mMap)
- 判断mClear的值,如果为true,清空mMap。(是否调用clear())
- 同步mModified数据到mMap中,然后清空mModified。
- 最后返回一个MemoryCommitResult对象。(它的参数mapToWriteToDisk指向了最终需要写入磁盘的mMap对象)

sharedPreferences.edit()
.putString("key1", "value1") // key1 不会被 clear 掉,commit 之后依旧会被写入磁盘中
.clear()
.commit();复制代码
private MemoryCommitResult commitToMemory() {
MemoryCommitResult mcr = new MemoryCommitResult();
synchronized (SharedPreferencesImpl.this) {
// We optimistically don't make a deep copy until
// a memory commit comes in when we're already
// writing to disk.
if (mDiskWritesInFlight > 0) {
// We can't modify our mMap as a currently
// in-flight write owns it. Clone it before
// modifying it.
// noinspection unchecked
mMap = new HashMap<String, Object>(mMap);
}
// 2.将 mMap 赋值给 mcr.mapToWriteToDisk,mcr.mapToWriteToDisk 指向的就是最终写入磁盘的数据
mcr.mapToWriteToDisk = mMap;
// 1.mDiskWritesInFlight 代表的是“此时需要将数据写入磁盘,但还未处理或未处理完成的次数”
// 1.将 mDiskWritesInFlight 自增1(这里是唯一会增加 mDiskWritesInFlight 的地方)
mDiskWritesInFlight++;
boolean hasListeners = mListeners.size() > 0;
if (hasListeners) {
mcr.keysModified = new ArrayList<String>();
mcr.listeners =
new HashSet<OnSharedPreferenceChangeListener>(mListeners.keySet());
}
synchronized (this) {
// 3.只有调用clear()方法,mClear才为 true
if (mClear) {
if (!mMap.isEmpty()) {
mcr.changesMade = true;
// 当 mClear 为 true,清空 mMap
mMap.clear();
}
mClear = false;
}
// 4.遍历 mModified
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> e : mModified.entrySet()) {
String k = e.getKey(); // 获取 key
Object v = e.getValue(); // 获取 value
// 当 value 的值是 "this" 或者 null,将对应 key 的键值对数据从 mMap 中移除
if (v == this || v == null) {
if (!mMap.containsKey(k)) {
continue;
}
mMap.remove(k);
} else { // 否则,更新或者添加键值对数据
if (mMap.containsKey(k)) {
Object existingValue = mMap.get(k);
if (existingValue != null && existingValue.equals(v)) {
continue;
}
}
mMap.put(k, v);
}
mcr.changesMade = true;
if (hasListeners) {
mcr.keysModified.add(k);
}
}
// 将 mModified 同步到 mMap 之后,清空 mModified 历史记录
mModified.clear();
}
}
//5.返回
return mcr;
}
7.5.2 enqueueDiskWrite
- 调用
enqueueDiskWrite方法将数据写入到磁盘中。
- 创建一个Runnable对象,负责写磁盘操作。
- 调用
writeToFile方法写入磁盘 - 写入磁盘后,将mDiskWritesInflight自减1,代表写磁盘的需求减少1个。
private void enqueueDiskWrite(final MemoryCommitResult mcr, final Runnable postWriteRunnable) {
// 创建一个 Runnable 对象 负责写磁盘操作
final Runnable writeToDiskRunnable = new Runnable() {
public void run() {
synchronized (mWritingToDiskLock) {
// 顾名思义了,这就是最终通过文件操作将数据写入磁盘的方法了
writeToFile(mcr);
}
synchronized (SharedPreferencesImpl.this) {
// 写入磁盘后,将 mDiskWritesInFlight 自减1,代表写磁盘的需求减少一个
mDiskWritesInFlight--;
}
if (postWriteRunnable != null) {
// 执行 postWriteRunnable(提示,在 apply 中,postWriteRunnable 才不为 null)
postWriteRunnable.run();
}
}
};
// 如果传进的参数 postWriteRunnable 为 null,那么 isFromSyncCommit 为 true
// 温馨提示:从上面的 commit() 方法源码中,可以看出调用 commit() 方法传入的 postWriteRunnable 为 null
final boolean isFromSyncCommit = (postWriteRunnable == null);
// Typical #commit() path with fewer allocations, doing a write on the current thread.
if (isFromSyncCommit) {
boolean wasEmpty = false;
synchronized (SharedPreferencesImpl.this) {
// 如果此时只有一个 commit 请求(注意,是 commit 请求,而不是 apply )未处理,那么 wasEmpty 为 true
wasEmpty = mDiskWritesInFlight == 1;
}
if (wasEmpty) {
// 当只有一个 commit 请求未处理,那么无需开启线程进行处理,直接在本线程执行 writeToDiskRunnable 即可
writeToDiskRunnable.run();
return;
}
}
// 将 writeToDiskRunnable 方法线程池中执行
// 程序执行到这里,有两种可能:
// 1. 调用的是 commit() 方法,并且当前不只有一个 commit 请求未处理(多个)
// 2. 调用的是 apply() 方法
QueuedWork.singleThreadExecutor().execute(writeToDiskRunnable);
}
7.5.3 writeToFile
- 先把已存在的老的 SP 文件重命名(加“.bak”后缀),然后删除老的 SP 文件,这相当于做了备份(灾备)
- 向
mFile中一次性写入 所有键值对数据,即mcr.mapToWriteToDisk(这就是commitToMemory所说的保存了 所有键值对数据的字段) 一次性写入到磁盘。 - 如果写入成功则删除备份(灾备)文件,同时记录了这次同步的时间
- 如果往磁盘写入数据失败,则删除这个半成品的 SP 文件
private void writeToFile(MemoryCommitResult mcr) {
// Rename the current file so it may be used as a backup during the next read
if (mFile.exists()) {
if (!mcr.changesMade) {
// If the file already exists, but no changes were
// made to the underlying map, it's wasteful to
// re-write the file. Return as if we wrote it
// out.
mcr.setDiskWriteResult(true);
return;
}
if (!mBackupFile.exists()) {
if (!mFile.renameTo(mBackupFile)) {
Log.e(TAG, "Couldn't rename file " + mFile
+ " to backup file " + mBackupFile);
mcr.setDiskWriteResult(false);
return;
}
} else {
mFile.delete();
}
}
// Attempt to write the file, delete the backup and return true as atomically as
// possible. If any exception occurs, delete the new file; next time we will restore
// from the backup.
try {
FileOutputStream str = createFileOutputStream(mFile);
if (str == null) {
mcr.setDiskWriteResult(false);
return;
}
XmlUtils.writeMapXml(mcr.mapToWriteToDisk, str);
FileUtils.sync(str);
str.close();
ContextImpl.setFilePermissionsFromMode(mFile.getPath(), mMode, 0);
try {
final StructStat stat = Libcore.os.stat(mFile.getPath());
synchronized (this) {
mStatTimestamp = stat.st_mtime;
mStatSize = stat.st_size;
}
} catch (ErrnoException e) {
// Do nothing
}
// Writing was successful, delete the backup file if there is one.
mBackupFile.delete();
mcr.setDiskWriteResult(true);
return;
} catch (XmlPullParserException e) {
Log.w(TAG, "writeToFile: Got exception:", e);
} catch (IOException e) {
Log.w(TAG, "writeToFile: Got exception:", e);
}
// Clean up an unsuccessfully written file
if (mFile.exists()) {
if (!mFile.delete()) {
Log.e(TAG, "Couldn't clean up partially-written file " + mFile);
}
}
mcr.setDiskWriteResult(false);
}
7.6 apply()异步写磁盘源码
- 首先通过
commitToMemory()方法,将mModified同步写入到内存的SharedPreferences.mMap中。 - 调用
enqueueDiskWrite方法将数据异步写入到磁盘中。(可以查看上面的源码)
public void apply() {
// 将 mModified 保存的写记录同步到内存中的 mMap 中,并且返回一个 MemoryCommitResult 对象
final MemoryCommitResult mcr = commitToMemory();
final Runnable awaitCommit = new Runnable() {
public void run() {
try {
mcr.writtenToDiskLatch.await();
} catch (InterruptedException ignored) {
}
}
};
QueuedWork.add(awaitCommit);
Runnable postWriteRunnable = new Runnable() {
public void run() {
awaitCommit.run();
QueuedWork.remove(awaitCommit);
}
};
// 将数据落地到磁盘上,注意,传入的 postWriteRunnable 参数不为 null,所以在
// enqueueDiskWrite 方法中会开启子线程异步将数据写入到磁盘中
SharedPreferencesImpl.this.enqueueDiskWrite(mcr, postWriteRunnable);
// Okay to notify the listeners before it's hit disk
// because the listeners should always get the same
// SharedPreferences instance back, which has the
// changes reflected in memory.
notifyListeners(mcr);
}
8. 相关问题
8.1 commit与apply的区别?
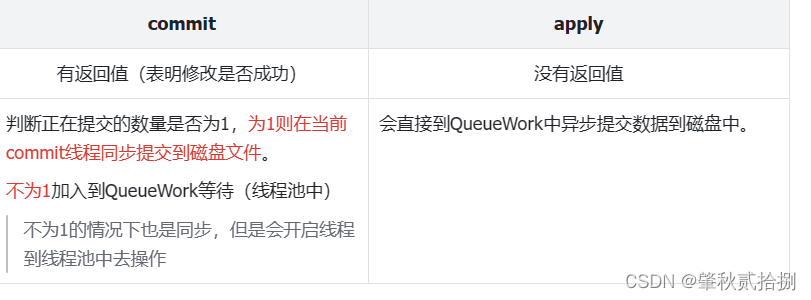
- 不过它们将mModified中的数据提交到内存当中都是一样的,都是同步的过程。
- 调用enqueueDiskWrite时传入的参数就决定了它们是在同步还是异步
- apply:
// 将数据落地到磁盘上,注意,传入的 postWriteRunnable 参数不为 null,所以在
// enqueueDiskWrite 方法中会开启子线程异步将数据写入到磁盘中
SharedPreferencesImpl.this.enqueueDiskWrite(mcr, postWriteRunnable);
8.2 apply何时被写入磁盘?

8.3 为什么采用ArrayMap这种数据结构、
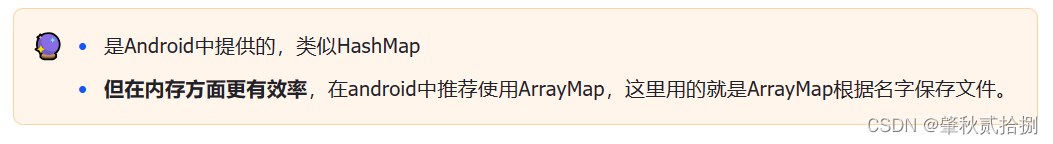
8.4 SharedPreference如何保证线程安全?

8.5 ANR问题

8.6 注意事项

val key = "DataStore"
val sp = getSharedPreferences("文件名", Context.MODE_PRIVATE)
sp.edit { putInt(key, 0) } // 使用 Int 类型的数据覆盖相同的 key
sp.getString(key, ""); // 使用相同的 key 读取 Sting 类型的数据
8.7 Android8.0对SP的优化

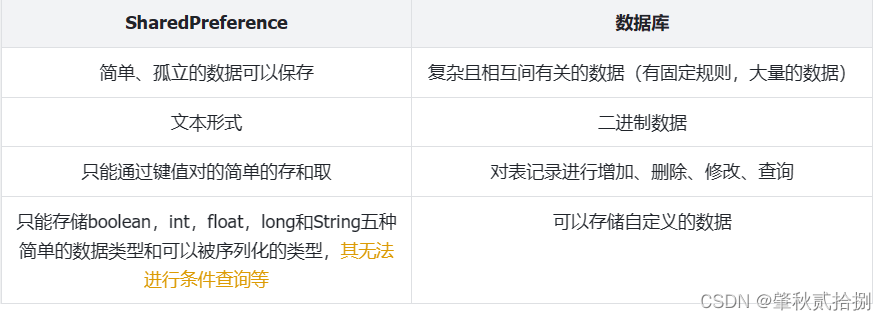
8.8 SharedPreference 和 数据库 区别
8.9 为什么SP不是进程安全的?

8.10 SharedPreference的缺点
- 加载缓慢:SharedPreferences 文件的加载使用了异步线程,而且加载线程并没有设置优先级,如果这个时候读取数据就需要等待文件加载线程的结束。这就导致主线程等待低优先线程锁的问题,比如一个 100KB 的 SP 文件读取等待时间大约需要 50 ~ 100ms。
- 跨进程不安全:由于没有使用跨进程的锁,就算使用 MODE_MULTI_PROCESS,SharedPreferences 在跨进程频繁读写有可能导致数据全部丢失。根据
- 造成程序卡顿:由于提供了异步落盘的 apply 机制,在崩溃或者其它一些异常情况可能会导致数据丢失。所以当应用收到系统广播,或者被调用onPause等一些时机,系统会强制把所有的SharedPreferences对象的数据落地到磁盘。如果没有落地完成,这时候主线程会被一直阻塞。这样非常容易造成卡顿,甚至是ANR。