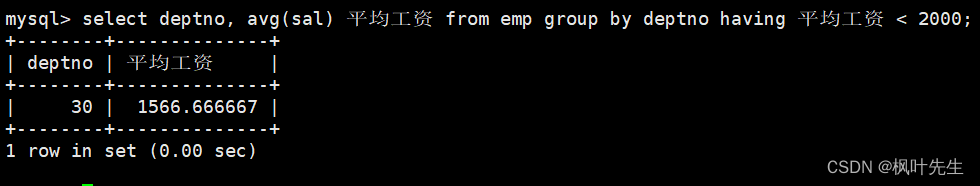
目录
一、Spring是什么,它能够做什么
spring的组成
二、什么是控制反转(或依赖注入)
三、 如何在spring当中定义和配置一个JavaBean
四、注入方式
1.构造函数注入
2.Setter方法注入
3.自动装配
五、简单属性配置与复杂属性配置
简单属性配置:
复杂属性配置:
六、spring上下文与tomcat整合
一、Spring是什么,它能够做什么
Spring是一个开源框架,它由Rod Johnson创建。它是为了解决企业应用开发的复杂性而创建的。
Spring使用基本的JavaBean来完成以前只可能由EJB完成的事情。
然而,Spring的用途不仅限于服务器端的开发。从简单性、可测试性和松耦合的角度而言,任何Java应用都可以从Spring中受益。
目的:解决企业应用开发的复杂性
功能:使用基本的JavaBean代替EJB,并提供了更多的企业应用功能
范围:任何Java应用,包括Web应用程序、桌面应用程序、批处理应用程序等。
简单来说,Spring是一个轻量级的控制反转(IoC)和面向切面(AOP)的容器框架。
spring的组成

组成 Spring 框架的每个模块(或组件)都可以单独存在,或者与其他一个或多个模块联合实现。每个模块的功能如下:
Spring Core(核心模块):
提供了IoC容器和依赖注入功能,用于管理对象的生命周期和依赖关系。Spring Context(上下文模块):
基于核心模块,提供了更广泛的应用程序上下文支持,包括国际化、事件传播、资源加载等。Spring AOP(面向切面编程模块):
提供了AOP功能,用于将横切关注点与业务逻辑分离,实现日志记录、事务管理等功能。Spring JDBC(数据库访问模块):
提供了对JDBC的封装和简化,简化了数据库访问的代码编写。Spring ORM(对象关系映射模块):
提供了对ORM框架的集成支持,如Hibernate、MyBatis等,简化了数据库操作和对象持久化的开发。Spring Web(Web开发模块):
提供了用于构建Web应用程序的功能,包括Spring MVC框架、RESTful Web服务、WebSocket等。Spring Security(安全性模块):
提供了一套综合的安全性框架,用于认证、授权和保护应用程序的资源。Spring Test(测试模块):
提供了测试支持,包括单元测试、集成测试和端到端测试,方便进行测试驱动开发和持续集成。
二、什么是控制反转(或依赖注入)
控制反转(Inversion of Control,IoC)和依赖注入(Dependency Injection,DI)是两个相关的概念,用于解耦和管理组件之间的依赖关系。
控制反转(IoC)是一种设计原则,它将组件的控制权从组件自身转移到外部容器中。传统的程序设计中,组件通常负责自己的创建和管理,而在IoC中,组件不再负责自己的创建和管理,而是由外部容器来负责。这样做的好处是,组件不再与具体的实现细节紧密耦合,而是通过接口或抽象类与外部容器进行交互,从而提高了代码的可维护性和可测试性。
依赖注入(DI)是IoC的一种具体实现方式。它通过将组件所依赖的其他组件(依赖项)注入到组件中,来解决组件之间的依赖关系。依赖注入可以通过构造函数、属性或方法参数等方式进行。通过依赖注入,组件不需要自己创建和管理它所依赖的组件,而是由外部容器负责创建和注入依赖项。这样可以使组件之间的依赖关系更加清晰和可控,提高了代码的可测试性和可扩展性。
分析实现
首先需建一个maven工程,在pom.xml中导入spring的jar包依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.1.10.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>给客户添加一个文件上传的接口,实现文件上传的功能
1.建立一个UserBiz接口
public interface UserBiz {
public void update();
}2.实现接口完成功能
public class UserBizImpl implements UserBiz {
public void update() {
System.out.println("用户功能实现类");
}
}3.客户要求更改需求
public class UserBizImpl2 implements UserBiz {
public void update() {
System.out.println("更改用户需求");
}
}4.编写Userservlet,Goodsservlet
public class UserAction {
private UserBiz userBiz= new UserBizImpl2();
public String Update(){
userBiz.update();
return "list";
}
}public class GoodsAction {
private UserBiz userBiz= new UserBizImpl2();
public String Update(){
userBiz.update();
return "list";
}
}5.新建一个spring的xml,博主在这命名为spring_context
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean class="com.ctb.web.UserAction" id="userAction">
<property name="iub" ref="iub"></property>
</bean>
<bean class="com.ctb.web.GoodsAction" id="goodsAction">
<property name="iub" ref="impl1"></property>
</bean>
<bean class="com.ctb.biz.Impl.UserBizImpl2" id="iub"></bean>
<bean class="com.ctb.biz.Impl.UserBizImpl1" id="impl1"></bean>
</beans>测试类
package com.ctb.demo;
import com.ctb.web.GoodsAction;
import com.ctb.web.UserAction;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/**
* @author 彪
* @remark
* @create 2023-08-16 21:30
*/
public class demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//加载spring核心配置文件(建模),获取spring的上下文对象,上下文对象中可以获取任何Javabean对象
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring_context.xml");
UserAction userAction= (UserAction) context.getBean("userAction");
userAction.upload();
GoodsAction goodsAction= (GoodsAction) context.getBean("goodsAction");
goodsAction.upload();
}
}
三、 如何在spring当中定义和配置一个JavaBean
- 在Spring中定义JavaBean可以使用XML配置文件或注解。
- 使用XML配置文件时,可以使用
<bean>元素来定义和配置JavaBean,包括类名、属性值、依赖项等。 - 使用注解时,可以使用
@Component、@Service、@Repository等注解来标记JavaBean,并使用@Autowired注解来实现依赖注入。
四、注入方式
1.构造函数注入
- 构造函数注入是通过在类的构造函数中传递依赖项来实现的。
- 在使用构造函数注入时,需要在类中定义一个或多个构造函数,接受依赖项作为参数。
- Spring容器会根据配置文件或注解中的定义,自动解析依赖项,并在创建对象时将其传递给构造函数。
- 构造函数注入可以保证对象的依赖项在创建时就被满足,使得对象在创建后具有完整的状态。
package com.ctb.ioc.web;
import com.ctb.ioc.service.UserService;
import java.util.List;
public class UserAction {
/**
* 手动实例化的弊端
* 1.如果依赖的接口实现需要大批量改动及迭代时,维护的成本极高
* 2.当接口的实现类不统一,维护成本更高
*/
private UserService userService ;
private String uname;
private int age;
private List<String> hobby;
public UserAction() {
}
public UserAction(String uname, int age, List<String> hobby) {
this.uname = uname;
this.age = age;
this.hobby = hobby;
}
public UserService getUserService() {
return userService;
}
public void setUserService(UserService userService) {
this.userService = userService;
}
public void pop(){
System.out.println("名字为:"+this.uname);
System.out.println("年龄为:"+this.age);
System.out.println("爱好为:"+this.hobby);
}
public String update(){
userService.update();
return "list";
}
}spring_context.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
default-autowire="byName"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- 在spring配置文件spring-context.xml中配置,那么该类javabean就交给spring容器管理 -->
<bean class="com.ctb.ioc.web.UserAction" id="userAction">
<property name="userService" ref="userService"></property>
<constructor-arg name="uname" value="奥特曼" ></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="age" value="66" ></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="hobby" >
<list>
<value>打飞机</value>
<value>打篮球</value>
</list>
</constructor-arg>
</bean>
<bean class="com.ctb.ioc.web.GoodsAction" id="goodsAction">
<property name="userService" ref="userServiceImpl2"></property>
<property name="gname" value="赵六"></property>
<property name="age" value="18"></property>
<property name="peoples">
<list>
<value>张三</value>
<value>李四</value>
<value>王五</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<bean class="com.ctb.ioc.service.impl.UserServiceImpl" id="userService" ></bean>
<bean class="com.ctb.ioc.service.impl.UserServiceImpl2" id="userServiceImpl2"></bean>
</beans>2.Setter方法注入
- Setter方法注入是通过调用对象的Setter方法来设置依赖项的值。
- 在使用Setter方法注入时,需要在类中定义相应的Setter方法,用于接收依赖项的值。
- Spring容器会根据配置文件或注解中的定义,自动调用Setter方法,并将依赖项的值传递给对应的Setter方法。
- Setter方法注入可以在对象创建后动态地设置依赖项的值,使得对象的依赖关系更加灵活和可变。
package com.ctb.ioc.web;
import com.ctb.ioc.service.UserService;
import java.util.List;
public class GoodsAction {
/**
* 在不同的控制器中进行方法调用
*/
private UserService userService;
private String gname;
private int age;
private List<String> peoples;
public String getGname() {
return gname;
}
public void setGname(String gname) {
this.gname = gname;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public List<String> getPeoples() {
return peoples;
}
public void setPeoples(List<String> peoples) {
this.peoples = peoples;
}
public UserService getUserService() {
return userService;
}
public void setUserService(UserService userService) {
this.userService = userService;
}
public void pop(){
System.out.println("名称:"+this.gname);
System.out.println("年龄:"+this.age);
System.out.println("使用人:"+this.peoples);
}
public String update(){
userService.update();
return "list";
}
}spring_context.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
default-autowire="byName"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean class="com.ctb.ioc.web.UserAction" id="userAction">
<property name="userService" ref="userServiceImpl"></property>
</bean>
<bean class="com.ctb.ioc.web.GoodsAction" id="goodsAction">
<property name="userService" ref="userServiceImpl2"></property>
<property name="gname" value="赵六"></property>
<property name="age" value="18"></property>
<property name="peoples">
<list>
<value>张三</value>
<value>李四</value>
<value>王五</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<bean class="com.ctb.ioc.service.impl.UserServiceImpl" id="userService" ></bean>
<bean class="com.ctb.ioc.service.impl.UserServiceImpl2" id="userServiceImpl2"></bean>
</beans>3.自动装配
根据类型(byType)自动装配:
- 在目标对象的构造函数、Setter方法或字段上使用
@Autowired注解。- Spring容器会根据依赖项的类型,在容器中查找匹配的对象,并自动注入到目标对象中。
- 如果存在多个匹配的对象,可以使用
@Qualifier注解指定具体的对象。根据名称(byName)自动装配:
- 在目标对象的构造函数、Setter方法或字段上使用
@Autowired注解,并结合@Qualifier注解。- 在
@Qualifier注解中指定要注入的对象的名称。- Spring容器会根据依赖项的名称,在容器中查找匹配的对象,并自动注入到目标对象中。
自动装配的其他选项:
@Autowired注解还可以与@Primary注解一起使用,指定首选的自动装配对象。- 如果依赖项无法找到匹配的对象,可以使用
@Autowired(required = false)注解,允许依赖项为null。
byName
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
default-autowire="byName"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- 在spring配置文件spring-context.xml中配置,那么该类javabean就交给spring容器管理 -->
<bean class="com.ctb.ioc.web.UserAction" id="userAction">
<property name="userService" ref="userService"></property>
<constructor-arg name="uname" value="奥特曼" ></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="age" value="66" ></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="hobby" >
<list>
<value>打飞机</value>
<value>打篮球</value>
</list>
</constructor-arg>
</bean>
<bean class="com.ctb.ioc.web.GoodsAction" id="goodsAction">
<property name="userService" ref="userServiceImpl2"></property>
<property name="gname" value="赵六"></property>
<property name="age" value="18"></property>
<property name="peoples">
<list>
<value>张三</value>
<value>李四</value>
<value>王五</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<bean class="com.ctb.ioc.service.impl.UserServiceImpl" id="userService" ></bean>
<bean class="com.ctb.ioc.service.impl.UserServiceImpl2" id="userServiceImpl2"></bean>
</beans>byType
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
default-autowire="byType"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- 在spring配置文件spring-context.xml中配置,那么该类javabean就交给spring容器管理 -->
<bean class="com.ctb.ioc.web.UserAction" id="userAction">
<property name="userService" ref="userService"></property>
<constructor-arg name="uname" value="奥特曼" ></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="age" value="66" ></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="hobby" >
<list>
<value>打飞机</value>
<value>打篮球</value>
</list>
</constructor-arg>
</bean>
<bean class="com.ctb.ioc.web.GoodsAction" id="goodsAction">
<property name="userService" ref="userServiceImpl2"></property>
<property name="gname" value="赵六"></property>
<property name="age" value="18"></property>
<property name="peoples">
<list>
<value>张三</value>
<value>李四</value>
<value>王五</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<bean class="com.ctb.ioc.service.impl.UserServiceImpl" id="userService" ></bean>
<bean class="com.ctb.ioc.service.impl.UserServiceImpl2" id="userServiceImpl2"></bean>
</beans>五、简单属性配置与复杂属性配置
-
简单属性配置:
- 简单属性配置是指设置对象的基本数据类型或字符串类型的属性值。
- 在XML配置文件中,可以使用
<property>元素来配置简单属性。 - 例如,假设有一个名为
person的JavaBean,有一个名为name的属性,可以使用以下方式进行简单属性配置:<bean id="person" class="com.example.Person"> <property name="name" value="John Doe" /> </bean> - 在注解配置中,可以使用
@Value注解来配置简单属性。 - 例如,使用注解配置上述的
person对象的name属性:@Value("John Doe") private String name; @Value("John Doe") private String name;
-
复杂属性配置:
- 复杂属性配置是指设置对象的引用类型或集合类型的属性值。
- 在XML配置文件中,可以使用
<property>元素的ref属性来配置引用类型的属性。 - 例如,假设有一个名为
person的JavaBean,有一个名为address的属性,可以使用以下方式进行复杂属性配置:<bean id="person" class="com.example.Person"> <property name="address" ref="addressBean" /> </bean> <bean id="addressBean" class="com.example.Address"> <!-- 设置addressBean的其他属性 --> </bean> - 在注解配置中,可以使用
@Autowired或@Resource注解来配置引用类型的属性。 - 例如,使用注解配置上述的
person对象的address属性:@Autowired private Address address; @Autowired private Address address; - 对于集合类型的属性,可以使用<array>、
<list>、<map>、<set>等元素进行配置,或者使用@Value注解配合#{}表达式进行配置。
数组(array)注入
<property name="books" >
<array>
<value>1</value>
<value>12</value>
<value>123</value>
<value>122234</value>
</array>
</property>List注入
<property name="hobbys">
<list>
<value>1</value>
<value>2</value>
<value>3</value>
</list>
</property>Map注入
<property name="card">
<map>
<entry key="JAVA" value="100"></entry>
<entry key="Python" value="100"></entry>
</map>
</property>Set注入
<property name="games">
<set>
<value>1</value>
<value>2</value>
</set>
</property>六、spring上下文与tomcat整合
- Spring上下文是Spring框架的核心部分,它负责管理和提供应用程序中的对象和依赖关系。
- 在将Spring与Tomcat整合时,可以使用Spring的
ContextLoaderListener来加载Spring上下文。- 需要在web.xml文件中配置
ContextLoaderListener,并指定Spring配置文件的位置。- 这样,Tomcat启动时会加载Spring上下文,并将其与Web应用程序进行整合。
SpringLoadlistener.java
@WebListener
public class SpringLoadlistener implements ServletContextListener {
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) {
System.out.println("初始化将Spring的上下文放入tomcat");
//将Spring的上下文放入tomcat
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("/Spring-Context.xml");
//获取tomcat上下文
ServletContext servletContext = sce.getServletContext();
servletContext.setAttribute("springcontext",context);
}
}UserServlet.java
@WebServlet("/userlist")
public class UserServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doPost(req,resp);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//处理请求的时候获取spring上下文
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext springcontext = (ClassPathXmlApplicationContext) req.getServletContext().getAttribute("springcontext");
UserAction useraction = (UserAction) springcontext.getBean("userAction");
System.out.println(useraction);
useraction.Update();
}
}spring ioc的讲解到这就结束啦 !!关注博主不迷路😁😁