《剑指Offer》链表题大全 9道题
- 链表
- 1. 从尾到头打印链表
- 本题考点
- 栈
- 2. 在O(1)时间删除链表结点
- 3. 删除链表中重复的节点
- 总结:删除节点的两种方法
- 1. a-》b 直接让a的值等于b的值,a的next等于b的next
- 2. a-》b-》c 让a的next指向c(只有修改next才管用)
- java版本(画个草图就知道怎么做了 并且 java没有指针)
- 4. 链表中倒数第k个节点
- 遍历两次
- 遍历一次(需要再开一个指针而已)但是本题不行,因为题目有长度限制,我们需要先知道链表长度
- 5. 链表中环的入口结点(快慢指针)
- 6. 反转链表
- 方法一: 迭代
- 方法二:递归
- 7. 合并两个排序的链表
- 8. 复杂链表的复刻
- 9. 二叉搜索树与双向链表
链表
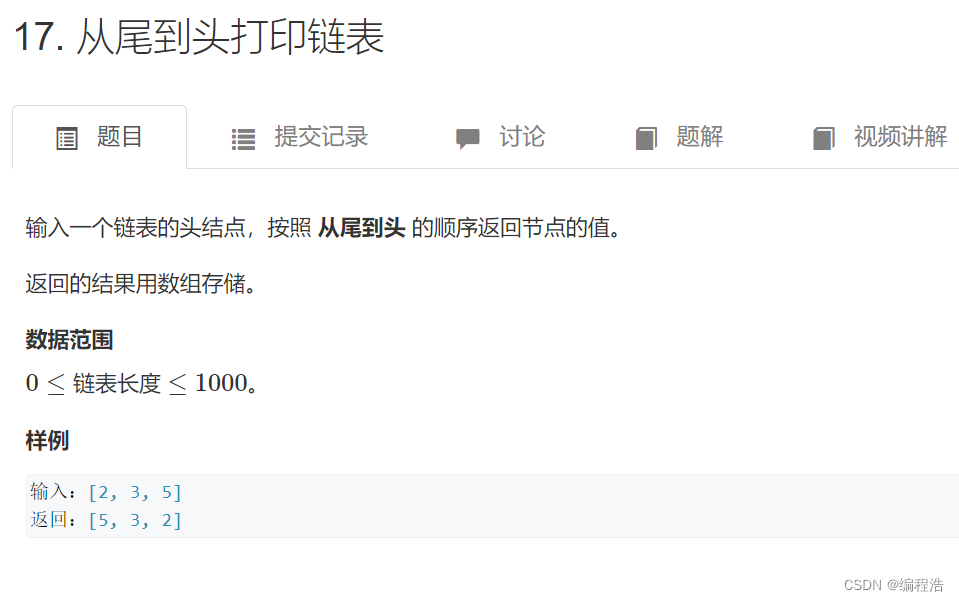
1. 从尾到头打印链表
原题链接
原题链接
本题考点
- 顺序打印链表的掌握(简单)
- 数组的翻转reverse
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
#include<algorithm>
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> printListReversingly(ListNode* head) {
vector<int> res;
while (head) {
res.push_back(head->val);
head = head->next;
}
reverse(res.begin(),res.end());
return res;
}
};
栈
/**
* @author bingo
* @since 2018/12/19
*/
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
/**
* 从尾到头打印链表
*
* @param head 链表头结点
* @return 结果数组
*/
public int[] printListReversingly(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
ListNode cur = head;
int cnt = 0;
while (cur != null) {
stack.push(cur.val);
cur = cur.next;
++cnt;
}
int[] res = new int[cnt];
int i = 0;
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
res[i++] = stack.pop();
}
return res;
}
}
2. 在O(1)时间删除链表结点
原题链接
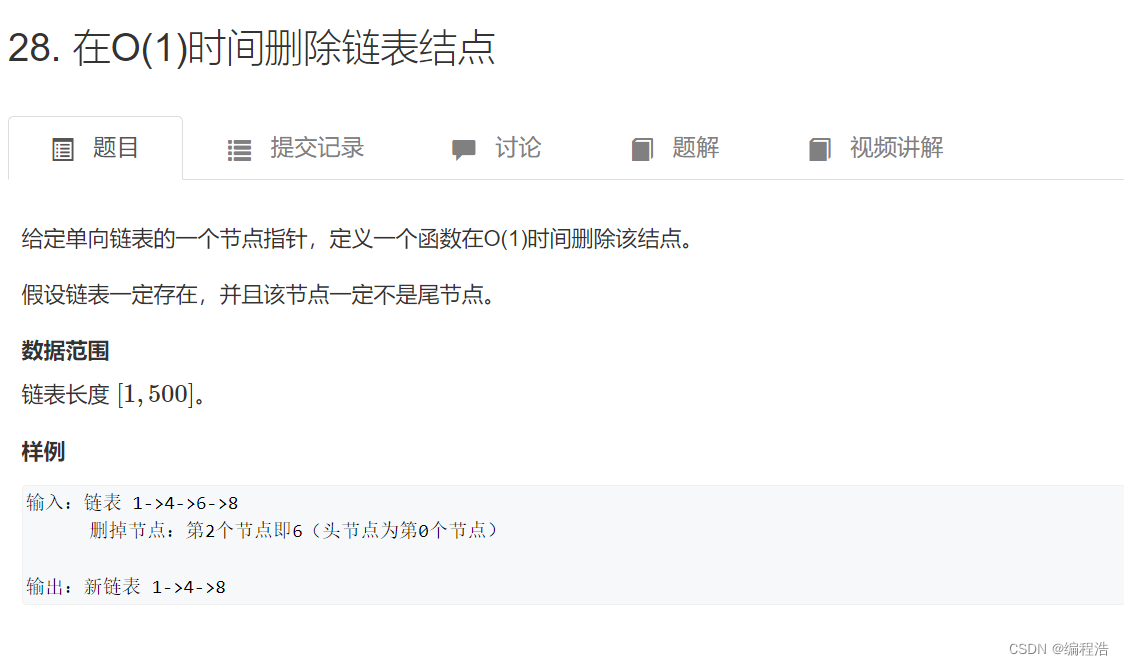
所给的是要删除的节点
那么我们把要删除的节点的指等于下一个指
所指向的地址等于下一个所指向的地址
这样就把该节点删除了
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
void deleteNode(ListNode* node) {
node->val = node->next->val;
node->next = node->next->next;
}
};
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public void deleteNode(ListNode node) {
node.val = node.next.val;
node.next = node.next.next;
}
}
3. 删除链表中重复的节点
原题链接
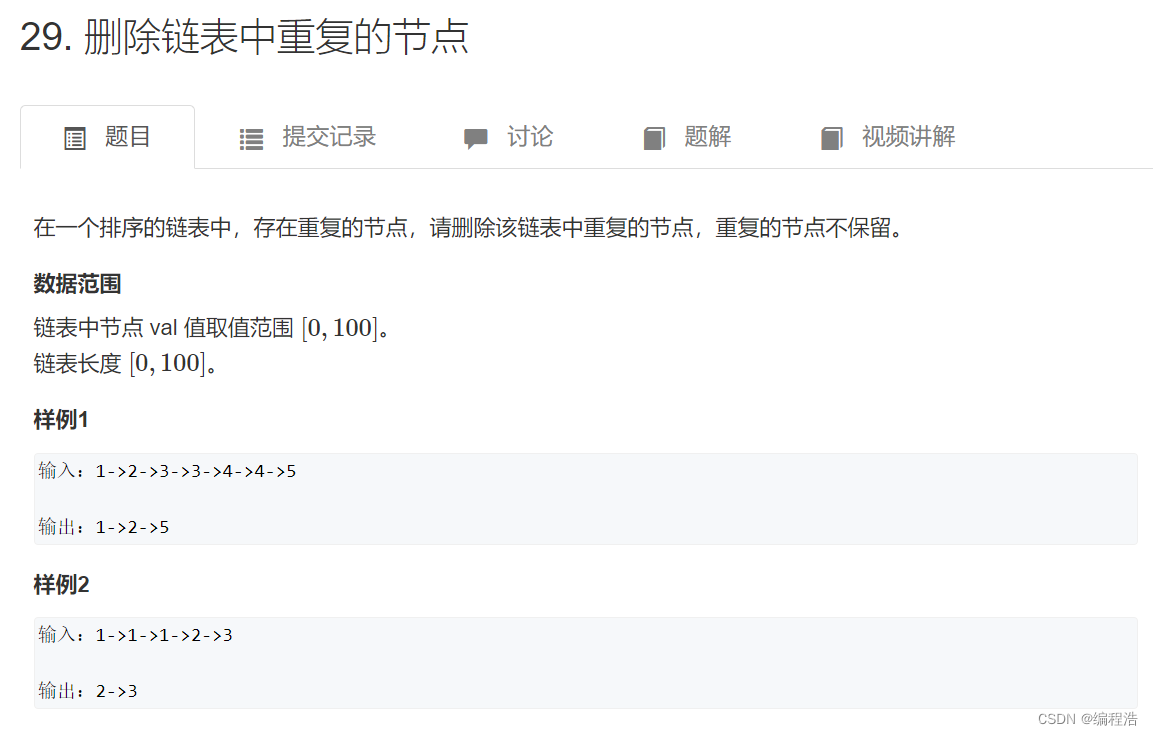
本题需要注意:
- 增加一个空的头节点,便于删除第一个节点(如果要删除的话)
- 如何删除一串节点?必须找到先前一个节点,令先前的节点的next指向要删除一串的后面的那一个
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* deleteDuplication(ListNode* head) {
auto dummy = new ListNode(-1); //建立虚拟头结点
dummy->next = head;//虚拟头结点指向头结点
auto p = dummy;
while(p->next) //p的下一个节点不为空
{
auto q = p->next;
//q的下一个节点不为空,且q的下一个节点的值等于p的下一个节点的值
while(q->next && q->next->val == p->next->val) q= q->next;
//如果q==p的下一个节点 p=q
if(q==p->next) p=q;
//如果不是说明存在重复元素,则p指向q的下一个节点即非重复节点
else p->next = q->next;
}
return dummy->next;
}
}
总结:删除节点的两种方法
1. a-》b 直接让a的值等于b的值,a的next等于b的next
2. a-》b-》c 让a的next指向c(只有修改next才管用)
java版本(画个草图就知道怎么做了 并且 java没有指针)
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplication(ListNode head) {
if(head == null)
return null;
if(head.next == null)
return head;
ListNode l = null;
ListNode l1 = head;
ListNode l2 = head.next;
while(l2!=null){
if(l1.val != l2.val){
l = l1;
l1 = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
} else {
while(l2 != null && l1.val == l2.val){
l2 = l2.next;
}
if(l2 == null){
if(l == null)
return null;
l.next = null;
break;
} else {
if(l == null){
head = l2;
l1 = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
continue;
}
l.next = l2;
l1 = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
}
}
return head;
}
}
4. 链表中倒数第k个节点
原题链接

遍历两次
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* findKthToTail(ListNode* head, int k) {
int n = 0;
for (auto p = head; p; p = p->next) n ++ ;
if (n < k) return nullptr;
auto p = head;
for (int i = 0; i < n - k; i ++ ) p = p->next;
return p;
}
};
遍历一次(需要再开一个指针而已)但是本题不行,因为题目有长度限制,我们需要先知道链表长度
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* findKthToTail(ListNode* p, int k) {
auto *n = p;
while (n && k) n = n -> next, -- k;
if (k) return nullptr;
while (n) p = p -> next, n = n -> next;
return p;
}
};
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode findKthToTail(ListNode pListHead, int k) {
if (k == 0) return null;
int len = cmpLen(pListHead);
if (k > len) return null;
int count = 0;
ListNode cur = pListHead;
while (count != (len - k)) {
cur = cur.next;
count++;
}
return cur;
}
private int cmpLen(ListNode pListHead) {
ListNode cur = pListHead;
int count = 0;
while (cur != null) {
count++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return count;
}
}
5. 链表中环的入口结点(快慢指针)
原题链接

/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *entryNodeOfLoop(ListNode *head) {
if (!head || !head->next) return 0;
ListNode *first = head, *second = head;
while (first && second)
{
first = first->next;
second = second->next;
if (second) second = second->next;
else return 0;
if (first == second)
{
first = head;
while (first != second)
{
first = first->next;
second = second->next;
}
return first;
}
}
return 0;
}
};
巧就巧在巧*****的找到相遇位置之后,重新初始化一个指针去走,最后会相遇在入口处。(可以用数学证明)
class Solution {
private ListNode hasCycle(ListNode head){
if(head == null) return null;
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null){
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if(fast == slow){
return slow;
}
}
return null;
}
public ListNode entryNodeOfLoop(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = hasCycle(head);
if(slow == null){
return null;
}
ListNode fast = head;
while(fast != slow){
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
6. 反转链表
原题链接
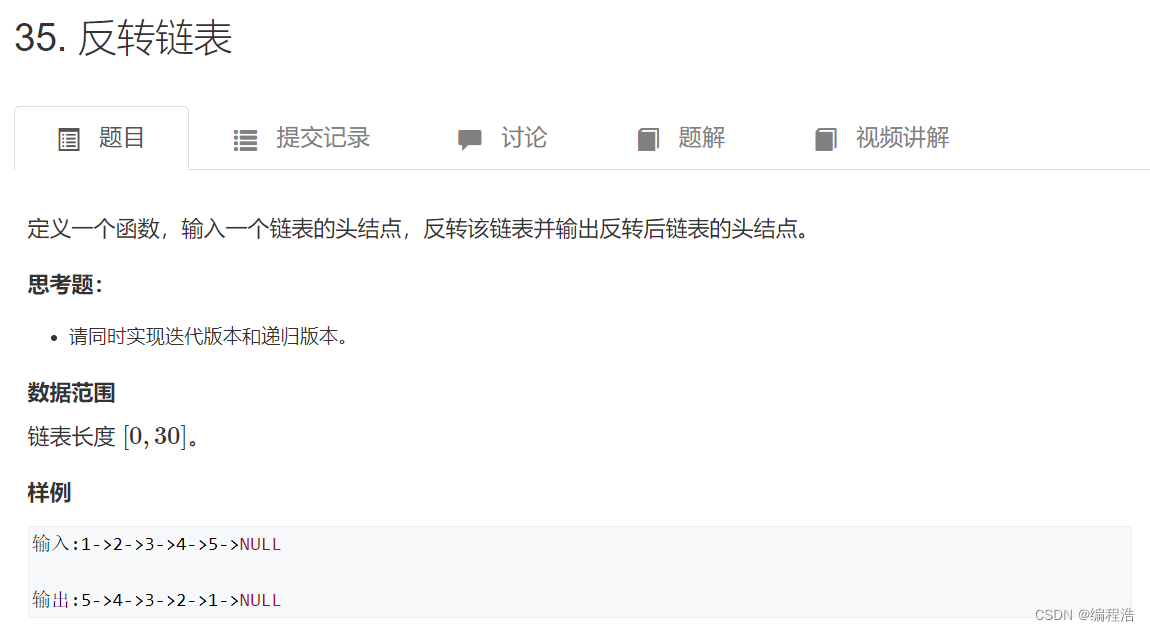
方法一: 迭代
1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4
i j
1 <- 2 -> 3 -> 4
i j
就像这样迭代
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
ListNode *prev = nullptr;
ListNode *cur = head;
while (cur)
{
ListNode *next = cur->next;
cur->next = prev;
prev = cur, cur = next;
}
return prev;
}
};
方法二:递归
1->2->3->4
因为用递归,翻转顺序指定是
从后往前
但是注意的是,返回的值应该是头节点,也就是4的值
那么如何递归?
- 接收返回值
- 递归当前两个节点
- 返回返回值
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
if (!head || !head->next) return head;
ListNode *tail = reverseList(head->next);
head->next->next = head;
head->next = nullptr;
return tail;
}
};
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if(head == null)
return null;
ListNode l = head.next;
head.next = null;
while(l != null){
ListNode ll = l.next;
l.next = head;
head = l;
l = ll;
}
return head;
}
}
7. 合并两个排序的链表
原题链接
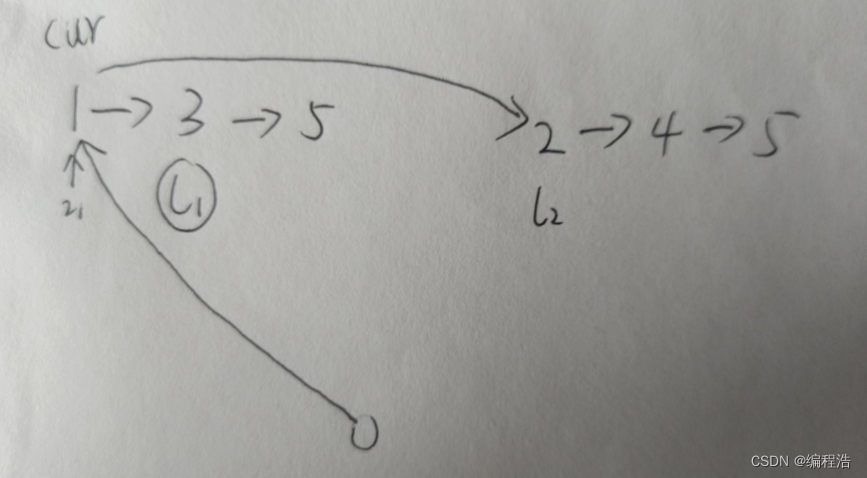
定义一个头节点,然后定义一个链表cur指向辅助
主要是完成
直接在两个表上的链路连接
比如 1->3 2->4合并
因为1小于2
那么直接让1->2(前提 l1的角标已经移到3)
如图
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* merge(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
ListNode *dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode *cur = dummy;
while (l1 != NULL && l2 != NULL) {
if (l1 -> val < l2 -> val) {
cur -> next = l1;
l1 = l1 -> next;
}
else {
cur -> next = l2;
l2 = l2 -> next;
}
cur = cur -> next;
}
cur -> next = (l1 != NULL ? l1 : l2);
return dummy -> next;
}
};
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode merge(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
// 1. 先判空
if(l1 == null) return l2;
if(l2 == null) return l1;
// 2. 创建头节点 便于返回答案
ListNode Head = new ListNode(0);
ListNode cur = Head;
while(l1 != null && l2 != null){
ListNode p1 = l1.next;
ListNode p2 = l2.next;
if(l1.val <= l2.val){
cur.next = l1;
l1 = p1;
} else {
cur.next = l2;
l2 = p2;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
if(l1 == null && l2 != null)
cur.next = l2;
if(l1 != null && l2 == null)
cur.next = l1;
return Head.next;
}
}
8. 复杂链表的复刻
原题链接

/**
* Definition for singly-linked list with a random pointer.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next, *random;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL), random(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *copyRandomList(ListNode *head) {
for(auto p = head; p ; ) //遍历原链表
{
auto np = new ListNode(p->val); //复刻节点
auto next = p->next; //留存原链表当前节点p的下一个节点
p->next = np;//将原链表当前节点p指向复刻节点
np->next = next;//复刻节点np指向原链表当前节点的下一个节点
p = next; //p指针后移
}
for (auto p = head; p; p = p->next->next)//对原链表random指针的复刻。
{
if (p->random)
p->next->random = p->random->next;
}
auto dummy = new ListNode(-1); //虚拟头结点
auto cur = dummy; //尾节点
for (auto p = head; p; p = p->next) //将原链表和复刻链表拆分出来,并将原链表复原。
{
cur->next = p->next;
cur = cur->next;
p->next = p->next->next;
}
return dummy->next;
}
};
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list with a random pointer.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next, random;
* ListNode(int x) { this.val = x; }
* };
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode copyRandomList(ListNode head) {
if(head == null)
return null;
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null){
ListNode temp = new ListNode(cur.val);
temp.next = cur.next;
cur.next = temp;
cur = cur.next.next;
}
cur = head;
while(cur != null){
ListNode temp = cur.next;
if(cur.random != null){
temp.random = cur.random.next;
} else {
temp.random = new ListNode(-1);
}
cur = cur.next.next;
}
// 创建一个头节点 便于返回节点
ListNode H = new ListNode(0);
H.next = head.next;
cur = head;
while(cur != null){
ListNode temp = cur.next;
cur.next = cur.next.next;
if(temp.next != null){
temp.next = temp.next.next;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return H.next;
}
}
9. 二叉搜索树与双向链表
原题链接
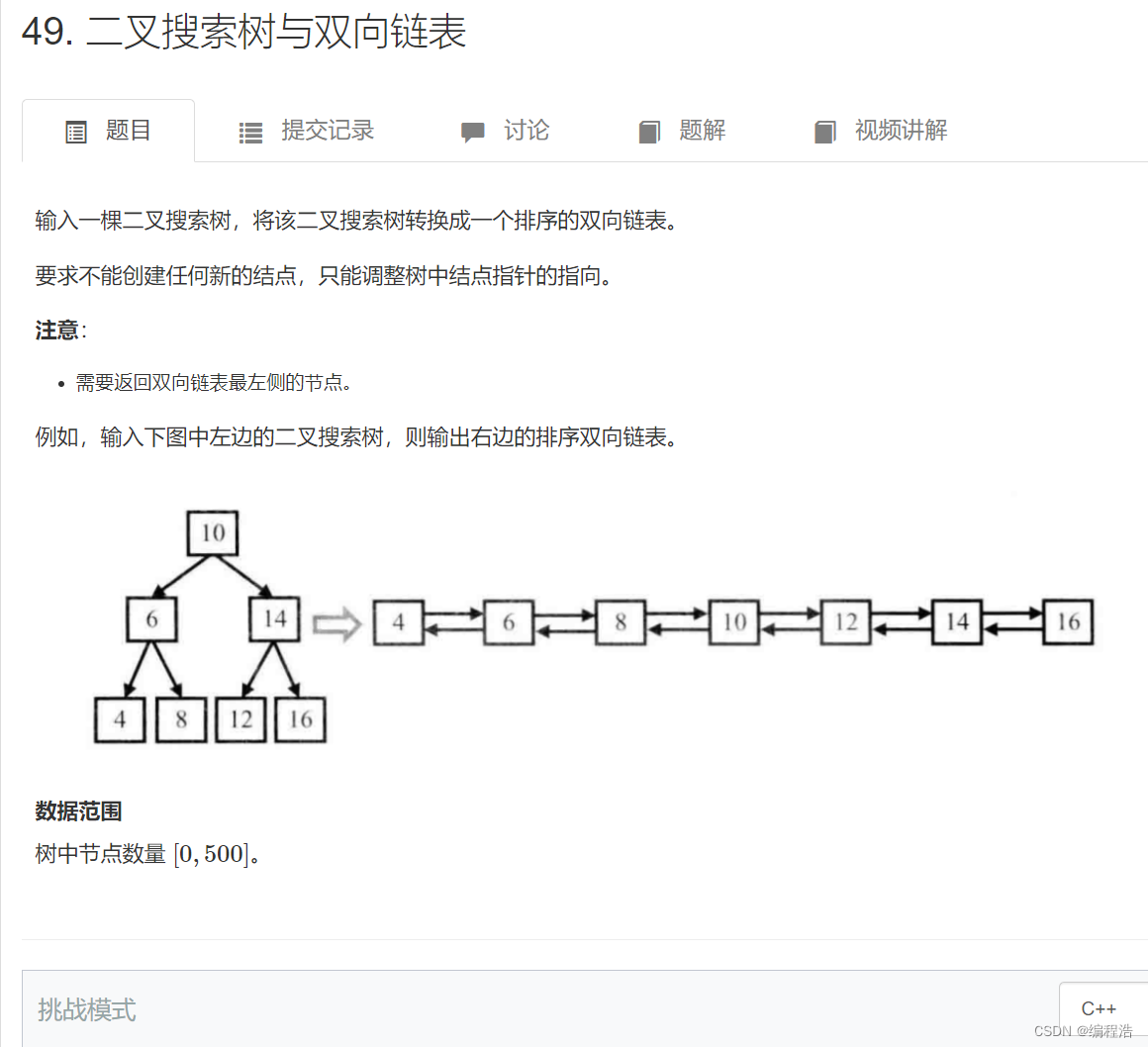
就在中序递归遍历的基础上改了一点点,用一个pre指针保存中序遍历的前一个结点。
因为是中序遍历,遍历顺序就是双线链表的建立顺序;
每一个结点访问时它的左子树肯定被访问过了,所以放心大胆的改它的left指针,不怕树断掉;
同理,pre指向的结点保存的数肯定小于当前结点,所以其左右子树肯定都访问过了,所以其right指针也可以直接改。
最后需要一直向左找到双向链表的头结点。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* pre = NULL;
TreeNode* convert(TreeNode* root) {
dfs(root);
while(root && root->left) root = root->left;
return root;
}
void dfs(TreeNode* root){
if(!root) return;
dfs(root->left);
root->left = pre;
if(pre) pre->right = root;
pre = root;
dfs(root->right);
}
};
class Solution {
TreeNode first = null;
TreeNode last = null;
public TreeNode convert(TreeNode root) {
helper(root);
return first;
}
private void helper(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
helper(node.left);
if (last == null) {
first = node;
} else {
last.right = node;
node.left = last;
}
last = node;
helper(node.right);
}
}






![[JavaWeb]【九】web后端开发-SpringBootWeb案例(菜单)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/b5b3627582b24c54b61835d28f0675e2.png)