目录
- 1. stack/queue
- 1.1 模拟实现
- 2. 优先级队列
- 2.1 模拟实现
- 2.2 仿函数
1. stack/queue
stack文档说明
queue文档说明
stack和queue被称为容器适配器。
容器适配器是什么?
它是一种特殊的容器类型,通过封装已有的容器类型来提供特定功能的接口函数,以满足不同的需求。
而stack和queue底层封装的是deque容器。
deque(双端队列)容器不仅支持头部和尾部数据的插入和删除,也支持随机存取、访问和修改(迭代器),但是每个方面的功能又不是特别突出,尤其是随机存取和中间位置插入删除数据,效率比较低,因此很少单独使用deque,而且将其作为某个容器的适配器。
stack和queue的结构特性都是只能在两端进行数据的操作,无需随机存取和中间位置插入删除,因此用deque来适配就非常合适。
1.1 模拟实现
#include <iostream>
#include <deque>
using namespace std;
namespace lzh {
//stack
//第二个模板参数默认使用deque
template<class T, class Container = deque<T>>
class stack {
public:
void push(const T& x) {
_con.push_back(x);
}
void pop() {
_con.pop_back();
}
T& top() {
return _con.back();
}
const T& top() const {
return _con.back();
}
size_t size()const {
return _con.size();
}
bool empty()const {
return _con.empty();
}
private:
Container _con;
};
//queue
template<class T, class Container = deque<T>>
class queue {
public:
void push(const T& x) {
_con.push_back(x);
}
void pop() {
_con.pop_front();
}
T& front() {
return _con.front();
}
T& back() {
return _con.back();
}
const T& front() const {
return _con.front();
}
const T& back() const {
return _con.back();
}
size_t size()const {
return _con.size();
}
bool empty()const {
return _con.empty();
}
private:
Container _con;
};
}
2. 优先级队列
priority_queue文档说明
priority_queue是一种特殊的队列,它可以根据元素的优先级(或者大小)自动进行排序,并且优先级最高的先出队。
本质是二叉堆结构

它也是一个容器适配器,底层封装了vector容器,并且元素的优先级是通过第三个模板参数仿函数来控制的。
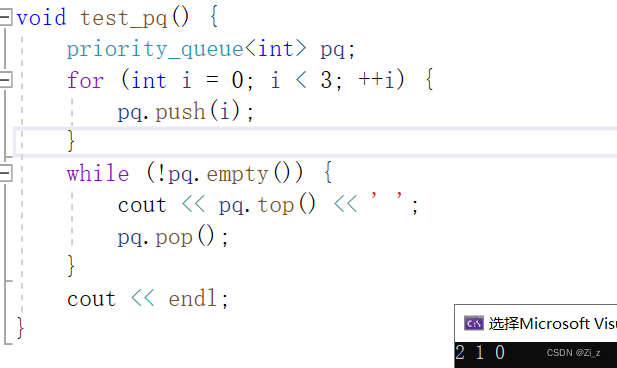 默认是大堆 -
默认是大堆 - less<T>,若想实现小堆则要显式传递三个参数封装的容器类型和仿函数:

2.1 模拟实现
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
namespace lzh {
template<class T, class Container = vector<T>>
class priority_queue {
void adjustDown(int fatherIdx) {
int childIdx = fatherIdx * 2 + 1;
while (childIdx < (int)_con.size()) {
if (childIdx + 1 < (int)_con.size() && _con[childIdx + 1] > _con[childIdx]) {
++childIdx;
}
if (_con[childIdx] > _con[fatherIdx]) {
swap(_con[childIdx], _con[fatherIdx]);
fatherIdx = childIdx;
childIdx = fatherIdx * 2 + 1;
}
else {
break;
}
}
}
void adjustUp(int childIdx) {
int fatherIdx = (childIdx - 1) / 2;
while (childIdx > 0 && _con[childIdx] > _con[fatherIdx]) {
swap(_con[childIdx], _con[fatherIdx]);
childIdx = fatherIdx;
fatherIdx = (childIdx - 1) / 2;
}
}
public:
priority_queue() { }
template <class InputIterator>
priority_queue(InputIterator first, InputIterator last) {
while (first != last) {
_con.push_back(*first);
++first;
}
for (int i = (_con.size() - 2) / 2; i >= 0; --i) {
adjustDown(i);
}
}
bool empty() const {
return _con.empty();
}
size_t size() const {
return _con.size();
}
// 堆顶元素不允许修改,因为:堆顶元素修改可以会破坏堆的特性
const T& top() const {
return _con.front();
}
void push(const T& x) {
_con.push_back(x);
adjustUp(_con.size() - 1);
}
void pop() {
swap(_con.front(), _con.back());
_con.pop_back();
adjustDown(0);
}
private:
Container _con;
};
}
2.2 仿函数
默认实现的是大堆,因为比较那里写死了,若要实现小堆结构则需要修改向下和向上调整算法的比较逻辑,但实际上库里实现的优先级队列是没办法修改的,所以真正的做法是使用仿函数作为第三个模板参数传递给容器,来实现大小堆的切换。
仿函数本质是一个类类型,类中重载了()运算符:
//仿函数且类模板
template<class T>
class Less {
public:
//若为自定义类型则该类中实现了小于运算符重载
bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y) {
return x < y;
}
};
void test_less() {
//函数对象
Less lessFunc;
cout << lessFunc(1, 2) << endl;
//显式调用
//cout << lessFunc.operator()(1, 2) << endl;
}
可以发现该对象可以像函数一样来使用。
类似于C语言中的函数指针
用仿函数来灵活调整调整算法的逻辑,控制是大堆还是小堆:
using namespace std;
template<class T>
class Less {
public:
//若为自定义类型则该类中实现了小于运算符重载
bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y) {
return x < y;
}
};
template<class T>
class Greater {
public:
bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y) {
return x > y;
}
};
namespace lzh {
template<class T, class Container = vector<T>, class Compare = less<T>>
class priority_queue {
void adjustDown(int fatherIdx) {
//定义仿函数对象
Compare cmp;
int childIdx = fatherIdx * 2 + 1;
while (childIdx < (int)_con.size()) {
//通过函数对象进行比较
if (childIdx + 1 < (int)_con.size() &&
cmp(_con[childIdx], _con[childIdx + 1])) {
++childIdx;
}
//通过函数对象进行比较
if (cmp(_con[fatherIdx], _con[childIdx])) {
swap(_con[fatherIdx], _con[childIdx]);
fatherIdx = childIdx;
childIdx = fatherIdx * 2 + 1;
}
else {
break;
}
}
}
void adjustUp(int childIdx) {
//定义仿函数对象
Compare cmp;
int fatherIdx = (childIdx - 1) / 2;
while (childIdx > 0 && cmp(_con[fatherIdx], _con[childIdx])) {
swap(_con[fatherIdx], _con[childIdx]);
childIdx = fatherIdx;
fatherIdx = (childIdx - 1) / 2;
}
}
//...其他成员
}
}
int main() {
//第三个模板参数
//Less默认是建大堆
//而Greater是建小堆
//和库里的实现一致
//第二和第三个模板参数有缺省值
//若要大堆,可以只传第一个元素类型
//而要小堆则三个都需要传递
lzh::priority_queue<int, vector<int>, Less<int>> pq;
pq.push(3);
pq.push(5);
pq.push(1);
pq.push(4);
while (!pq.empty()) {
cout << pq.top() << ' ';
pq.pop();
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
通过传递不同的仿函数类型,便可以控制是建大堆还是小堆。