目录
前言:
1. 删除链表中所有值为key的节点
方法一:正常删除,头结点另外讨论
方法二:虚拟头结点法
方法三:递归
2.反转链表
方法一:双指针迭代
方法二:递归法解析:
3.链表的中间结点
方法:快慢指针法
4. 链表中倒数第k个结点
方法:快慢指针方法
5.合并两个有序链表
方法:迭代
前言:
数据结构想要学的好,刷题少不了,我们不仅要多刷题,还要刷好题!为此我开启了一个必做好题锦集的系列,每篇大约5题左右。此为第一篇选择题篇,该系列会不定期更新敬请期待!
1. 删除链表中所有值为key的节点
移除链表元素![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-linked-list-elements/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-linked-list-elements/
题目描述:
给你一个链表的头节点 head 和一个整数 val ,请你删除链表中所有满足 Node.val == val 的节点,并返回 新的头节点 。


方法一:正常删除,头结点另外讨论
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
while(head!=null&&head.val==val){
head=head.next;
}
if(head==null){
return head;
}
ListNode cur=head;
while (cur.next!=null){
if(cur.next.val==val){
cur.next=cur.next.next;
}else {
cur=cur.next;
}
}
return head;
}解析:

但会漏掉头结点

方法二:虚拟头结点法
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
if(head==null){
return head;
}
ListNode newnode=new ListNode();
newnode.next=head;
head=newnode;
ListNode cur=head;
while (cur.next!=null){
if(cur.next.val==val){
cur.next=cur.next.next;
}else {
cur=cur.next;
}
}
return head.next;
}解析:

方法三:递归
class Solution {
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
if (head == null) {
return head;
}
head.next = removeElements(head.next, val);
return head.val == val ? head.next : head;
}
}
递归方法之前就是一个压栈的过程,递归方法之后就是一个弹栈的过程
2.反转链表
反转链表![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-linked-list/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-linked-list/
题目描述:
给你单链表的头节点 head ,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。

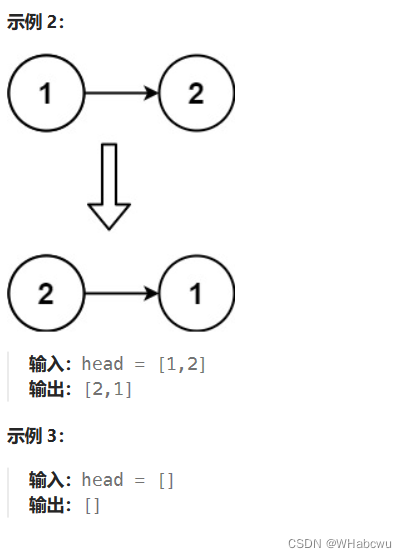

方法一:双指针迭代
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre=null;
ListNode cur=head;
while(cur!=null){
ListNode tmp=cur.next;
cur.next=pre;
pre=cur;
cur=tmp;
}
return pre;
}解析:
我们可以申请两个指针,第一个指针叫 pre,最初是指向 null 的。第二个指针 cur 指向 head,然后不断遍历 cur。每次迭代到 cur,都将 cur 的 next 指向 pre,然后 pre 和 cur 前进一位。都迭代完了(cur 变成 null 了),pre 就是最后一个节点了。
方法二:递归法解析:
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if(head==null || head.next==null) {
return head;
}
ListNode cur = reverseList(head.next);
head.next.next = head;
head.next = null;
return cur;
}解析:
3.链表的中间结点
链表的中间结点![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/middle-of-the-linked-list/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/middle-of-the-linked-list/
题目描述:
给你单链表的头结点 head ,请你找出并返回链表的中间结点。如果有两个中间结点,则返回第二个中间结点。
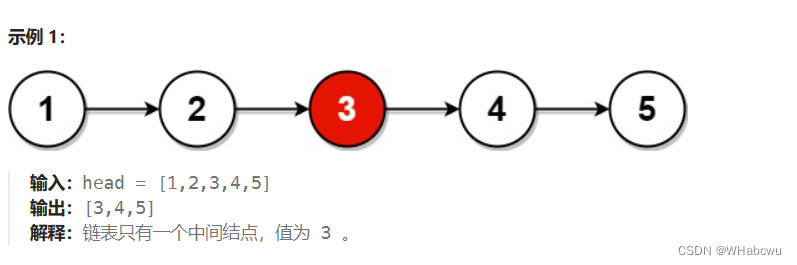
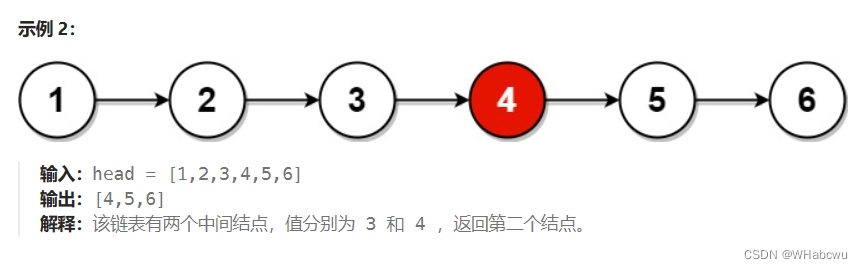

方法:快慢指针法
public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
if(head==null){
return null;
}
ListNode fast=head;
ListNode slow=head;
while(fast!=null&&fast.next!=null){
fast=fast.next.next;
slow=slow.next;
}
return slow;
}解析:
用两个指针
slow与fast一起遍历链表。slow一次走一步,fast一次走两步。那么当fast到达链表的末尾时,slow必然位于中间。
4. 链表中倒数第k个结点
题目描述:
输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点。

方法:快慢指针方法
public ListNode FindKthToTail(ListNode head,int k) {
if(head==null||k<=0){
return null;
}
ListNode slow=head;
ListNode fast=head;
while(k-1>0){
fast=fast.next;
if(fast==null){
return null;
}
k--;
}
while(fast!=null&&fast.next!=null){
fast=fast.next;
slow=slow.next;
}
return slow;
}解析:
首先让快指针先行k-1步,然后让快慢指针每次同行一步,直到快指针fast==null&&fast.next==null,慢指针就是倒数第K个节点。


5.合并两个有序链表
合并两个有序链表![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/merge-two-sorted-lists/题目描述:
https://leetcode.cn/problems/merge-two-sorted-lists/题目描述:
将两个升序链表合并为一个新的 升序 链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
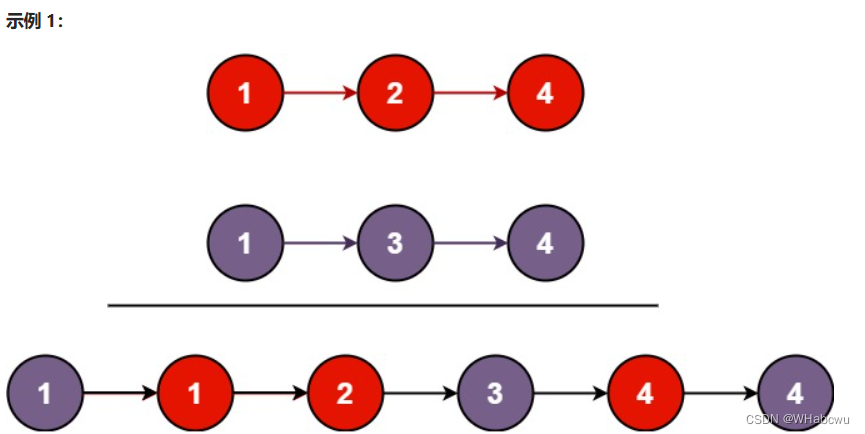


方法:迭代
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode head1, ListNode head2) {
if(head1==null){
return head2;
}
if(head2==null){
return head1;
}
ListNode listNode = new ListNode();
ListNode cur=listNode;
while(head1!=null&&head2!=null){
if(head1.val<head2.val){
cur.next=head1;
head1=head1.next;
}else{
cur.next=head2;
head2=head2.next;
}
cur=cur.next;
}
if(head1==null){
cur.next=head2;
}else{
cur.next=head1;
}
return listNode.next;
}解析:

对head1与head2里的元素进行比较,谁小就与cur连接,比如head1的值小,就将hea1与cur相连然后向后走一步成为新的head1,cur向后走一步成为新的cur,依次类推进行比较

以上为我个人的小分享,如有问题,欢迎讨论!!!
都看到这了,不如关注一下,给个免费的赞 ![]()