原始笔记链接:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=Mzg4MjgxMjgyMg==&mid=2247486680&idx=1&sn=edf41d4f95395d7294bc958ea68d3a68&chksm=cf51be21f826373790bc6d79bcea6eb2cb3d09bb1860bba0af0fd5e60c448ca006976503e460#rd
↑ \uparrow ↑点击上述链接即可阅读全文
IEEE TPAMI 2023 | CoIR: Compressive Implicit Radar
毫米波雷达成像论文阅读笔记: IEEE TPAMI 2023 | CoIR: Compressive Implicit Radar
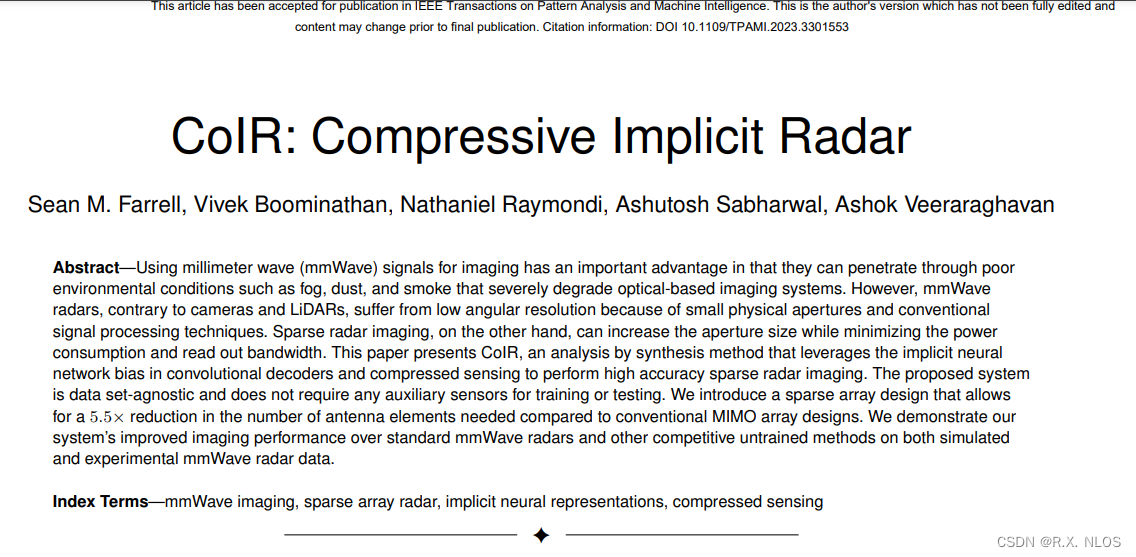
Abstract
-
背景
- mmWave radars suffer from low angular resolution due to small apertures and conventional signal processing
- 稀疏阵列雷达 can increase aperture size while minimizing power consumption and readout bandwidth
-
方法 :提出 Compressive Implicit Radar (CoIR)
-
目标: high accuracy sparse radar imaging using a single radar chip
-
Leverages : CNN decoder and compressed sensing
-
贡献:
✅ 设计稀疏线阵: with 5.5x fewer antennas than conventional MIMO arrays
✅ 提出ComDecoder :a fully convolutional implicit neural network architecture
✅ 证明了CoIR的有效性 :in both simulation and real-world experiments,且 不需要 auxiliary sensors
-
-
实验结果
- improved performance over standard mmWave radars and other untrained methods on simulated and real data
- System does not require training data or auxiliary sensors
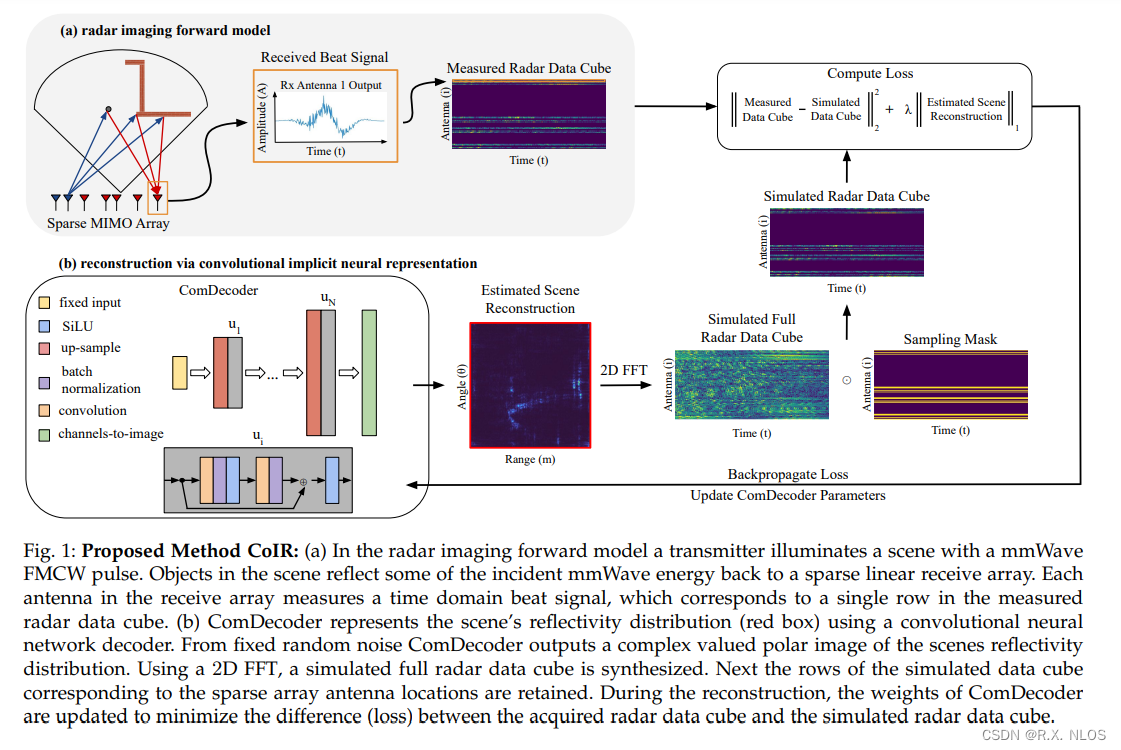
1 INTRODUCTION
基于光学的Depth imaging及其缺点
- Depth imaging
- crucial for applications like SLAM, autonomous driving, security monitoring
- Typical sensors: cameras, LiDAR
- Cameras: high-resolution near-field depth imaging
- LiDAR: directly outputs dense point cloud with high range/angular resolution
- Limitation : degraded performance in visually degraded environments like fog, smoke
毫米波雷达成像的优点和挑战
- 优点
- penetrate through fog/smoke without performance degradation
- 挑战
- low angular resolution δ ≈ λ / d \delta ≈ \lambda/d δ≈λ/d
- Increasing d d d increases cost, power consumption and readout bandwidth
已有提高角分辨率的工作和缺陷
- 已有思路
- Large physical arrays
- MIMO arrays
- SAR
- Sensor fusion
- Optimization with handcrafted priors
- Deep learning
- 不足
- Slow acquisition
- Increased hardware complexity
- Require large datasets
- Limited generalizability
The proposed CoIR:
-
Key observation:
- INR provides inductive bias towards natural solutions for imaging inverse problems
-
方法
- Leverages implicit neural representations (INRs) + compressed sensing
-
贡献
- Designed sparse linear array with 5.5x fewer antennas
- Proposed convolutional decoder architecture ComDecoder
- Demonstrated improved performance over standard mmWave radars and competitive untrained methods
2 RELATED WORK
2.1 mmWave Imaging Systems
-
提高角度分辨率的方法及其缺点
- Large physical arrays: expensive, large data volumes
- MIMO arrays: requires many radar chips to synthesize large aperture
- SAR techniques:slow imaging, bulky scanners
- Sensor fusion: fails if one modality fails
- Deep learning: requires large labeled datasets, limited generalizability
-
proposed CoIR 的不同:
-
仅使用 single chip sparse MIMO array
-
使用 未经训练 的 神经网络
✅ 无需训练数据
-
2.2 Sparse Radar Imaging
-
稀疏雷达成像技术:
- 1 Sparse aperture array designs
- 2 Sparse reconstruction methods
-
1 Sparse aperture array designs
-
使用欠奈奎斯特采样 减少 天线数
-
优化方法:
✅ Convex relaxations
✅ Prior knowledge of number of reflectors
-
-
2 Sparse reconstruction methods
-
Super-resolution algorithms
✅ MUSIC, ESPRIT
✅ Require incoherent signals, known number of targets
-
Compressed sensing (CS) optimization:
✅ 使用稀疏先验,如 spatial sparsity, TV norm
✅ Challenging to design priors, scene dependent
-
-
proposed CoIR 的不同:
-
Sparse array design
🚩 inspired by prior work but modified due to hardware constraints
-
Uses untrained neural network
🚩 as complex prior instead of handcrafted prior
✅ Neural network prior shows affinity for natural features and noise robustness
-
2.3 Implicit Neural Representations
-
两类INR architectures:
- 1 Convolutional methods
- 2 Coordinate-based MLP methods
-
1 Convolutional methods ,适合:
- Compressed sensing
- Image super-resolution
- Image denoising
- Accelerated MRI
-
2 Coordinate-based MLP methods ,适合:
- Novel view synthesis
- Dynamic illumination
- PDE solutions
- Image deconvolution
-
CoIR中的ComDecoder:
-
属于 Convolutional methods
-
tailored for sparse radar imaging
-
Key properties:
🚩 Convolutional operations capture local spatial information
🚩 Upsampling induces notion of resolution per layer
🚩 Residual blocks smooth optimization and propagate information between layers
🚩 Together these inductive biases improve performance on sparse radar imaging
-
Differences from prior works:
✅ CoIR uses untrained INR as complex prior for sparse radar imaging
✅ Prior works use INR for natural images or other imaging modalities
-
3 RADAR IMAGING BACKGROUND
-
发射信号模型
- y t x ( t ) = e j 2 π ( f 0 t + 1 2 B τ t 2 ) , 0 ≤ t ≤ T y_{tx}(t) = e^{j2π(f_0t + \frac{1}{2}Bτt^2)}, 0 \leq t \leq T ytx(t)=ej2π(f0t+21Bτt2),0≤t≤T
- f 0 f_0 f0: carrier frequency
- B B B: chirp bandwidth
- T T T: pulse duration
-
场景模型 (离散反射体分布)
- x ‾ [ n r , n θ ] ∈ C K × L \overline{x}[n_r, n_\theta] \in \mathbb{C}^{K\times L} x[nr,nθ]∈CK×L
- n r n_r nr: range bin index
- n θ n_\theta nθ: angle bin index
-
回波信号模型
- z [ n , m ] = ∑ n r = 0 K − 1 ∑ n θ = 0 L − 1 x ‾ [ n r , n θ ] e j 2 π ψ θ ( n θ ) m e j 2 π ψ r ( n r ) n + w [ n , m ] z[n,m] = \sum_{n_r=0}^{K-1} \sum_{n_\theta=0}^{L-1} \overline{x}[n_r, n_\theta] e^{j2π\psi_\theta(n_\theta)m} e^{j2π\psi_r(n_r)n} + w[n,m] z[n,m]=∑nr=0K−1∑nθ=0L−1x[nr,nθ]ej2πψθ(nθ)mej2πψr(nr)n+w[n,m]
- ψ θ ( n θ ) = f 0 d c sin ( b θ [ n θ ] ) \psi_\theta(n_\theta) = \frac{f_0 d}{c}\sin(b_\theta[n_\theta]) ψθ(nθ)=cf0dsin(bθ[nθ]): spatial frequency
- ψ r ( n r ) = B N 2 b r [ n r ] c \psi_r(n_r) = \frac{B}{N}\frac{2b_r[n_r]}{c} ψr(nr)=NBc2br[nr]: normalized temporal frequency
- w [ n , m ] w[n,m] w[n,m]: noise
-
Compact matrix form
-
z = F ( x ‾ ) + w z = F(\overline{x}) + w z=F(x)+w
-
F F F: 2D FFT
-
Goal: recover x ‾ \overline{x} x from under-sampled measurements z z z
-
4 PROPOSED METHOD
-
目标 :
- Recover scene reflectivity x ‾ \overline{x} x from under-sampled measurements z z z
-
Measurements :
-
z = M ⊙ F ( x ‾ ) + w z = M\odot F(\overline{x}) + w z=M⊙F(x)+w
-
M M M: binary mask implementing under-sampling
-
w w w: noise
-
-
困难 :
- under-sampling causes grating lobes in sparse array PSF leading to aliasing in image
-
解决方法
-
Optimize weights of untrained deep CNN G ( C ; p ) G(C;p) G(C;p) to solve inverse problem
✅ G G G: untrained CNN,
✅ C C C: fixed noise input,
✅ p p p: CNN parameters
-
Optimization objective:
🚩 p ^ = arg min p ∣ ∣ z − M ⊙ F ( G ( C ; p ) ) ∣ ∣ 2 + λ L ∣ ∣ G ( C ; p ) ∣ ∣ 1 \hat{p} = \argmin_p ||z - M\odot F(G(C;p))||_2 + \lambda_L||G(C;p)||_1 p^=argminp∣∣z−M⊙F(G(C;p))∣∣2+λL∣∣G(C;p)∣∣1
🚩 λ L \lambda_L λL: sparsity regularization strength
-
Key observation:
🚩 INR provides inductive bias towards natural solutions for imaging inverse problems
-
-
优点 :
-
CNN architecture has high impedance to noise
-
Learned solution balances fitting salient features and suppressing artifacts
-
4.1 Sparse Aperture Design
- 目标
- Design a sparse MIMO virtual array that improves imaging accuracy when used with ComDecoder
- 设计准测 (metrics)
- PSF main lobe half-power beamwidth (HPBW)
- Peak sidelobe level (SLL)
- Presence of grating lobes
- 硬件约束
- Max aperture 86λ/2
- Limited to 4 TX and 4 RX due to commercial single radar chip
- 设计方法
- Select 4-element minimum redundancy array for RX to avoid grating lobes
- Grid search over TX positions to minimize SLL
- 比较对象(baselines)
- Full: Ideal full Nyquist sampled array
- Sub-apt: Largest Nyquist sampled MIMO array given constraints
- Sub-samp: Largest sub-Nyquist array given constraints
- 设计结果
- RX: [0, 1, 4, 6] λ/2
- TX: [0, 46, 59, 79] λ/2
- Gives 5.5x fewer antennas than conventional MIMO array
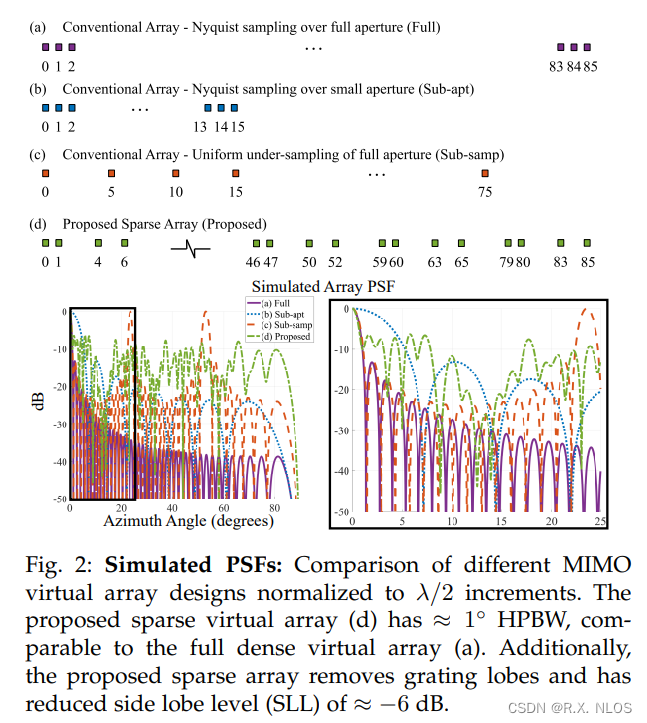
- 优点 :
- Avoids grating lobes
- Minimizes HPBW
- Minimizes SLL
- Satisfies hardware constraints
4.2 Neural Network Architecture
提出 ComDecoder:convolutional decoder architecture
-
ComDecoder :
- Maps latent variables C to image G(C;p)
- 优化:Parameters p optimized to reconstruct image
-
网络结构 :
- Series of upsampling and residual convolution blocks
- Use SiLU activation instead of ReLU
- No upsampling in last layer, uses 1x1 conv instead
-
超参数 :
- 6 layers (including last layer)
- 128 channels per layer
- Fixed input C sampled from uniform distribution
-
优化过程 :
- Update network weights p using backpropagation and Adam
- Takes <50 s per 256x256 image using 2000 iterations
-
优点 :
- SiLU increased expressivity over ReLU
- Upsampling reinforces multi-resolution nature
- Residual blocks enable information flow between layers
- Inductive biases improve performance on sparse radar imaging
5 COMPETING UNTRAINED METHODS
7个baselines: Compared CoIR against several untrained methods
-
1 Delay-and-Sum (DAS)
- Standard beamforming method
-
2 Sparse DAS
- DAS with under-sampled measurements
-
3 Gradient Descent with L1 Regularization (GD+L1 Reg)
- Directly optimizes reflectivity distribution with sparsity prior
-
4 Implicit Neural Representations:
-
4.1 INR-ReLU
✅ MLP-based, uses Fourier feature encoding
-
4.2 SIREN
✅ MLP-based, uses sinusoidal activation functions
-
-
5 Deep Image Prior (DIP)
- U-Net style convolutional autoencoder
-
6 DeepDecoder
- Decoder-only convolutional network
-
7 ConvDecoder
- Variant of DeepDecoder with some modifications
6 SIMULATION RESULTS
在仿真数据上评估所提出的CoIR
-
仿真数据生成:
- Synthesizes radar data cube from 2D reflectivity images
- Uses LiDAR point clouds to generate realistic reflectivity distributions
-
评估标准:
- PSNR, SSIM, MAE between reconstruction and ground truth image
-
实验:
-
1 Vary SNR from 35dB to 11dB
✅ ComDecoder gave superior PSNR over all methods at all SNRs
✅ ComDecoder and DIP gave comparable SSIM
✅ ComDecoder and DIP gave lowest MAE
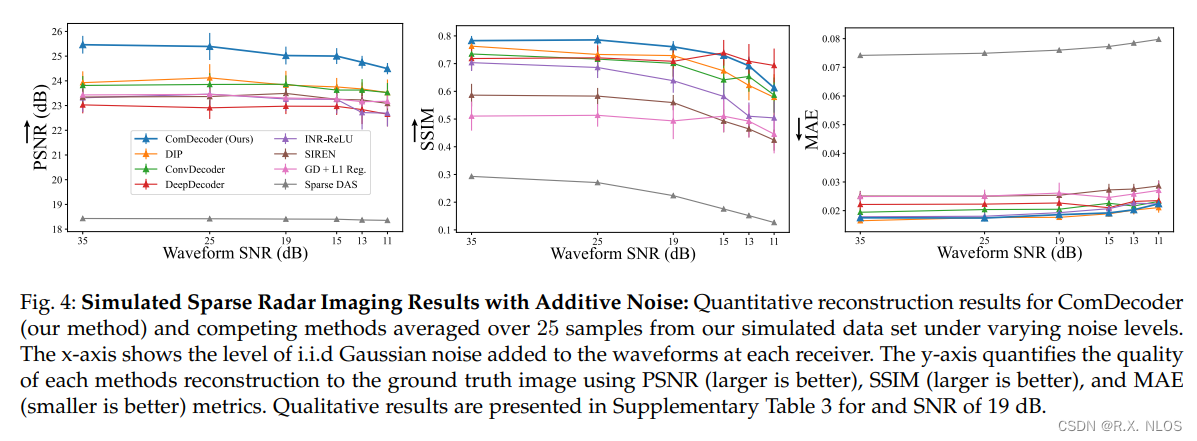
-
2 Visualize reconstructions at 19dB SNR
✅ ComDecoder gave most accurate recovery of extended reflectors
✅ Other CNN methods also improved over Sparse DAS
✅ SIREN struggled to distinguish clutter and true reflectors

-
3 Additional analyses:
✅ Compared different CNN decoder architectures
✅ Evaluated computational complexity (in supplementary)
-
-
总结:
- ComDecoder 在 simulated data 上 SOTA
7 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
在真实采集的Coloradar dataset上评估所有方法
-
Radar system:
-
77 GHz FMCW with 1.282 GHz bandwidth
-
86λ/2 uniform linear array
-
-
Metrics :
- 与 full array DAS reconstruction 进行对比
-
Experiments :
-
1 不同场景下的重建效果
✅ ComDecoder accurately recovered dominant features
✅ DIP also performed well but more artifacts than ComDecoder
✅ SIREN struggled in indoor scene due to noise
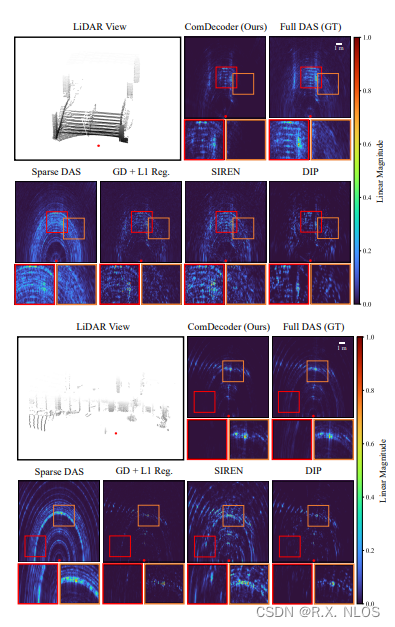
-
2 Evaluate 鲁棒性 across multiple outdoor scenes
✅ ComDecoder gave high fidelity reconstructions closest to DAS
✅ SIREN fit strong reflectors but also artifacts
✅ GD+L1 located dominant reflectors but artifacts remained
✅ DIP performed well but more artifacts than ComDecoder
-
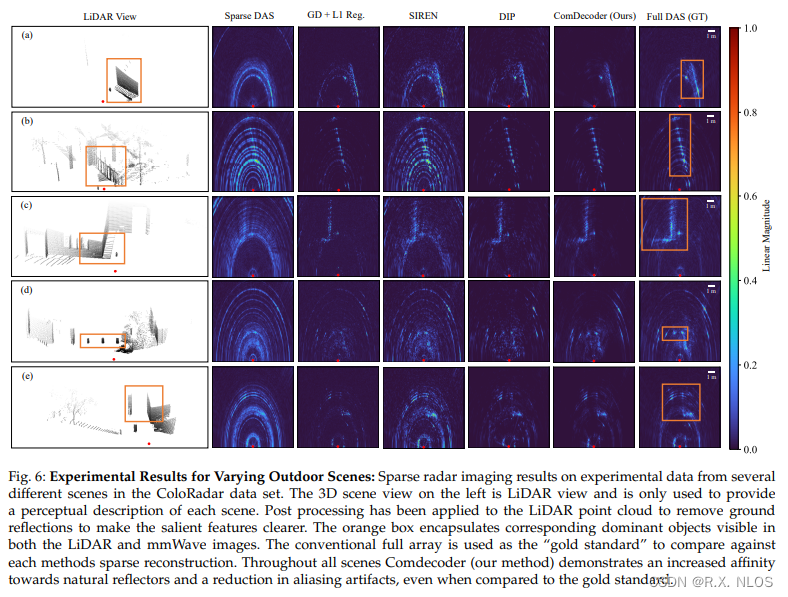
- 总结:
- ComDecoder 在 real data 上 SOTA
- 显著好于其他untrained methods
8 DISCUSSION & LIMITATIONS
Limitations
- 1 Assume static scene in forward model
- Cannot handle moving objects
- 2 Single bounce scattering model may not match real-world
- 3 Slow optimization time (tens of seconds)
- Explore different initialization strategies
Future work
- 1 Demonstrated 2D range-angle slices due to linear array
- 2D array needed for full 3D, but increases complexity
- 2 CoIR could benefit other array-based imaging modalities:
- SAR, ultrasound, etc.
9 CONCLUSION
Proposed CoIR
-
1 Designed sparse linear array with 5.5x fewer antennas
-
2 Proposed convolutional decoder architecture ComDecoder
-
3 Demonstrated superior performance on simulated and real mmWave radar data