目录
一、什么是MyBatis
二、MyBatis框架的搭建
1、搭建MyBatis框架
2、设置MyBaits项目的配置
三、使用MyBatis完成数据库的操作
1、MyBatis程序中sql语句的即时执行和预编译
1.1、即时执行(${})
1.2、预编译(#{})
1.3、即时执行和预编译的优缺点
2、传统的MyBatis程序的写法(XML方式)
2.1、查询表中所有的成员信息
2.2、根据某个字段来查询表中单个成员信息
2.3、根据字段删除表中信息
2.4、根据字段名修改表中的信息
2.5、添加操作
2.6、特殊的添加:返回自增id
2.7、like查询
2.8、实体类中的属性和数据库表中的字段名不一致出现的问题的三种解决方式
3、使用注解的方式在MyBatis程序中构造SQL语句
3.1、多表联查(一对一)
3.2、多表联查(一对多)
4、安装MyBatis X插件
四、动态SQL的使用
1、<if>标签
2、<trim>标签
3、<where>标签
4、<set>标签
5、<foreach>标签
一、什么是MyBatis
MyBatis是一款持久层框架,它支持自定义SQL,存储过程以及高级映射,MyBatis可以通过简单的XML或注解来配置和映射原始类型和接口为数据库中的记录。简单来说MyBatis是更简单完成程序和数据库交互的工具,也就是更简单的操作和读取数据库工具。MyBaits的底层是基于JDBC实现的。
二、MyBatis框架的搭建
MyBaits在程序和数据库之间是起到一个桥梁的作用。
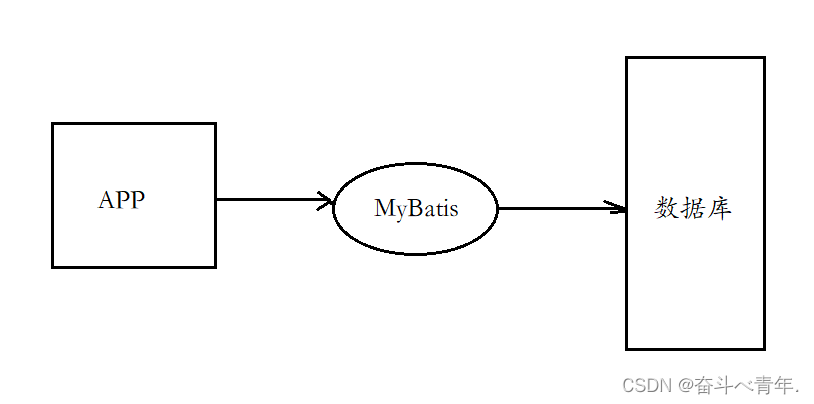
1、搭建MyBatis框架
MyBatis项目是基于Spring Boot项目的,所以我们只需要添加一个MyBatios框架即可。创建Spring Boot项目在之前的博客中有,这里就直接展示添加MyBatis框架即可。

这里需要注意的是,由于我们创建好MyBatis项目之后,并没有设置MyBatis连接MySql数据库详细信息,所以新创建的项目,点击运行之后会报错。
2、设置MyBaits项目的配置
1️⃣设置数据库的连接地址和XML文件的保存格式和位置
#设置数据库的相关连接信息
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/mycnblog?characterEncoding=utf8
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=123456
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
#设置MyBatis xml 存放路径和命名格式
mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:mybatis/*Mapper.xml
#配置MyBatis 执行是打印SQL(可选配置)
mybatis.configuration.log-impl=org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
#设置某个文件中日志的级别,应为StdOutImpl类中的日志级别为debug,而项目默认为info,所以设置我们自己的类中打印的日志为debug级别
logging.level.com.example.demo=debug三、使用MyBatis完成数据库的操作
1、MyBatis程序中sql语句的即时执行和预编译
我们在JDBC中在构造sql语句的时候,常常给字段的值用问号(?)代替,最后在使用方法对这些问好进行赋值,这是预编译。使用预编译的好处可以防止sql注入。当然还有一种sql的执行方式就是即时执行。下面我们来了解一下MyBatis程序中的即使执行和预编译的构建方式
1.1、即时执行(${})
就像下面我们写道的根据某个字段查询单个信息的时候,我们传递了参数,在xml文件中对相应的字段进行赋值的时候使用${}这种方式就是构造sql语句即时执行的方式。
<select id="getUserById" resultType="com.example.demo.model.Userinfo">
select * from userinfo where id=${id}
</select>
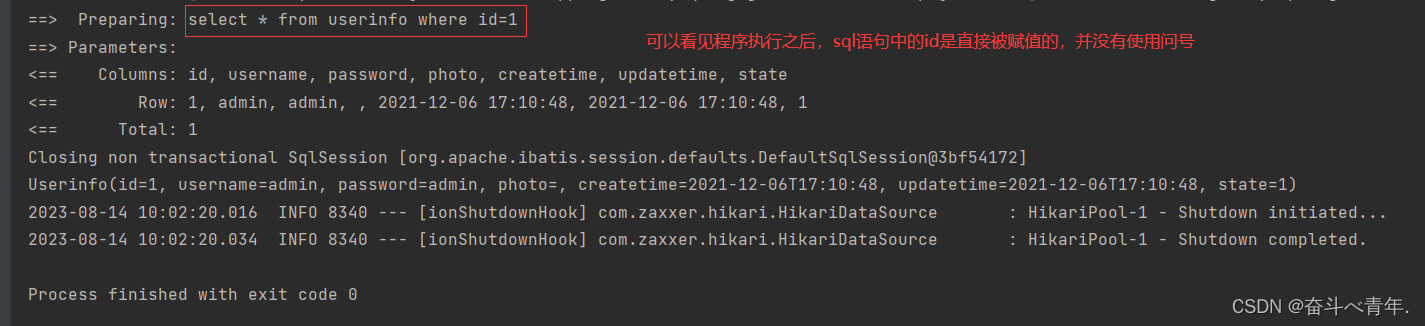
1.2、预编译(#{})
这种写法在程序执行的时候,我们可以看到sql语句中id的值先是被?将位置占着的。这里?表示的是只能是值,而不能是sql语句,这就防止了sql注入。
<select id="getUserById" resultType="com.example.demo.model.Userinfo">
select * from userinfo where id=#{id}
</select>
1.3、即时执行和预编译的优缺点
🍂预编译(#{})
1️⃣优点
- 它的执行是安全的,可以防止sql注入。预编译他会将传入的值当成value来看待,判断这个value是否和数据库中这个字段中的值是否相等,相等就会执行成功,不相等会查找不到。
- 在使用#{}这种写法的时候,如果我们传递的参数是字符串类型的,我们不需要使用单引号(' ')将#{}括起来,执行的时候,他会自动给value添加单引号。
2️⃣缺点
- 不能传递SQL命令,当传递SQL命令的时候他会给这个命令自动添加单引号(' '),但是给SQL命令添加单引号SQL语句就会报错。
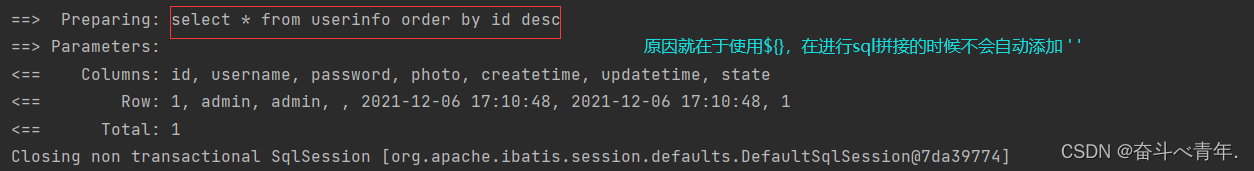
//UserMapper.java类 /* * 传递排序规则 * */ List<Userinfo> getAllByOrder(@Param("myorder")String myorder); //UserMapper.xml文件 <select id="getAllByOrder" resultType="com.example.demo.model.Userinfo"> select * from userinfo order by id #{myorder} </select> //测试类 class UserMapperTest { @Test void getAllByOrder() { List<Userinfo> list = userMapper.getAllByOrder("desc"); System.out.println(list); } }
当时当我们将#{}换成${},再次运行就会执行成功。
select * from userinfo order by id ${myorder}
🍂即时执行(${})
1️⃣优点
- 当我们逛淘宝的时候,筛选商品点击价格按照从低到高,这个时候传递的就是SQL命令。从低到高传递的就是asc,从高到低传递的就是desc。
2️⃣缺点
- 它的执行不安全的,存在sql注入。
- 在使用${}时,如果传入的参数是字符串类型的数据,还需要再构造sql的语句的时候使用单引号将传入的参数引住('${}')。
🍂SQL注入
使用一些特殊的sql语句来完成一些非法的操作。
可以看到数据库中用户表的用户名和密码都是admin。
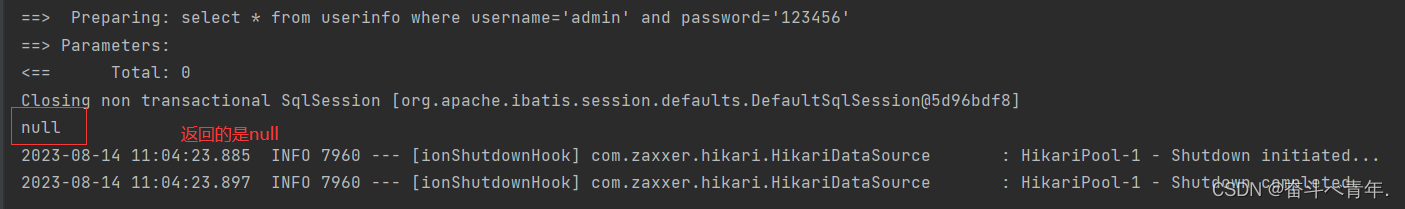
- 正常情况下,我们使用不正确的密码是登录不成功的。
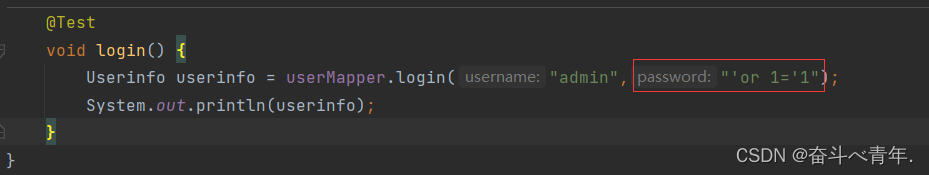
/* * 用户登录的场景 * */ Userinfo login(@Param("username")String username,@Param("password")String password); }<select id="login" resultType="com.example.demo.model.Userinfo"> select * from userinfo where username='${username}' and password='${password}' </select>
- 但是非法的情况下,我们给password的属性填写一个sql语句,就可以成功登录。
这就是最简单的SQL注入。
✨总结
- 当业务需要传递SQL命令是,只能使用${},不能使用#{}。
- 如果要使用${},那么传递的参数一定要是能被穷举的,否则不能使用。
- 能使用#{}的时候就不使用${}.
2、传统的MyBatis程序的写法(XML方式)
2.1、查询表中所有的成员信息
这里需要我们创建两个文件
1️⃣创建一个接口,来声明方法供给Service层调用这些方法。
2️⃣创建一个XML文件,实现接口中的方法
我们想要在demol包中创建一个UserInfo类,这个类中的属性要和数据库中表的字段名相对应。这里我们用来演示的用户表。
1️⃣在创建MyBatis项目中的类之前,我们先来创建数据库中的表信息。
- 创建数据库
drop database if exists mycnblog;
create database mycnblog DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8mb4;
-- 使用数据数据
use mycnblog;
-- 创建表[用户表]
drop table if exists userinfo;
create table userinfo(
id int primary key auto_increment,
username varchar(100) not null,
password varchar(32) not null,
photo varchar(500) default '',
createtime timestamp default current_timestamp,
updatetime timestamp default current_timestamp,
`state` int default 1
) default charset 'utf8mb4';
-- 创建文章表
drop table if exists articleinfo;
create table articleinfo(
id int primary key auto_increment,
title varchar(100) not null,
content text not null,
createtime timestamp default current_timestamp,
updatetime timestamp default current_timestamp,
uid int not null,
rcount int not null default 1,
`state` int default 1
)default charset 'utf8mb4';
-- 创建视频表
drop table if exists videoinfo;
create table videoinfo(
vid int primary key,
`title` varchar(250),
`url` varchar(1000),
createtime timestamp default current_timestamp,
updatetime timestamp default current_timestamp,
uid int
)default charset 'utf8mb4';2️⃣UserInfo类
package com.example.demo.model;
import lombok.Data;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
@Data
public class Userinfo {
private int id;
private String username;
private String password;
private String photo;
private LocalDateTime createtime;
private LocalDateTime updatetime;
private int state;
}3️⃣UserMapper接口
在Mapper包当中创建一个UserMapper接口,用来声明方法。这里Mapper包就相当于之前项目中创建的dao包。这里我们实现的方法是查询表中所有的数据。在MyBaits项目中数据持久层不在使用五大类注解,而是使用@Mapper注解。
package com.example.demo.mapper;
import com.example.demo.model.Userinfo;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
import java.util.List;
@Mapper//这是数据持久层的标志
public interface UserMapper {
List<Userinfo> getAll();
}
4️⃣UserMapper.xml文件
用来实现接口中的方法,这里两个文件的关联并不是使用文件名,而是使用XML文件的配置。
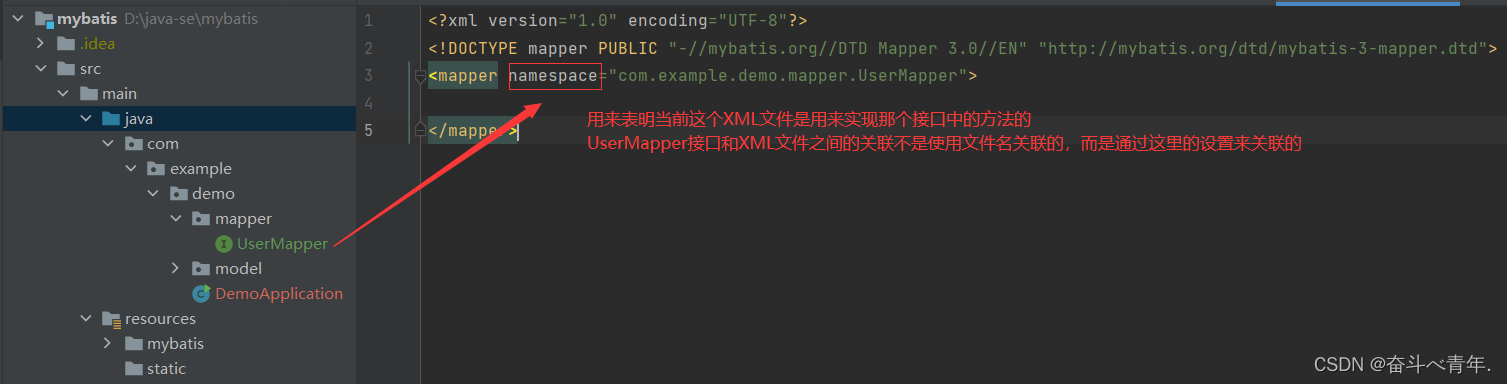
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.example.demo.mapper.UserMapper">
<select id="getAll" resultType="com.example.demo.model.Userinfo">
select * from userinfo
</select>
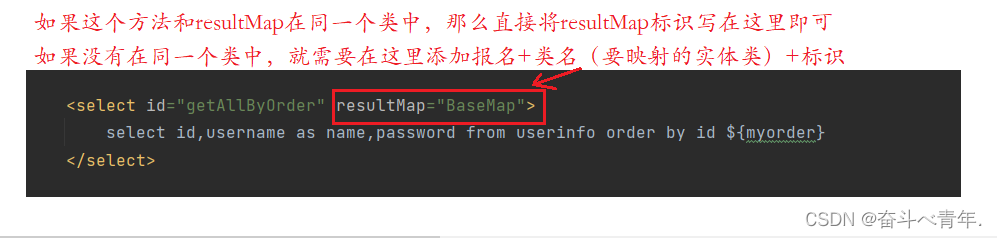
</mapper>这里在XML文件中实现查询语句的时候,需要设置方法的名称和UserMapper中声明的方法名称相同,在XML文件设置方法名称需要使用id属性。还需要设置返回值类型。可以使用resultType属性或者resultMap属性来设置。
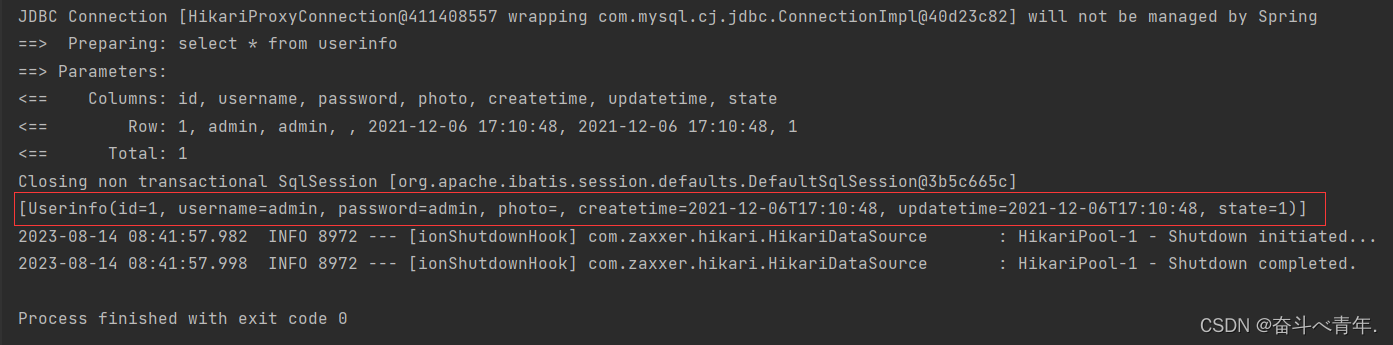
5️⃣这里我们创建一个测试类,来检测我们的所写的代码的执行结果
@SpringBootTest//不能省略,告诉当前的测试程序,目前项目是运行在Spring容器中的
class UserMapperTest {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Test
void getAll() {
List<Userinfo> list = userMapper.getAll();
System.out.println(list);
}
}
上述构建查询方法的步骤,在进行数据库增删改查的操作时,大体步骤都是相同的,只是在细节上有差异。 当然这种写法是传统的写法,后序我们还会说道使用注解的方式来构造sql语句。
2.2、根据某个字段来查询表中单个成员信息
这里根据字段查询单个信息和查询表中所有成员信息不同,查询单个信息需要给这个方法传递参数。
✨注意
- 这里需要注意的是我们在MyBatis代码的时候,创建的方法需要传递参数,那么参数的数据类型不能使用基础的数据类型,需要使用基础数据类型的包装类。这是因为使用包装类的时候。如果前端没有给你传递参数的时候,包装类是可以接收null值的,但是如果是基础数据类型,那么你的后端程序直接会报500(内部服务器错误)。但是这里的问题好像被MyBatis进行了修改,如果你传的参数是基础的数据类型,那么他在执行的时候会自动发生装包的操作,将基础数据类型转变为它的类类型。
- 还需要注意的是,如果MyBatis程序方法中传递的参数不是我们自己定义的类的对象,需要使用@Param注解,将@Param注解中的参数动态的传递给XML文件的代码中。这里@Param注解中的参数可以和我们方法的参数相同也可以不同,但是这里小编建议还是写成相同的,这样可以省去很多麻烦。
import java.util.List;
@Mapper//这是数据持久层的标志
public interface UserMapper {
/*
* 根据id查询一条信息
* */
Userinfo getUserById(@Param("id")Integer id);
}
<select id="getUserById" resultType="com.example.demo.model.Userinfo">
select * from userinfo where id=#{id}
</select>@SpringBootTest//不能省略,告诉当前的测试程序,目前项目是运行在Spring容器中的
class UserMapperTest {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Test
void getUserById() {
Userinfo userinfo = userMapper.getUserById(1);
System.out.println(userinfo.toString());
}
2.3、根据字段删除表中信息
删除信息,默认返回的是受影响的行数,所以我们在声明方法的时候设置的返回值类型为int.
/*
* 根据id删除成员
* */
int delById(@Param("id")Integer id); <delete id="delById">
delete from userinfo where id=#{id}
</delete> @Test
void delById() {
int id = 2;
int result = userMapper.delById(id);
System.out.println("受影响的行数:"+result);
}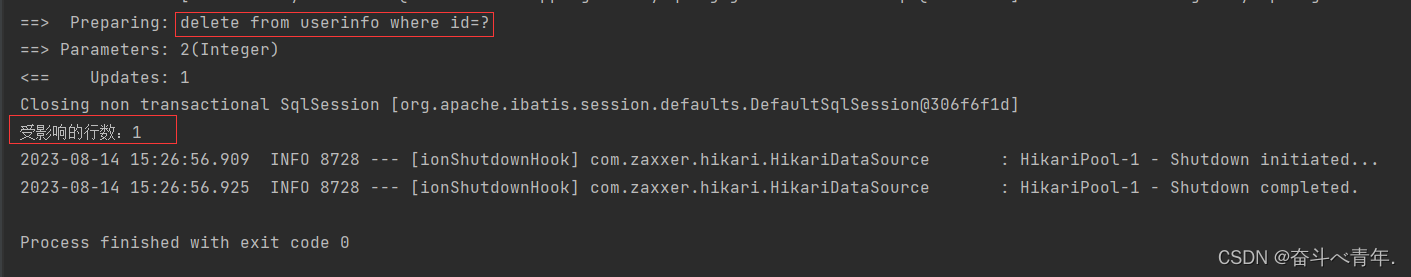 这里我们在测试类进行的删除操作会影响到数据库中的数据,为了不让我们的我们的测试代码修改数据库中的数据,我们可以在测试类的删除或者修改数据的方法上添加一个@Transactional注解,让程序执行完成之后实现数据回滚的操作。
这里我们在测试类进行的删除操作会影响到数据库中的数据,为了不让我们的我们的测试代码修改数据库中的数据,我们可以在测试类的删除或者修改数据的方法上添加一个@Transactional注解,让程序执行完成之后实现数据回滚的操作。
2.4、根据字段名修改表中的信息
修改的实现和删除一样在xml文件中的update标签中不用设置返回值类型(resultMap或者resultType),默认的返回值是受影响的行数,所以在UserMapper接口中声明方法的时候,返回值类型为int。
之前的方法中我们传递的都是属性,这个方法中我们传递一个自定义的类对象。
/*
* 根据id修改成员信息
* */
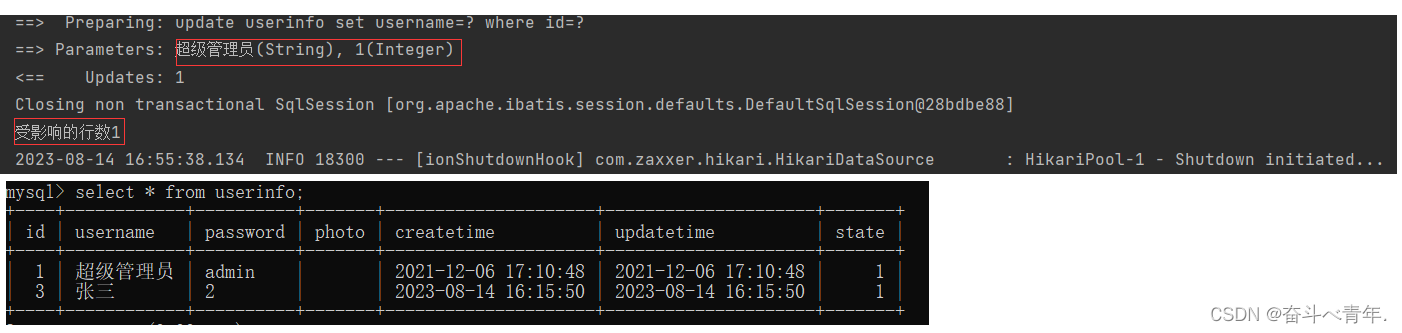
int update(Userinfo userinfo);虽然我们在传递参数的时候传递的是userinfo对象,但是在xml文件中实现修改的时候,不用写userinfo.属性名,还是和之前一样直接写属性即可。
<update id="update" >
update userinfo set username=#{username} where id=#{id}
</update> @Test
void update() {
Userinfo userinfo = new Userinfo();
userinfo.setId(1);
userinfo.setUsername("超级管理员");
int result = userMapper.update(userinfo);
System.out.println("受影响的行数"+result);
}
2.5、添加操作
添加操作和修改操作相同在接口中声明方法的时候,定义的返回值类型是int,因为默认的返回值是受影响的行数,在XML文件实现add方法时,也不需要规定返回值类型。
/*
* 添加操作
* */
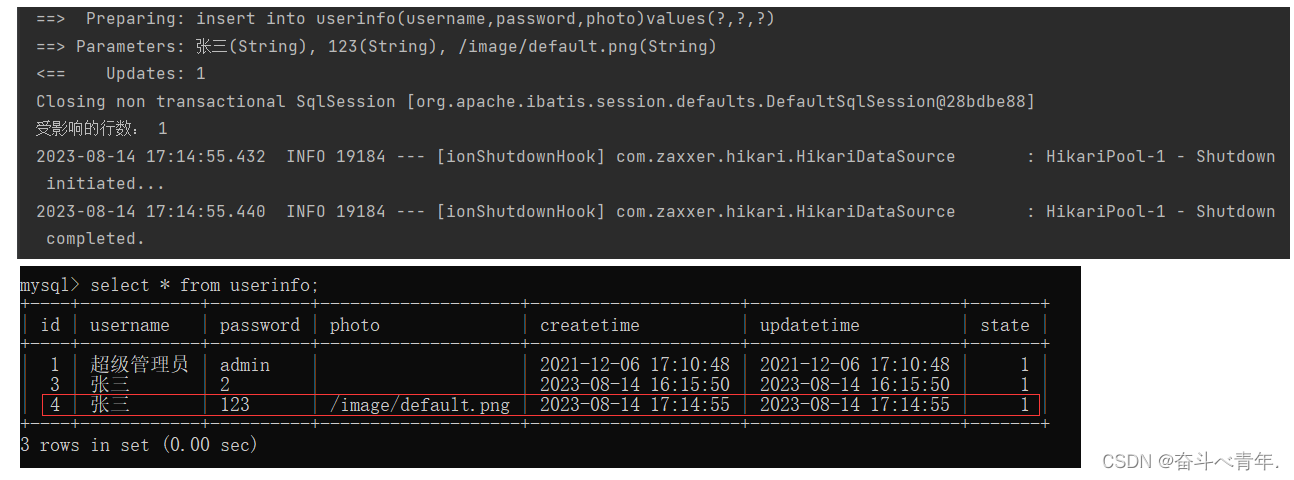
int add(Userinfo userinfo);这里我们只需要添加username、password和photo属性的值,其他的cteatetime和updatetime的值会根据当前时间自动添加。
<insert id="add">
insert into userinfo(username,password,photo)values(#{username},#{password},#{photo})
</insert> @Test
void add() {
Userinfo userinfo = new Userinfo();
userinfo.setUsername("张三");
userinfo.setPassword("123");
userinfo.setPhoto("/image/default.png");
int result = userMapper.add(userinfo);
System.out.println("受影响的行数: "+result);
}
2.6、特殊的添加:返回自增id
之前的方法默认情况下返回的是受影响的行数,如果想要返回自增id,具体实现如下。
这个方法的声明和之前的添加方法的声明是相同的,但是在XML文件中的具体实现有些差别。这里再声明方法的时候返回值类型是int,不要将它认为是自增id的数据类型,它还是受影响的行数的返回值类型。
/*
* 添加操作:返回自增id
* */
int insert(Userinfo userinfo);在XML文件中的insert标签中添加useGenerateKeys、keyColumn和keyProperty属性。
<insert id="insert" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyColumn="id" keyProperty="id">
insert into userinfo(username,password,photo)values(#{username},#{password},#{photo})
</insert>
- useGeneratedKeys:表示获取数据库中开启自增主键的值。在insert标签中表示的意思为获取本次添加的成员的自增主键的值。默认值为false.
- keyColumn:表示设置自增主键在数据表中的字段名。
- keyProperty:表示将获取到的自增主键的值赋值给keyProperty所指的属性(实体类).
通过XML文件中insert方法的实现,我们直接将自增主键的值设置到了userinfo(实体类)的id属性中了,所以在测试类中只需要在打印的时候打印userinfo对象的id属性值,就可以得到自增主键的值。
@Test
void insert() {
Userinfo userinfo = new Userinfo();
userinfo.setUsername("李四");
userinfo.setPassword("123");
userinfo.setPhoto("");
//因为在接口中声明的insert方法的参数为userinfo,所以测试的时候可以直接将userinfo对象传给这个insert方法
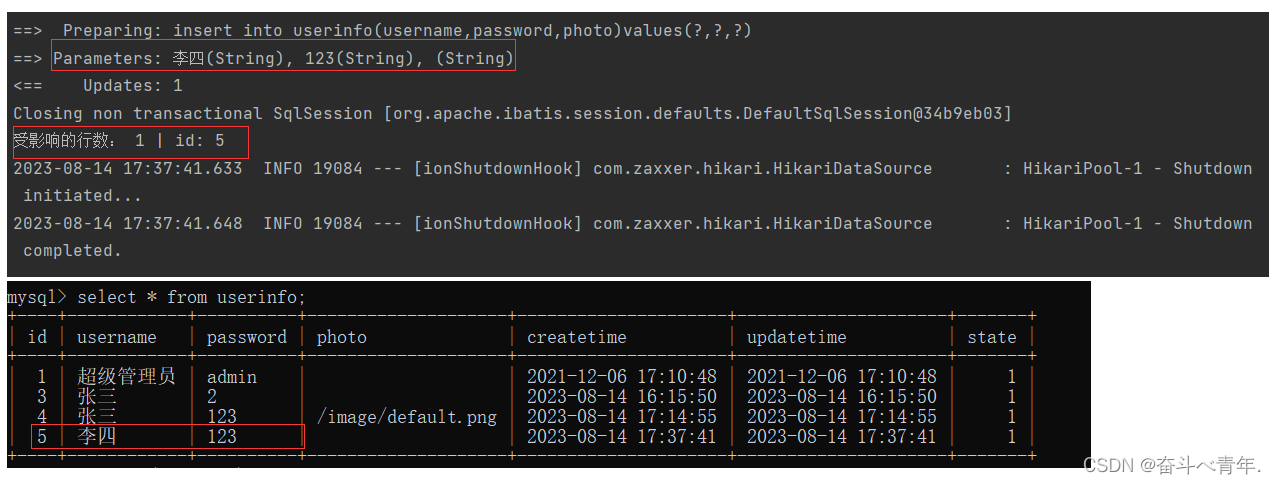
int result = userMapper.insert(userinfo);
System.out.println("受影响的行数: "+result+" | id: "+userinfo.getId());
}
2.7、like查询
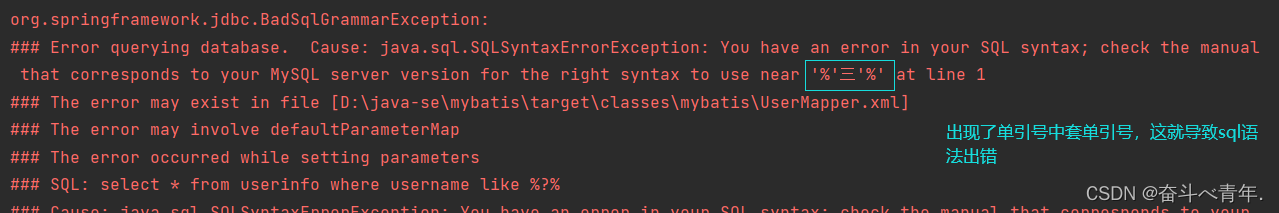
like查询,我们按照学习MySQL是使用的语法在XML文件中构造sql语句,在执行的时候会出现报错的问题。
/*
* like查询
* */
List<Userinfo> getLikeList(@Param("username")String username); <select id="getLikeList" resultType="com.example.demo.model.Userinfo">
select * from userinfo where username like %#{username}%
</select> @Test
void getLikeList() {
String username = "三";
List<Userinfo> list = userMapper.getLikeList(username);
System.out.println(list);
}
有的老铁就会说了,使用预编译的方式不行,那就使用即时执行的方式,这种方式执行确实结果是对的,但是这里使用即时执行的方式并不满足使用它的条件,会出现sql注入的情况。
✨两种解决方法
1️⃣第一种解决方法是在XML中继续直接使用#{username},我们在业务代码中给username赋值为%三%
select * from userinfo where username like #{username}@Test void getLikeList() { String username = "%三%"; List<Userinfo> list = userMapper.getLikeList(username); System.out.println(list); }
虽然这种方式可以解决问题,但是在业务代码中写,看起来就是不太好看。
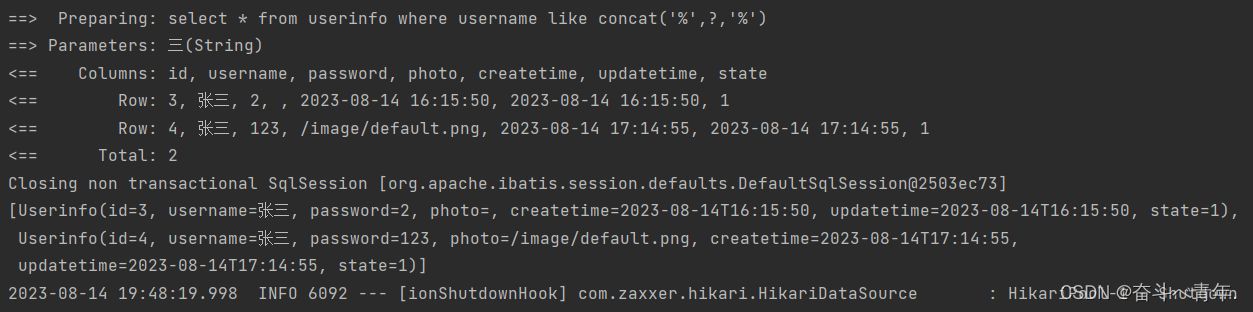
2️⃣第二种解决方法是使用SQL语法中的concat字段,对多个字符进行拼接。
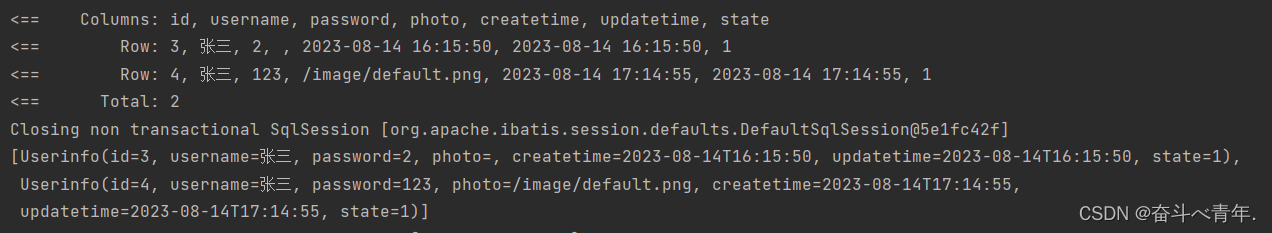
select * from userinfo where username like concat('%',#{username},'%')@Test void getLikeList() { String username = "三"; List<Userinfo> list = userMapper.getLikeList(username); System.out.println(list); }
这种写法既不会出现单引号套单引号的问题,在业务代码中进行like查询传参的时候,也没有出现使用多余的符号的问题。
2.8、实体类中的属性和数据库表中的字段名不一致出现的问题的三种解决方式
MyBatis是通过实体类的属性名称和数据库中的字段名进行映射的,如果实体类中的属性名和数据库表中的字段名不同,在进行查询的时候,出现的结果中字段的值会为null.
✨解决方案
- 将实体类中的属性名修改成和数据库表中的数据修改成一致的。这种方式只适合于当前这个实体类,只有你一个人使用了,如果其他人的代码中也使用了你创建的实体类,那么就不能使用这种方式来修改了。
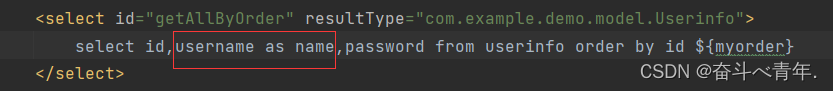
- 使用SQL语句中的as对数据表中的字段名进行重命名,让字段名等于创建的实体类的属性名。
- 定义一个resultMap,将属性名和字段名进行手动映射。
3、使用注解的方式在MyBatis程序中构造SQL语句
3.1、多表联查(一对一)
这里我们查询一篇文章对应的作者的名字,站在文章的角度进行多表联合查询就是一对一的情况。
使用注解的方式在MyBaits程序中构造SQL语句,我们想要使用SQL的查询,就可以在接口中的方法上加上注解@Select,想要使用删除,可以在接口的方法上添加@Delete,想要使用插入可以在方法上添加@Insert,想要实现修改可以在方法上添加@Update,然后将要执行的sql语句写在这些注解的参数中即可。
1️⃣创建文章实体类
import lombok.Data;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
@Data
public class ArticleInfo {
private int id;
private String title;
private String content;
private LocalDateTime createtime;
private LocalDateTime updatetime;
private int uid;
private int rcount;
private int state;
//链表字段
private String username;
}
2️⃣定义接口
package com.example.demo.mapper;
import com.example.demo.model.ArticleInfo;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select;
import java.util.List;
@Mapper
public interface ArticleMapper {
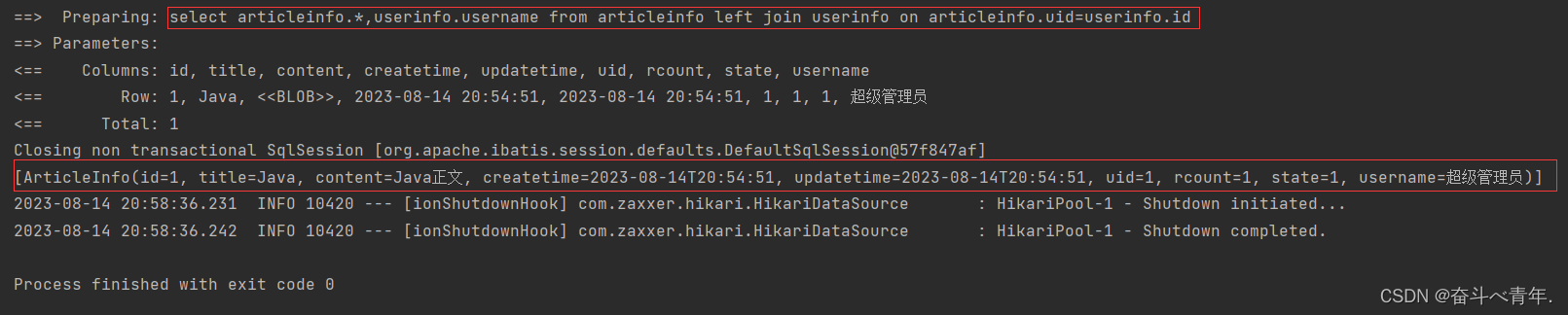
@Select("select articleinfo.*,userinfo.username from articleinfo left join userinfo on articleinfo.uid=userinfo.id")
List<ArticleInfo> getAll();
}
3️⃣创建单元测试
package com.example.demo.mapper;
import com.example.demo.model.ArticleInfo;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import java.util.List;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
@SpringBootTest
class ArticleMapperTest {
@Autowired
private ArticleMapper articleMapper;
@Test
void getAll() {
List<ArticleInfo> list = articleMapper.getAll();
System.out.println(list);
}
}4️⃣执行结果
3.2、多表联查(一对多)
一对多的多表查询,这里我们将查询步骤分为三步
- 根据id找到用户信息
- 根据uid查询文章列表
- 然后将得到的文章信息和用户信息进行组装即可
1️⃣首先我们需要在userinfo类(用户实体类)中添加一个alist属性,最后用来将得到文章信息组装到userinfo对象中。
package com.example.demo.model;
import lombok.Data;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.util.List;
@Data
public class Userinfo {
private int id;
private String username;
private String password;
private String photo;
private LocalDateTime createtime;
private LocalDateTime updatetime;
private int state;
private List<ArticleInfo> alist;
}2️⃣然后在数据持久层的UserMapper类和ArticleMapper类中添加查询的方法
- UserMapper接口中添加根据id查找用户的方法
@Select("select * from userinfo where id=#{id}")
Userinfo getUserById2(@Param("id")Integer id);- ArticleMapper接口中添加根据uid查找文章的方法
@Select("select * from articleinfo where uid=#{uid}")
List<ArticleInfo> getListByUid(@Param("uid")Integer uid);3️⃣在UserMapperTest单元测试类中创建一个getUserList方法,在这个方法中调用上述两个方法,最后调用setAlist方法,将getListByUid方法中得到的文章列表添加到userinfo对象中,就完成了多表查询的一对多的情况
package com.example.demo.mapper;
import com.example.demo.model.ArticleInfo;
import com.example.demo.model.Userinfo;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import java.util.List;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
@SpringBootTest//不能省略,告诉当前的测试程序,目前项目是运行在Spring容器中的
class UserMapperTest {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Autowired
private ArticleMapper articleMapper;
@Test
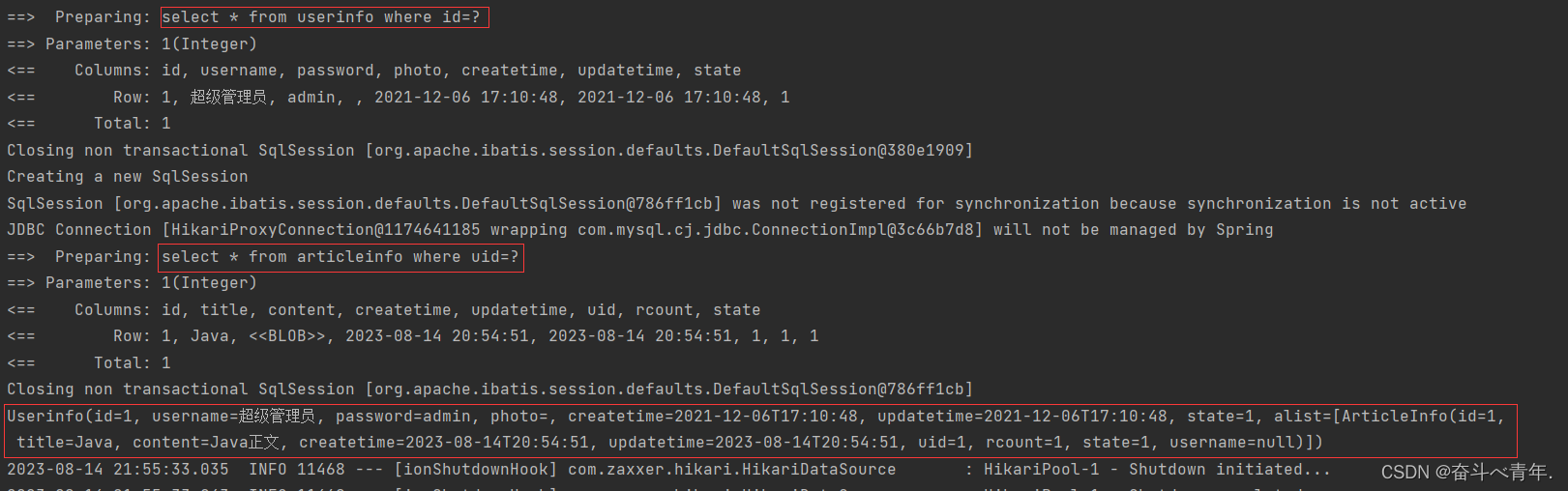
void getUserList(){
int uid = 1;
//1.根据uid查询userinfo
Userinfo userinfo = userMapper.getUserById2(uid);
//2.根据uid查询文章列表
List<ArticleInfo> list = articleMapper.getListByUid(uid);
//3.组装数据
userinfo.setAlist(list);
System.out.println(userinfo);
}
}4️⃣执行结果
4、安装MyBatis X插件
上述我们将在接口中声明的方法在xml文件中实现之后,当接口中只有几个方法的时候,我们想要找一个方法在XML文件中的具体实现,我们可以点到XML文件中找,但是如果存接口中存在很多的方法,想要找XML中对接口中的某个方法的具体实现,就需要我们一行一行的找,效率非常慢,这时候我们就需要安装MyBatis X插件,它可以方便开发MyBatis,实现XML和对应的接口(方法)之间的快速跳转。
四、动态SQL的使用
动态sql是MyBatis的强大特性之一,能够完成不同条件下不同的sql拼接。
1、<if>标签
我们在上网时,经常需要填写一些表单,其中有些选项是必填的,有些是选填的,那么这个时候在MyBatis程序中按照XML的方式构造sql语句时,是不能完全胜任的。比如填通讯信息的时候,出现了一个选填项是填写QQ号,如果不填这个选项,前端传给后端代码中的这个数据的值为null,现在规定让这一项在数据库中默认为空,如果如不使用<if>标签,那么在XML中是无法完成这个规定。在数据库中null和空是两个概念。
✨语法
<!-- test中的表达式是满足使用多个条件 -->
<if test="表达式">
<!-- 满足表达式的条件,就会进入执行其中的内容 -->
....
</if>1️⃣在接口中声明方法
/*
* 动态sql添加操作<if>
* */
int add2(Userinfo userinfo);2️⃣在XML文件中实现动态sql,这里再sql语句中添加<if>标签用来判断是否设置了photo的值,如果没有设置,那就不添加这个字段在sql语句中,如果添加这个字段的值,就会在sql语句中添加这个字段。
<insert id="add2">
insert into userinfo(username,password
<if test="photo != null">
,photo
</if>
)values(#{username},#{password}
<if test="photo != null">
,#{photo}
</if>
)
</insert>3️⃣测试单元
//给对象的属性设置值得时候,给photo属性添加值
@Test
void add2() {
Userinfo userinfo = new Userinfo();
userinfo.setUsername("张三");
userinfo.setPassword("123");
userinfo.setPhoto("cat.png");
int result = userMapper.add2(userinfo);
System.out.println("执行的结果: "+result);
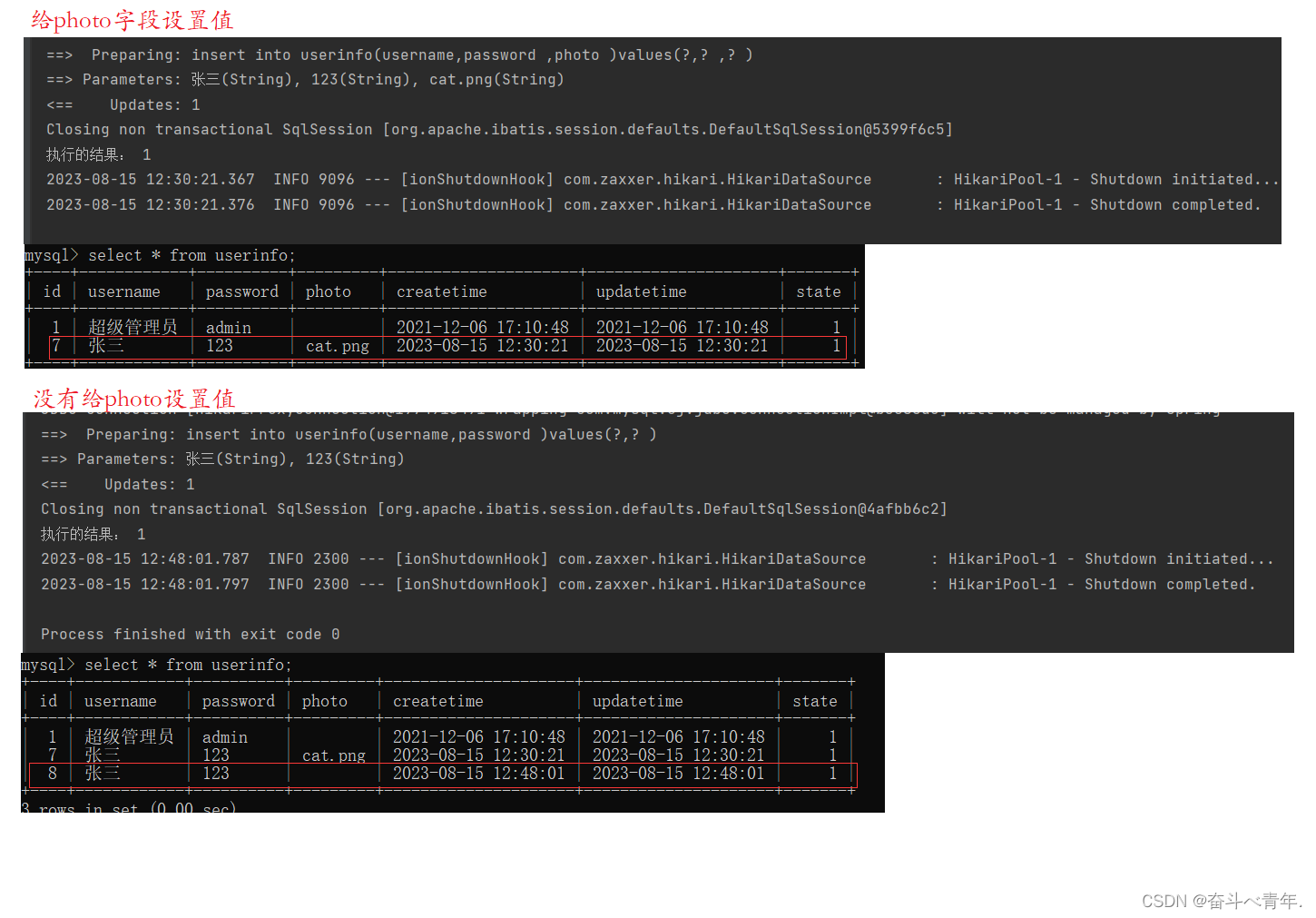
}4️⃣执行结果
可以看到如果给photo没有设置值,那么在数据看中photo这一列是空的,不会出现null.这就解决了表单中可选项的填写问题了。如果填了表单中的可选项就会将值保存在数据库中,如果没有填写可选项,那么数据库中这个字段就不会有值。
2、<trim>标签
上面我们说的表单中存在某个选填项,假设表单上所有的选项都是选填的,那么使用<if>标签就不能满足我们的需求了。因为在判断给字段是否传值时,使用<if>标签将字段包裹起来了,但是字段和字段之间要使用(,)逗号隔开,所以我们还需要将逗号拼接上。但是我们不知道用户选填了那些字段,所以将逗号拼接上之后,还需要考虑逗号不能出现在开始的字段前面,结束的字段后面不能出现逗号。这个就需要使用<trim>标签中的属性来解决了。
✨<trim>标签的属性
- prefix:表示整个语句块,以prefix的值作为前缀
- suffix:表示整个语句块,以suffix的值作为后缀
- prefixOverrides:表示整个语句块要去除掉的前缀
- suffixOverrides:表示整个语句块要去除掉的后缀
1️⃣在接口中声明方法
/*
* 动态sql <trim>标签
* */
int add3(Userinfo userinfo);2️⃣在XML文件中实现方法,由于<trim>标签中的prefix和suffix属性可以添加整个语句块的前缀和后缀,所以这里我们直接使用这两个属性拼接括号,我们在<if>标签中将逗号拼接在字段的后面,使用suffixOverrides属性指定要去除语句块中某个后缀(逗号),整个时候就会将语句块中最后一个字段之后的逗号去掉。
<insert id="add3">
insert into userinfo
<trim prefix="(" suffix=")" suffixOverrides=",">
<if test="username != null">
username,
</if>
<if test="password != null">
password,
</if>
<if test="photo!=null">
photo,
</if>
</trim>
values
<trim prefix="(" suffix=")" suffixOverrides=",">
<if test="username != null">
#{username},
</if>
<if test="password != null">
#{password},
</if>
<if test="photo != null">
#{photo}
</if>
</trim>
</insert>
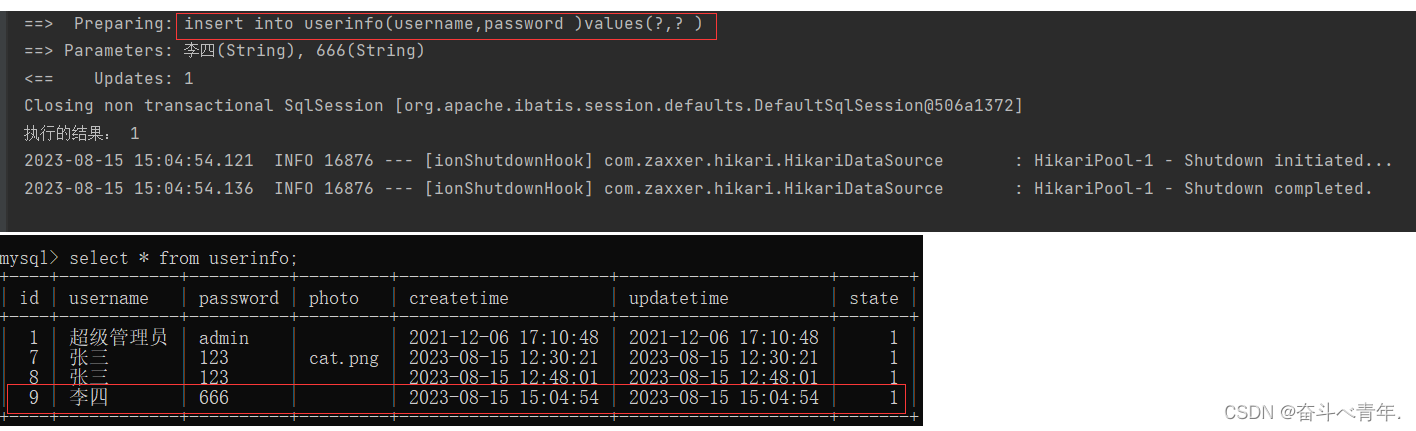
3️⃣单元测试,这里我们只添加名字和密码,不添加照片的属性。
@Test
void add3() {
Userinfo userinfo = new Userinfo();
userinfo.setUsername("李四");
userinfo.setPassword("666");
int result = userMapper.add2(userinfo);
System.out.println("执行的结果: "+result);
}4️⃣执行结果
可以看到执行结果中字段中没有将photo拼接上,并且语句块中结尾的字段之后也没有逗号。数据保存在数据库中,也是按照我们的预想执行的,没有添加照片字段的值,photo列为空,不是null.
3、<where>标签
当传入对象之后,<where>标签会判断对象中的属性来决定是否生成"where"关键字,如果对象中的属性都没有传值的情况下,就不会生成where关键字,如果是查询操作的话就会将表中所有的数据查出来。where标签还可以将字段前面拼接的"and"字段去掉。
1️⃣接口中声明方法
/*
* 动态sql <where>标签
* */
List<Userinfo> getListByWhere(Userinfo userinfo);2️⃣在XML文件中实现方法
<select id="getListByWhere" resultType="com.example.demo.model.Userinfo">
select * from userinfo
<where>
<if test="id>0">
id=#{id}
</if>
<if test="username!=null">
and username=#{username}
</if>
<if test="password!=null">
and password=#{password}
</if>
</where><where>标签可以实现的效果,<trim>标签也可以实现。
<select id="getListByWhere" resultType="com.example.demo.model.Userinfo">
select * from userinfo
<trim prefix="where" prefixOverrides="and">
<if test="id>0">
id=#{id}
</if>
<if test="username!=null">
and username=#{username}
</if>
<if test="password!=null">
and password=#{password}
</if>
</trim>
</select>
通过<trim>标签的prefix将where作为代码块的前缀,如果代码块中没有字段,则where不会加在sql语句中,prefixOverrides属性将整个语句块要去除掉的前缀(and)去除。
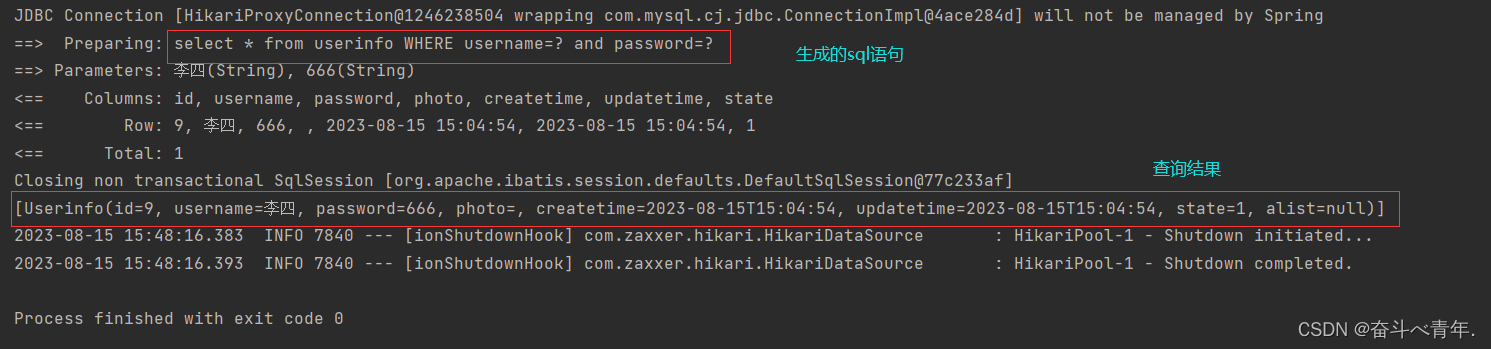
3️⃣单元测试,在这里没有传递id,那么程序执行的时候,where标签会将username字段之前的and去掉。
@Test
void getListByWhere() {
Userinfo userinfo = new Userinfo();
userinfo.setUsername("李四");
userinfo.setPassword("666");
List<Userinfo> list = userMapper.getListByWhere(userinfo);
System.out.println(list);
}
4️⃣执行结果
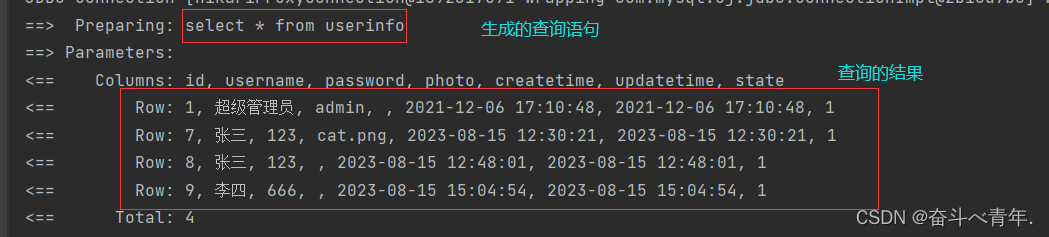
- 有属性值传入的时候
- 没有属性值传入的时候
4、<set>标签
<set>标签和<where>标签在sql语句中添加方式相同,只不过where标签用在查询,set标签用在修改。但是<set>标签是去掉代码块的后缀的,而<where>标签是去掉代码块的前缀的。
1️⃣接口中声明方法
/*
* 动态sql <set>标签
* */
int update2(Userinfo userinfo);2️⃣XML中实现方法
<update id="update2">
update userinfo
<set>
<if test="username!=null">
username=#{username},
</if>
<if test="password!=null">
password=#{password},
</if>
<if test="photo!=null">
photo=#{photo},
</if>
</set>
where id=#{id}
</update>3️⃣单元测试
@Test
void update2() {
Userinfo userinfo = new Userinfo();
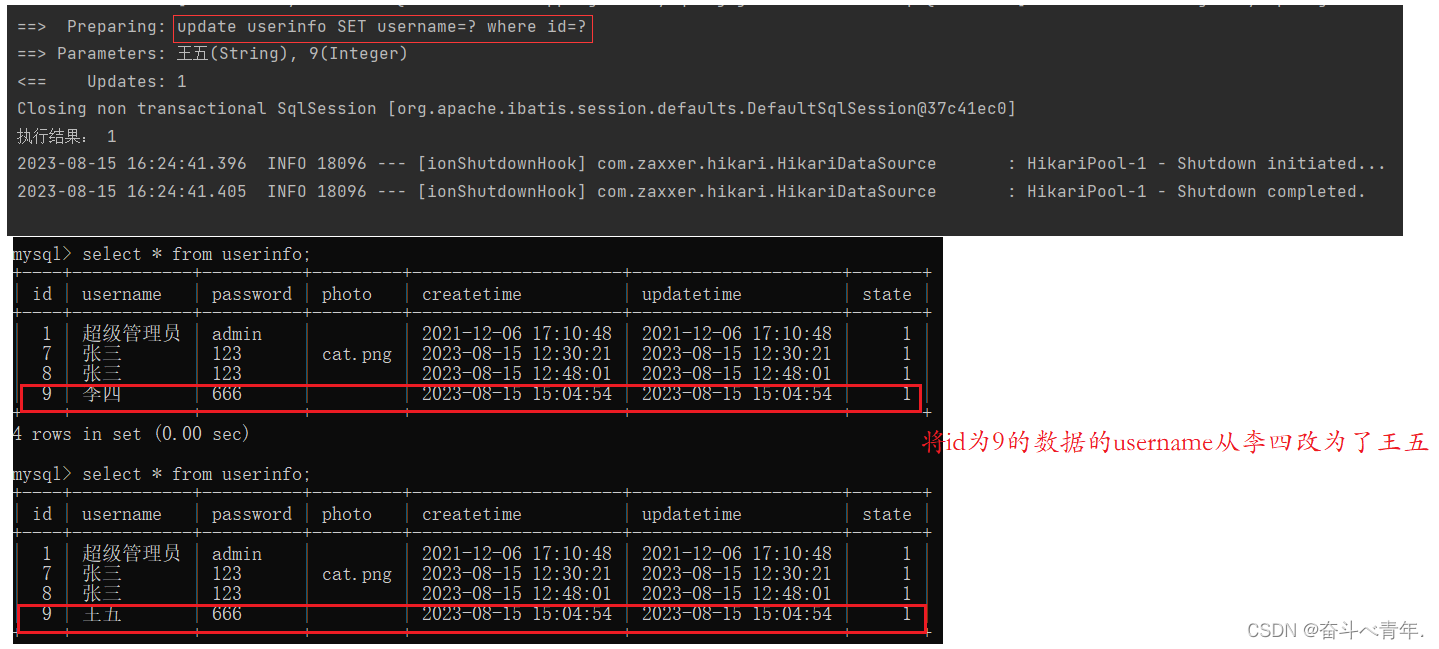
userinfo.setId(9);
userinfo.setUsername("王五");
int result = userMapper.update2(userinfo);
System.out.println("执行结果: "+result);
}4️⃣执行结果
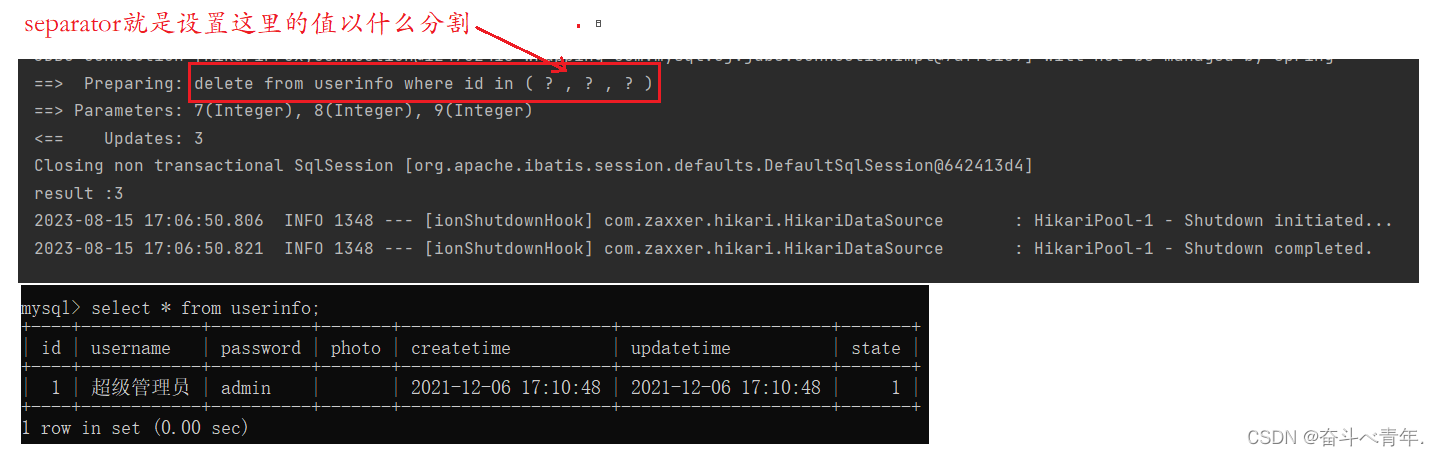
5、<foreach>标签
如果我们想要删除多条数据的时候就会使用到<foreach>标签。前端传过来要删除的一组数据,这个时候后端接收到的是一个集合,sql语句中没有办法操作集合,<foreach>标签可以通过循环遍历的方式将集合中的数据取出来给sql语句,这就会就完成删除多条数据的操作。
✨<foreach>标签的属性
- collection:绑定方法参数中的集合,如List,Set,Map或数组对象
- item:遍历时的每一个对象
- open:表示该语句以什么开始,最常用的是左括弧’(’
- close:表示该语句以什么结束,最常用的是右括弧’)’
- separator:每次遍历之间间隔的字符串,表示循环的时候用什么分割每一项的值
1️⃣接口中声明方法
/*
*动态sql <foreach>标签
* */
int delById2(List<Integer> ids);2️⃣在XML中实现方法
这里设置的item属性是遍历集合中每个对象的别名,item中设置的值要和#{}中的值相同,否则程序就会报错。
<delete id="delById2">
delete from userinfo where id in
<foreach collection="ids" open="(" close=")" item="id" separator=",">
#{id}
</foreach>
</delete>
3️⃣单元测试
@Test
void delById2() {
List<Integer> list =new ArrayList<Integer>();
list.add(7);
list.add(8);
list.add(9);
int result = userMapper.delById2(list);
System.out.println("result :"+result);
}4️⃣执行结果