前言:
👏作者简介:我是笑霸final,一名热爱技术的在校学生。
📝个人主页:个人主页1 || 笑霸final的主页2
📕系列专栏:java系列
📧如果文章知识点有错误的地方,请指正!和大家一起学习,一起进步👀
🔥如果感觉博主的文章还不错的话,👍点赞👍 + 👀关注👀 + 🤏收藏🤏
目录
- 一、ReentrantLock概述
- 二、ReentrantLock的类结构图
- 三、ReentrantLock(非公平锁)的实现过程解析
- 3.1加锁lock.lock();
- 3.2 加锁失败后acquire(1)尝试获取锁
- 3.2.1 tryAcquire()再次尝试获取锁
- 3.2.1 addWaiter() 添加到等待队列
- 3.2.3 acquireQueued()阻塞方法
- 四、思维导图
一、ReentrantLock概述
ReentrantLock是一种基于
AQS框架的应用实现,是JDK中的一种线程并发访问的同步手段。它具有与synchronized类似的功能,但提供了比synchronized更强大、灵活的锁机制。
特点:
- 可重入性:与synchronized一样,ReentrantLock也支持可重入锁。这意味着同一个线程可以多次获取同一个锁,只要在每次获取锁之前都释放了之前的锁。
- 支持公平锁和非公平锁选择:ReentrantLock可以选择使用公平锁或非公平锁。公平锁按照线程请求锁的顺序进行分配,而非公平锁不保证按照顺序分配。
- 支持可中断获取锁:使用ReentrantLock时,可以通过调用lockInterruptibly()方法来尝试获取锁,并在等待过程中能够被中断。
- 支持设置超时时间:通过tryLock(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)方法,可以尝试在指定的超时时间内获取锁。
- ReentrantLock内部实现了加锁的操作,并且支持重入锁。
AQS:
- AQS使用一个FIFO(先入先出)的等待队列来实现线程之间的协作.
- AQS提供了一些基本的同步控制方法,如acquire()、tryAcquire()、release()等
- AQS内部维护了一个volatile的int型变量state,这个state代表着同步状态,通过CAS(CompareAndSwap)操作来实现同步状态的获取和释放。
一般情况下state的值为0或1,分别表示锁未被持有或锁已被持有 (如ReentrantLock)。但在其他的同步器中,state的值可以代表不同的含义,比如Semaphore同步器中,state的值代表着可以获取的许可数量。
二、ReentrantLock的类结构图
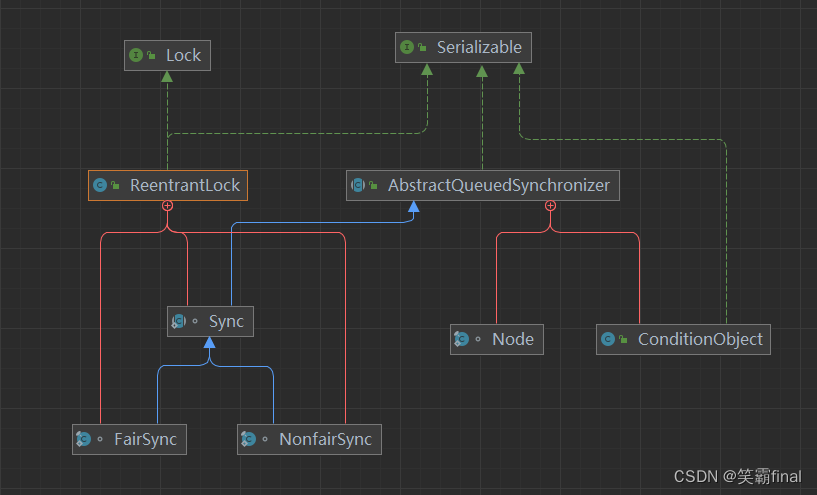
- RenentrantLock实现了Lock接口,Lock接口提供了锁的通用api,比如加锁lock,解锁unlock等操作。
- RenentrantLock有一个内部类 Sync而FairSync和NonfairSync继承Sync来实现非公平锁和公平锁。
- Node也是一个内部类表示等待队列中的节点,用于存储等待获取锁的线程。
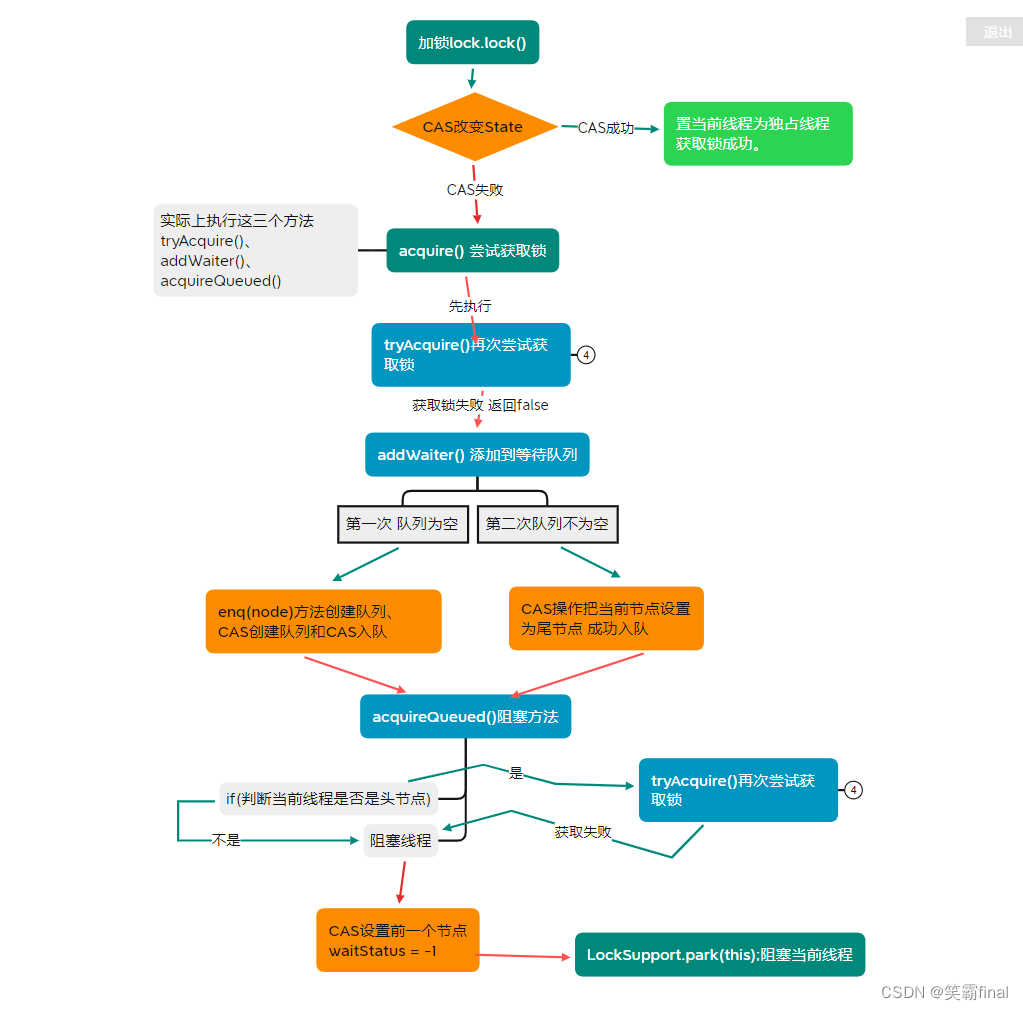
三、ReentrantLock(非公平锁)的实现过程解析
3.1加锁lock.lock();
实际上底层调用的是sync.lock();方法这里我们讲非公平锁。
final void lock() {
if (compareAndSetState(0, 1))
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());
else
acquire(1);
}
过程:
会先使用CAS改变State的值 从0到1,成功后 设置当前线程为独占线程,获取锁成功。
如果CAS失败 才会进入下面的流程 执行acquire(1);尝试获取锁
3.2 加锁失败后acquire(1)尝试获取锁
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
selfInterrupt();
}
可见会执行tryAcquire()、addWaiter()、acquireQueued()这三个方法我们来仔细看看。
3.2.1 tryAcquire()再次尝试获取锁
先看代码
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
return nonfairTryAcquire(acquires);
}
进入nonfairTryAcquire
final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) {
if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
流程
先判断当前State的值是否为0
- 进入if后 还是
CAS获取锁- 获取锁成功
设置当前线程为独占线程流程结束获取锁失败
判断当前线程是否是 独占线程(可重入实现原理)
- 是当前线程 State+1 标记获取锁的次数 返回 true
- 不是当前线程 就跳过当前if 直接返回
false
3.2.1 addWaiter() 添加到等待队列
注意
如果上一步返回为true 就不会执行此方法
private Node addWaiter(Node mode) {
Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode);
// Try the fast path of enq; backup to full enq on failure
Node pred = tail;
if (pred != null) {
node.prev = pred;
if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) {
pred.next = node;
return node;
}
}
enq(node);
return node;
}
可见
第一次tail就是为null 不会进入if 而是先enq(node);去创建队列
非第一次就会CAS操作把当前节点设置为尾节点 成功入队 返回node 然后执行acquireQueued()方法
看看enq(node)如何创建队列
private Node enq(final Node node) {
for (;;) {
Node t = tail;
if (t == null) { // Must initialize
if (compareAndSetHead(new Node()))
tail = head;
} else {
node.prev = t;
if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) {
t.next = node;
return t;
}
}
}
}
fo循环
先通过CAS创建队列 并设置头节点
然后第二次for循环 通过CAS入队 成功返回当前节点也 执行acquireQueued()方法
3.2.3 acquireQueued()阻塞方法
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return interrupted;
}
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
也是for循环
final Node p = node.predecessor();获取当前队列头节点 如果当前是头节点又会执行tryAcquire(arg)获取锁- 如果获取锁失败 或者不是头节点 就会执行下面的if
shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node)
private static boolean shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(Node pred, Node node) {
int ws = pred.waitStatus;
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL)
/*
* This node has already set status asking a release
* to signal it, so it can safely park.
*/
return true;
if (ws > 0) {
/*
* Predecessor was cancelled. Skip over predecessors and
* indicate retry.
*/
do {
node.prev = pred = pred.prev;
} while (pred.waitStatus > 0);
pred.next = node;
} else {
/*
* waitStatus must be 0 or PROPAGATE. Indicate that we
* need a signal, but don't park yet. Caller will need to
* retry to make sure it cannot acquire before parking.
*/
compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL);
}
return false;
}
- 先获取 当前
waitStatus字段用于表示节点在等待队列中的状态。
用来比对当前置节点的状态 结合外层for循环 进入 compareAndSetWaitStatusCAS操作前置节点的状态设置为 -1(waitStatus=-1)- 最后调用
LockSupport.park(this);阻塞当前线程
四、思维导图