执行算子(hash join 算子)
- 连接算子
- hash join算子
- ExecInitHashJoin函数
- HashJoinState结构体
- TupleTableSlot 结构体
- JoinState结构体
- PlanState结构体
- ExecInitHashJoin函数部分代码介绍
- ExecHashJoin函数
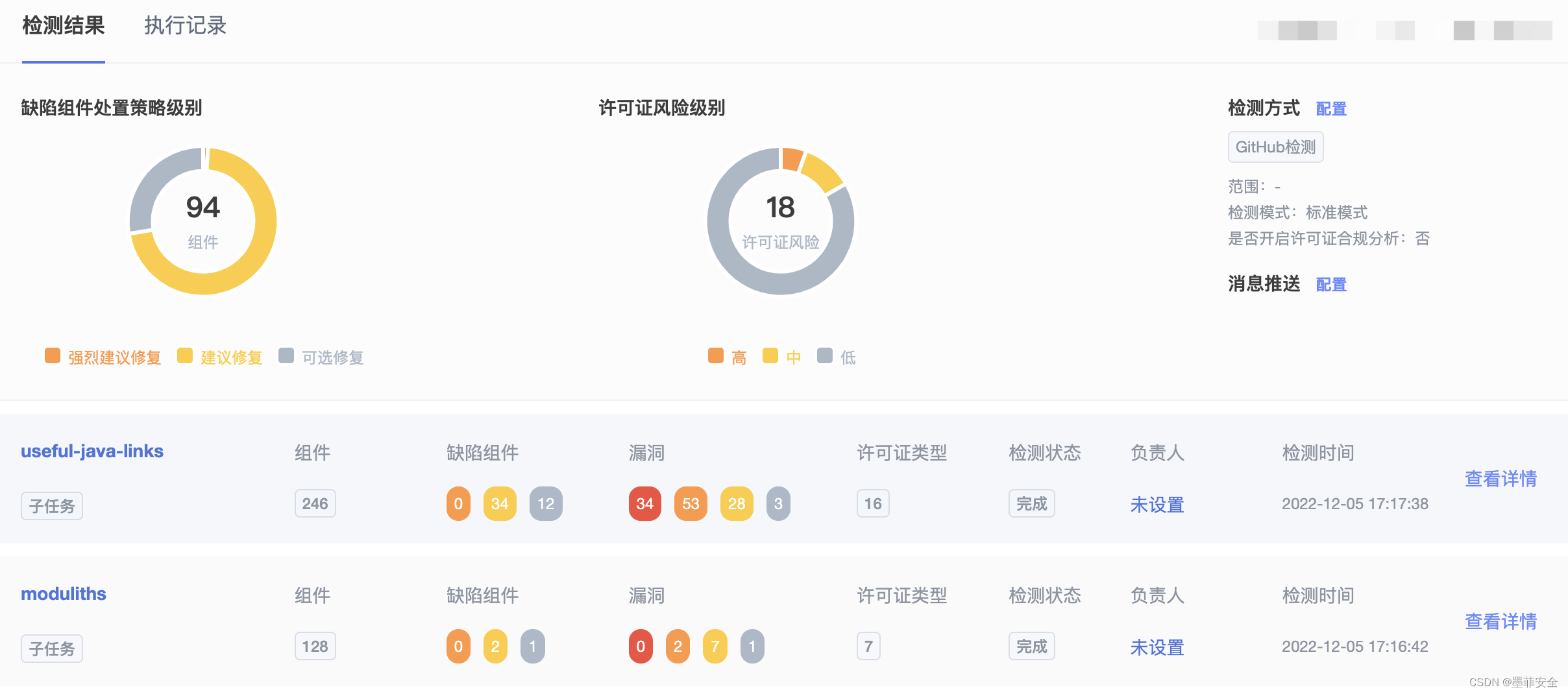
- 调试信息
- ExecEndHashJoin函数
- ExecReScanHashJoin函数
- 总结
声明:本文的部分内容参考了他人的文章。在编写过程中,我们尊重他人的知识产权和学术成果,力求遵循合理使用原则,并在适用的情况下注明引用来源。
本文主要参考了 OpenGauss1.1.0 的开源代码和《OpenGauss数据库源码解析》一书
连接算子
连接算子用于处理表关联,openGauss支持 12 种连接类型(inner join、left join、right join、full join、semi join、anti join等),提供了 3 种连接算子:hash join、merge join、nested loop join 算子;本文先来看看hash join 算子。
hash join算子
hash join 算子用于 hash 连接处理,对应的代码源文件是“nodeHashJoin.cpp”。hash 连接是做大数据集连接时的常用方式,优化器使用两个表中较小的表(或数据源)利用连接键在内存中建立哈希表,然后扫描较大的表并探测哈希表,找出与哈希表匹配的行。这种方式适用于较小的表完全可以放于内存中的情况,这样总成本就是访问两个表的成本之和。但是在表很大的情况下并不能完全放入内存,执行器会将它分割成若干不同的分区,不能放入内存的部分就把该分区写入磁盘的临时段,此时要有较大的临时段从而尽量提高 I/O 的性能。算子对应的主要函数如下表所示。
| 主要函数 | 说 明 |
|---|---|
| ExecInitHashJoin | 初始化 hash join 状态节点 |
| ExecHashJoin | 利用哈希表迭代获取元组 |
| ExecEndHashJoin | 清理 hash join 状态节点 |
| ExecReScanHashJoin | 重置 hash join 状态节点 |
为了更好地理解和学习 hash join 算子的相关操作,我们还是从一个实际案例来入手吧。首先执行以下 sql 语句:
-- 创建 orders 表
CREATE TABLE orders (
order_id INT,
customer_id INT,
order_date DATE
);
-- 创建 customers 表
CREATE TABLE customers (
customer_id INT,
customer_name VARCHAR(100)
);
-- 插入一些数据
INSERT INTO orders VALUES (1, 101, '2023-08-01');
INSERT INTO orders VALUES (2, 102, '2023-08-02');
INSERT INTO customers VALUES (101, 'Alice');
INSERT INTO customers VALUES (102, 'Bob');
-- 执行连接查询
SELECT o.order_id, c.customer_name, o.order_date
FROM orders o
INNER JOIN customers c ON o.customer_id = c.customer_id;
order_id | customer_name | order_date
----------+---------------+---------------------
1 | Alice | 2023-08-01 00:00:00
2 | Bob | 2023-08-02 00:00:00
(2 rows)
ExecInitHashJoin函数
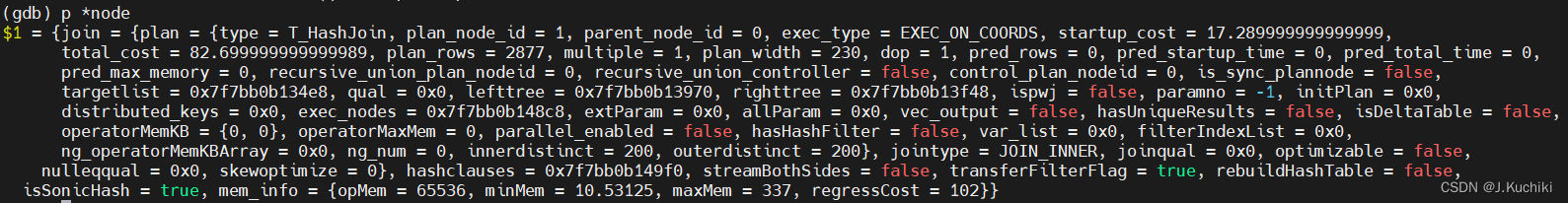
首先,在函数 ExecInitHashJoin 中插入断点,调试信息如下,通过打印可以看到函数的调用关系。
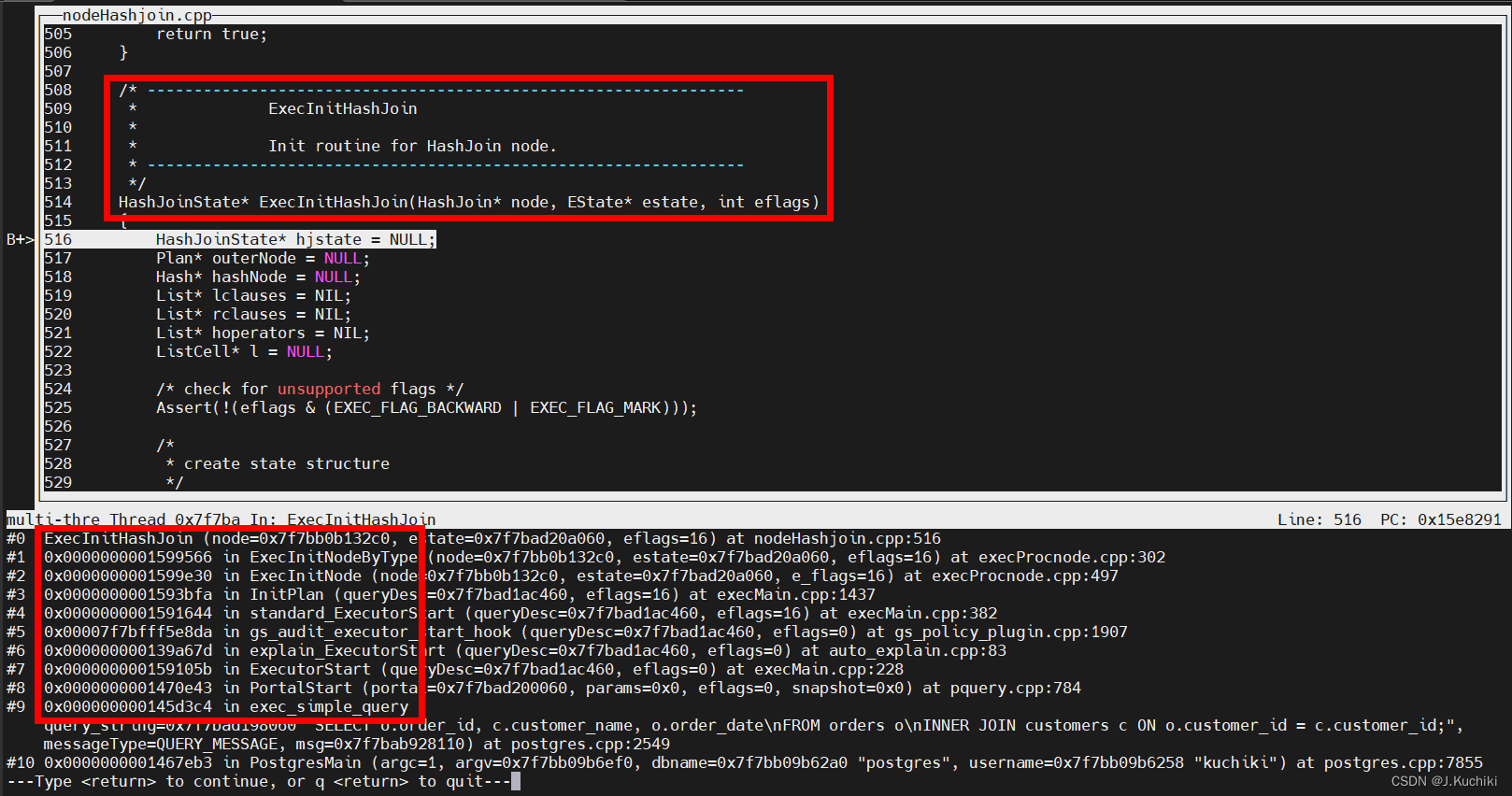
我们来看一下 ExecInitHashJoin 函数的源码吧:(路径:src/gausskernel/runtime/executor/nodeHashjoin.cpp)。
/* ----------------------------------------------------------------
* ExecInitHashJoin
*
* Init routine for HashJoin node.
* ----------------------------------------------------------------
*/
HashJoinState* ExecInitHashJoin(HashJoin* node, EState* estate, int eflags)
{
HashJoinState* hjstate = NULL;
Plan* outerNode = NULL;
Hash* hashNode = NULL;
List* lclauses = NIL;
List* rclauses = NIL;
List* hoperators = NIL;
ListCell* l = NULL;
/* check for unsupported flags */
Assert(!(eflags & (EXEC_FLAG_BACKWARD | EXEC_FLAG_MARK)));
/*
* create state structure
*/
hjstate = makeNode(HashJoinState);
hjstate->js.ps.plan = (Plan*)node;
hjstate->js.ps.state = estate;
hjstate->hj_streamBothSides = node->streamBothSides;
hjstate->hj_rebuildHashtable = node->rebuildHashTable;
/*
* Miscellaneous initialization
*
* create expression context for node
*/
ExecAssignExprContext(estate, &hjstate->js.ps);
/*
* initialize child expressions
*/
hjstate->js.ps.targetlist = (List*)ExecInitExpr((Expr*)node->join.plan.targetlist, (PlanState*)hjstate);
hjstate->js.ps.qual = (List*)ExecInitExpr((Expr*)node->join.plan.qual, (PlanState*)hjstate);
hjstate->js.jointype = node->join.jointype;
hjstate->js.joinqual = (List*)ExecInitExpr((Expr*)node->join.joinqual, (PlanState*)hjstate);
hjstate->js.nulleqqual = (List*)ExecInitExpr((Expr*)node->join.nulleqqual, (PlanState*)hjstate);
hjstate->hashclauses = (List*)ExecInitExpr((Expr*)node->hashclauses, (PlanState*)hjstate);
/*
* initialize child nodes
*
* Note: we could suppress the REWIND flag for the inner input, which
* would amount to betting that the hash will be a single batch. Not
* clear if this would be a win or not.
*/
outerNode = outerPlan(node);
hashNode = (Hash*)innerPlan(node);
outerPlanState(hjstate) = ExecInitNode(outerNode, estate, eflags);
innerPlanState(hjstate) = ExecInitNode((Plan*)hashNode, estate, eflags);
/*
* tuple table initialization
*/
//这两句代码为 Hash Join 算子节点初始化了结果元组槽和外部输入表的元组槽,以便在执行过程中进行计算和数据处理。
// 初始化 Hash Join 算子节点的结果元组槽(TupleTableSlot),它是用于存储计算结果的容器。
ExecInitResultTupleSlot(estate, &hjstate->js.ps);
// 初始化 Hash Join 算子节点的额外元组槽,这个槽用于存储外部输入表的元组。
hjstate->hj_OuterTupleSlot = ExecInitExtraTupleSlot(estate);
/* set up null tuples for outer joins, if needed */
switch (node->join.jointype) {
case JOIN_INNER:
case JOIN_SEMI:
case JOIN_RIGHT_SEMI:
break;
case JOIN_LEFT:
case JOIN_ANTI:
case JOIN_LEFT_ANTI_FULL:
hjstate->hj_NullInnerTupleSlot = ExecInitNullTupleSlot(estate, ExecGetResultType(innerPlanState(hjstate)));
break;
case JOIN_RIGHT:
case JOIN_RIGHT_ANTI:
case JOIN_RIGHT_ANTI_FULL:
hjstate->hj_NullOuterTupleSlot = ExecInitNullTupleSlot(estate, ExecGetResultType(outerPlanState(hjstate)));
break;
case JOIN_FULL:
hjstate->hj_NullOuterTupleSlot = ExecInitNullTupleSlot(estate, ExecGetResultType(outerPlanState(hjstate)));
hjstate->hj_NullInnerTupleSlot = ExecInitNullTupleSlot(estate, ExecGetResultType(innerPlanState(hjstate)));
break;
default:
ereport(ERROR,
(errcode(ERRCODE_UNRECOGNIZED_NODE_TYPE),
errmodule(MOD_EXECUTOR),
errmsg("unrecognized join type: %d for hashjoin", (int)node->join.jointype)));
}
/*
* now for some voodoo. our temporary tuple slot is actually the result
* tuple slot of the Hash node (which is our inner plan). we can do this
* because Hash nodes don't return tuples via ExecProcNode() -- instead
* the hash join node uses ExecScanHashBucket() to get at the contents of
* the hash table. -cim 6/9/91
*/
{
// 从一个 Hash Join 算子状态结构体 hjstate 中获取内部计划(inner plan)的状态,并将其赋值给一个名为 hashstate 的指针变量
HashState* hashstate = (HashState*)innerPlanState(hjstate);
// 从 Hash 算子的状态结构体 hashstate 中获取一个指向结果元组槽(TupleTableSlot)的指针,并将其赋值给变量 slot。
TupleTableSlot* slot = hashstate->ps.ps_ResultTupleSlot;
// 将上述获取到的结果元组槽指针赋值给 Hash Join 算子状态结构体 hjstate 的成员变量 hj_HashTupleSlot。
hjstate->hj_HashTupleSlot = slot;
}
/*
* initialize tuple type and projection info
* result tupleSlot only contains virtual tuple, so the default
* tableAm type is set to HEAP.
*/
// 为 Hash Join 算子状态结构体中的计划状态(PlanState)分配结果类型
// 这将根据目标列表(targetlist)来推断结果的类型,并且使用 TAM_HEAP 类型分配存储空间。
ExecAssignResultTypeFromTL(&hjstate->js.ps, TAM_HEAP);
// 为 Hash Join 算子状态结构体中的计划状态分配投影信息(ProjectionInfo)。
// 投影信息用于对结果进行投影,通常包括计算目标列表中的表达式并生成结果元组。
ExecAssignProjectionInfo(&hjstate->js.ps, NULL);
// 为 Hash Join 算子状态结构体中的外部元组槽(hj_OuterTupleSlot)设置描述符。
// 它将外部元组槽与外部计划(左输入)的结果类型进行关联,以确保正确的元组类型和数据存储。
ExecSetSlotDescriptor(hjstate->hj_OuterTupleSlot, ExecGetResultType(outerPlanState(hjstate)));
/*
* initialize hash-specific info
*/
hjstate->hj_HashTable = NULL;
hjstate->hj_FirstOuterTupleSlot = NULL;
hjstate->hj_CurHashValue = 0;
hjstate->hj_CurBucketNo = 0;
hjstate->hj_CurSkewBucketNo = INVALID_SKEW_BUCKET_NO;
hjstate->hj_CurTuple = NULL;
/*
* Deconstruct the hash clauses into outer and inner argument values, so
* that we can evaluate those subexpressions separately. Also make a list
* of the hash operator OIDs, in preparation for looking up the hash
* functions to use.
*/
// 初始化存储用于连接的哈希表的关键信息列表、哈希操作符列表和连接状态
List* lclauses = NIL; // 用于存储左侧关键信息列表
List* rclauses = NIL; // 用于存储右侧关键信息列表
List* hoperators = NIL; // 用于存储哈希操作符列表
foreach (l, hjstate->hashclauses) {
FuncExprState* fstate = (FuncExprState*)lfirst(l); // 获取函数表达式状态
OpExpr* hclause = NULL; // 声明一个操作符表达式
Assert(IsA(fstate, FuncExprState)); // 确保是函数表达式状态
hclause = (OpExpr*)fstate->xprstate.expr; // 获取操作符表达式
Assert(IsA(hclause, OpExpr)); // 确保是操作符表达式
lclauses = lappend(lclauses, linitial(fstate->args)); // 将左侧关键信息添加到列表
rclauses = lappend(rclauses, lsecond(fstate->args)); // 将右侧关键信息添加到列表
hoperators = lappend_oid(hoperators, hclause->opno); // 将哈希操作符添加到列表
}
// 设置 Hash Join 算子状态结构体中的相关属性
hjstate->hj_OuterHashKeys = lclauses; // 设置左侧关键信息列表
hjstate->hj_InnerHashKeys = rclauses; // 设置右侧关键信息列表
hjstate->hj_HashOperators = hoperators; // 设置哈希操作符列表
// 子 Hash 节点需要评估内部哈希键
((HashState*)innerPlanState(hjstate))->hashkeys = rclauses;
hjstate->js.ps.ps_TupFromTlist = false; // 初始化是否从目标列表获取元组标志
hjstate->hj_JoinState = HJ_BUILD_HASHTABLE; // 设置连接状态为构建哈希表
hjstate->hj_MatchedOuter = false; // 初始化是否匹配外部表元组的标志
hjstate->hj_OuterNotEmpty = false; // 初始化外部表是否非空的标志
return hjstate;
}
函数的三个入参分别解释如下:
- HashJoin* node:这是要初始化的 Hash Join 节点,它是一个指向 HashJoin 结构体的指针,表示查询计划中的 Hash Join 算子节点。
调试信息如下:
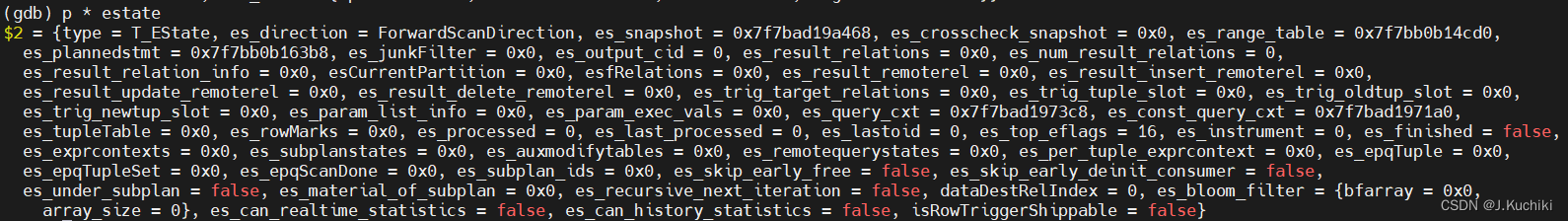
- EState* estate:这是查询的执行状态对象,它是一个指向 EState 结构体的指针,用于存储查询执行过程中的状态信息。
- int eflags:这是一个表示执行标志位的整数,用于指定执行 Hash Join 算子时的一些特定选项和标志。
HashJoinState结构体
其中,HashJoinState 在执行 Hash Join 算子时起着关键的作用,它用于存储 Hash Join 算子在运行过程中的各种状态信息和参数。
hash join 算子对应的 状态节点 HashJoinState 代码如下:(路径:src/include/nodes/execnodes.h)
// 定义 Hash Join 算子的状态结构体
typedef struct HashJoinState {
JoinState js; /* 继承 NodeTag 的 JoinState 结构体 */
List* hashclauses; /* 哈希连接的表达式状态列表 */
List* hj_OuterHashKeys; /* 外表的哈希键表达式状态列表 */
List* hj_InnerHashKeys; /* 内表的哈希键表达式状态列表 */
List* hj_HashOperators; /* 哈希操作符 OID 列表 */
HashJoinTable hj_HashTable; /* 哈希连接表 */
uint32 hj_CurHashValue; /* 当前哈希值 */
int hj_CurBucketNo; /* 当前哈希桶编号 */
int hj_CurSkewBucketNo; /* 当前倾斜哈希桶编号 */
HashJoinTuple hj_CurTuple; /* 当前哈希连接元组 */
/* hj_PreTuple 是一个指向 hj_CurTuple 之前的元组的指针,用于在哈希表中删除匹配的元组,特别用于右半连接和反连接 */
HashJoinTuple hj_PreTuple;
TupleTableSlot* hj_OuterTupleSlot; /* 外表元组槽 */
TupleTableSlot* hj_HashTupleSlot; /* 哈希表元组槽 */
TupleTableSlot* hj_NullOuterTupleSlot; /* 用于空的外表元组槽 */
TupleTableSlot* hj_NullInnerTupleSlot; /* 用于空的内表元组槽 */
TupleTableSlot* hj_FirstOuterTupleSlot;/* 第一个外表元组槽 */
int hj_JoinState; /* 哈希连接的当前状态 */
bool hj_MatchedOuter; /* 是否匹配了外表元组 */
bool hj_OuterNotEmpty; /* 外表是否不为空 */
bool hj_streamBothSides; /* 是否同时处理外表和内表的元组流 */
bool hj_rebuildHashtable; /* 是否需要重建哈希表 */
} HashJoinState;
TupleTableSlot 结构体
TupleTableSlot 的结构体,该结构体表示一个元组槽,用于在数据库系统中处理元组的存储、传递和处理。源码如下:(路径:src/include/executor/tuptable.h)
typedef struct TupleTableSlot {
NodeTag type; // 结构体的类型标记
bool tts_isempty; // 标记槽是否为空
bool tts_shouldFree; // 是否应该释放 tts_tuple 内存
bool tts_shouldFreeMin; // 是否应该释放 tts_mintuple 内存
bool tts_slow; // 用于 slot_deform_tuple 的保存状态
Tuple tts_tuple; // 物理元组,如果是虚拟的则为 NULL
#ifdef PGXC
/*
* PGXC 扩展以支持从远程 Datanode 发送的元组。
*/
char* tts_dataRow; // DataRow 格式中的元组数据
int tts_dataLen; // 数据行的实际长度
bool tts_shouldFreeRow; // 是否应该释放 tts_dataRow 内存
struct AttInMetadata* tts_attinmeta; // 存储从 DataRow 提取值的信息
Oid tts_xcnodeoid; // 来自哪个节点的数据行的 Oid
MemoryContext tts_per_tuple_mcxt; // 每个元组的内存上下文
#endif
TupleDesc tts_tupleDescriptor; // 槽的元组描述符
MemoryContext tts_mcxt; // 槽本身所在的上下文
Buffer tts_buffer; // 元组的缓冲区,无效则为 InvalidBuffer
int tts_nvalid; // tts_values 中有效值的数量
Datum* tts_values; // 每个属性的当前值
bool* tts_isnull; // 每个属性的当前是否为 NULL 标记
MinimalTuple tts_mintuple; // 最小元组,没有则为 NULL
HeapTupleData tts_minhdr; // 仅用于最小元组的工作区
long tts_off; // slot_deform_tuple 的保存状态
long tts_meta_off; // slot_deform_cmpr_tuple 的保存状态
TableAmType tts_tupslotTableAm; // 槽的元组表类型
} TupleTableSlot;
调试信息如下:

JoinState结构体
JoinState 结构体如下:(路径:src/include/nodes/execnodes.h)
/* ----------------
* JoinState information
*
* Superclass for state nodes of join plans.
* ----------------
*/
typedef struct JoinState {
PlanState ps; /* 计划状态,用于继承基本的节点信息 */
JoinType jointype; /* 连接的类型,描述连接的方式(内连接、左连接、右连接等) */
List* joinqual; /* 连接条件表达式列表(除了 ps.qual 外的其他条件) */
List* nulleqqual; /* 用于处理 NULL 值的连接条件表达式列表 */
} JoinState;
PlanState结构体
PlanState 结构体如下:(路径:src/include/nodes/execnodes.h)
/* ----------------
* PlanState node
*
* We never actually instantiate any PlanState nodes; this is just the common
* abstract superclass for all PlanState-type nodes.
* ----------------
*/
typedef struct PlanState {
NodeTag type; /* 节点类型标签 */
Plan* plan; /* 关联的 Plan 节点 */
EState* state; /* 执行时,各个节点的状态指向整个顶层 Plan 的一个 EState */
Instrumentation* instrument; /* 可选的运行时统计信息 */
/*
* 所有 Plan 类型共用的结构数据。这些链接到子状态树的链接与相关的计划树中的链接平行(除了 subPlan 列表,在计划树中不存在)。
*/
List* targetlist; /* 在该节点计算的目标列表 */
List* qual; /* 隐式的 AND 连接的条件 */
struct PlanState* lefttree; /* 输入的计划树(可能有多个) */
struct PlanState* righttree;
List* initPlan; /* Init 子计划节点(无相关的表达式子查询) */
List* subPlan; /* 在我的表达式中的 SubPlanState 节点 */
/*
* 管理基于参数变化的重新扫描的状态。
*/
Bitmapset* chgParam; /* 变化的 Params 的 ID 集合 */
HbktScanSlot hbktScanSlot;
/*
* 大多数(如果不是全部)节点类型都需要的其他运行时状态。
*/
TupleTableSlot* ps_ResultTupleSlot; /* 存储我的结果元组的槽位 */
ExprContext* ps_ExprContext; /* 节点的表达式计算上下文 */
ProjectionInfo* ps_ProjInfo; /* 进行元组投影的信息 */
bool ps_TupFromTlist; /* 处理目标列表中的集合值函数的状态标志 */
bool vectorized; /* 是否为矢量化? */
MemoryContext nodeContext; /* 此节点的内存上下文 */
bool earlyFreed; /* 节点内存是否已释放? */
uint8 stubType; /* 节点存根执行类型,参见 @PlanStubType */
vectarget_func jitted_vectarget; /* 指向代码生成的目标列表表达式的 LLVM IR 函数指针。 */
/*
* 描述当前计划节点中的问题,主要用于数据倾斜和不准确的行数的问题去重复
*/
List* plan_issues;
bool recursive_reset; /* 节点是否已经重置? */
bool qual_is_inited;
int64 ps_rownum; /* 存储当前行号 */
} PlanState;
ExecInitHashJoin函数部分代码介绍
下面,我们来拆分的看一下 ExecInitHashJoin 函数吧。这里只介绍一些重点部分,其余部分可参考源码中的注释。先看如下代码段:
/*
* initialize child expressions
*/
hjstate->js.ps.targetlist = (List*)ExecInitExpr((Expr*)node->join.plan.targetlist, (PlanState*)hjstate);
hjstate->js.ps.qual = (List*)ExecInitExpr((Expr*)node->join.plan.qual, (PlanState*)hjstate);
hjstate->js.jointype = node->join.jointype;
hjstate->js.joinqual = (List*)ExecInitExpr((Expr*)node->join.joinqual, (PlanState*)hjstate);
hjstate->js.nulleqqual = (List*)ExecInitExpr((Expr*)node->join.nulleqqual, (PlanState*)hjstate);
hjstate->hashclauses = (List*)ExecInitExpr((Expr*)node->hashclauses, (PlanState*)hjstate);
以第一句(hjstate->js.ps.targetlist = (List*)ExecInitExpr((Expr*)node->join.plan.targetlist, (PlanState*)hjstate);)为例进行分析:
这句代码的作用是将 HashJoinState 结构体中的 targetlist 字段初始化为经过表达式初始化函数 ExecInitExpr 处理后的结果。
函数 ExecInitExpr 是初始化表达式节点的函数,其作用是为给定的表达式节点创建执行时所需的状态结构体,并将该节点进行适当的初始化。
调试信息如下:
以下两句代码是在获取 Hash Join 节点的输入子计划,其中:
- outerPlan(node):获取了 Hash Join 节点的外部输入子计划,也就是左侧的输入。
- (Hash*)innerPlan(node):获取了 Hash Join 节点的内部输入子计划,也就是右侧的输入,并将其强制转换为 Hash 类型的指针。
outerNode = outerPlan(node);
hashNode = (Hash*)innerPlan(node);
调试信息如下:
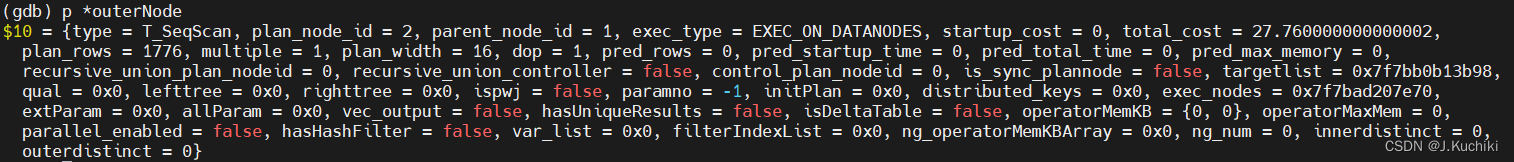
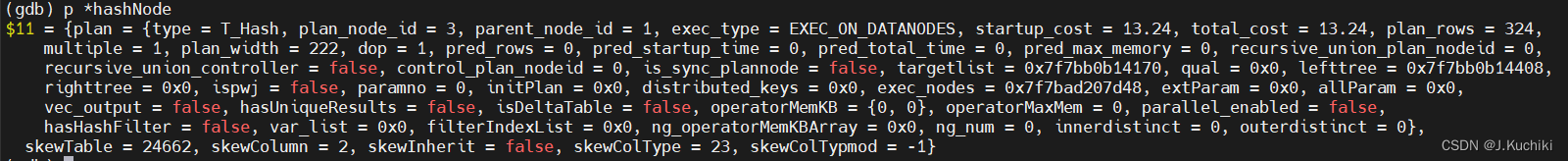
以下这段 switch 语句是用于为 Hash Join 算子节点设置外连接(outer join)操作所需的空元组(null tuples)。外连接是一种连接操作,它不仅返回符合连接条件的元组,还会返回没有匹配的元组,并用 NULL 值填充缺失的列。
/* set up null tuples for outer joins, if needed */
switch (node->join.jointype) {
case JOIN_INNER:
case JOIN_SEMI:
case JOIN_RIGHT_SEMI:
break;
case JOIN_LEFT:
case JOIN_ANTI:
case JOIN_LEFT_ANTI_FULL:
hjstate->hj_NullInnerTupleSlot = ExecInitNullTupleSlot(estate, ExecGetResultType(innerPlanState(hjstate)));
break;
case JOIN_RIGHT:
case JOIN_RIGHT_ANTI:
case JOIN_RIGHT_ANTI_FULL:
hjstate->hj_NullOuterTupleSlot = ExecInitNullTupleSlot(estate, ExecGetResultType(outerPlanState(hjstate)));
break;
case JOIN_FULL:
hjstate->hj_NullOuterTupleSlot = ExecInitNullTupleSlot(estate, ExecGetResultType(outerPlanState(hjstate)));
hjstate->hj_NullInnerTupleSlot = ExecInitNullTupleSlot(estate, ExecGetResultType(innerPlanState(hjstate)));
break;
default:
ereport(ERROR,
(errcode(ERRCODE_UNRECOGNIZED_NODE_TYPE),
errmodule(MOD_EXECUTOR),
errmsg("unrecognized join type: %d for hashjoin", (int)node->join.jointype)));
}
具体来说,这段代码做了以下工作:
- 根据连接类型
(node->join.jointype)的不同,决定是否需要设置空元组。- 对于内连接(INNER JOIN)、半连接(SEMI JOIN)和右半连接(RIGHT SEMI JOIN),不需要设置空元组,所以这些情况下代码直接跳过。
- 对于左连接(LEFT JOIN)、反向半连接(ANTI JOIN)以及左反全连接(LEFT ANTI FULL JOIN),需要为内部表设置空元组。这样在左连接中,如果没有匹配的内部表元组,外部表的元组将会与一个 NULL 值填充的空元组进行连接。
- 对于右连接(RIGHT JOIN)、反向右半连接(RIGHT ANTI JOIN)以及右反全连接(RIGHT ANTI FULL JOIN),需要为外部表设置空元组。这样在右连接中,如果没有匹配的外部表元组,内部表的元组将会与一个 NULL 值填充的空元组进行连接。
- 对于全连接(FULL JOIN),需要为内部表和外部表都设置空元组,以满足连接操作的要求。
ExecHashJoin函数
ExecHashJoin 函数的作用是执行 Hash Join 连接操作,它将两个输入关系(外部和内部)的元组按照给定的连接条件进行连接,并输出满足条件的连接结果。在 Hash Join 中,通过构建哈希表来加速连接过程。在函数 ExecInitHashJoin 中插入断点,调试信息如下,通过打印可以看到函数的调用关系。
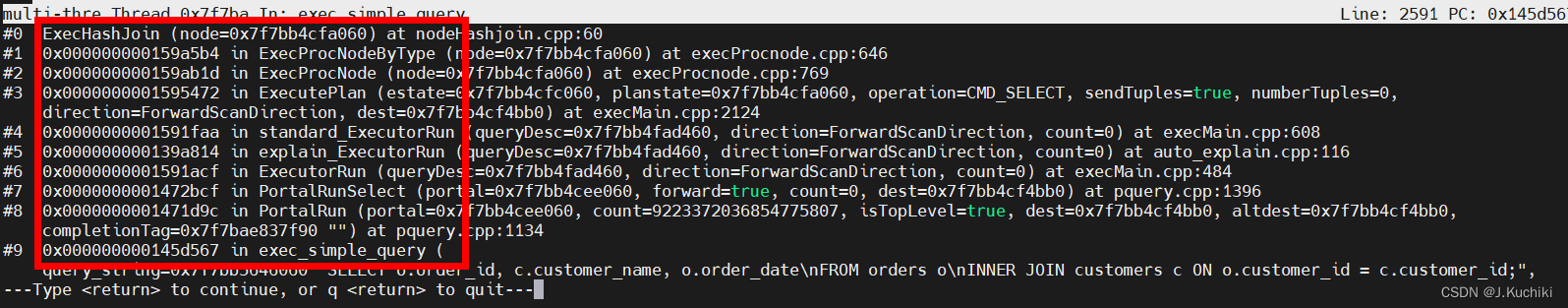
ExecHashJoin 函数源码如下:(路径:src/gausskernel/runtime/executor/nodeHashjoin.cpp)
/* ----------------------------------------------------------------
* ExecHashJoin
*
* This function implements the Hybrid Hashjoin algorithm.
*
* Note: the relation we build hash table on is the "inner"
* the other one is "outer".
* ----------------------------------------------------------------
*/
/* return: a tuple or NULL */
TupleTableSlot* ExecHashJoin(HashJoinState* node)
{
PlanState* outerNode = NULL; // 外部计划节点的状态
HashState* hashNode = NULL; // 哈希节点的状态
List* joinqual = NIL; // 连接条件
List* otherqual = NIL; // 其他条件
ExprContext* econtext = NULL; // 表达式计算上下文
ExprDoneCond isDone; // 表达式计算结束状态
HashJoinTable hashtable; // 哈希连接表
TupleTableSlot* outerTupleSlot = NULL; // 外部元组槽
uint32 hashvalue; // 哈希值
int batchno; // 哈希批次号
MemoryContext oldcxt; // 旧内存上下文
JoinType jointype; // 连接类型
/*
* 从 HashJoin 节点获取信息
*/
joinqual = node->js.joinqual; // 获取连接条件
otherqual = node->js.ps.qual; // 获取其他条件
hashNode = (HashState*)innerPlanState(node); // 获取内部计划节点的状态,即哈希节点状态
outerNode = outerPlanState(node); // 获取外部计划节点的状态
hashtable = node->hj_HashTable; // 获取哈希连接表
econtext = node->js.ps.ps_ExprContext; // 获取表达式计算上下文
jointype = node->js.jointype; // 获取连接类型
/*
* 检查是否仍在从先前的连接元组中投影出元组
* 这是因为在投影表达式中存在返回集合的函数
* 如果是这样,尝试投影另一个元组
*/
if (node->js.ps.ps_TupFromTlist) {
TupleTableSlot* result = NULL;
// 通过执行投影操作生成新的元组
result = ExecProject(node->js.ps.ps_ProjInfo, &isDone);
// 如果投影操作返回多个结果,直接返回当前结果
if (isDone == ExprMultipleResult)
return result;
/* 完成当前源元组的处理... */
node->js.ps.ps_TupFromTlist = false;
}
/*
* Reset per-tuple memory context to free any expression evaluation
* storage allocated in the previous tuple cycle. Note this can't happen
* until we're done projecting out tuples from a join tuple.
*/
// 重置一个表达式上下文
ResetExprContext(econtext);
/*
* run the hash join state machine
* 运行哈希联接状态机
*/
for (;;) {
switch (node->hj_JoinState) {
case HJ_BUILD_HASHTABLE: {
/*
* First time through: build hash table for inner relation.
*/
Assert(hashtable == NULL);
/*
* If the outer relation is completely empty, and it's not
* right/full join, we can quit without building the hash
* table. However, for an inner join it is only a win to
* check this when the outer relation's startup cost is less
* than the projected cost of building the hash table.
* Otherwise it's best to build the hash table first and see
* if the inner relation is empty. (When it's a left join, we
* should always make this check, since we aren't going to be
* able to skip the join on the strength of an empty inner
* relation anyway.)
*
* If we are rescanning the join, we make use of information
* gained on the previous scan: don't bother to try the
* prefetch if the previous scan found the outer relation
* nonempty. This is not 100% reliable since with new
* parameters the outer relation might yield different
* results, but it's a good heuristic.
*
* The only way to make the check is to try to fetch a tuple
* from the outer plan node. If we succeed, we have to stash
* it away for later consumption by ExecHashJoinOuterGetTuple.
*/
// remove node->hj_streamBothSides after stream hang problem sloved.
if (HJ_FILL_INNER(node)) {
/* no chance to not build the hash table */
node->hj_FirstOuterTupleSlot = NULL;
} else if ((HJ_FILL_OUTER(node) || (outerNode->plan->startup_cost < hashNode->ps.plan->total_cost &&
!node->hj_OuterNotEmpty)) &&
!node->hj_streamBothSides) {
node->hj_FirstOuterTupleSlot = ExecProcNode(outerNode);
if (TupIsNull(node->hj_FirstOuterTupleSlot)) {
node->hj_OuterNotEmpty = false;
/*
* If the outer relation is completely empty, and it's not right/full join,
* we should deinit the consumer in right tree earlier.
* It should be noticed that we can not do early deinit
* within predpush.
*/
#ifdef ENABLE_MULTIPLE_NODES
if (((PlanState*)node) != NULL && !CheckParamWalker((PlanState*)node)) {
ExecEarlyDeinitConsumer((PlanState*)node);
}
#endif
ExecEarlyFree((PlanState*)node);
EARLY_FREE_LOG(elog(LOG, "Early Free: HashJoin early return NULL"
" at node %d, memory used %d MB.", (node->js.ps.plan)->plan_node_id,
getSessionMemoryUsageMB()));
return NULL;
} else
node->hj_OuterNotEmpty = true;
} else
node->hj_FirstOuterTupleSlot = NULL;
/*
* create the hash table, sometimes we should keep nulls
*/
oldcxt = MemoryContextSwitchTo(hashNode->ps.nodeContext);
hashtable = ExecHashTableCreate((Hash*)hashNode->ps.plan, node->hj_HashOperators,
HJ_FILL_INNER(node) || node->js.nulleqqual != NIL);
MemoryContextSwitchTo(oldcxt);
node->hj_HashTable = hashtable;
/*
* execute the Hash node, to build the hash table
*/
WaitState oldStatus = pgstat_report_waitstatus(STATE_EXEC_HASHJOIN_BUILD_HASH);
hashNode->hashtable = hashtable;
hashNode->ps.hbktScanSlot.currSlot = node->js.ps.hbktScanSlot.currSlot;
(void)MultiExecProcNode((PlanState*)hashNode);
(void)pgstat_report_waitstatus(oldStatus);
/* Early free right tree after hash table built */
ExecEarlyFree((PlanState*)hashNode);
EARLY_FREE_LOG(elog(LOG, "Early Free: Hash Table for HashJoin"
" is built at node %d, memory used %d MB.",
(node->js.ps.plan)->plan_node_id, getSessionMemoryUsageMB()));
/*
* If the inner relation is completely empty, and we're not
* doing a left outer join, we can quit without scanning the
* outer relation.
*/
if (hashtable->totalTuples == 0 && !HJ_FILL_OUTER(node)) {
/*
* When hash table size is zero, no need to fetch left tree any more and
* should deinit the consumer in left tree earlier.
* It should be noticed that we can not do early deinit
* within predpush.
*/
#ifdef ENABLE_MULTIPLE_NODES
if (((PlanState*)node) != NULL && !CheckParamWalker((PlanState*)node)) {
ExecEarlyDeinitConsumer((PlanState*)node);
}
#endif
return NULL;
}
/*
* need to remember whether nbatch has increased since we
* began scanning the outer relation
*/
hashtable->nbatch_outstart = hashtable->nbatch;
/*
* Reset OuterNotEmpty for scan. (It's OK if we fetched a
* tuple above, because ExecHashJoinOuterGetTuple will
* immediately set it again.)
*/
node->hj_OuterNotEmpty = false;
node->hj_JoinState = HJ_NEED_NEW_OUTER;
}
/* fall through */
case HJ_NEED_NEW_OUTER:
/*
* 如果没有外部元组,尝试获取下一个
*/
outerTupleSlot = ExecHashJoinOuterGetTuple(outerNode, node, &hashvalue);
// 如果外部元组为空,表示批处理结束或可能整个连接结束
if (TupIsNull(outerTupleSlot)) {
if (HJ_FILL_INNER(node)) {
// 准备扫描未匹配的内部元组
ExecPrepHashTableForUnmatched(node);
// 切换到扫描未匹配内部元组的状态
node->hj_JoinState = HJ_FILL_INNER_TUPLES;
} else {
// 切换到需要获取新批次的状态
node->hj_JoinState = HJ_NEED_NEW_BATCH;
}
// 继续下一次循环
continue;
}
// 设置外部元组到执行上下文中
econtext->ecxt_outertuple = outerTupleSlot;
// 标记当前外部元组还未匹配
node->hj_MatchedOuter = false;
/*
* Find the corresponding bucket for this tuple in the main
* hash table or skew hash table.
*/
// 找到当前元组对应的主哈希表或倾斜哈希表中的桶
node->hj_CurHashValue = hashvalue;
// 获取当前元组所属的桶编号和批次编号
ExecHashGetBucketAndBatch(hashtable, hashvalue, &node->hj_CurBucketNo, &batchno);
// 获取当前元组所属的倾斜桶编号(如果有)
node->hj_CurSkewBucketNo = ExecHashGetSkewBucket(hashtable, hashvalue);
// 将当前元组指针初始化为 NULL
node->hj_CurTuple = NULL;
/*
* The tuple might not belong to the current batch (where
* "current batch" includes the skew buckets if any).
*/
// 如果当前元组所属的批次编号不是当前批次,并且不属于任何倾斜桶
if (batchno != hashtable->curbatch && node->hj_CurSkewBucketNo == INVALID_SKEW_BUCKET_NO) {
/*
* 需要将这个外部元组推迟到后续批次。
* 将其保存到对应的外部批次文件中。
*/
Assert(batchno > hashtable->curbatch);
// 提取外部元组的最小元组形式
MinimalTuple tuple = ExecFetchSlotMinimalTuple(outerTupleSlot);
// 将元组保存到对应的外部批次文件中,同时更新溢出大小
ExecHashJoinSaveTuple(tuple, hashvalue, &hashtable->outerBatchFile[batchno]);
*hashtable->spill_size += sizeof(uint32) + tuple->t_len;
pgstat_increase_session_spill_size(sizeof(uint32) + tuple->t_len);
// 继续循环,仍然保持在 HJ_NEED_NEW_OUTER 状态
continue;
}
/* OK, let's scan the bucket for matches */
node->hj_JoinState = HJ_SCAN_BUCKET;
/* Prepare for the clear-process if necessary */
if (jointype == JOIN_RIGHT_ANTI || jointype == JOIN_RIGHT_SEMI)
node->hj_PreTuple = NULL;
/* fall through */
case HJ_SCAN_BUCKET:
/*
* We check for interrupts here because this corresponds to
* where we'd fetch a row from a child plan node in other join
* types.
*/
CHECK_FOR_INTERRUPTS();
/*
* Scan the selected hash bucket for matches to current outer
*/
if (!ExecScanHashBucket(node, econtext)) {
/* out of matches; check for possible outer-join fill */
node->hj_JoinState = HJ_FILL_OUTER_TUPLE;
continue;
}
/*
* We've got a match, but still need to test non-hashed quals.
* ExecScanHashBucket already set up all the state needed to
* call ExecQual.
*
* If we pass the qual, then save state for next call and have
* ExecProject form the projection, store it in the tuple
* table, and return the slot.
*
* Only the joinquals determine tuple match status, but all
* quals must pass to actually return the tuple.
*/
if (joinqual == NIL || ExecQual(joinqual, econtext, false)) {
node->hj_MatchedOuter = true;
/*
* for right-anti join: skip and delete the matched tuple;
* for right-semi join: return and delete the matched tuple;
* for right-anti-full join: skip and delete the matched tuple;
*/
if (jointype == JOIN_RIGHT_ANTI || jointype == JOIN_RIGHT_SEMI ||
jointype == JOIN_RIGHT_ANTI_FULL) {
if (node->hj_PreTuple)
node->hj_PreTuple->next = node->hj_CurTuple->next;
else if (node->hj_CurSkewBucketNo != INVALID_SKEW_BUCKET_NO)
hashtable->skewBucket[node->hj_CurSkewBucketNo]->tuples = node->hj_CurTuple->next;
else
hashtable->buckets[node->hj_CurBucketNo] = node->hj_CurTuple->next;
if (jointype == JOIN_RIGHT_ANTI || jointype == JOIN_RIGHT_ANTI_FULL)
continue;
} else {
HeapTupleHeaderSetMatch(HJTUPLE_MINTUPLE(node->hj_CurTuple));
/* Anti join: we never return a matched tuple */
if (jointype == JOIN_ANTI || jointype == JOIN_LEFT_ANTI_FULL) {
node->hj_JoinState = HJ_NEED_NEW_OUTER;
continue;
}
/* Semi join: we'll consider returning the first match, but after
* that we're done with this outer tuple */
if (jointype == JOIN_SEMI)
node->hj_JoinState = HJ_NEED_NEW_OUTER;
}
if (otherqual == NIL || ExecQual(otherqual, econtext, false)) {
TupleTableSlot* result = NULL;
result = ExecProject(node->js.ps.ps_ProjInfo, &isDone);
if (isDone != ExprEndResult) {
node->js.ps.ps_TupFromTlist = (isDone == ExprMultipleResult);
return result;
}
} else
InstrCountFiltered2(node, 1);
} else {
InstrCountFiltered1(node, 1);
/* For right Semi/Anti join, we set hj_PreTuple following hj_CurTuple */
if (jointype == JOIN_RIGHT_ANTI || jointype == JOIN_RIGHT_SEMI)
node->hj_PreTuple = node->hj_CurTuple;
}
break;
case HJ_FILL_OUTER_TUPLE:
/*
* The current outer tuple has run out of matches, so check
* whether to emit a dummy outer-join tuple. Whether we emit
* one or not, the next state is NEED_NEW_OUTER.
*/
node->hj_JoinState = HJ_NEED_NEW_OUTER;
if (!node->hj_MatchedOuter && HJ_FILL_OUTER(node)) {
/*
* Generate a fake join tuple with nulls for the inner
* tuple, and return it if it passes the non-join quals.
*/
econtext->ecxt_innertuple = node->hj_NullInnerTupleSlot;
if (otherqual == NIL || ExecQual(otherqual, econtext, false)) {
TupleTableSlot* result = NULL;
result = ExecProject(node->js.ps.ps_ProjInfo, &isDone);
if (isDone != ExprEndResult) {
node->js.ps.ps_TupFromTlist = (isDone == ExprMultipleResult);
return result;
}
} else
InstrCountFiltered2(node, 1);
}
break;
case HJ_FILL_INNER_TUPLES:
/*
* We have finished a batch, but we are doing right/full/rightAnti join,
* so any unmatched inner tuples in the hashtable have to be
* emitted before we continue to the next batch.
*/
if (!ExecScanHashTableForUnmatched(node, econtext)) {
/* no more unmatched tuples */
node->hj_JoinState = HJ_NEED_NEW_BATCH;
continue;
}
/*
* Generate a fake join tuple with nulls for the outer tuple,
* and return it if it passes the non-join quals.
*/
econtext->ecxt_outertuple = node->hj_NullOuterTupleSlot;
if (otherqual == NIL || ExecQual(otherqual, econtext, false)) {
TupleTableSlot* result = NULL;
result = ExecProject(node->js.ps.ps_ProjInfo, &isDone);
if (isDone != ExprEndResult) {
node->js.ps.ps_TupFromTlist = (isDone == ExprMultipleResult);
return result;
}
} else
InstrCountFiltered2(node, 1);
break;
case HJ_NEED_NEW_BATCH:
/*
* Try to advance to next batch. Done if there are no more.
*/
if (!ExecHashJoinNewBatch(node)) {
ExecEarlyFree(outerPlanState(node));
EARLY_FREE_LOG(elog(LOG, "Early Free: HashJoin Probe is done"
" at node %d, memory used %d MB.",
(node->js.ps.plan)->plan_node_id, getSessionMemoryUsageMB()));
return NULL; /* end of join */
}
node->hj_JoinState = HJ_NEED_NEW_OUTER;
break;
default:
ereport(ERROR, (errcode(ERRCODE_UNEXPECTED_NODE_STATE),
errmodule(MOD_EXECUTOR), errmsg("unrecognized hashjoin state: %d", (int)node->hj_JoinState)));
}
}
}
可以看到 ExecHashJoin 函数已经非常的长,我们还是来拆分的看一下 吧。这里只介绍一些重点部分,其余部分可参考源码中的注释。先看如下代码段:
/*
* 检查是否仍在从先前的连接元组中投影出元组
* 这是因为在投影表达式中存在返回集合的函数
* 如果是这样,尝试投影另一个元组
*/
if (node->js.ps.ps_TupFromTlist) {
TupleTableSlot* result = NULL;
// 通过执行投影操作生成新的元组
result = ExecProject(node->js.ps.ps_ProjInfo, &isDone);
// 如果投影操作返回多个结果,直接返回当前结果
if (isDone == ExprMultipleResult)
return result;
/* 完成当前源元组的处理... */
node->js.ps.ps_TupFromTlist = false;
}
以上代码中条件判断语句 if (node->js.ps.ps_TupFromTlist) 是在判断什么呢?
这个条件判断用于检查是否之前已经从上一个连接操作(比如上一个join)的投影表达式中返回了一个或多个元组。
什么意思?来看一个案例吧:
当进行多表连接操作时,涉及多个表的列,我们可以使用投影操作从连接结果中选择特定的列。假设有以下两个表:
- 表 employees 包含员工信息,如 employee_id、employee_name 等列。
- 表 salaries 包含员工薪资信息,如 employee_id、salary_amount 等列。
现在,我们希望进行一个内连接操作,连接 employees 表和 salaries 表,以便找到每个员工的工资信息。查询可能如下所示:
SELECT e.employee_id, e.employee_name, s.salary_amount
FROM employees e
INNER JOIN salaries s ON e.employee_id = s.employee_id;
在执行这个查询时,查询执行计划会涉及到投影操作,以便将所需的列从连接结果中选择出来。这里的 SELECT 子句中指定了需要的列:e.employee_id、e.employee_name 和 s.salary_amount。
在执行这个投影操作时,ExecProject 函数会计算投影表达式,生成满足条件的元组,包含指定的列值。如果在处理过程中发现一个员工关联了多个工资记录,那么 JOIN 操作会生成多个连接结果,其中每个连接结果都包含一个员工的不同工资记录。在这种情况下,ExecProject 可能会多次返回元组,直到所有可能的连接结果都被处理完。
其中,ExecProject 函数用于执行投影操作,它将从输入元组中选取特定的列(属性),应用投影表达式(可能包含函数调用、运算等),并生成一个新的输出元组。这个函数在数据库查询执行计划中的很多阶段都会使用,例如投影操作、投影到目标列、计算表达式等。
ExecProject 函数的输入包括 ProjectionInfo 结构,其中包含了执行投影操作所需的信息,包括投影的目标列表、表达式上下文等。,以及一个 ExprDoneCond 类型的指针,用于指示执行是否已完成。
ExecProject 函数源码如下:(路径:src/gausskernel/runtime/executor/execQual.cpp)
/*
* ExecProject
*
* projects a tuple based on projection info and stores
* it in the previously specified tuple table slot.
*
* Note: the result is always a virtual tuple; therefore it
* may reference the contents of the exprContext's scan tuples
* and/or temporary results constructed in the exprContext.
* If the caller wishes the result to be valid longer than that
* data will be valid, he must call ExecMaterializeSlot on the
* result slot.
*/
TupleTableSlot* ExecProject(ProjectionInfo* projInfo, ExprDoneCond* isDone)
{
/*
* sanity checks
*/
Assert(projInfo != NULL);
/*
* get the projection info we want
*/
TupleTableSlot *slot = projInfo->pi_slot;
ExprContext *econtext = projInfo->pi_exprContext;
/* Assume single result row until proven otherwise */
if (isDone != NULL)
*isDone = ExprSingleResult;
/*
* Clear any former contents of the result slot. This makes it safe for
* us to use the slot's Datum/isnull arrays as workspace. (Also, we can
* return the slot as-is if we decide no rows can be projected.)
*/
(void)ExecClearTuple(slot);
/*
* Force extraction of all input values that we'll need. The
* Var-extraction loops below depend on this, and we are also prefetching
* all attributes that will be referenced in the generic expressions.
*/
if (projInfo->pi_lastInnerVar > 0) {
tableam_tslot_getsomeattrs(econtext->ecxt_innertuple, projInfo->pi_lastInnerVar);
}
if (projInfo->pi_lastOuterVar > 0) {
tableam_tslot_getsomeattrs(econtext->ecxt_outertuple, projInfo->pi_lastOuterVar);
}
if (projInfo->pi_lastScanVar > 0) {
tableam_tslot_getsomeattrs(econtext->ecxt_scantuple, projInfo->pi_lastScanVar);
}
/*
* Assign simple Vars to result by direct extraction of fields from source
* slots ... a mite ugly, but fast ...
*/
int numSimpleVars = projInfo->pi_numSimpleVars;
if (numSimpleVars > 0) {
Datum* values = slot->tts_values;
bool* isnull = slot->tts_isnull;
int* varSlotOffsets = projInfo->pi_varSlotOffsets;
int* varNumbers = projInfo->pi_varNumbers;
int i;
if (projInfo->pi_directMap) {
/* especially simple case where vars go to output in order */
for (i = 0; i < numSimpleVars; i++) {
char* slotptr = ((char*)econtext) + varSlotOffsets[i];
TupleTableSlot* varSlot = *((TupleTableSlot**)slotptr);
int varNumber = varNumbers[i] - 1;
Assert (varNumber < varSlot->tts_tupleDescriptor->natts);
Assert (i < slot->tts_tupleDescriptor->natts);
values[i] = varSlot->tts_values[varNumber];
isnull[i] = varSlot->tts_isnull[varNumber];
}
} else {
/* we have to pay attention to varOutputCols[] */
int* varOutputCols = projInfo->pi_varOutputCols;
for (i = 0; i < numSimpleVars; i++) {
char* slotptr = ((char*)econtext) + varSlotOffsets[i];
TupleTableSlot* varSlot = *((TupleTableSlot**)slotptr);
int varNumber = varNumbers[i] - 1;
int varOutputCol = varOutputCols[i] - 1;
Assert (varNumber < varSlot->tts_tupleDescriptor->natts);
Assert (varOutputCol < slot->tts_tupleDescriptor->natts);
values[varOutputCol] = varSlot->tts_values[varNumber];
isnull[varOutputCol] = varSlot->tts_isnull[varNumber];
}
}
}
/*
* If there are any generic expressions, evaluate them. It's possible
* that there are set-returning functions in such expressions; if so and
* we have reached the end of the set, we return the result slot, which we
* already marked empty.
*/
if (projInfo->pi_targetlist) {
if (!ExecTargetList(
projInfo->pi_targetlist, econtext, slot->tts_values, slot->tts_isnull, projInfo->pi_itemIsDone, isDone))
return slot; /* no more result rows, return empty slot */
}
/*
* Successfully formed a result row. Mark the result slot as containing a
* valid virtual tuple.
*/
return ExecStoreVirtualTuple(slot);
}
紧接着,ExecHashJoin 函数最后有一段很长的 for 循环语句,这段代码是关于哈希连接(Hash Join)算法的实现,它用于将两个输入数据集进行连接操作,根据特定的连接条件和限制返回匹配的结果。下面大致解释代码中每个部分的功能:
- 这段代码位于一个无限循环中,表示每次循环迭代都会处理一个连接操作;
- 代码首先根据当前连接状态(node->hj_JoinState)的不同,进入不同的操作分支;
- 在状态 HJ_BUILD_HASHTABLE 下,开始构建哈希表;
- 首次通过:为内部关系构建哈希表。
- 如果外部关系为空并且不是右/全连接,可以直接退出而不构建哈希表。
- 根据启动成本和哈希表构建成本的比较决定是否构建哈希表。
- 如果外部关系为空,需要进行一些清理工作,并返回结果。
- 构建哈希表,并执行 Hash 结点来填充哈希表。
- 在状态 HJ_NEED_NEW_OUTER 下,准备获取下一个外部元组进行连接;
- 尝试从外部计划节点获取下一个外部元组。
- 如果没有外部元组,根据连接类型和状态转换需要,进入下一个状态。
- 否则,设置当前外部元组,准备进行哈希匹配
- 在状态 HJ_SCAN_BUCKET 下,扫描哈希桶进行匹配;
- 检查中断,以便在需要时可以中断扫描。
- 扫描选定的哈希桶以查找与当前外部元组匹配的元组。
- 如果找不到匹配,进入下一个状态。
- 如果找到匹配,进一步测试其他条件。
- 如果通过所有条件,生成结果并返回。
- 在状态 HJ_FILL_OUTER_TUPLE 下,生成外部连接的空元组;
- 如果当前外部元组没有匹配,且需要生成外部连接元组,生成一个带有内部元组为空值的外部连接元组
- 在状态 HJ_FILL_INNER_TUPLES 下,生成内部连接的空元组;
- 如果当前批次处理完成,且需要生成内部连接的未匹配元组,生成一个带有外部元组为空值的内部连接元组。
- 在状态 HJ_NEED_NEW_BATCH 下,准备处理下一个批次。
- 尝试进入下一个批次,如果没有更多批次,则结束连接操作。
其中,node->hj_JoinState 是一个状态变量,用于跟踪哈希连接的不同阶段和状态。以下是每个状态值的含义:
| 状态 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| HJ_BUILD_HASHTABLE | 在第一次循环中,构建内部关系的哈希表。 |
| HJ_NEED_NEW_OUTER | 需要获取下一个外部元组,以便与哈希表中的匹配进行比较。 |
| HJ_SCAN_BUCKET | 在哈希表的特定存储桶中扫描匹配的元组。 |
| HJ_FILL_OUTER_TUPLE | 当前外部元组已经没有匹配,需要生成一个虚拟的外连接元组。 |
| HJ_FILL_INNER_TUPLES | 批次处理结束后,在右/内连接中生成未匹配的内部元组。 |
| HJ_NEED_NEW_BATCH | 需要切换到下一个处理批次。 |
在循环的 HJ_BUILD_HASHTABLE 状态选择中,ExecHashTableCreate 函数用于创建一个哈希表的实例。调用函数如下,它接受三个参数::
hashtable = ExecHashTableCreate((Hash*)hashNode->ps.plan, node->hj_HashOperators,
HJ_FILL_INNER(node) || node->js.nulleqqual != NIL);
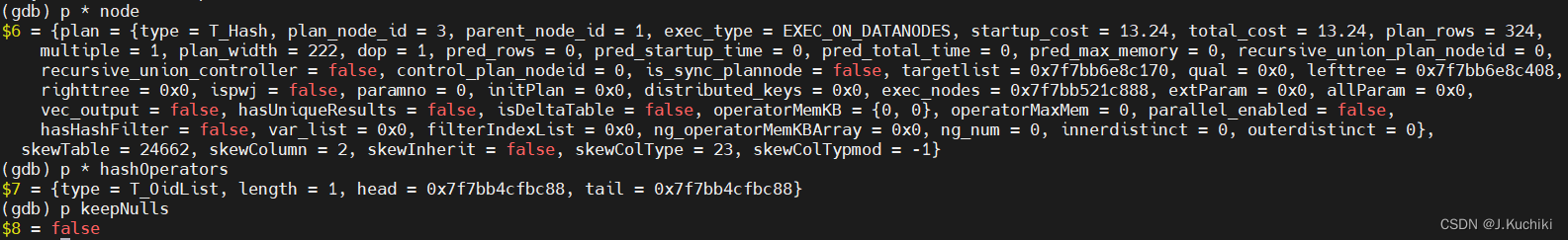
(Hash*)hashNode->ps.plan:哈希节点的计划节点信息,通过类型转换将哈希节点的计划节点信息传递给哈希表构建函数。哈希表构建函数需要计划节点信息来了解哈希表的配置参数。node->hj_HashOperators:用于指定要使用的哈希函数和比较函数的数组。这些函数将用于将关系中的值映射到哈希桶中。HJ_FILL_INNER(node) || node->js.nulleqqual != NIL:这部分逻辑决定了哈希表是否要保留空值的条目。如果连接是一个内连接(HJ_FILL_INNER(node)为 true),或者连接操作中有空值比较的条件(node->js.nulleqqual不为空),则哈希表会保留空值的条目。这在处理连接操作时是非常重要的。调试信息如下:
ExecHashTableCreate 函数源码如下:(路径:src/gausskernel/runtime/executor/nodeHash.cpp)
/* ----------------------------------------------------------------
* ExecHashTableCreate
*
* create an empty hashtable data structure for hashjoin.
* ----------------------------------------------------------------
*/
HashJoinTable ExecHashTableCreate(Hash* node, List* hashOperators, bool keepNulls)
{
HashJoinTable hashtable; // 哈希表的控制块,用于存储哈希连接操作中的状态和信息
Plan* outerNode = NULL; // 外部计划节点,表示哈希连接操作的外部输入
int nbuckets; // 哈希表的桶数,即哈希值范围的分区数量
int nbatch; // 哈希表的批次数,用于分批构建哈希表
int num_skew_mcvs; // 哈希偏斜优化中的最大多列值数目
int log2_nbuckets; // 哈希表桶数的对数,用于计算哈希桶索引
int nkeys; // 连接键的数量,即连接条件中的谓词数目
int i; // 循环计数器
int64 local_work_mem = SET_NODEMEM(node->plan.operatorMemKB[0], node->plan.dop); // 用于哈希表的局部内存分配,根据操作的内存设置和并行度进行调整
int64 max_mem = (node->plan.operatorMaxMem > 0) ? SET_NODEMEM(node->plan.operatorMaxMem, node->plan.dop) : 0; // 用于哈希表的最大内存分配,根据操作的内存设置和并行度进行调整
ListCell* ho = NULL; // 遍历外部输入的计划节点列表的游标
MemoryContext oldcxt; // 用于保存旧的内存上下文,以便稍后进行切换
/*
* Get information about the size of the relation to be hashed (it's the
* "outer" subtree of this node, but the inner relation of the hashjoin).
* Compute the appropriate size of the hash table.
*/
// 将外部输入的计划节点(即外部表)赋值给变量 outerNode,表示外部表的计划节点。
outerNode = outerPlan(node);
// 这是一个函数调用,用于选择合适的哈希表大小和分批策略。
ExecChooseHashTableSize(PLAN_LOCAL_ROWS(outerNode) / SET_DOP(node->plan.dop), // 估计外部表的本地行数,即预估哈希表的输入行数。
outerNode->plan_width, // 外部表的计划宽度,即每行的字节数。
OidIsValid(node->skewTable), // 判断是否存在哈希偏斜表。
&nbuckets, // 用于存储计算得到的哈希表桶数。
&nbatch, // 用于存储计算得到的哈希表批次数。
&num_skew_mcvs, // 用于存储计算得到的哈希偏斜优化中的多列值数目。
local_work_mem); // 局部内存分配大小,即哈希表的一部分内存分配。
/*
* If we allows mem auto spread, we should set nbatch to 1 to avoid disk
* spill if estimation from optimizer differs from that from executor
*/
// 在某些条件下对 nbatch 和 nbuckets 进行调整,以避免在使用哈希连接操作时产生磁盘溢出
if (node->plan.operatorMaxMem > 0 && nbatch > 1 && nbuckets < INT_MAX / nbatch) {
if (nbuckets * nbatch < (int)(MaxAllocSize / sizeof(HashJoinTuple))) {
nbuckets *= nbatch;
nbatch = 1;
}
}
#ifdef HJDEBUG
printf("nbatch = %d, nbuckets = %d\n", nbatch, nbuckets);
#endif
/* nbuckets must be a power of 2 */
log2_nbuckets = my_log2(nbuckets);
Assert(nbuckets == (1 << log2_nbuckets));
/*
* 初始化哈希表控制块。
*
* 哈希表控制块只是从执行器的每个查询内存上下文中进行 palloc 分配的。
*/
// 分配一个大小为 HashJoinTableData 结构的内存块,并将其转换为 HashJoinTable 类型
hashtable = (HashJoinTable)palloc(sizeof(HashJoinTableData));
// 设置哈希桶的数量
hashtable->nbuckets = nbuckets;
// 设置哈希桶数量的对数
hashtable->log2_nbuckets = log2_nbuckets;
// 指向哈希桶的数组,初始为空
hashtable->buckets = NULL;
// 是否保留空值的标志
hashtable->keepNulls = keepNulls;
// 是否启用哈希偏斜优化,初始为 false
hashtable->skewEnabled = false;
// 指向哈希偏斜桶的数组,初始为空
hashtable->skewBucket = NULL;
// 哈希偏斜桶的长度,初始为 0
hashtable->skewBucketLen = 0;
// 哈希偏斜桶的数量,初始为 0
hashtable->nSkewBuckets = 0;
// 哈希偏斜桶的编号数组,初始为空
hashtable->skewBucketNums = NULL;
// 哈希表的批次数,即分区的数量
hashtable->nbatch = nbatch;
// 当前正在处理的批次号,初始为 0
hashtable->curbatch = 0;
// 原始批次数,用于记录哈希表创建时的批次数
hashtable->nbatch_original = nbatch;
// 从外部批次开始的批次号,用于记录外部哈希表的起始批次号
hashtable->nbatch_outstart = nbatch;
// 是否允许哈希表扩展,初始为 true
hashtable->growEnabled = true;
// 哈希表中的总元组数,初始为 0
hashtable->totalTuples = 0;
// 内部批次文件,初始为空
hashtable->innerBatchFile = NULL;
// 外部批次文件数组,初始为空
hashtable->outerBatchFile = NULL;
// 当前哈希表的内存使用量,初始为 0
hashtable->spaceUsed = 0;
// 哈希表的内存使用峰值,初始为 0
hashtable->spacePeak = 0;
// 溢写到磁盘的次数,初始为 0
hashtable->spill_count = 0;
// 哈希表允许的最大内存空间,单位为字节
hashtable->spaceAllowed = local_work_mem * 1024L;
// 哈希表在哈希偏斜优化情况下的内存使用量,初始为 0
hashtable->spaceUsedSkew = 0;
// 哈希表在哈希偏斜优化情况下允许使用的内存空间,基于哈希表允许的内存空间
hashtable->spaceAllowedSkew = hashtable->spaceAllowed * SKEW_WORK_MEM_PERCENT / 100;
// 存储哈希表数据的块信息,初始为空
hashtable->chunks = NULL;
// 哈希表的列宽度,初始为 0
hashtable->width[0] = hashtable->width[1] = 0;
// 是否由系统资源引起的标志,初始为 false
hashtable->causedBySysRes = false;
// 是否在查询内存模式下允许自动内存扩展的标志,初始为 false
hashtable->maxMem = max_mem * 1024L;
// 自动内存扩展的次数,初始为 0
hashtable->spreadNum = 0;
/*
* 获取每个哈希键要使用的哈希函数的信息,并记住连接操作是否严格。
*/
nkeys = list_length(hashOperators); // 获取哈希键的数量
hashtable->outer_hashfunctions = (FmgrInfo*)palloc(nkeys * sizeof(FmgrInfo)); // 为外部哈希函数分配内存
hashtable->inner_hashfunctions = (FmgrInfo*)palloc(nkeys * sizeof(FmgrInfo)); // 为内部哈希函数分配内存
hashtable->hashStrict = (bool*)palloc(nkeys * sizeof(bool)); // 为哈希连接操作的严格性分配内存
i = 0; // 初始化计数器 i
foreach (ho, hashOperators) { // 遍历哈希操作符列表
Oid hashop = lfirst_oid(ho); // 获取当前哈希操作符的 OID
Oid left_hashfn; // 用于存储左侧哈希函数的 OID
Oid right_hashfn; // 用于存储右侧哈希函数的 OID
// 获取哈希操作符对应的左侧和右侧哈希函数的 OID
if (!get_op_hash_functions(hashop, &left_hashfn, &right_hashfn))
ereport(ERROR,
(errcode(ERRCODE_UNDEFINED_FUNCTION),
errmodule(MOD_EXECUTOR),
errmsg("could not find hash function for hash operator %u", hashop)));
// 根据左侧和右侧哈希函数的 OID 获取对应的函数信息并存储到哈希表中
fmgr_info(left_hashfn, &hashtable->outer_hashfunctions[i]);
fmgr_info(right_hashfn, &hashtable->inner_hashfunctions[i]);
// 获取哈希操作符的严格性,存储到哈希表中
hashtable->hashStrict[i] = op_strict(hashop);
i++; // 增加计数器
}
/*
* Create temporary memory contexts in which to keep the hashtable working
* storage. See notes in executor/hashjoin.h.
*/
// 为哈希表和哈希批处理创建内存上下文
hashtable->hashCxt = AllocSetContextCreate(CurrentMemoryContext,
"HashTableContext",
ALLOCSET_DEFAULT_MINSIZE, // 初始内存分配大小
ALLOCSET_DEFAULT_INITSIZE, // 初始上下文大小
ALLOCSET_DEFAULT_MAXSIZE, // 最大上下文大小
STANDARD_CONTEXT, // 上下文标志
local_work_mem * 1024L); // 本地工作内存大小
// 基于哈希表的上下文创建用于哈希批处理的内存上下文
hashtable->batchCxt = AllocSetContextCreate(hashtable->hashCxt,
"HashBatchContext",
ALLOCSET_DEFAULT_MINSIZE, // 初始内存分配大小
ALLOCSET_DEFAULT_INITSIZE, // 初始上下文大小
ALLOCSET_DEFAULT_MAXSIZE, // 最大上下文大小
STANDARD_CONTEXT, // 上下文标志
local_work_mem * 1024L); // 本地工作内存大小
/* Allocate data that will live for the life of the hashjoin */
oldcxt = MemoryContextSwitchTo(hashtable->hashCxt);
if (nbatch > 1) {
/*
* allocate and initialize the file arrays in hashCxt
*/
hashtable->innerBatchFile = (BufFile**)palloc0(nbatch * sizeof(BufFile*));
hashtable->outerBatchFile = (BufFile**)palloc0(nbatch * sizeof(BufFile*));
/* The files will not be opened until needed... */
/* ... but make sure we have temp tablespaces established for them */
PrepareTempTablespaces();
}
/*
* Prepare context for the first-scan space allocations; allocate the
* hashbucket array therein, and set each bucket "empty".
*/
MemoryContextSwitchTo(hashtable->batchCxt);
hashtable->buckets = (HashJoinTuple*)palloc0(nbuckets * sizeof(HashJoinTuple));
/*
* Set up for skew optimization, if possible and there's a need for more
* than one batch. (In a one-batch join, there's no point in it.)
*/
if (nbatch > 1)
ExecHashBuildSkewHash(hashtable, node, num_skew_mcvs);
MemoryContextSwitchTo(oldcxt);
return hashtable;
}
调试信息如下:

调试信息
以下为 ExecHashJoin 函数的一些相关调试信息:
lefttree:表示哈希连接操作的左侧输入关系,通常是外部关系。
righttree:表示哈希连接操作的右侧输入关系,通常是内部关系。
再次执行 ExecHashJoin 函数可以发现,node 发生了部分变化,是因为哈希连接操作通常分为多个阶段,每个阶段需要处理不同的元组和执行不同的操作。
ExecEndHashJoin函数
ExecEndHashJoin 函数用于结束哈希连接节点的执行,对于执行哈希连接操作所分配的内存和资源进行释放和清理。函数逐步执行注释中所描述的步骤,首先释放哈希表,然后释放表达式上下文,接着清空各个元组槽,最后清理外部和内部分支的节点。这样可以确保在哈希连接节点的执行结束后,相关的资源被妥善地释放和清理,避免内存泄漏和资源浪费。函数源码如下:(路径:src/gausskernel/runtime/executor/nodeHashjoin.cpp)
/* ----------------------------------------------------------------
* ExecEndHashJoin
*
* clean up routine for HashJoin node
* ----------------------------------------------------------------
*/
void ExecEndHashJoin(HashJoinState* node) {
/*
* 释放哈希表
*/
if (node->hj_HashTable) {
ExecHashTableDestroy(node->hj_HashTable);
node->hj_HashTable = NULL;
}
/*
* 释放表达式上下文
*/
ExecFreeExprContext(&node->js.ps);
/*
* 清空元组表
*/
(void)ExecClearTuple(node->js.ps.ps_ResultTupleSlot); // 清空结果元组槽
(void)ExecClearTuple(node->hj_OuterTupleSlot); // 清空外部分支元组槽
(void)ExecClearTuple(node->hj_HashTupleSlot); // 清空哈希分支元组槽
/*
* 清理子树节点
*/
ExecEndNode(outerPlanState(node)); // 清理外部分支节点
ExecEndNode(innerPlanState(node)); // 清理内部分支节点
}
ExecReScanHashJoin函数
ExecReScanHashJoin 函数是用于重新扫描哈希连接节点的执行,当哈希连接节点需要重新扫描时,该函数会根据情况执行相应的操作。
首先,它会检查是否已经进行过递归重置,如果是,则重新扫描右子树和左子树。否则,它会根据哈希表是否存在以及其他条件,来决定是重用现有哈希表还是需要销毁并重建哈希表。
随后,函数会重置哈希连接节点的一些内部状态,确保下次执行正常。
最后,它会调用子节点的重新扫描函数,进行递归操作。这样,哈希连接节点就可以在需要重新扫描时,按照规定的步骤进行操作,保证正确的执行和结果。
void ExecReScanHashJoin(HashJoinState* node) {
/* 如果已经重置过,只需要重新扫描右子树和左子树 */
if (node->js.ps.recursive_reset && node->js.ps.state->es_recursive_next_iteration) {
if (node->js.ps.righttree->chgParam == NULL)
ExecReScan(node->js.ps.righttree);
if (node->js.ps.lefttree->chgParam == NULL)
ExecReScan(node->js.ps.lefttree);
node->js.ps.recursive_reset = false;
return;
}
/*
* 在多批次连接中,目前需要以较复杂的方式进行重新扫描,主要因为批次临时文件可能已被释放。
* 但是如果是单批次连接,并且内部子节点没有参数更改,那么我们可以重用现有的哈希表而不重新构建它。
*/
if (node->hj_HashTable != NULL) {
if (!node->js.ps.plan->ispwj && node->hj_HashTable->nbatch == 1 && node->js.ps.righttree->chgParam == NULL &&
!node->hj_rebuildHashtable && node->js.jointype != JOIN_RIGHT_SEMI &&
node->js.jointype != JOIN_RIGHT_ANTI) {
/*
* 可以重用哈希表;也不需要重新扫描内部。
*
* 但是,如果是右连接/全连接,最好重置表中包含的内部元组匹配标志。
*/
if (HJ_FILL_INNER(node))
ExecHashTableResetMatchFlags(node->hj_HashTable);
/*
* 同样,我们需要重置外部关系是否为空的状态,这样外部的新扫描会正确更新它,如果这次外部关系是空的话。
* (现在清除它是没有问题的,因为ExecHashJoin在这次不需要这个信息。对于其他情况,哈希表不存在
* 或者我们正在销毁它,我们会保留这个状态,因为ExecHashJoin在第一次执行时会需要它。)
*/
node->hj_OuterNotEmpty = false;
/* ExecHashJoin可以跳过构建哈希表的步骤 */
node->hj_JoinState = HJ_NEED_NEW_OUTER;
} else {
/* 必须销毁并重建哈希表 */
ExecHashTableDestroy(node->hj_HashTable);
node->hj_HashTable = NULL;
node->hj_JoinState = HJ_BUILD_HASHTABLE;
/*
* 如果子节点的chgParam不为空,则计划将由第一个ExecProcNode重新扫描。
*/
// 切换到右子树的下一个分区
if (node->js.ps.righttree->chgParam == NULL)
ExecReScan(node->js.ps.righttree);
}
} else {
if (node->js.ps.plan->ispwj) {
// 不需要销毁哈希表,只需要构建它。
node->hj_HashTable = NULL;
node->hj_JoinState = HJ_BUILD_HASHTABLE;
// 切换到右子树的下一个分区
if (node->js.ps.righttree->chgParam == NULL) {
ExecReScan(node->js.ps.righttree);
}
}
}
/* 总是重置元组内状态 */
node->hj_CurHashValue = 0;
node->hj_CurBucketNo = 0;
node->hj_CurSkewBucketNo = INVALID_SKEW_BUCKET_NO;
node->hj_CurTuple = NULL;
node->js.ps.ps_TupFromTlist = false;
node->hj_MatchedOuter = false;
node->hj_FirstOuterTupleSlot = NULL;
/*
* 如果子节点的chgParam不为空,则计划将由第一个ExecProcNode重新扫描。
*/
if (node->js.ps.lefttree->chgParam == NULL)
ExecReScan(node->js.ps.lefttree);
}
总结
哈希连接(Hash Join)是一种常见的关系型数据库查询算法,用于合并两个表的数据,其中一个表作为构建哈希表的输入,另一个表的记录则与哈希表进行匹配。以下是哈希连接算子的完整操作流程和涉及的主要函数调用关系:
- 初始化阶段:
- ExecInitHashJoin: 初始化哈希连接节点,分配并初始化数据结构。
- ExecInitNode: 初始化连接算子节点和子节点,为执行做准备。
- 构建哈希表:
- ExecHashJoin: 在首次执行时,为连接的构建阶段。首先从内部子树(例如右侧表)逐个获取记录,计算哈希值,并将其插入哈希表的对应桶中。
- ExecHashTableCreate: 创建哈希表数据结构,分配内存并初始化哈希表参数。
- ExecHashGetHashValue: 计算哈希值。
- 执行哈希连接:
- ExecHashJoin: 在每个执行周期中,从外部子树(例如左侧表)逐个获取记录,计算哈希值,并在哈希表中查找匹配的记录。
- ExecScanHashBucket: 扫描哈希表中的特定桶,寻找与当前外部记录匹配的内部记录。
- ExecHashTableGetTuple: 从哈希表中获取匹配的内部记录。
- 处理匹配和非匹配情况:
- 如果找到匹配的内部记录,哈希连接将创建一个结果记录,包含左右两个表的数据,并输出到结果集。
- 如果没有找到匹配的内部记录,根据连接类型的不同,可能会执行额外的操作,如生成外连接的 NULL 值,或准备进行非匹配的处理。
- 重复执行:
- 如果存在可重用的哈希表且不需要重新构建,则在重新扫描时重复使用哈希表,以加速查询。
- ExecReScanHashJoin: 用于重复执行哈希连接,可能会重用哈希表或重新构建哈希表。
- 结束和资源释放:
- ExecEndHashJoin: 结束哈希连接节点的执行,释放相关的资源,包括哈希表和表槽等。
- ExecEndNode: 结束连接算子节点和子节点的执行,释放相关资源。
hash join 算子的核心思想是通过哈希表将两个表的数据进行分组和关联,以加速连接操作。函数之间的调用关系确保了哈希表的正确构建、匹配和处理。这个算法对于大规模数据连接操作能够提供高效的性能。