文章目录
- 链表
- BM1 反转链表
- BM2 链表内指定区间反转
- BM3 链表中的节点每k个一组翻转
- BM4 合并两个排序的链表
- BM5 合并k个已排序的链表
- BM6 判断链表中是否有环
- BM7 链表中环的入口结点
- BM8 链表中倒数最后k个结点
- BM9 删除链表的倒数第n个节点
- BM10 两个链表的第一个公共结点
链表
BM1 反转链表
题目
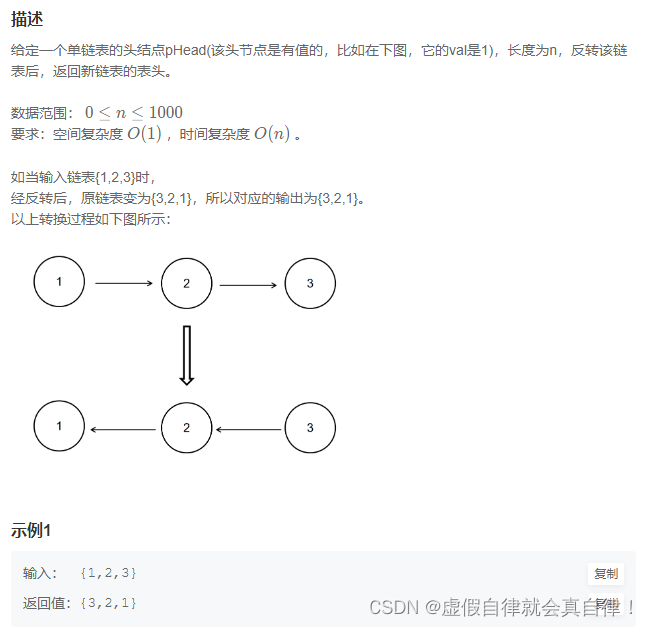
/**
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* ReverseList(ListNode* head) {
if(head == nullptr) return head;
ListNode* cur = head;
ListNode* pre = nullptr;
ListNode* temp;
while(cur)
{
temp = cur->next;//保存cur下一个节点
cur->next = pre;//反转
pre = cur;
cur = temp;
}
return pre;
}
};
BM2 链表内指定区间反转

自己写的时候,思路正确,但是处理不好反转后的拼接
/**
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseBetween(ListNode* head, int m, int n) {
if(m == n) return head;
ListNode* dummyhead = new ListNode(-1);
dummyhead->next = head;
//反转链表的前部分
ListNode* start = dummyhead;
for(int i=1; i<m; i++)
start = start->next;//结点1
cout << "start: "<< start->val <<endl;
//反转链表的尾巴 第n个结点
ListNode* right = start->next;
for(int i=m; i<n; i++)
right = right->next;//结点4
cout << "right: "<< right->val <<endl;
//反转链表的头尾
ListNode* left = start->next;//2
ListNode* end = right->next;//5
//切断 left 1 2 3 4
start->next = nullptr;
right->next = nullptr;
reverlist(left);
//接回原来的链表
start->next = right;//1->4
left->next = end;//2->5
return dummyhead->next;
}
void reverlist(ListNode* node)
{
ListNode* pre = nullptr;
ListNode* cur = node;
ListNode* temp;
while(cur)
{
temp = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = temp;
}
}
};
写法2
/**
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
/**
* 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
*
*
* @param head ListNode类
* @param m int整型
* @param n int整型
* @return ListNode类
*/
ListNode* reverseBetween(ListNode* head, int m, int n) {
if(m == n) return head;
ListNode* dummyhead = new ListNode(-1);
dummyhead->next = head;
//写法1
/*//反转链表的前部分
ListNode* start = dummyhead;
for(int i=1; i<m; i++)
start = start->next;//结点1
cout << "start: "<< start->val <<endl;
//反转链表的尾巴 第n个结点
ListNode* right = start->next;
for(int i=m; i<n; i++)
right = right->next;//结点4
cout << "right: "<< right->val <<endl;
//反转链表的头尾
ListNode* left = start->next;//2
ListNode* end = right->next;//5
//切断 left 1 2 3 4
start->next = nullptr;
right->next = nullptr;
reverlist(left);
//接回原来的链表
start->next = right;//1->4
left->next = end;//2->5
return dummyhead->next;*/
//写法2
ListNode* pre = dummyhead;
ListNode* cur = head;
//找到结点m
for(int i=1; i<m; i++)
{
pre = cur;//m-1
cur = cur->next;//m
}
//从m到n反转 依次断掉指向后续的指针,反转指针方向
ListNode* temp;
for(int i=m; i<n; i++)
{
temp = cur->next;//要反转的结点
cur->next = temp->next;//指向n
temp->next = pre->next;//反转
pre->next = temp;//指向m
}
return dummyhead->next;
}
void reverlist(ListNode* node)
{
ListNode* pre = nullptr;
ListNode* cur = node;
ListNode* temp;
while(cur)
{
temp = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = temp;
}
}
};
BM3 链表中的节点每k个一组翻转
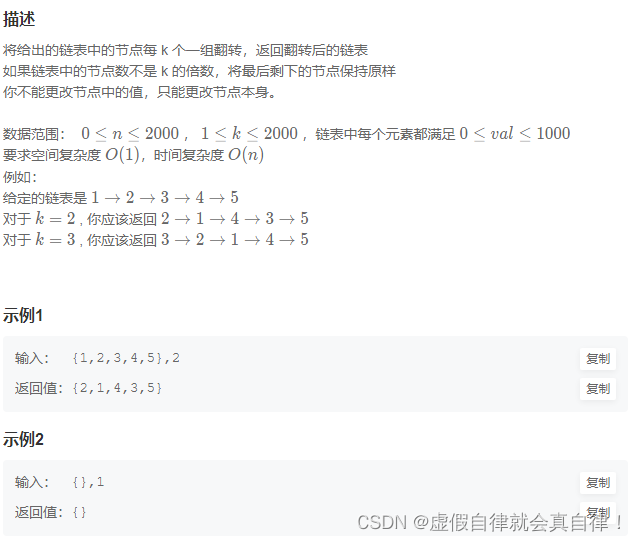
自己写的乱七八糟,看了解答之后觉得好聪明啊,关键是要找到反转前的局部链表的尾巴,这个也是要返回的链表头,然后建立每一组的连接!!
/**
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseKGroup(ListNode* head, int k) {
//每一组局部链表的表头 反转前局部链表的尾巴
ListNode* tail = head;
//找到尾巴
for(int i=0; i<k; i++)
{
//如果链表不够长 返回结果
if(tail == nullptr) return head;
tail = tail->next;
}
//反转局部链表
ListNode* pre = nullptr;
ListNode* cur = head;
ListNode* temp;
//在到达当前段尾节点前
while(cur != tail)
{
temp = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = temp;
}
//反转后链表尾部连接下一组表头
head->next = reverseKGroup(tail, k);
return pre;
}
};
模拟的写法,将一条链表分为链表长度/k块链表,如果处不尽则说明后面会有剩下的那一块是不满长度为k的。
最初需要定义虚拟表头dummyhead(最终结果)和局部链表的反转前的表头start。然后遍历每一组局部链表,并反转。反转后需要将start与反转后的局部链表头pre连接(反转前局部链表的尾部),再更新下一组的局部链表的表头,也就是将start更新到最前。
/**
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseKGroup(ListNode* head, int k) {
if(k<=1) return head;
if(head == nullptr) return nullptr;
int len = getLength(head);
int part = len / k;//分组
ListNode* dummyhead = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode* start = dummyhead;//每一组局部链表的表头
for(int i=0; i<part; i++)
{
//局部链表反转后的尾巴
ListNode* pre = nullptr;
for(int j=0; j<k; j++)
{
ListNode* temp = head->next;
head->next = pre;
pre = head;
head = temp;
}
start->next = pre;//链表头连接 反转后的局部链表 的表头
while(start->next) start = start->next;//更新下一组的表头
}
start->next = head;
return dummyhead->next;
}
private:
//获取链表长度
int getLength(ListNode* node)
{
int len = 0;
if(node == nullptr) return len;
while(node)
{
len++;
node = node->next;
}
return len;
}
};
BM4 合并两个排序的链表
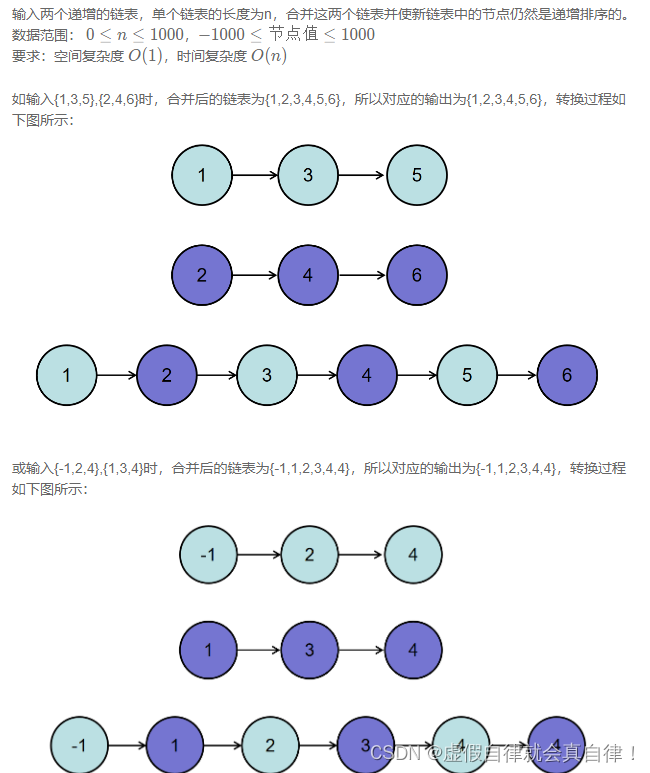
/**
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* Merge(ListNode* pHead1, ListNode* pHead2) {
if(!pHead1 && !pHead2) return nullptr;
if(!pHead1) return pHead2;
if(!pHead2) return pHead1;
ListNode* dummyhead = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode* cur = dummyhead;
while(pHead1 && pHead2)
{
if(pHead1->val <= pHead2->val)
{
cur->next = pHead1;
pHead1 = pHead1->next;//1->2
//cout << " cur:" << cur->next->val << " pHead1:" << pHead1->val << endl;
}
else if(pHead1->val > pHead2->val)
{
cur->next = pHead2;
pHead2 = pHead2->next;
//cout << " cur:" << cur->next->val << " pHead2:" << pHead2->val << endl;
}
cur = cur->next;//连接新链表
}
//如果还有剩下的结点 单独处理最后一个结点
cur->next = (pHead2 == nullptr) ? pHead1 : pHead2;
return dummyhead->next;
}
};
方法2,取较小的结点
/**
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* Merge(ListNode* pHead1, ListNode* pHead2) {
if(!pHead1 && !pHead2) return nullptr;
if(!pHead1) return pHead2;
if(!pHead2) return pHead1;
ListNode* dummyhead = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode* cur = dummyhead;
while(pHead1 && pHead2)
{
if(pHead1->val > pHead2->val) swap(pHead1, pHead2);
cur->next = pHead1;//建立新连接
pHead1 = pHead1->next;//更新
cur = cur->next;//更新
}
cur->next = (pHead2 == nullptr) ? pHead1 : pHead2;
return dummyhead->next;
}
};
BM5 合并k个已排序的链表

这个写法会把负数的结点吞掉,例如输入:[{-5},{-9,-8,-7,-5,1,1,1,3},{-10,-7,-6,-6,-6,0,1,3,3},{-10,-8,-7,-2,3,3},{-1,4},{-5,-4,-1}],输出是{-5,0,1,1,1,1,3,3,3,3,3,4}
/**
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists) {
// write code here
ListNode* dummyhead = new ListNode(-1);
dummyhead->next = lists[0];
ListNode* cur = dummyhead;
for(int i=1; i<lists.size();)
{
cur->next = mergeList(lists[i], lists[i+1]);
cur = cur->next;
i += 2;
}
return dummyhead->next;
}
ListNode* mergeList(ListNode* head1, ListNode* head2)
{
if(head1 == nullptr) return head2;
if(head2 == nullptr) return head1;
ListNode* dummyhead = new ListNode(0);
ListNode* cur = dummyhead;
while(head1 && head2)
{
if(head1->val >= head2->val) swap(head1, head2);
cur->next = head1;
head1 = head1->next;
cur = cur->next;
}
cur->next = (head1 == nullptr) ? head2 : head1;
return dummyhead->next;
}
};
加入并归排序后的,可以输出负数结点了
/**
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists) {
return divideMerge(lists, 0, lists.size()-1);
}
//划分合并区间函数
ListNode* divideMerge(vector<ListNode *> &lists, int left, int right){
if(left > right)
return NULL;
//中间一个的情况
else if(left == right)
return lists[left];
//从中间分成两段,再将合并好的两段合并
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
return mergeList(divideMerge(lists, left, mid), divideMerge(lists, mid + 1, right));
}
ListNode* mergeList(ListNode* head1, ListNode* head2)
{
if(!head1 && !head2) return nullptr;
if(head1 == nullptr) return head2;
if(head2 == nullptr) return head1;
ListNode* dummyhead = new ListNode(0);
ListNode* cur = dummyhead;
while(head1 && head2)
{
if(head1->val >= head2->val) swap(head1, head2);
cur->next = head1;
head1 = head1->next;
cur = cur->next;
}
cur->next = (head1 == nullptr) ? head2 : head1;
return dummyhead->next;
}
};
BM6 判断链表中是否有环
判断给定的链表中是否有环。如果有环则返回true,否则返回false。
思路就是,快慢指针同时出发,慢指针走一步,快指针走两步。快指针肯定先进入环,慢指针后入环,如果两个指针相遇说明有环,如果没有相遇,遍历结束说明没有换。
第一次写的时候,有一组很长的链表没有通过,while循环内没有对fast的下一个结点进行判断,可能会一直在循环里边不终止。加了一个判断,如果fast有下一个结点才更新,否则也是说明链表走到头了。又或者是while的判断条件加上fast->next != null
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) {
if(head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr) return false;
ListNode* fast = head;
ListNode* slow = head;
while(fast && slow)
{
slow = slow->next;
//下面这个if-else是改正后的写法
if(fast->next) fast = fast->next->next;
else return false;
if(fast == slow) return true;
}
return false;//如果fast先遇到null说明没有环
}
};
BM7 链表中环的入口结点
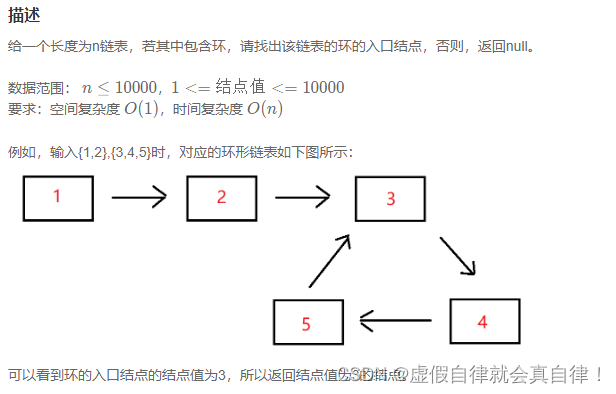
上一题是判断有没有环,这个是有环然后要找到环入口。
思路,也是快慢指针。
- 首先,快慢指针同时出发,慢指针走一步,快指针走两步。快指针肯定先进入环,慢指针后入环,如果两个指针相遇说明有环,如果没有相遇,遍历结束说明没有环。
- 然后,第一次相遇时,在这个地方,重新定义两个指针,慢指针从头开始走,快指针在换里边走同时移动一步,如果相遇就找到了环入口,否则返回null。
/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) :
val(x), next(NULL) {
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* EntryNodeOfLoop(ListNode* pHead) {
if(pHead == nullptr) return nullptr;
ListNode* fast = pHead;
ListNode* slow = pHead;
while(fast!=nullptr && fast->next != nullptr)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
if(slow == fast)
{
slow = pHead;
ListNode* entrynode = fast;
while(entrynode)
{
//先判断 有可能就是一个闭环链表
if(entrynode == slow) return entrynode;
slow = slow->next;
entrynode = entrynode->next;
}
}
}
return nullptr;
}
};
BM8 链表中倒数最后k个结点

思路-快慢指针:
- 首先,快指针先走K步,在这里要注意两个特殊情况,一个是链表不够长,一个是正好需要返回倒数最后一个结点(第一个结点)。
- 然后,慢指针从头开始,和快指针同时前进,快指针走到链表尾,慢指针走到第k个结点了。
/**
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* FindKthToTail(ListNode* pHead, int k) {
//空链表
if (pHead == nullptr) return pHead;
ListNode* fast = pHead;
while(k--)
{
if(fast->next == nullptr && k>0) return nullptr;//链表不够长
if(fast->next == nullptr) return pHead;//倒数最后一个
fast = fast->next;
//cout << " fast: " << fast->val;
}
while(fast)
{
pHead = pHead->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
return pHead;
}
};
BM9 删除链表的倒数第n个节点

思路在上一题的基础上,在保存一个倒数第K-1个节点,然后逻辑删除就可以了。
/**
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
if(head == nullptr) return head;
ListNode* fast = head;
while(n--)
{
if(fast->next==nullptr && n>0) return nullptr;
if(fast->next==nullptr)
{
return head->next;//逻辑删除
}
cout << " fast: " << fast->val;
fast = fast->next;
}
ListNode* slow = head;
ListNode* temp;
while(fast)
{
temp = slow;//倒数第k-1个结点
slow = slow->next;//倒数第k个结点
fast = fast->next;
}
temp->next = slow->next;
return head;
}
};
BM10 两个链表的第一个公共结点
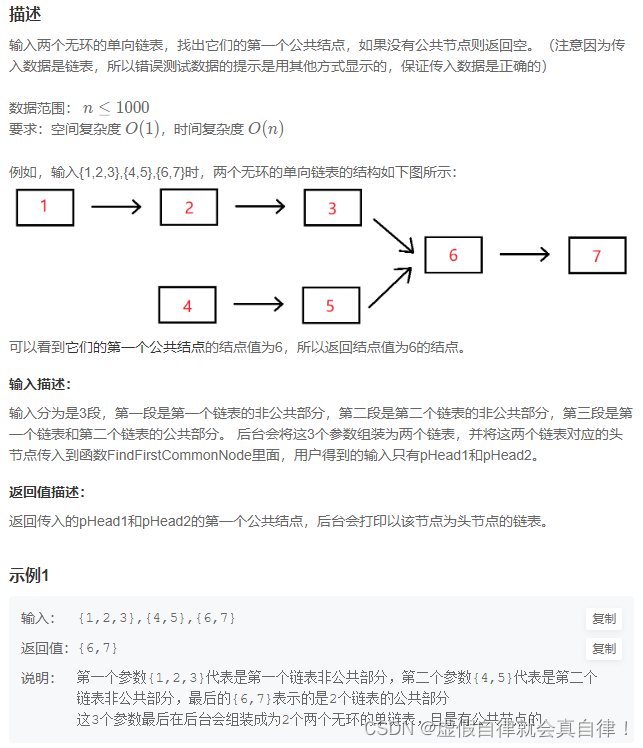
思路:统计长度,计算长度差len,长的链表先走len步,然后再和短链表一起走,如果两结点相同说明有公共结点。
/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) :
val(x), next(NULL) {
}
};*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* FindFirstCommonNode( ListNode* pHead1, ListNode* pHead2) {
if(!pHead1 || !pHead2) return nullptr;
int len1 = getLenofList(pHead1);
int len2 = getLenofList(pHead2);
if(len1 < len2)
{
swap(pHead1, pHead2);
swap(len1, len2);
}
int len = len1 - len2;
while(len--)
{
pHead1 = pHead1->next;
}
//cout << pHead1->val<<endl;
while(pHead1)
{
if(pHead1 == pHead2) return pHead1;
pHead1 = pHead1->next;
pHead2 = pHead2->next;
}
return nullptr;
}
int getLenofList(ListNode* head)
{
int res = 0;
if(head == nullptr) return res;
while(head)
{
res++;
head = head->next;
}
return res;
}
};