介绍
视频教程地址在此:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Pm4y1H7Tb/
大家好,欢迎来到本视频!今天,我们将一同探索Python编程世界中的一个有趣而创意的库——Turtle库。无需专业绘画技能,你就可以轻松地用代码绘制出美丽的图形、艺术作品甚至是动画。
Turtle库灵感来自于海龟,它允许你像控制海龟一样来控制一个绘图画布。让我们看看如何使用这个库来创造独特的艺术。
首先,我们导入Turtle库,然后创建一个海龟对象,可以命名为"t"。随后,我们就可以使用各种方法来控制海龟的移动、绘制形状和改变颜色。
只需几行代码,你就可以绘制出直线、圆、多边形甚至是心形。通过改变参数,你可以调整图形的大小、角度和颜色,让你的创意无限延展。
Turtle库不仅仅是静态图形,它还支持动画!你可以使用循环和定时来创建精彩的动画效果。比如,我们可以绘制出一个移动的螺旋图案,让海龟成为你的艺术舞台上的舞者。
但这还不止!Turtle库也可以用于教育和学习。它能够帮助初学者理解编程概念,如循环和条件语句,通过可视化的方式更加直观地展示。
无论你是艺术家、初学者还是教育工作者,Turtle库都能够激发你的创造力和好奇心。通过简单的代码,你可以创造出令人惊叹的图像和动画。
下面给出几个案例,大家只需要复制粘贴后运行代码就可以看到效果:
气球飞舞
效果
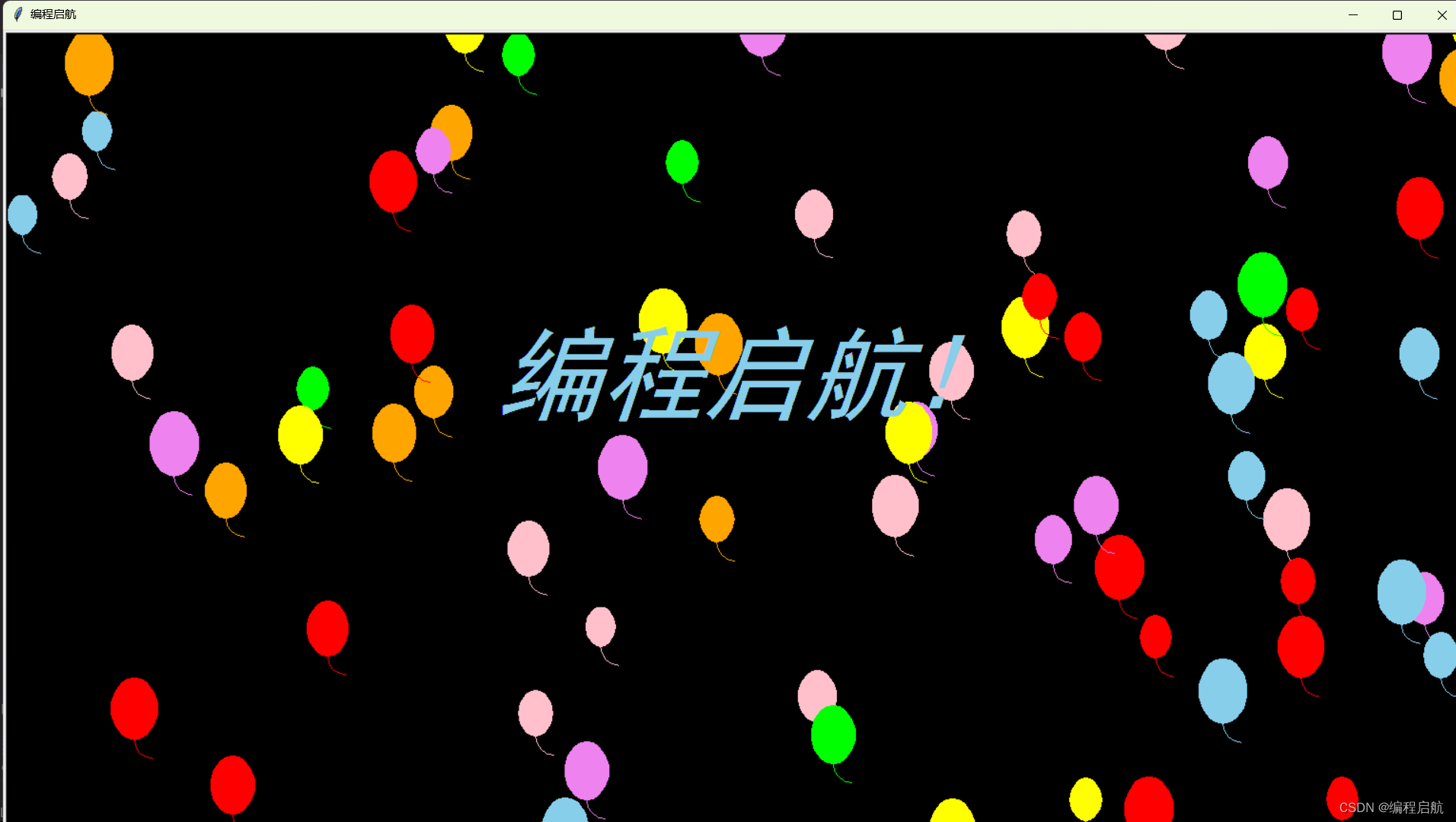
代码
import turtle as tu
import random as ra
import math
tu.title("编程启航")
tu.setup(1.0, 1.0)
t = tu.Pen()
t.ht()
colors = ['red','skyblue','orange','yellow','lime','pink','violet']
class Balloon(): #每个气球(气球类)
def __init__(self):
self.r = ra.randint(12,20) #气球的半径
self.x = ra.randint(-1000,1000) #气球的横坐标
self.y = ra.randint(-500,500) #气球的纵坐标
self.f = ra.uniform(-3.14,3.14) #气球左右移动呈正弦函数
self.speed = ra.randint(5,10) #气球移动速度
self.color = ra.choice(colors) #气球的颜色
self.outline = 1 #气球的外框大小(可不要)
def move(self): #气球移动函数
if self.y <= 500: #当气球还在画布中时
self.y += self.speed #设置上下移动速度
self.x += self.speed * math.sin(self.f) #设置左右移动速度
self.f += 0.1 #可以理解成标志,改变左右移动的方向
else: #当气球漂出了画布时,重新生成一个气球
self.r = ra.randint(12,20)
self.x = ra.randint(-1000,1000)
self.y = -500
self.f = ra.uniform(-3.14,3.14)
self.speed = ra.randint(5,10)
self.color = ra.choice(colors)
self.outline = 1
def draw(self): #画气球函数,就是用turtle画气球
t.penup()
t.goto(self.x,self.y)
t.pendown()
t.color(self.color)
t.left(45)
t.begin_fill()
t.fillcolor(self.color)
for i in range(2):
t.circle(self.r*2, 90)
t.circle(self.r, 90)
t.end_fill()
t.hideturtle()
t.circle(self.r,-45)
t.right(90)
t.circle(20,90)
Balloons = [] #用列表保存所有气球
for i in range(100):
Balloons.append(Balloon())
tu.bgcolor('black')
while True: #开始漂浮
tu.tracer(0)
t.clear()
for i in range(len(Balloons)): #在画布中设置50个漂浮的气球
Balloons[i].move()
Balloons[i].draw()
tu.penup() #写祝福
tu.goto(-250,20)
tu.pendown()
tu.color("skyblue")
tu.write("编程启航!",font=("黑体", 80,"italic")) #"italic"表示斜体
tu.hideturtle()
tu.update()
tu.mainloop()
时钟程序
效果
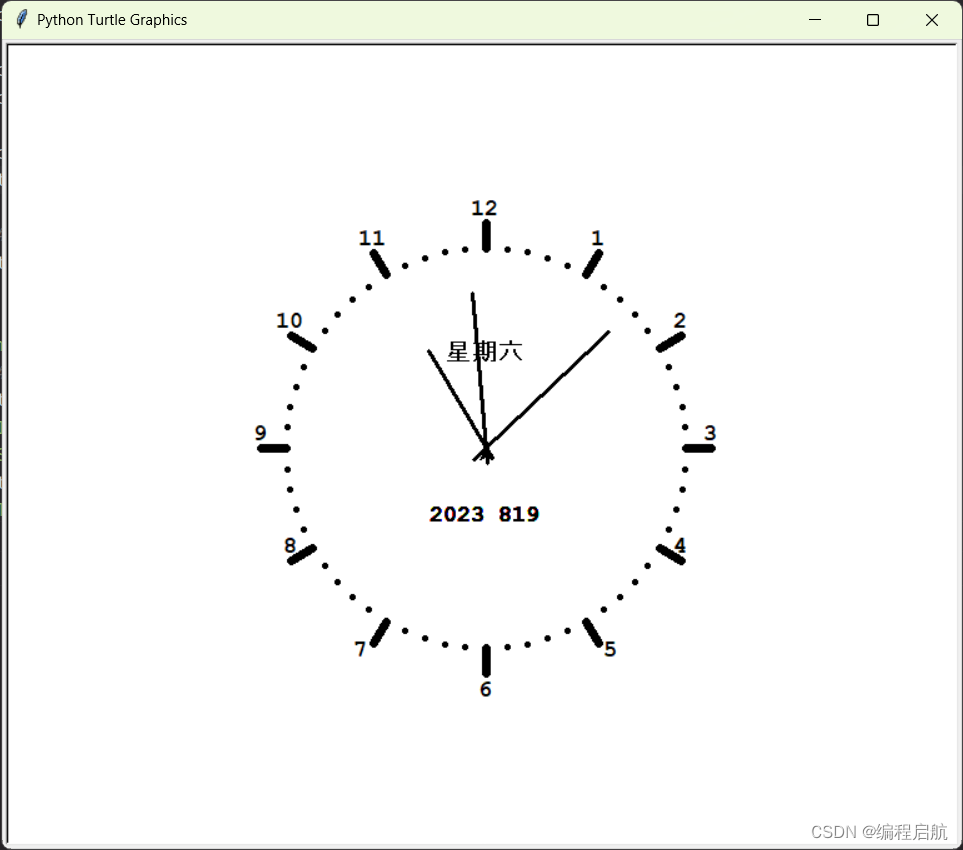
代码:
# coding=utf-8
import turtle
from datetime import *
# 抬起画笔,向前运动一段距离放下
def Skip(step):
turtle.penup()
turtle.forward(step)
turtle.pendown()
def mkHand(name, length):
# 注册Turtle形状,建立表针Turtle
turtle.reset()
Skip(-length * 0.1)
# 开始记录多边形的顶点。当前的乌龟位置是多边形的第一个顶点。
turtle.begin_poly()
turtle.forward(length * 1.1)
# 停止记录多边形的顶点。当前的乌龟位置是多边形的最后一个顶点。将与第一个顶点相连。
turtle.end_poly()
# 返回最后记录的多边形。
handForm = turtle.get_poly()
turtle.register_shape(name, handForm)
def Init():
global secHand, minHand, hurHand, printer
# 重置Turtle指向北
turtle.mode("logo")
# 建立三个表针Turtle并初始化
mkHand("secHand", 135)
mkHand("minHand", 125)
mkHand("hurHand", 90)
secHand = turtle.Turtle()
secHand.shape("secHand")
minHand = turtle.Turtle()
minHand.shape("minHand")
hurHand = turtle.Turtle()
hurHand.shape("hurHand")
for hand in secHand, minHand, hurHand:
hand.shapesize(1, 1, 3)
hand.speed(0)
# 建立输出文字Turtle
printer = turtle.Turtle()
# 隐藏画笔的turtle形状
printer.hideturtle()
printer.penup()
def SetupClock(radius):
# 建立表的外框
turtle.reset()
turtle.pensize(7)
for i in range(60):
Skip(radius)
if i % 5 == 0:
turtle.forward(20)
Skip(-radius - 20)
Skip(radius + 20)
if i == 0:
turtle.write(int(12), align="center", font=("Courier", 14, "bold"))
elif i == 30:
Skip(25)
turtle.write(int(i / 5), align="center", font=("Courier", 14, "bold"))
Skip(-25)
elif (i == 25 or i == 35):
Skip(20)
turtle.write(int(i / 5), align="center", font=("Courier", 14, "bold"))
Skip(-20)
else:
turtle.write(int(i / 5), align="center", font=("Courier", 14, "bold"))
Skip(-radius - 20)
else:
turtle.dot(5)
Skip(-radius)
turtle.right(6)
def Week(t):
week = ["星期一", "星期二", "星期三",
"星期四", "星期五", "星期六", "星期日"]
return week[t.weekday()]
def Date(t):
y = t.year
m = t.month
d = t.day
return "%s %d%d" % (y, m, d)
def Tick():
# 绘制表针的动态显示
t = datetime.today()
second = t.second + t.microsecond * 0.000001
minute = t.minute + second / 60.0
hour = t.hour + minute / 60.0
secHand.setheading(6 * second)
minHand.setheading(6 * minute)
hurHand.setheading(30 * hour)
turtle.tracer(False)
printer.forward(65)
printer.write(Week(t), align="center",
font=("Courier", 14, "bold"))
printer.back(130)
printer.write(Date(t), align="center",
font=("Courier", 14, "bold"))
printer.home()
turtle.tracer(True)
# 100ms后继续调用tick
turtle.ontimer(Tick, 100)
def main():
# 打开/关闭龟动画,并为更新图纸设置延迟。
turtle.tracer(False)
Init()
SetupClock(160)
turtle.tracer(True)
Tick()
turtle.mainloop()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
运动炫彩小球
效果
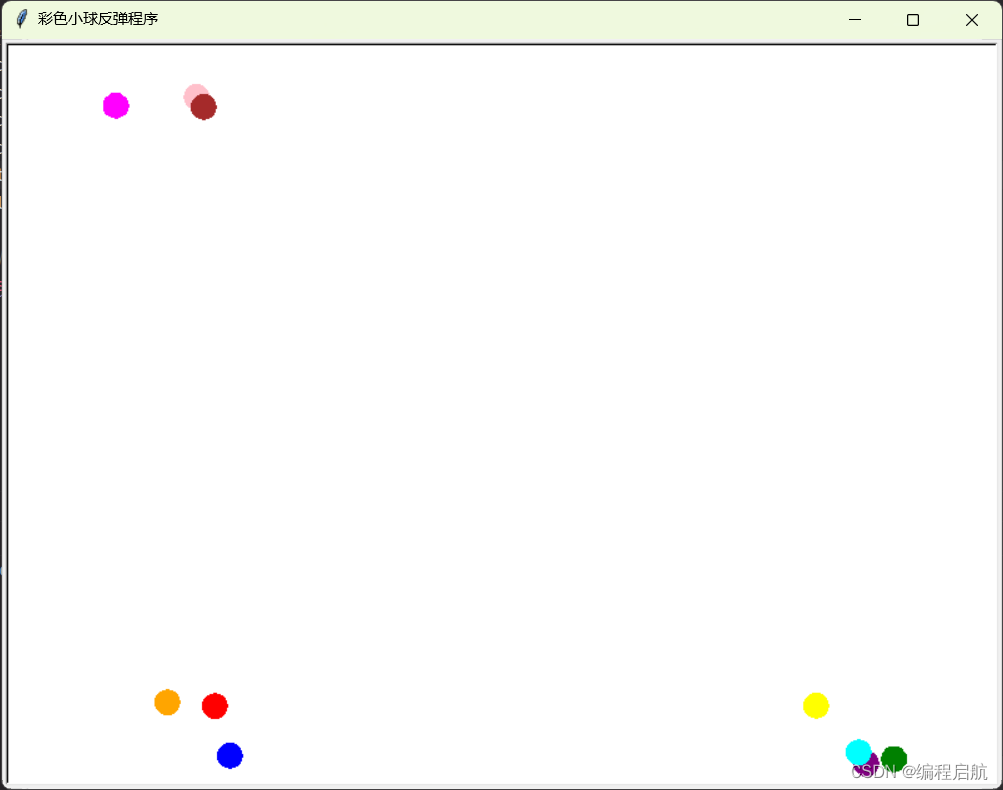
代码
import turtle
import random
# 设置窗口
window = turtle.Screen()
window.title("彩色小球反弹程序")
window.bgcolor("white")
window.setup(width=800, height=600)
turtle.tracer(False)
balls = []
# 创建小球类
class Ball(turtle.Turtle):
def __init__(self, color):
super().__init__()
self.shape("circle")
self.color(color)
self.penup()
self.speed(0)
self.dx = random.uniform(0.8,1.2) * random.choice([-1, 1]) # 随机初始x速度
self.dy = random.uniform(0.8,1.2)* random.choice([-1, 1]) # 随机初始y速度
def move(self):
self.setx(self.xcor() + self.dx)
self.sety(self.ycor() + self.dy)
# 碰撞检测
if self.xcor() > 380 or self.xcor() < -380:
self.dx *= -1
if self.ycor() > 280 or self.ycor() < -280:
self.dy *= -1
# 创建十个小球
ball_colors = ["red", "blue", "green", "purple", "orange", "pink", "cyan", "yellow", "magenta", "brown"]
for color in ball_colors:
ball = Ball(color)
balls.append(ball)
# 主循环
while True:
for ball in balls:
ball.move()
turtle.update()
# 关闭窗口
window.bye()
更多效果见视频:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Pm4y1H7Tb/
结语
在本文中,我们介绍了Python中令人兴奋的Turtle库,它为编程和艺术创作提供了全新的可能性。无论您是初学者还是有经验的开发者,Turtle库都是一个值得尝试的工具。通过简单的代码,您可以创造出独特的图形、艺术作品和动画。现在,动起手指,开始您的创意绘图之旅吧!
希望本视频能够帮助你对Turtle库有一个初步的了解。如果您想要深入学习和探索更多高级特性,不妨查阅Turtle库的官方文档以及更多的教程资源。