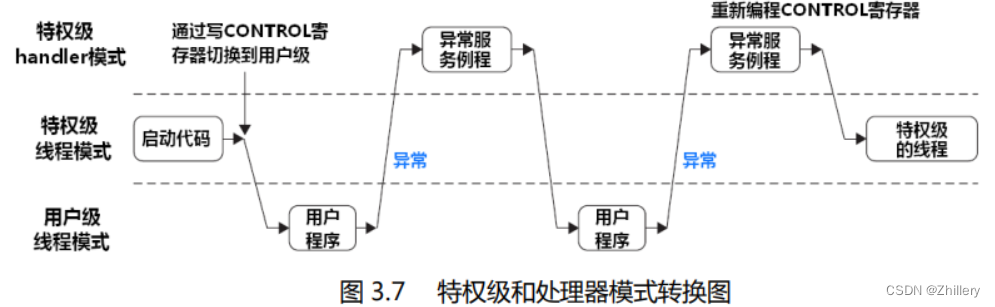
这里写自定义目录标题
- 需要实现的效果
- 前端需要的json格式:一定是一个完整的树结构
- 错误
- 错误的返回格式
- 错误的返回格式实现的效果
- 正确
- 正确的返回格式
- 正确的展示画面
- 后端
- 逻辑分析
- 代码总览
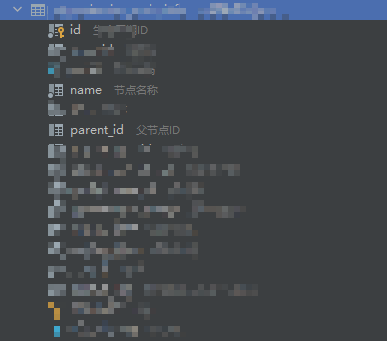
- 数据库表结构
需要实现的效果
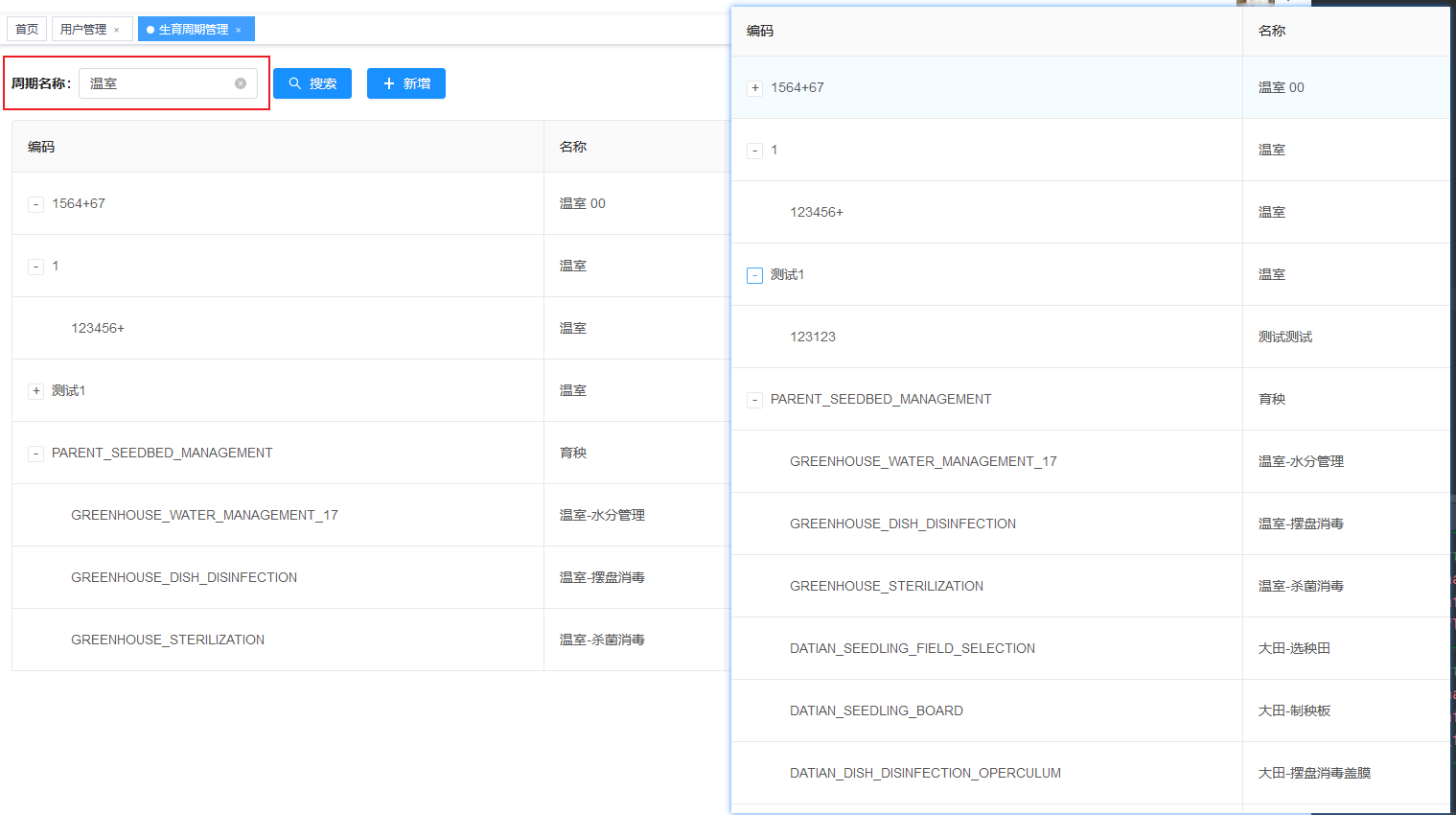
前端需要的json格式:一定是一个完整的树结构
错误
错误的返回格式
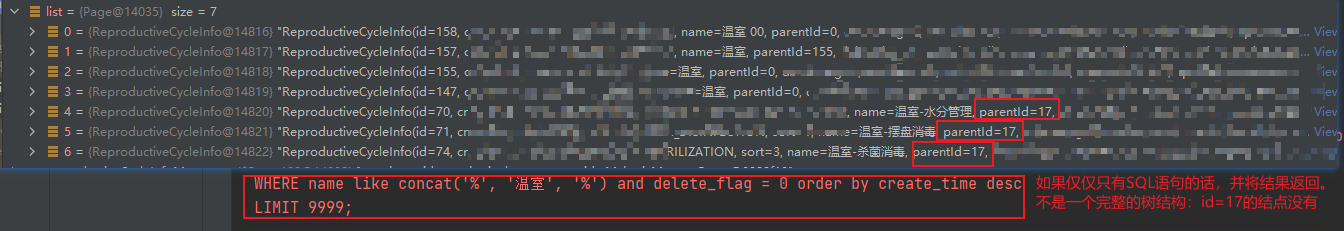
错误的返回格式实现的效果
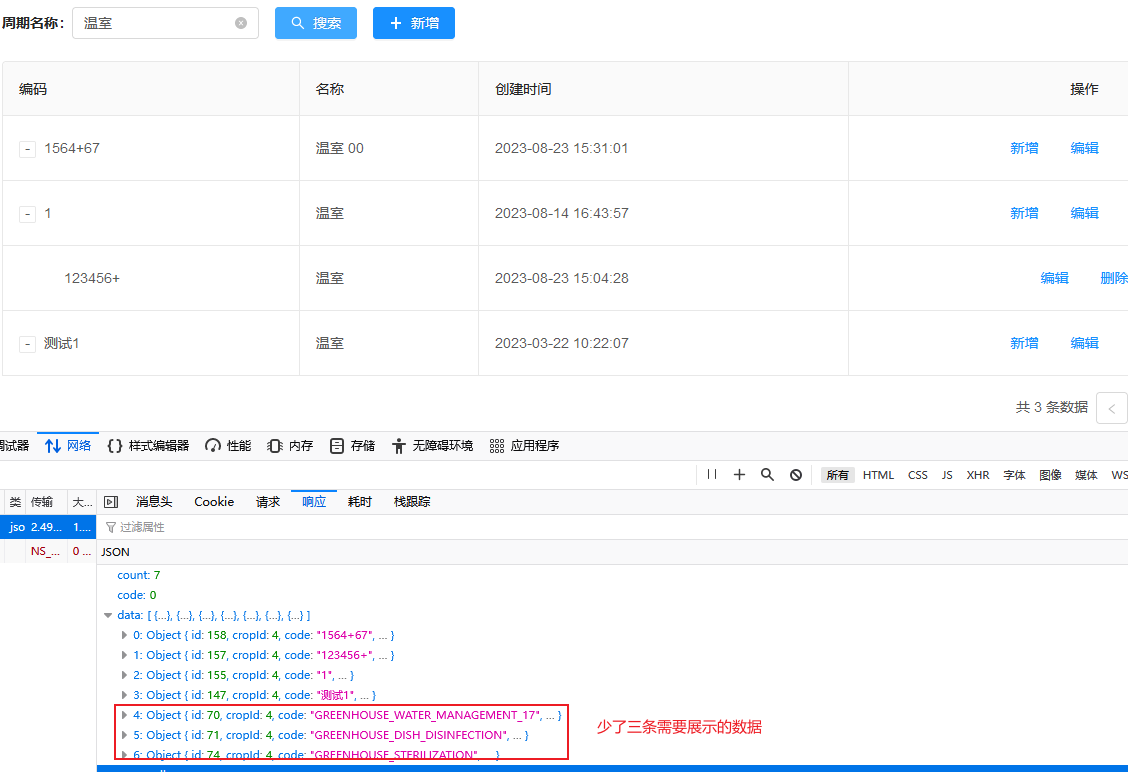
正确
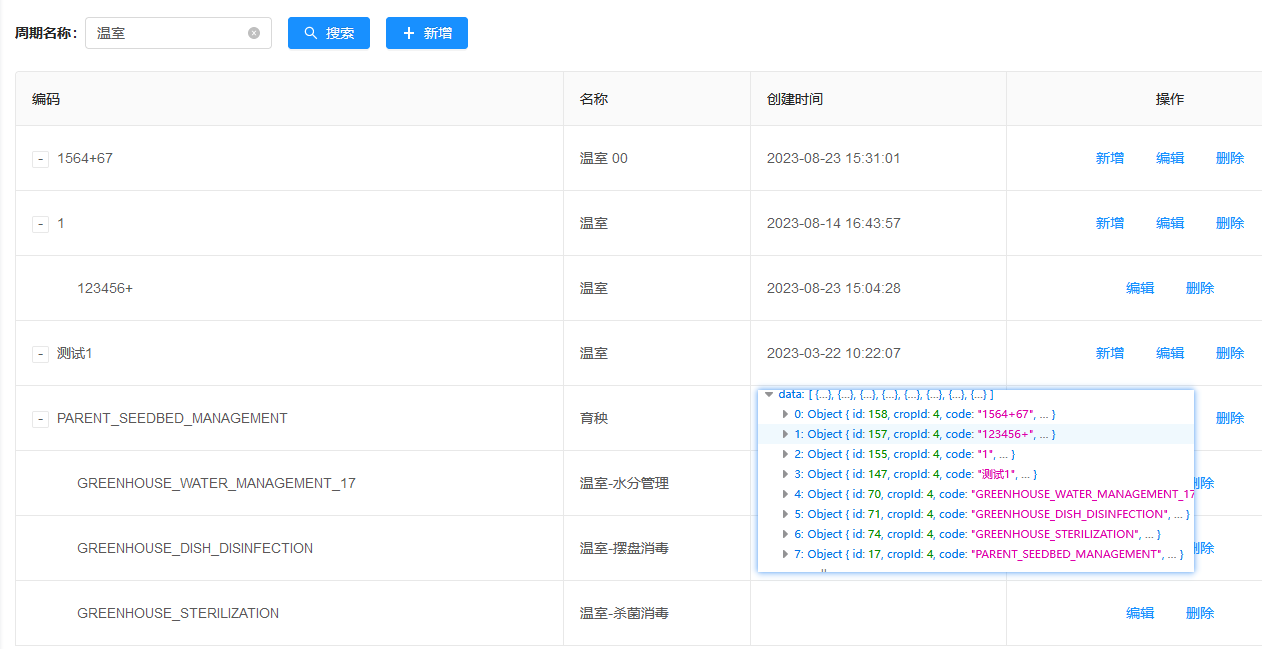
正确的返回格式
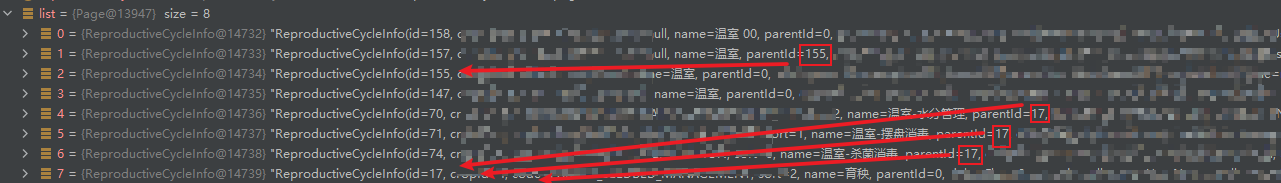
正确的展示画面
后端
逻辑分析
1. 根据搜索条件,查出符合的数据
List<ReproductiveCycleInfo> list = reproductiveCycleInfoMapper.selectReproductiveCycleInfoList(reproductiveCycleInfo);
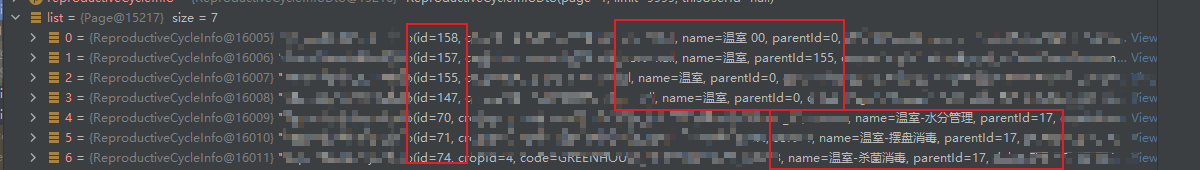
这一步不能直接返回给前端的,因为前端的组件是需要完整的一个树结构。
从图中可以看到,我们 id in(70,71,72)的父节点 id = 17 没有找到,所以 这就不是一个完整的树结构。
2. 符合的数据里面我们需要发现还需要找到几个父节点数据
// parentId = 0,表示他已经没有父节点了
Set<Long> collect = list.stream().filter(x -> x.getParentId() != 0).map(ReproductiveCycleInfo::getParentId).collect(Collectors.toSet());
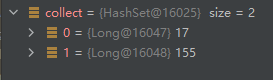
3. 开始找父节点的信息
if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(collect)) {
for (Long x : collect) {
getParentInfoByParentId(x, list);
}
}
3.1 根据节点的id找到节点
/**
* 根据节点id找出节点,并添加到结果集里面
*
* @param nodeId 当前需要找的节点id
* @param list 返回的结果集
*/
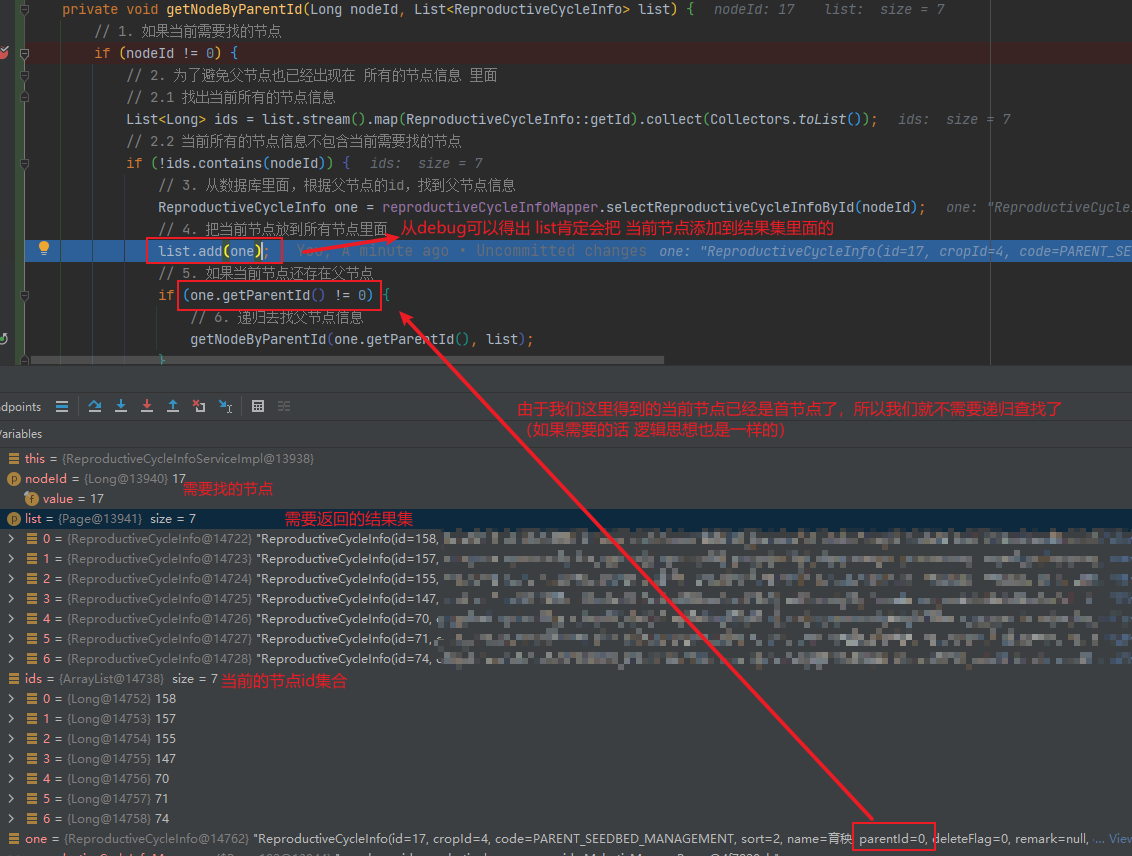
private void getNodeByParentId(Long nodeId, List<ReproductiveCycleInfo> list) {
// 1. 如果当前需要找的节点
if (nodeId != 0) {
// 2. 为了避免父节点也已经出现在 所有的节点信息 里面
// 2.1 找出当前所有的节点信息
List<Long> ids = list.stream().map(ReproductiveCycleInfo::getId).collect(Collectors.toList());
// 2.2 当前所有的节点信息不包含当前需要找的节点
if (!ids.contains(nodeId)) {
// 3. 从数据库里面,根据父节点的id,找到父节点信息
ReproductiveCycleInfo one = reproductiveCycleInfoMapper.selectReproductiveCycleInfoById(nodeId);
// 4. 把当前节点放到所有节点里面
list.add(one);
// 5. 如果当前节点还存在父节点
if (one.getParentId() != 0) {
// 6. 递归去找父节点信息
getNodeByParentId(one.getParentId(), list);
}
}
}
}
以找17节点为例子:
代码总览
从这里也可以看出我这里其实代码已经有逻辑耦合了。毕竟 node != 0 判断了两次了,这其实没必要。还可以优化一下。
@Override
public List<ReproductiveCycleInfo> selectReproductiveCycleInfoListByName(ReproductiveCycleInfoDto reproductiveCycleInfo) {
List<ReproductiveCycleInfo> list = reproductiveCycleInfoMapper.selectReproductiveCycleInfoList(reproductiveCycleInfo);
Set<Long> collect = list.stream().filter(x -> x.getParentId() != 0).map(ReproductiveCycleInfo::getParentId).collect(Collectors.toSet());
if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(collect)) {
for (Long x : collect) {
getNodeByParentId(x, list);
}
}
return list;
}
/**
* 根据节点id找出节点,并添加到结果集里面
*
* @param nodeId 当前需要找的节点id
* @param list 返回的结果集
*/
private void getNodeByParentId(Long nodeId, List<ReproductiveCycleInfo> list) {
// 1. 如果当前需要找的节点
if (nodeId != 0) {
// 2. 为了避免父节点也已经出现在 所有的节点信息 里面
// 2.1 找出当前所有的节点信息
List<Long> ids = list.stream().map(ReproductiveCycleInfo::getId).collect(Collectors.toList());
// 2.2 当前所有的节点信息不包含当前需要找的节点
if (!ids.contains(nodeId)) {
// 3. 从数据库里面,根据父节点的id,找到父节点信息
ReproductiveCycleInfo one = reproductiveCycleInfoMapper.selectReproductiveCycleInfoById(nodeId);
// 4. 把当前节点放到所有节点里面
list.add(one);
// 5. 如果当前节点还存在父节点
if (one.getParentId() != 0) {
// 6. 递归去找父节点信息
getNodeByParentId(one.getParentId(), list);
}
}
}
}
数据库表结构
起码得满足有这些极端并约定 parentId = 0 是表示是首节点了.