对比(协商)缓存
比较一下再去决定是用缓存还是重新获取数据,这样会减少网络请求,提高性能。
对比缓存的工作原理
客户端第一次请求服务器的时候,服务器会把数据进行缓存,同时会生成一个缓存标识符,这个缓存标识符会被发送到客户端,客户端第二次请求服务器的时候,会把缓存标识符发送到服务器,服务器会根据缓存标识符进行判断,如果缓存标识符相同,则服务器会判断缓存是否过期,如果没有过期,则服务器会返回 304,告诉客户端使用缓存,如果缓存标识符不同,则服务器会返回 200,同时返回新的数据。
- 客户端:
if-modified-since - 服务端:
Last-Modified对比最后的修改时间返回内容
缺点是内容没变化修改时间变化了也会重新读取内容,时间不精确,(精确到秒),如果一秒内改了多次也监控不到。
下面我们通过判断文件的修改时间是否对的上,一样的话直接返回 304 告诉读取缓存
新建 cache.js 文件
const http = require("http");
const fs = require("fs");
const path = require("path");
const url = require("url");
const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
const { pathname } = url.parse(req.url);
const filePath = path.join(__dirname, pathname);
console.log(pathname);
res.setHeader("Cache-Control", "no-cache");
// 第二次请求会带上 if-modified-since 请求头
let ifModifiedSince = req.headers["if-modified-since"];
fs.stat(filePath, (err, statObj) => {
if (err) return res.end();
let lastModified = statObj.ctime.toGMTString();
// 判断文件的修改时间是否对的上,一样的话直接返回 304 告诉读取缓存
if (ifModifiedSince && lastModified === ifModifiedSince) {
res.statusCode = 304;
return res.end();
}
res.setHeader("Last-Modified", lastModified);
if (err) return (res.statusCode = 404), res.end("Not Found");
// 判断是否是文件
if (statObj.isFile()) {
fs.createReadStream(filePath).pipe(res);
} else {
res.statusCode = 404;
res.end("Not Found");
}
});
});
server.listen(5000);
然后新建 public 文件夹,里面添加 index.html 和 style.css
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>凯小默测试对比缓存:通过修改时间</title>
</head>
<body>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="/public/style.css">
</body>
</html>
body {
background-color: seagreen;
}
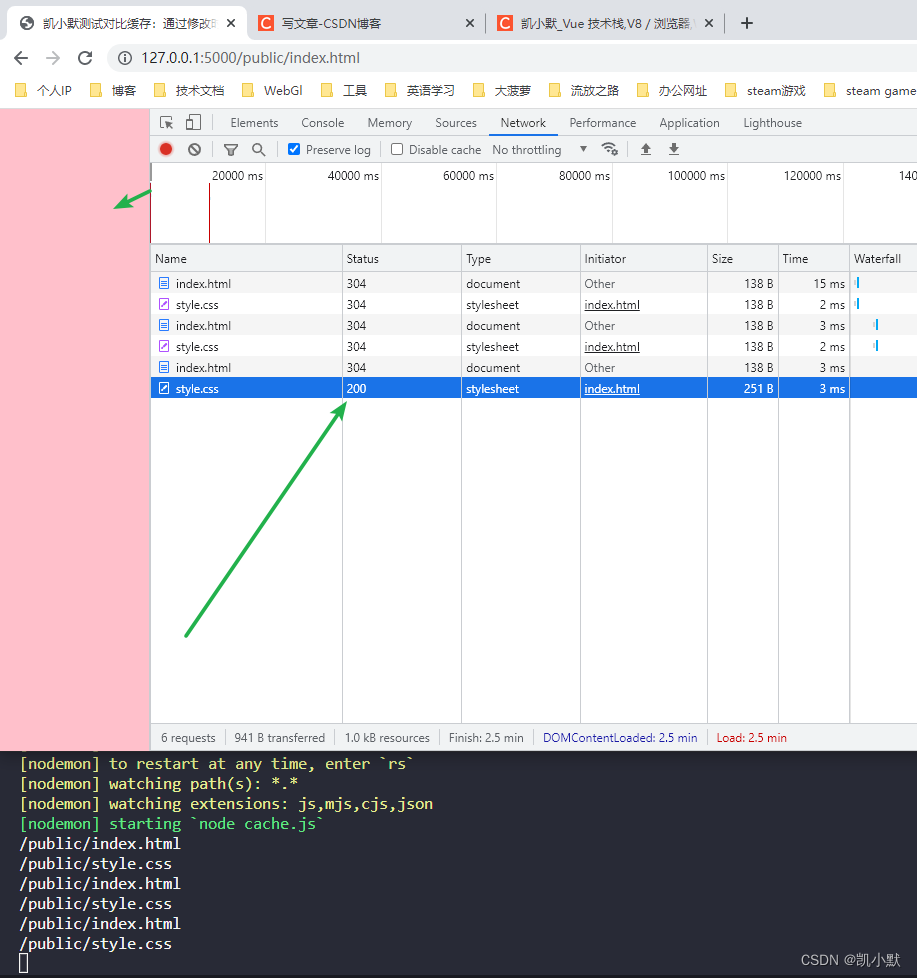
我们启动服务,访问 http://127.0.0.1:5000/public/index.html,可以看到第二次请求的资源变成了 304
nodemon cache.js
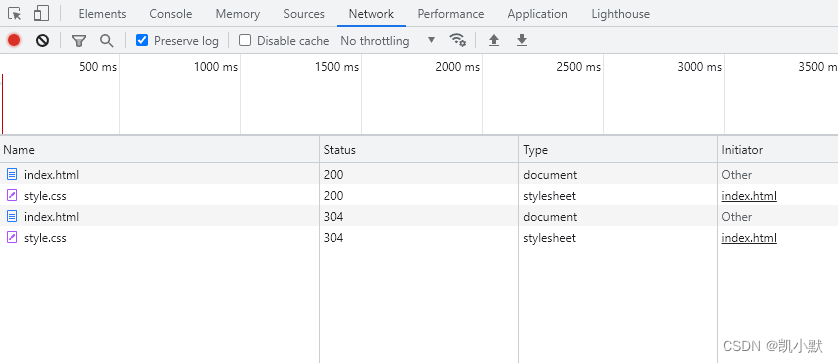
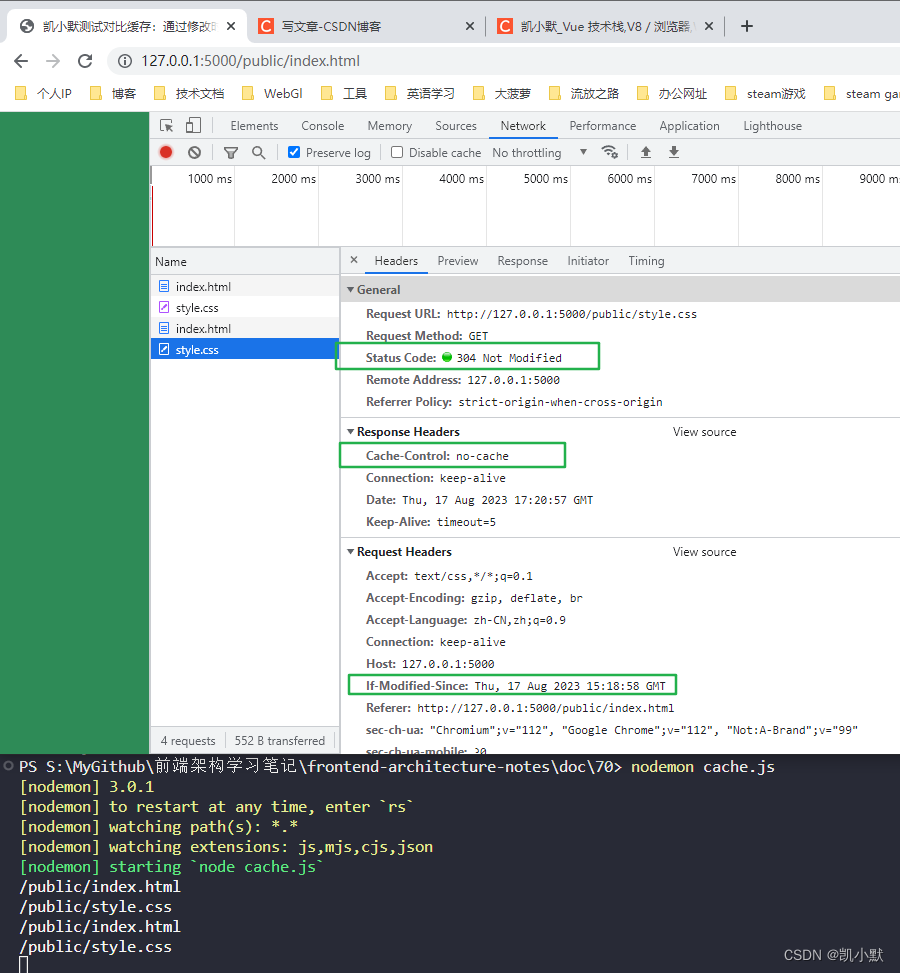
我们修改 style.css 文件,背景改成 pink,然后刷新访问,我们可以看到状态码变成 200,读取到了新的资源
body {
background-color: pink;
}