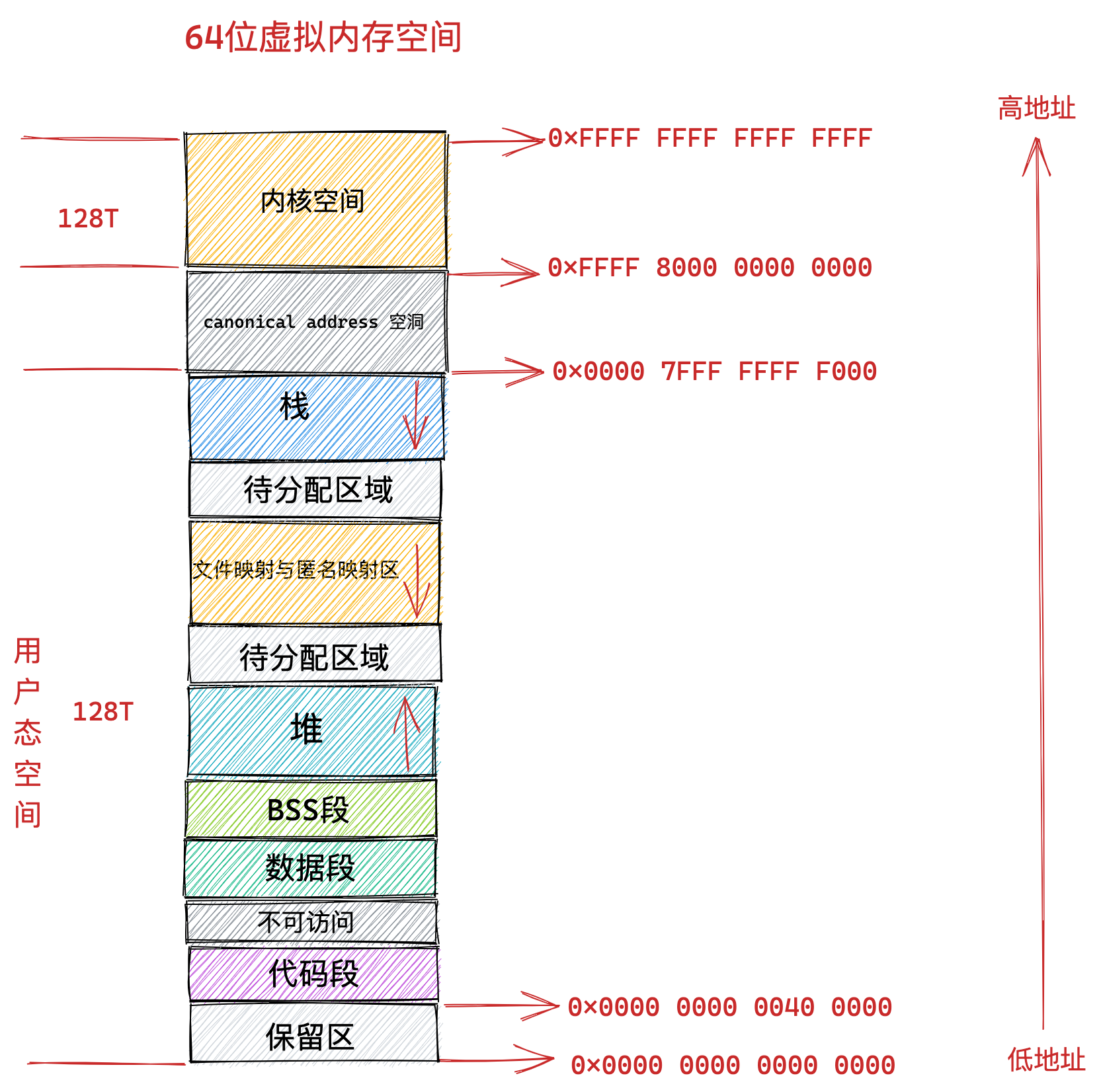
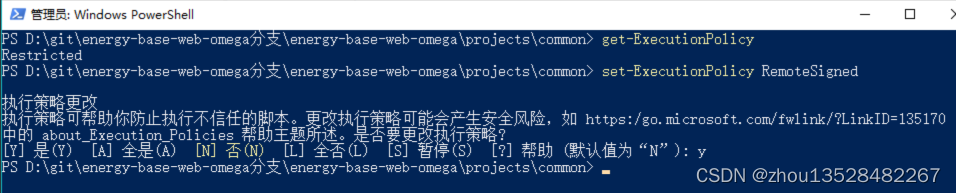
Adam优化器的工作方式是通过不断更新一阶矩估计和二阶矩估计来自适应地调整学习率,并利用动量法来加速训练过程。这种方式可以在不同的参数更新方向和尺度上进行自适应调整,从而更有效地优化模型。
- https://arxiv.org/pdf/1412.6980.pdf
参数
这些参数在Adam优化器中用于计算参数的更新值,并最终更新模型的参数。具体的计算公式可以查阅Adam优化器的算法原理。
x:参数(权重和偏置)的值。对于Adam优化器而言,这是模型的可学习参数,通过优化算法进行更新。g1:梯度向量。该向量包含了每个参数对应的梯度值,用于计算梯度的一阶矩估计。g2:梯度平方向量。该向量包含了每个参数对应的梯度平方值,用于计算梯度的二阶矩估计。m:一阶矩向量。该向量包含了每个参数对应的一阶矩估计值,将梯度的一阶矩估计累加,用于计算参数更新的动力学部分。v:二阶矩向量。该向量包含了每个参数对应的二阶矩估计值,将梯度平方的二阶矩估计累加,用于计算参数更新的动力学部分。mh:偏置修正的一阶矩向量。由于初始时m和v的值都接近于0,导致在迭代初期时估计的动量和学习率偏向较高。为了解决这个问题,采用了偏置修正,即每个参数对应的一阶矩估计值除以一个衰减因子,用于修正初始阶段的动量偏向。vh:偏置修正的二阶矩向量。该向量类似于mh,但是用于修正二阶矩估计的初始阶段偏向。
float * x = (float *)opt->adam.x->data; // view of the parameters
float * g1 = (float *)opt->adam.g1->data; // gradient
float * g2 = (float *)opt->adam.g2->data; // gradient squared
float * m = (float *)opt->adam.m->data; // first moment
float * v = (float *)opt->adam.v->data; // second moment
float * mh = (float *)opt->adam.mh->data; // first moment hat
float * vh = (float *)opt->adam.vh->data; // second moment hat
-
初始化变量:Adam优化器会初始化两个变量m和v,分别用来存储梯度的一阶矩估计和二阶矩估计。这两个变量的维度与模型的参数维度相同。
-
计算梯度:在每个训练批次中,根据当前的参数值计算梯度。
-
更新一阶矩估计:通过指数加权移动平均的方式更新一阶矩估计m。具体而言,对于每个参数的梯度,将其乘以一个衰减系数β1(通常取值为0.9),然后加到对应的一阶矩估计m上。
-
更新二阶矩估计:通过指数加权移动平均的方式更新二阶矩估计v。具体而言,对于每个参数的梯度的平方,将其乘以一个衰减系数β2(通常取值为0.999),然后加到对应的二阶矩估计v上。
-
偏差修正:由于初始时m和v的值都为0,会导致它们在训练初期偏向于0。为了修正这个偏差,需要进行偏差修正操作。具体而言,将一阶矩估计m和二阶矩估计v除以1减去β1和1减去β2的指数衰减权重。
-
更新参数:根据一阶矩估计m和二阶矩估计v,以及学习率α,更新模型的参数。具体而言,对于每个参数,将其当前值减去学习率乘以一阶矩估计m除以二阶矩估计v的平方根。
-
重复步骤2-6:重复执行步骤2-6,直到达到停止条件(如达到最大迭代次数或梯度收敛)。
- PS:需要优化的params
ADAM
//
// ADAM
//
// ref: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1412.6980.pdf
//
static enum ggml_opt_result ggml_opt_adam(
struct ggml_context * ctx,
struct ggml_opt_context * opt,
struct ggml_opt_params params,
struct ggml_tensor * f,
struct ggml_cgraph * gf,
struct ggml_cgraph * gb) {
GGML_ASSERT(ggml_is_scalar(f));
// these will store the parameters we want to optimize
struct ggml_tensor * ps[GGML_MAX_PARAMS];
int np = 0;
int nx = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < gf->n_nodes; ++i) {
if (gf->nodes[i]->is_param) {
GGML_PRINT_DEBUG("found param %d: grad->op = %d\n", np, gf->nodes[i]->grad->op);
GGML_ASSERT(np < GGML_MAX_PARAMS);
ps[np++] = gf->nodes[i];
nx += ggml_nelements(gf->nodes[i]);
}
}
if ((opt->params.type != params.type) || (opt->nx != nx) || (opt->params.past != params.past)) {
int iter = opt->iter;
ggml_opt_init(opt->ctx, opt, params, nx);
opt->iter = iter;
}
// constants
const float sched = params.adam.sched;
const float decay = params.adam.decay * sched;
const float alpha = params.adam.alpha * sched;
const float beta1 = params.adam.beta1;
const float beta2 = params.adam.beta2;
const float eps = params.adam.eps;
float * x = opt->adam.x->data; // view of the parameters
float * g1 = opt->adam.g1->data; // gradient
float * g2 = opt->adam.g2->data; // gradient squared
float * m = opt->adam.m->data; // first moment
float * v = opt->adam.v->data; // second moment
float * mh = opt->adam.mh->data; // first moment hat
float * vh = opt->adam.vh->data; // second moment hat
float * pf = params.past > 0 ? opt->adam.pf->data : NULL; // past function values
// update view
ggml_opt_get_params(np, ps, x);
// compute the function value
ggml_graph_reset (gf);
ggml_set_f32 (f->grad, 1.0f);
ggml_graph_compute_with_ctx(ctx, gb, params.n_threads);
opt->adam.fx_prev = ggml_get_f32_1d(f, 0);
opt->adam.fx_best = opt->adam.fx_prev;
if (pf) {
pf[opt->iter % params.past] = opt->adam.fx_prev;
}
// initialize
if (opt->just_initialized) {
opt->adam.n_no_improvement = 0;
opt->just_initialized = false;
}
float * fx_best = &opt->adam.fx_best;
float * fx_prev = &opt->adam.fx_prev;
int * n_no_improvement = &opt->adam.n_no_improvement;
int iter0 = opt->iter;
// run the optimizer
for (int t = 0; t < params.adam.n_iter; ++t) {
opt->iter = iter0 + t + 1;
GGML_PRINT_DEBUG ("=== iter %d ===\n", t);
GGML_PRINT_DEBUG ("f = %10.6f\n", ggml_get_f32_1d(f, 0));
GGML_PRINT_DEBUG_5("df/dx0 = %10.6f\n", ggml_get_f32_1d(ps[0]->grad, 0));
GGML_PRINT_DEBUG_5("df/dx1 = %10.6f\n", ggml_get_f32_1d(ps[1]->grad, 0));
for (int i = 0; i < np; ++i) {
GGML_PRINT_DEBUG("param %d: %10.6f, g = %10.6f\n", i,
ggml_get_f32_1d(ps[i], 0), ggml_get_f32_1d(ps[i]->grad, 0));
}
const int64_t t_start_wall = ggml_time_us();
const int64_t t_start_cpu = ggml_cycles();
UNUSED(t_start_wall);
UNUSED(t_start_cpu);
{
// update the gradient
ggml_opt_get_grad(np, ps, g1);
// m_t = beta1*m_t-1 + (1 - beta1)*g_t
ggml_vec_scale_f32(nx, m, beta1);
ggml_vec_mad_f32 (nx, m, g1, 1.0f - beta1);
// g2 = g1^2
ggml_vec_sqr_f32 (nx, g2, g1);
// v_t = beta2*v_t-1 + (1 - beta2)*g_t^2
ggml_vec_scale_f32(nx, v, beta2);
ggml_vec_mad_f32 (nx, v, g2, 1.0f - beta2);
// m^hat = m_t / (1 - beta1^t)
// v^hat = v_t / (1 - beta2^t)
// x_t = x_t-1 - sched*(alpha*m^hat/(sqrt(v^hat) + eps) + decay*x_t-1)
// x_t = x_t-1 - sched*alpha*m^hat/(sqrt(v^hat) + eps) - sched*decay*x_t-1
// x_t = x_t-1*(1-sched*decay) - sched*alpha*m^hat/(sqrt(v^hat) + eps)
// x_t = x_t-1*(1-sched*decay) + sched*decay*(-alpha/decay)*m^hat/(sqrt(v^hat) + eps)
// x_t = mix(x_t-1, (-alpha/decay)*m^hat/(sqrt(v^hat) + eps), sched*decay)
ggml_vec_cpy_f32 (nx, mh, m);
ggml_vec_cpy_f32 (nx, vh, v);
ggml_vec_scale_f32(nx, mh, alpha/(1.0f - powf(beta1, opt->iter)));
ggml_vec_scale_f32(nx, vh, 1.0f/(1.0f - powf(beta2, opt->iter)));
ggml_vec_sqrt_f32 (nx, vh, vh);
ggml_vec_acc1_f32 (nx, vh, eps);
ggml_vec_div_f32 (nx, mh, mh, vh);
ggml_vec_scale_f32(nx, x, 1.0f - decay);
ggml_vec_sub_f32 (nx, x, x, mh);
// update the parameters
ggml_opt_set_params(np, ps, x);
}
ggml_graph_reset (gf);
ggml_set_f32 (f->grad, 1.0f);
ggml_graph_compute_with_ctx(ctx, gb, params.n_threads);
const float fx = ggml_get_f32_1d(f, 0);
// check convergence
if (fabsf(fx - fx_prev[0])/fx < params.adam.eps_f) {
GGML_PRINT_DEBUG("converged\n");
return GGML_OPT_OK;
}
// delta-based convergence test
if (pf != NULL) {
// need at least params.past iterations to start checking for convergence
if (params.past <= iter0 + t) {
const float rate = (pf[(iter0 + t)%params.past] - fx)/fx;
if (fabsf(rate) < params.delta) {
return GGML_OPT_OK;
}
}
pf[(iter0 + t)%params.past] = fx;
}
// check for improvement
if (params.max_no_improvement > 0) {
if (fx_best[0] > fx) {
fx_best[0] = fx;
n_no_improvement[0] = 0;
} else {
++n_no_improvement[0];
if (n_no_improvement[0] >= params.max_no_improvement) {
return GGML_OPT_OK;
}
}
}
fx_prev[0] = fx;
{
const int64_t t_end_cpu = ggml_cycles();
GGML_PRINT_DEBUG("time iter: %5.3f s\n", ((float)(t_end_cpu - t_start_cpu))/CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
UNUSED(t_end_cpu);
const int64_t t_end_wall = ggml_time_us();
GGML_PRINT_DEBUG("wall time iter: %5.3f s\n", (t_end_wall - t_start_wall)/1e6);
UNUSED(t_end_wall);
}
}
return GGML_OPT_DID_NOT_CONVERGE;
}
CG
- https://github1s.com/ggerganov/ggml/blob/HEAD/src/ggml.c#L18414-L18610
CODE
#include "ggml.h"
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cassert>
#include <random>
#include "ggml.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <random>
#define MAX_NARGS 2
#if defined(__GNUC__)
#pragma GCC diagnostic ignored "-Wdouble-promotion"
#endif
//
// logging
//
#define GGML_DEBUG 0
#if (GGML_DEBUG >= 1)
#define GGML_PRINT_DEBUG(...) printf(__VA_ARGS__)
#else
#define GGML_PRINT_DEBUG(...)
#endif
#if (GGML_DEBUG >= 5)
#define GGML_PRINT_DEBUG_5(...) printf(__VA_ARGS__)
#else
#define GGML_PRINT_DEBUG_5(...)
#endif
#if (GGML_DEBUG >= 10)
#define GGML_PRINT_DEBUG_10(...) printf(__VA_ARGS__)
#else
#define GGML_PRINT_DEBUG_10(...)
#endif
#define GGML_PRINT(...) printf(__VA_ARGS__)
float frand(void) {
return (float)rand()/(float)RAND_MAX;
}
int irand(int n) {
return rand()%n;
}
void get_random_dims(int64_t * dims, int ndims) {
dims[0] = dims[1] = dims[2] = dims[3] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < ndims; i++) {
dims[i] = 1 + irand(4);
}
}
void get_random_dims_minmax(int64_t * dims, int ndims, int min, int max) {
dims[0] = dims[1] = dims[2] = dims[3] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < ndims; i++) {
dims[i] = min + irand(max-min);
}
}
struct ggml_tensor * get_random_tensor(
struct ggml_context * ctx0,
int ndims,
int64_t ne[],
float fmin,
float fmax) {
struct ggml_tensor * result = ggml_new_tensor(ctx0, GGML_TYPE_F32, ndims, ne);
switch (ndims) {
case 1:
for (int i0 = 0; i0 < ne[0]; i0++) {
((float *)result->data)[i0] = frand()*(fmax - fmin) + fmin;
}
break;
case 2:
for (int i1 = 0; i1 < ne[1]; i1++) {
for (int i0 = 0; i0 < ne[0]; i0++) {
((float *)result->data)[i1*ne[0] + i0] = frand()*(fmax - fmin) + fmin;
}
}
break;
case 3:
for (int i2 = 0; i2 < ne[2]; i2++) {
for (int i1 = 0; i1 < ne[1]; i1++) {
for (int i0 = 0; i0 < ne[0]; i0++) {
((float *)result->data)[i2*ne[1]*ne[0] + i1*ne[0] + i0] = frand()*(fmax - fmin) + fmin;
}
}
}
break;
case 4:
for (int i3 = 0; i3 < ne[3]; i3++) {
for (int i2 = 0; i2 < ne[2]; i2++) {
for (int i1 = 0; i1 < ne[1]; i1++) {
for (int i0 = 0; i0 < ne[0]; i0++) {
((float *)result->data)[i3*ne[2]*ne[1]*ne[0] + i2*ne[1]*ne[0] + i1*ne[0] + i0] = frand()*(fmax - fmin) + fmin;
}
}
}
}
break;
default:
assert(false);
};
return result;
}
float get_element(const struct ggml_tensor * t, int idx) {
return ((float *)t->data)[idx];
}
void set_element(struct ggml_tensor * t, int idx, float value) {
((float *)t->data)[idx] = value;
}
float run(int val){
return 0.1f;
}
struct ggml_init_params params = {
/* .mem_size = */ 1024*1024*10, // 设置内存大小为1GB
/* .mem_buffer = */ NULL, // 设置内存缓冲区为空
/* .no_alloc = */ false, // 允许内存分配
};
struct ggml_context * ctx = ggml_init(params); // 创建一个ggml_context结构体对象
int64_t ne1[4] = {2, 512, 1, 1};
int64_t ne2[4] = {512, 256, 1, 1};
int64_t ne3[4] = {1, 256, 1, 1};
int64_t ne4[4] = {256, 3, 1, 1};
int64_t ne5[4] = {3, 1, 1, 1};
int64_t mid_w[4] = {256, 256, 1, 1};
int64_t mid_b[4] = {256, 1, 1, 1};
struct res {ggml_cgraph ge;ggml_tensor * e;ggml_tensor * output;ggml_tensor * intput;ggml_tensor * target;};
res hf_getcompute_graph(){
struct ggml_tensor * X = ggml_new_tensor_1d(ctx, GGML_TYPE_F32, 2);// struct ggml_tensor * X = get_random_tensor(ctx, 2, ne1, -1, +1); // 创建一个2维随机张量a
struct ggml_tensor * target = ggml_new_tensor_1d(ctx, GGML_TYPE_F32, 3);
struct ggml_tensor * proj = get_random_tensor(ctx, 2, ne1, -1, +1);
struct ggml_tensor * fc1_weight = get_random_tensor(ctx, 2, ne2, -1, +1);
struct ggml_tensor * fc1_bias = get_random_tensor(ctx, 2, ne3, -1, +1);
struct ggml_tensor * fcout_weight = get_random_tensor(ctx, 2, ne4, -1, +1);
struct ggml_tensor * fcout_bias = get_random_tensor(ctx, 2, ne5, -1, +1);
struct ggml_tensor * fc3_weight = get_random_tensor(ctx, 2, mid_w, -1, +1);
struct ggml_tensor * fc3_bias = get_random_tensor(ctx, 2, mid_b, -1, +1);
struct ggml_tensor * fc4_weight = get_random_tensor(ctx, 2, mid_w, -1, +1);
struct ggml_tensor * fc4_bias = get_random_tensor(ctx, 2, mid_b, -1, +1);
struct ggml_tensor * fc5_weight = get_random_tensor(ctx, 2, mid_w, -1, +1);
struct ggml_tensor * fc5_bias = get_random_tensor(ctx, 2, mid_b, -1, +1);
ggml_set_param(ctx, fcout_weight); ggml_set_param(ctx, fcout_bias); ggml_set_param(ctx, fc3_weight); ggml_set_param(ctx, fc3_bias);
ggml_set_param(ctx, fc4_weight); ggml_set_param(ctx, fc4_bias); ggml_set_param(ctx, fc5_weight); ggml_set_param(ctx, fc5_bias);
ggml_tensor * proj_of_x = ggml_mul_mat(ctx, proj,X); // 512*1
ggml_tensor * fc1 = ggml_add(ctx, ggml_mul_mat(ctx, proj_of_x,fc1_weight), fc1_bias); // 1*256
ggml_tensor * fc1_ = ggml_view_2d(ctx,fc1,256,1,4*256,0);//ggml_transpose(ctx,fc1); // 256*1
// ggml_tensor * fc2 = ggml_mul_mat(ctx,fc3_weight,fc1_); // 256*1 ggml_tensor * fc2 = ggml_mul_mat(ctx,fc1_,fc3_weight); // 256*1 & 256*256 =>1*256
ggml_tensor * fc3 = ggml_add(ctx, ggml_mul_mat(ctx, fc3_weight, ggml_relu(ctx, fc1_)), fc3_bias);
ggml_tensor * fc4 = ggml_add(ctx, ggml_mul_mat(ctx, fc4_weight, ggml_relu(ctx, fc3)), fc4_bias);
ggml_tensor * fc5 = ggml_add(ctx, ggml_mul_mat(ctx, fc5_weight, ggml_relu(ctx, fc4)), fc5_bias);
ggml_tensor * fcout = ggml_add(ctx, ggml_mul_mat(ctx, fcout_weight, ggml_relu(ctx, fc5)), fcout_bias);// 3*1
ggml_tensor * fcout_ = ggml_sub(ctx,fcout,target);
struct ggml_tensor * e = ggml_sum(ctx, ggml_sqr(ctx, fcout_) ); // 计算张量d的平方和e
struct ggml_cgraph ge = ggml_build_forward(e); // 构建计算图ge
return {ge, e, fcout, X,target};
}
void hf_out(ggml_tensor * output){
printf("f = %f\n", ggml_get_f32_1d(output, 0));// cout<< "res "<<((float *)(fc2->data))[0];
printf("f = %f\n", ggml_get_f32_1d(output, 1));
printf("f = %f\n", ggml_get_f32_1d(output, 2));
}
void hf_free(){
ggml_free(ctx); // 释放上下文内存
}
res a = hf_getcompute_graph();
static int *istrain = new int(1);// delete istrain;
void hf_set_data_random(){
ggml_tensor * input = a.intput;
ggml_tensor * target = a.target;
std::random_device rd; // 获取随机数种子
std::mt19937 gen(rd()); // 使用随机数种子初始化随机数生成器
std::uniform_real_distribution<float> dis(0.0, 1.0); // 定义均匀分布函数,范围为[0.0, 1.0)
std::vector<float> digit(512); // 创建大小为512的vector<float>
for (int i = 0; i < digit.size(); i++) {
digit[i] = dis(gen); // 使用分布函数生成随机数,并赋值给vector的每个元素
}
memcpy(input->data, digit.data(), ggml_nbytes(input));
digit = {100.3f,200.5f,100.1f};
memcpy(target->data, digit.data(), ggml_nbytes(target));
*istrain = 1;
}
void hf_set_data(ggml_tensor * input,ggml_tensor * target,vector<float >& v_in ,vector<float >& v_out){
memcpy(input->data, v_in.data(), ggml_nbytes(input));
memcpy(target->data, v_out.data(), ggml_nbytes(target));
}
namespace hf_adam{
const string about = "this is a namespace for train only one epoch for adam";
static struct ggml_opt_params opt_params = ggml_opt_default_params(GGML_OPT_ADAM); // 获取默认的优化参数
static struct ggml_opt_context * opt = (struct ggml_opt_context *) alloca(sizeof(struct ggml_opt_context));
// static
static struct ggml_tensor * gfbuf = ggml_new_tensor_1d(ctx, GGML_TYPE_I32, sizeof(struct ggml_cgraph) / ggml_type_size(GGML_TYPE_I32)+ (sizeof(struct ggml_cgraph) % ggml_type_size(GGML_TYPE_I32) ? 1 : 0));
static struct ggml_tensor * gbbuf = ggml_new_tensor_1d(ctx, GGML_TYPE_I32, sizeof(struct ggml_cgraph) / ggml_type_size(GGML_TYPE_I32)+ (sizeof(struct ggml_cgraph) % ggml_type_size(GGML_TYPE_I32) ? 1 : 0));
// build forward + backward compute graphs
static struct ggml_cgraph * gf = (struct ggml_cgraph *) hf_adam::gfbuf->data;
static struct ggml_cgraph * gb = (struct ggml_cgraph *) hf_adam::gbbuf->data;
static int np;
static int nx;
}
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C" {
#endif
static inline bool ggml_is_scalar(const struct ggml_tensor * tensor) {
static_assert(GGML_MAX_DIMS == 4, "GGML_MAX_DIMS is not 4 - update this function");
return tensor->ne[0] == 1 && tensor->ne[1] == 1 && tensor->ne[2] == 1 && tensor->ne[3] == 1;
}
static void ggml_opt_get_params(int np, struct ggml_tensor * const ps[], float * x) {
int i = 0;
for (int p = 0; p < np; ++p) {
const int64_t ne = ggml_nelements(ps[p]) ;
// TODO: add function to get all elements at once
for (int64_t j = 0; j < ne; ++j) {
x[i++] = ggml_get_f32_1d(ps[p], j);
}
}
}
static void ggml_opt_get_grad(int np, struct ggml_tensor * const ps[], float * g) {
int i = 0;
for (int p = 0; p < np; ++p) {
const int64_t ne = ggml_nelements(ps[p]) ;
// TODO: add function to get all elements at once
for (int64_t j = 0; j < ne; ++j) {
g[i++] = ggml_get_f32_1d(ps[p]->grad, j);
}
}
}
// floating point type used to accumulate sums
typedef double ggml_float;
inline static void ggml_vec_add_f32 (const int n, float * z, const float * x, const float * y) { for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) z[i] = x[i] + y[i]; }
inline static void ggml_vec_add1_f32(const int n, float * z, const float * x, const float v) { for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) z[i] = x[i] + v; }
inline static void ggml_vec_acc_f32 (const int n, float * y, const float * x) { for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) y[i] += x[i]; }
inline static void ggml_vec_acc1_f32(const int n, float * y, const float v) { for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) y[i] += v; }
inline static void ggml_vec_sub_f32 (const int n, float * z, const float * x, const float * y) { for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) z[i] = x[i] - y[i]; }
inline static void ggml_vec_set_f32 (const int n, float * x, const float v) { for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) x[i] = v; }
inline static void ggml_vec_cpy_f32 (const int n, float * y, const float * x) { for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) y[i] = x[i]; }
inline static void ggml_vec_neg_f32 (const int n, float * y, const float * x) { for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) y[i] = -x[i]; }
inline static void ggml_vec_mul_f32 (const int n, float * z, const float * x, const float * y) { for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) z[i] = x[i]*y[i]; }
inline static void ggml_vec_div_f32 (const int n, float * z, const float * x, const float * y) { for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) z[i] = x[i]/y[i]; }
static void ggml_opt_set_params(int np, struct ggml_tensor * const ps[], const float * x) {
int i = 0;
for (int p = 0; p < np; ++p) {
const int64_t ne = ggml_nelements(ps[p]) ;
// TODO: add function to set tensor from array
for (int64_t j = 0; j < ne; ++j) {
ggml_set_f32_1d(ps[p], j, x[i++]);
}
}
}
static void ggml_vec_dot_f32(const int n, float * s, const float * x, const float * y) {
#ifdef GGML_SIMD
float sumf = 0.0f;
const int np = (n & ~(GGML_F32_STEP - 1));
GGML_F32_VEC sum[GGML_F32_ARR] = { GGML_F32_VEC_ZERO };
GGML_F32_VEC ax[GGML_F32_ARR];
GGML_F32_VEC ay[GGML_F32_ARR];
for (int i = 0; i < np; i += GGML_F32_STEP) {
for (int j = 0; j < GGML_F32_ARR; j++) {
ax[j] = GGML_F32_VEC_LOAD(x + i + j*GGML_F32_EPR);
ay[j] = GGML_F32_VEC_LOAD(y + i + j*GGML_F32_EPR);
sum[j] = GGML_F32_VEC_FMA(sum[j], ax[j], ay[j]);
}
}
// reduce sum0..sum3 to sum0
GGML_F32_VEC_REDUCE(sumf, sum);
// leftovers
for (int i = np; i < n; ++i) {
sumf += x[i]*y[i];
}
#else
// scalar
ggml_float sumf = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
sumf += (ggml_float)(x[i]*y[i]);
}
#endif
*s = sumf;
}
inline static void ggml_vec_mad_f32(const int n, float * y, const float * x, const float v) {
// inline static void ggml_vec_mad_f32(const int n, float * restrict y, const float * restrict x, const float v) {
//#if defined(GGML_SIMD)
// const int np = (n & ~(GGML_F32_STEP - 1));
//
//GGML_F32_VEC vx = GGML_F32_VEC_SET1(v);
//
//GGML_F32_VEC ax[GGML_F32_ARR];
//GGML_F32_VEC ay[GGML_F32_ARR];
//
//for (int i = 0; i < np; i += GGML_F32_STEP) {
//for (int j = 0; j < GGML_F32_ARR; j++) {
//ax[j] = GGML_F32_VEC_LOAD(x + i + j*GGML_F32_EPR);
//ay[j] = GGML_F32_VEC_LOAD(y + i + j*GGML_F32_EPR);
//ay[j] = GGML_F32_VEC_FMA(ay[j], ax[j], vx);
//
//GGML_F32_VEC_STORE(y + i + j*GGML_F32_EPR, ay[j]);
//}
//}
//
leftovers
//for (int i = np; i < n; ++i) {
//y[i] += x[i]*v;
//}
//#else
scalar
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
y[i] += x[i]*v;
}
//#endif
}
//inline static void ggml_vec_scale_f32(const int n, float * y, const float v) { for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) y[i] *= v; }
inline static void ggml_vec_scale_f32(const int n, float * y, const float v) {
#if defined(GGML_USE_ACCELERATE)
vDSP_vsmul(y, 1, &v, y, 1, n);
#elif defined(GGML_SIMD)
const int np = (n & ~(GGML_F32_STEP - 1));
GGML_F32_VEC vx = GGML_F32_VEC_SET1(v);
GGML_F32_VEC ay[GGML_F32_ARR];
for (int i = 0; i < np; i += GGML_F32_STEP) {
for (int j = 0; j < GGML_F32_ARR; j++) {
ay[j] = GGML_F32_VEC_LOAD(y + i + j*GGML_F32_EPR);
ay[j] = GGML_F32_VEC_MUL(ay[j], vx);
GGML_F32_VEC_STORE(y + i + j*GGML_F32_EPR, ay[j]);
}
}
// leftovers
for (int i = np; i < n; ++i) {
y[i] *= v;
}
#else
// scalar
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
y[i] *= v;
}
#endif
}
inline static void ggml_vec_norm_f32 (const int n, float * s, const float * x) { ggml_vec_dot_f32(n, s, x, x); *s = sqrtf(*s); }
inline static void ggml_vec_sqr_f32 (const int n, float * y, const float * x) { for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) y[i] = x[i]*x[i]; }
inline static void ggml_vec_sqrt_f32 (const int n, float * y, const float * x) { for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) y[i] = sqrtf(x[i]); }
inline static void ggml_vec_log_f32 (const int n, float * y, const float * x) { for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) y[i] = logf(x[i]); }
inline static void ggml_vec_abs_f32 (const int n, float * y, const float * x) { for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) y[i] = fabsf(x[i]); }
inline static void ggml_vec_sgn_f32 (const int n, float * y, const float * x) { for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) y[i] = (x[i] > 0.f) ? 1.f : ((x[i] < 0.f) ? -1.f : 0.f); }
inline static void ggml_vec_step_f32 (const int n, float * y, const float * x) { for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) y[i] = (x[i] > 0.f) ? 1.f : 0.f; }
inline static void ggml_vec_tanh_f32 (const int n, float * y, const float * x) { for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) y[i] = tanhf(x[i]); }
inline static void ggml_vec_elu_f32 (const int n, float * y, const float * x) { for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) y[i] = (x[i] > 0.f) ? x[i] : expf(x[i])-1; }
inline static void ggml_vec_relu_f32 (const int n, float * y, const float * x) { for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) y[i] = (x[i] > 0.f) ? x[i] : 0.f; }
//
// ADAM
//
// ref: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1412.6980.pdf
//
struct ggml_tensor * ps[GGML_MAX_PARAMS];
void ggml_opt_adam(
struct ggml_context * ctx,
struct ggml_opt_context * opt,
struct ggml_opt_params params,
struct ggml_tensor * f,
struct ggml_cgraph * gf,
struct ggml_cgraph * gb) {
GGML_ASSERT(ggml_is_scalar(f));
// these will store the parameters we want to optimize
if ((opt->params.type != params.type) || (opt->nx != hf_adam::nx) || (opt->params.past != params.past)) {
int iter = opt->iter;
ggml_opt_init(opt->ctx, opt, params, hf_adam::nx);
opt->iter = iter;
}
// constants
const float sched = params.adam.sched;
const float decay = params.adam.decay * sched;
const float alpha = params.adam.alpha * sched;
const float beta1 = params.adam.beta1;
const float beta2 = params.adam.beta2;
const float eps = params.adam.eps;
float * x = (float *)opt->adam.x->data; // view of the parameters
float * g1 = (float *)opt->adam.g1->data; // gradient
float * g2 = (float *)opt->adam.g2->data; // gradient squared
float * m = (float *)opt->adam.m->data; // first moment
float * v = (float *)opt->adam.v->data; // second moment
float * mh = (float *)opt->adam.mh->data; // first moment hat
float * vh = (float *)opt->adam.vh->data; // second moment hat
float * pf = params.past > 0 ? (float *)opt->adam.pf->data : NULL; // past function values
// update view
ggml_opt_get_params(hf_adam::np, ps, x);
// compute the function value
ggml_graph_reset (gf);
ggml_set_f32 (f->grad, 1.0f);
ggml_graph_compute_with_ctx(ctx, gb, params.n_threads);
opt->adam.fx_prev = ggml_get_f32_1d(f, 0);
opt->adam.fx_best = opt->adam.fx_prev;
if (pf) {
pf[opt->iter % params.past] = opt->adam.fx_prev;
}
// initialize
if (opt->just_initialized) {
// opt->adam.n_no_improvement = 0; // *** stack smashing detected ***: terminated
opt->just_initialized = false;
}
float * fx_best = &opt->adam.fx_best;
float * fx_prev = &opt->adam.fx_prev;
int * n_no_improvement = &opt->adam.n_no_improvement;
int iter0 = opt->iter;
// run the optimizer
for (int t = 0; t < 20; ++t) {
// for (int t = 0; t < params.adam.n_iter; ++t) {
cout<< t <<endl;
opt->iter = iter0 + t + 1;
GGML_PRINT_DEBUG ("=== iter %d ===\n", t);
GGML_PRINT_DEBUG ("f = %10.6f\n", ggml_get_f32_1d(f, 0));
GGML_PRINT_DEBUG_5("df/dx0 = %10.6f\n", ggml_get_f32_1d(ps[0]->grad, 0));
GGML_PRINT_DEBUG_5("df/dx1 = %10.6f\n", ggml_get_f32_1d(ps[1]->grad, 0));
for (int i = 0; i < hf_adam::np; ++i) {
GGML_PRINT_DEBUG("param %d: %10.6f, g = %10.6f\n", i,
ggml_get_f32_1d(ps[i], 0), ggml_get_f32_1d(ps[i]->grad, 0));
}
const int64_t t_start_wall = ggml_time_us();
const int64_t t_start_cpu = ggml_cycles();
// UNUSED(t_start_wall);
// UNUSED(t_start_cpu);
{
// update the gradient
ggml_opt_get_grad(hf_adam::np, ps, g1); // np : 8 ,ps: ggml_tensor * [256] ,g1 float * 梯度向量。该向量包含了每个参数对应的梯度值,用于计算梯度的一阶矩估计。
// m_t = beta1*m_t-1 + (1 - beta1)*g_t
ggml_vec_scale_f32(hf_adam::nx, m, beta1);
ggml_vec_mad_f32 (hf_adam::nx, m, g1, 1.0f - beta1);
// g2 = g1^2
ggml_vec_sqr_f32 (hf_adam::nx, g2, g1);
// v_t = beta2*v_t-1 + (1 - beta2)*g_t^2
ggml_vec_scale_f32(hf_adam::nx, v, beta2);
ggml_vec_mad_f32 (hf_adam::nx, v, g2, 1.0f - beta2);
// m^hat = m_t / (1 - beta1^t)
// v^hat = v_t / (1 - beta2^t)
// x_t = x_t-1 - sched*(alpha*m^hat/(sqrt(v^hat) + eps) + decay*x_t-1)
// x_t = x_t-1 - sched*alpha*m^hat/(sqrt(v^hat) + eps) - sched*decay*x_t-1
// x_t = x_t-1*(1-sched*decay) - sched*alpha*m^hat/(sqrt(v^hat) + eps)
// x_t = x_t-1*(1-sched*decay) + sched*decay*(-alpha/decay)*m^hat/(sqrt(v^hat) + eps)
// x_t = mix(x_t-1, (-alpha/decay)*m^hat/(sqrt(v^hat) + eps), sched*decay)
ggml_vec_cpy_f32 (hf_adam::nx, mh, m);
ggml_vec_cpy_f32 (hf_adam::nx, vh, v);
ggml_vec_scale_f32(hf_adam::nx, mh, alpha/(1.0f - powf(beta1, opt->iter)));
ggml_vec_scale_f32(hf_adam::nx, vh, 1.0f/(1.0f - powf(beta2, opt->iter)));
ggml_vec_sqrt_f32 (hf_adam::nx, vh, vh);
ggml_vec_acc1_f32 (hf_adam::nx, vh, eps);
ggml_vec_div_f32 (hf_adam::nx, mh, mh, vh);
ggml_vec_scale_f32(hf_adam::nx, x, 1.0f - decay);
ggml_vec_sub_f32 (hf_adam::nx, x, x, mh);
// update the parameters
ggml_opt_set_params(hf_adam::np, ps, x);
}
ggml_graph_reset (gf);
ggml_set_f32 (f->grad, 1.0f);
ggml_graph_compute_with_ctx(ctx, gb, params.n_threads);
const float fx = ggml_get_f32_1d(f, 0);
// check convergence
if (fabsf(fx - fx_prev[0])/fx < params.adam.eps_f) {
GGML_PRINT_DEBUG("converged\n");
return ;
}
// delta-based convergence test
if (pf != NULL) {
// need at least params.past iterations to start checking for convergence
if (params.past <= iter0 + t) {
const float rate = (pf[(iter0 + t)%params.past] - fx)/fx;
if (fabsf(rate) < params.delta) {
return ;
}
}
pf[(iter0 + t)%params.past] = fx;
}
fx_prev[0] = fx;
{
const int64_t t_end_cpu = ggml_cycles();
GGML_PRINT_DEBUG("time iter: %5.3f s\n", ((float)(t_end_cpu - t_start_cpu))/CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
// UNUSED(t_end_cpu);
const int64_t t_end_wall = ggml_time_us();
GGML_PRINT_DEBUG("wall time iter: %5.3f s\n", (t_end_wall - t_start_wall)/1e6);
// UNUSED(t_end_wall);
}
}
return ;
}
struct rgb{ float r; float g; float b;};
void hf_play_init(){
ggml_opt_init(ctx, hf_adam::opt, hf_adam::opt_params, 0);
* hf_adam::gf = ggml_build_forward (a.e);
* hf_adam::gb = ggml_build_backward(ctx, hf_adam::gf, true);
hf_adam::np = 0;
hf_adam::nx = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < hf_adam::gf->n_nodes; ++i) {
if (hf_adam::gf->nodes[i]->is_param) {
GGML_PRINT_DEBUG("found param %d: grad->op = %d\n", np, gf->nodes[i]->grad->op);
GGML_ASSERT( hf_adam::np < GGML_MAX_PARAMS);
ps[ hf_adam::np++] = hf_adam::gf->nodes[i];
hf_adam::nx += ggml_nelements(hf_adam::gf->nodes[i]);
}
}
}
static bool flag = true;
void hf_play_start_train() {
ggml_cgraph ge = a.ge;
ggml_tensor * e = a.e;
ggml_tensor * output = a.output;
ggml_tensor * input = a.intput;
ggml_tensor * target = a.target;
if(flag){
cout<<"------init------" <<endl;
hf_play_init();
flag = false;
}
while(1){
if(*istrain){
// ggml_opt(ctx, opt_params, e); // 通过指定的优化参数优化张量e
cout<<"pppppppppppppppppppppppppppppppppppppppppppppppppp" <<endl;
cout<< hf_adam::about << endl;
ggml_opt_adam(ctx, hf_adam::opt, hf_adam::opt->params, a.e, hf_adam::gf, hf_adam::gb);// ggml_opt_resume_g(ctx, hf_adam::opt, a.e, hf_adam::gf, hf_adam::gb);
// ggml_opt_adam(ctx, hf_adam::opt, hf_adam::opt->params, a.e, hf_adam::gf, hf_adam::gb);
hf_set_data_random();
*istrain = 0;
}else{
cout<<"oooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooo" <<endl;
ggml_graph_reset(&a.ge); // 重置计算图
ggml_graph_compute_with_ctx(ctx, &a.ge, /*n_threads*/ 1); // 使用指定上下文计算计算图
float fe = ggml_get_f32_1d(e, 0); // 获取张量e的第一个元素值
printf("%s: e = %.4f\n", __func__, fe); // 输出e的值
hf_out(output);
for(int i=0;i<10000000;i++);
*istrain = 1;
}
}
return ;
}
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
int main(void) {
hf_play_start_train();
return 0;
}