写在前面
在工作中为了能够提高数据库的读写能力,经常会用到分库分表等技术,此时不可避免的就要涉及到动态数据源切换的内容,针对这个问题,spring提供了AbstractRoutingDataSource类来满足我们的需求,本文就一起来看下。
1:动态切换的原理
任何技术,原理都是最重要的,知道了原理,解决问题就只是时间问题了,所以,我们有必要先来看下数据源能够实现动态切换的原理,首先看下Datasource类源码,如下:
package javax.sql;
public interface DataSource extends CommonDataSource, Wrapper {
Connection getConnection() throws SQLException;
Connection getConnection(String username, String password)
throws SQLException;
}
可以看到,DataSource本质上就是一个jdbc connnection的工厂类,因此不同的datasource,其实就是不同的datasoruce实例了,对应到spring就是不同的datasource的bean,诸如c3p0,druid,hikaricp等连接池技术的连接池对象都是实现了该接口的,如下是druid的:
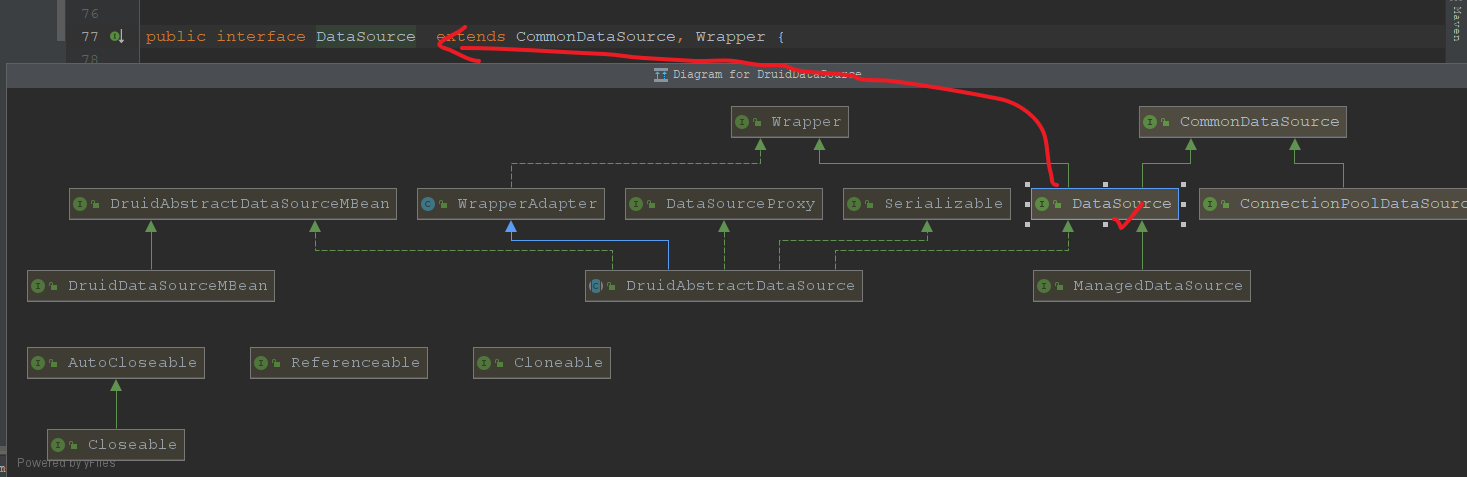
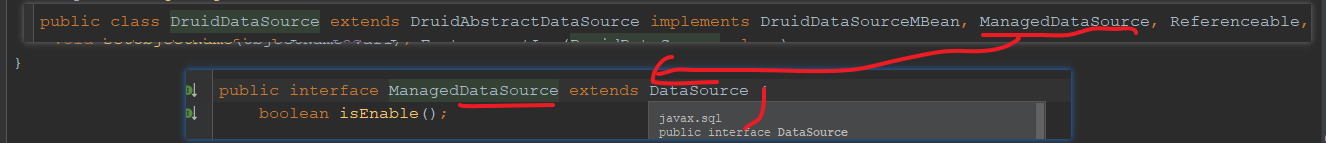
所以,在真正的操作数据之前,我们只需要更换datasource的实现类,那么最终获取到jdbc connection就是对应数据库的connection了,就可以操作对应的数据库,从而实现动态切换了,那么具体怎么做呢?可以这样,用一个map来维护一组数据源,之后根据用户指定的key来获取对应的数据源,就行了,伪代码如下:
void changeDataSource(String userSpecifiedKey) {
Map datsourceMap = new HashMap();
{
datsourceMap.put("key1", new YourDatasource1());
datsourceMap.put("key2", new YourDatasource2());
datsourceMap.put("key3", new YourDatasource3());
...
}
changeDataSourceTo(datsourceMap.get(userSpecifiedKey));
}
本文我们要学习的AbstractRoutingDatasource使用的也正是这种思想,接着来看下。
2:AbstractRoutingDatasource
源码如下:
注意只保留重要源码!!!
public abstract class AbstractRoutingDataSource extends AbstractDataSource implements InitializingBean {
// 默认的数据源
private Object defaultTargetDataSource;
// 所有可用的数据源字典
private Map<Object, DataSource> resolvedDataSources;
// 重要!!!
// spring bean生命周期中InitializingBean对应的方法,在该方法中设置外部指定的数据源到resolvedDataSources
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
if (this.targetDataSources == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Property 'targetDataSources' is required");
}
this.resolvedDataSources = new HashMap<Object, DataSource>(this.targetDataSources.size());
for (Map.Entry<Object, Object> entry : this.targetDataSources.entrySet()) {
Object lookupKey = resolveSpecifiedLookupKey(entry.getKey());
DataSource dataSource = resolveSpecifiedDataSource(entry.getValue());
this.resolvedDataSources.put(lookupKey, dataSource);
}
if (this.defaultTargetDataSource != null) {
this.resolvedDefaultDataSource = resolveSpecifiedDataSource(this.defaultTargetDataSource);
}
}
@Override
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return determineTargetDataSource().getConnection();
}
@Override
public Connection getConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException {
return determineTargetDataSource().getConnection(username, password);
}
protected DataSource determineTargetDataSource() {
Assert.notNull(this.resolvedDataSources, "DataSource router not initialized");
// 通过抽象方法determineCurrentLookupKey获取具体的key
Object lookupKey = determineCurrentLookupKey();
// 根据外部的key获取具体的数据源对象
DataSource dataSource = this.resolvedDataSources.get(lookupKey);
// 兜底,设置默认的数据源
if (dataSource == null && (this.lenientFallback || lookupKey == null)) {
dataSource = this.resolvedDefaultDataSource;
}
...
return dataSource;
}
// 抽象模板方法,有具体的子类提供实现
protected abstract Object determineCurrentLookupKey();
}
其中比较关键的点是public Connection getConnection()方法,在该方法中会调用determineTargetDataSource()方法获取数据源,而具体获取哪个数据源是由抽象方法determineCurrentLookupKey()的返回值来决定的,所以在工作中我们如果是要使用AbstractRoutingDataSource的话只要继承该类并实现determineTargetDataSource()抽象方法即可,如下一个可能的实现:
public class DynamicDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource {
@Override
protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() {
// 通过threadlocal来获取lookupKey
return CustomerDataSourceContextHolder.getCustomerType();
}
}
public class CustomerDataSourceContextHolder {
private static final ThreadLocal<String> contextHolder = new ThreadLocal<String>();
public static void setCustomerType(String dbType) {
contextHolder.set(dbType);
}
public static String getCustomerType() {
return contextHolder.get();
}
public static void clearCustomerType() {
contextHolder.remove();
}
}
我们就可以来配置DynamicDataSource为spring bean,可能如下:
<bean id="dynamicDataSource" class="com.jh.jcs.framework.sharding.DynamicDataSource">
<property name="defaultTargetDataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
<!-- 通过key-value的形式来关联数据源 -->
<property name="targetDataSources">
<map>
<entry value-ref="db22" key="db22"/>
<entry value-ref="db23" key="db23"/>
<entry value-ref="db24" key="db24"/>
<entry value-ref="db25" key="db25"/>
<entry value-ref="db26" key="db26"/>
<entry value-ref="db27" key="db27"/>
</map>
</property>
</bean>
最后我们可以通过aop来执行具体设置lookupKey的工作,可能源码如下:
@Aspect
@Component
@Slf4j
public class DynamicDataSourceAspect {
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.xxx.yyy.framework.annotation.DynamicDataSource)")
public void dynamicDataSourcePointcut() {
}
@Around("dynamicDataSourcePointcut()")
public Object dynamicDataSourceAround(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
// 获取参数,并通过解析参数来确定lookupKey
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
String lookupKey = resolveLookupKey(args);
// 设置lookupKey
CustomerDataSourceContextHolder.setCustomerType(lookupKey);
Object resultObj = joinPoint.proceed(args);
return resultObj;
}
}
写在后面
参考文章列表
【正确姿势】完全理解 Spring AbstractRoutingDataSource 实现动态(多)数据源切换(避免踩坑) 。